Which gland or organ produces adrenocorticotropic hormone?
Your pituitary gland makes the following hormones:
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH or corticotropin).
- Antidiuretic hormone (ADH, or vasopressin).
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
- Growth hormone (GH).
- Luteinizing hormone (LH).
- Oxytocin.
- Prolactin.
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
What hormone does the adreneal glands produce?
The adrenal medulla is the innermost core of the adrenal gland, which produces and releases the hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine. These two hormones are also known as adrenalin and noradrenaline respectively, and are also referred to as catecholamines or as neurotransmitters, because small amounts are also produced by the nervous system.
What does elevated ACTH mean?
- High ACTH and high cortisol levels: This may mean Cushing's disease.
- Low ACTH and high cortisol levels: This may mean Cushing's syndrome or a tumor of the adrenal gland.
- High ACTH and low cortisol levels: This may mean Addison disease.
- Low ACTH and low cortisol levels. This may mean hypopituitarism.
What is the function of the Adreno-cortico-tropic hormone?
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) is a hormone produced in the anterior pituitary gland of the brain. This hormone is involved in regulating the steroid hormone and cortisol levels, released from the adrenal gland. ACTH is also known as arginine vasopressin, adrenocorticotrophin, serum adrenocorticotropic hormone or corticotropin.
Where is adrenocorticotropic hormone made?
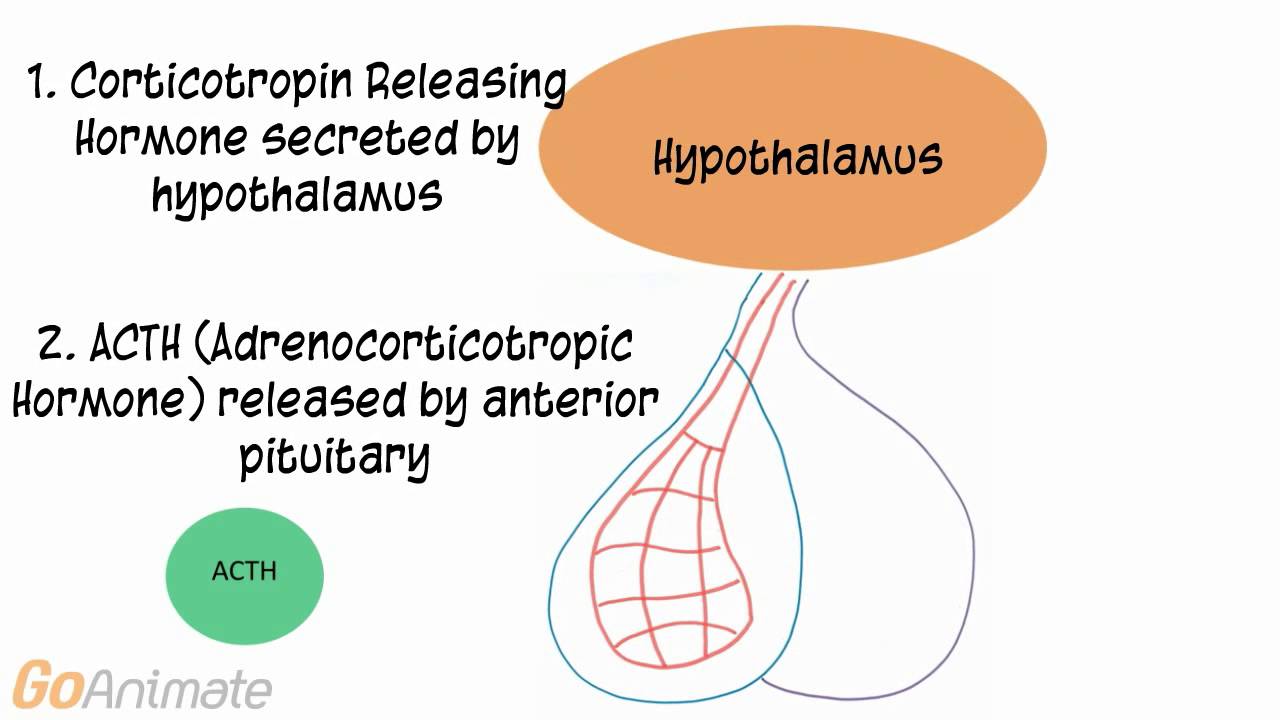
Adrenocorticotropic hormone is made in the corticotroph cells of the anterior pituitary gland. It is secreted in several intermittent pulses during the day into the bloodstream and transported around the body.
What happens if I have too much adrenocorticotropic hormone?
The effects of too much adrenocorticotropic hormone are mainly due to the increase in cortisol levels. Higher than normal levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone may be due to:
What hormones are detected by the adrenal gland?
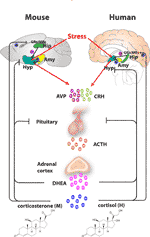
High levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone are detected by the adrenal gland receptors which stimulate the secretion of cortisol, causing blood levels of cortisol to rise. As the cortisol levels rise, they start to slow down the release of corticotrophin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus ...
Which hormone is released by the pituitary gland?
Corticotrophin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus acts on the pituitary (inset), which secretes ACTH. ACTH travels to the adrenal glands via the bloodstream (arrow). Cortisol from the adrenal then feeds back to the hypothalamus to shut down the cycle.
What is the rhythm of the adrenal glands?
This is called a diurnal (circadian) rhythm . Once adrenocorticotropic hormone reaches the adrenal glands, it binds on to receptors causing the adrenal glands to secrete more cortisol, resulting in higher levels of cortisol in the blood.
What is an adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) test?
ACTH is a hormone made by the pituitary gland, a small gland at the base of the brain. ACTH controls the production of another hormone called cortisol. Cortisol is made by the adrenal glands, two small glands located above the kidneys. Cortisol plays an important role in helping you to:
What does low ACTH mean?
Low ACTH and high cortisol levels: This may mean Cushing's syndrome or a tumor of the adrenal gland.
Why do I need an ACTH test?
You may need this test if you have symptoms of too much or too little cortisol.
What happens during an ACTH test?
A health care professional will take a blood sample from a vein in your arm, using a small needle. After the needle is inserted, a small amount of blood will be collected into a test tube or vial. You may feel a little sting when the needle goes in or out. This usually takes less than five minutes.
Why is cortisol important?
Cortisol plays an important role in helping you to: Respond to stress . Fight infection. Regulate blood sugar. Maintain blood pressure. Regulate metabolism, the process of how your body uses food and energy. Too much or too little cortisol can cause serious health problems.
What is the name of the disorder in which the pituitary gland makes too much ACTH?
Cushing's disease , a form of Cushing's syndrome. In this disorder, the pituitary gland makes too much ACTH. It is usually caused by a noncancerous tumor of the pituitary gland. Addison disease, a condition in which the adrenal gland doesn't make enough cortisol. Hypopituitarism, a disorder in which the pituitary gland does not make enough ...
Is there anything else I need to know about an ACTH test?
A test called an ACTH stimulation test is sometimes done instead of an ACTH test to diagnose Addison disease and hypopituitarism. An ACTH stimulation test is a blood test that measures cortisol levels before and after you've received an injection of ACTH.
What is adrenocorticotropic hormone?
Corticotrophin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus acts on the pituitary (inset), which secretes ACTH. ACTH travels to the adrenal glands via the bloodstream (arrow). Cortisol from the adrenal then feeds back to the hypothalamus to shut down the cycle.
Why is adrenocorticotropic hormone higher than normal?
Higher than normal levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone may be due to: Cushing's disease – this is the most common cause of increased adrenocorticotropic hormone. It is caused by a non-cancerous tumour called an adenoma located in the pituitary gland, which produces excess amounts of adrenocorticotropic hormone.
What happens if I have too little adrenocorticotropic hormone?
Lower than normal levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone may be due to:
What hormones are detected by the adrenal gland?
High levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone are detected by the adrenal gland receptors which stimulate the secretion of cortisol, causing blood levels of cortisol to rise. As the cortisol levels rise, they start to slow down the release of corticotrophin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus ...
What hormone is released when cortisol levels are low?
When cortisol levels in the blood are low, a group of cells in the hypothalamus release a hormone called corticotrophin-releasing hormone (CRH) which stimulates the pituitary gland to secrete adrenocorticotropic hormone into the bloodstream.
What is the rhythm of the adrenal glands?
This is called a diurnal (circadian) rhythm . Once adrenocorticotropic hormone reaches the adrenal glands, it binds on to receptors causing the adrenal glands to secrete more cortisol, resulting in higher levels of cortisol in the blood.
Which gland controls the secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone?
Secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone is controlled by three inter-communicating regions of the body, the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland and the adrenal glands. This is called the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis.
What is the axis of the adrenocorticotropic hormone?
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is a tropic hormone produced by the anterior pituitary. The hypothalamic-pituitary axis controls it. ACTH regulates cortisol and androgen production. Diseases associated with ACTH include Addison disease, Cushing syndrome, and Cushing disease. [1]
How do tropic hormones affect target cells?
Tropic hormones indirectly affect target cells by first stimulating other endocrine glands. Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) is released from the hypothalamus which stimulates the anterior pituitary to release adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). ACTH then acts on its target organ, the adrenal cortex. Adrenal Cortex.
How to test for secondary hypercortisolism?
A high-dose, typically 8 mg, dexamethasone-suppression test is done. A pituitary adenoma will still respond to the hypothalamic-pituitary axis; however, it needs more feedback to do so. Therefore, with a high-dose suppression test, the production of ACTH will decrease leading to a decrease in cortisol. Ectopic production of ACTH is not within the axis and will not respond to feedback mechanisms. Therefore, there will be no change in cortisol after a high-dose suppression test. A CRH-stimulation test can be done in place of the high- dose dexamethasone suppression test. Recall that CRH is released from the hypothalamus to stimulate the pituitary to secrete ACTH. If there is a further increase in ACTH and cortisol, the etiology is likely to be a pituitary adenoma. If there is no change in the levels of ACTH and cortisol, the etiology is likely to be ectopic.
Why is it important to increase glucocorticoids?
This is because the adrenal cortex is unable to produce cortisol. Treatment. Replace glucocorticoids via hydrocortisone. It is essential to increase the dosage of glucocorticoids during times of stress, such as illness, surgery, and trauma to avoid an adrenal crisis.
What is the role of ACTH in the body?
ACTH plays a role in glucose metabolism and immune function. The circadian rhythm influences cortisol secretion. The highest levels of cortisol are seen in the early morning, and the lowest levels are in the evening. This concept is important for diagnostic testing.
Where are the ACTH receptors located?
ACTH receptors are in the adrenal cortex, in particular, the zona fasciculata and zona reticularis. The receptors are G protein-coupled receptors, thus stimulating adenylyl cyclase. This leads to an increase in intracellular cAMP and activation of protein kinase A.[2]
Where does CRH release?
CRH is released from the hypothalamus. CRH stimulates the anterior pituitary to release ACTH. ACTH acts on the adrenal cortex to release cortisol and androgens. The increase in cortisol provides a negative feedback system to then decrease the amount of CRH released from the hypothalamus.
The root of violence? Mice become MEAN when they are injected with an antibody taken from the blood of human murderers, rapists and gang..
Experts from Akershus University Hospital, near Oslo, extracted antibodies from 16 violent convicts and found mice resorted to violence more...
Femail Today
'She looks 16!': Madonna, 63, shocks fans with 'baby face' appearance as she shares heavily-filtered snaps
What is Adrenocorticotropic Hormone?
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) is a hormone produced in the anterior pituitary gland of the brain. This hormone is involved in regulating the steroid hormone and cortisol levels, released from the adrenal gland.
What are the effects of high levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone?
Other external factors responsible for stimulating more ACTH production include both physical and psychological stress. As discussed above, the symptoms of high levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone include: Acne. Fatigue.
What is the cause of low levels of ACTH?
ACTH hormone deficiency refers to decreased or low levels of ACTH hormone in the body, which is mainly caused by the reduced production of ACTH hormone or by pituitary gland malfunctions.
What is an ACTH?
A tumour outside the pituitary gland. Other hormonal changes including low-level cortisol levels, high-level ACTH, Adrenal insufficiency, etc. This article concludes the introduction to the Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), their level of production and functions. To know more about the Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), ...
Why is ACTH higher in blood?
The higher levels of ACTH are mainly caused by the stimulation of adrenal gland receptors for more production of cortisol and therefore, resulting in the rise of cortisol levels in the blood cells. As there is a rise in the cortisol levels, it results in the slow down in the release of corticotrophin-releasing hormone from ...
What is the name of the hormone that stimulates the production of stress hormones from the cortex?
ACTH is also known as arginine vasopressin, adrenocorticotrophin, serum adrenocorticotropic hormone or corticotropin. Adrenocorticotropic hormone is the most vital hormone required for the functioning of adrenal glands, which stimulates the production of stress hormones from the cortex, called cortisol. Also Refer: Endocrine Glands.
Why is ACTH low?
The causes for the lower secretion of the adrenocorticotropic hormone can be due to hypopituitarism, side effects from pituitary gland surgery and other Cushing’s diseases. The symptoms of low levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone include:
What Is ACTH?
Adrenocorticotropic hormone ( ACTH ), also known as corticotropin, is a hormone secreted by the pituitary gland . ACTH is responsible for stimulating the production of cortisol by the adrenal gland [ 1 ].
What causes low ACTH?
Low ACTH can also be caused by tertiary adrenal insufficiency. This condition occurs when the hypothalamus gland doesn’t produce enough corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), which is the hormone that stimulates the release of ACTH. Causes of tertiary adrenal insufficiency include [ R, R ]: Tumors in the hypothalamus.
Why is my ACTH low?
Low ACTH levels may be caused by secondary adrenal insufficiency. In this condition, impairment of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus leads to decreased production of ACTH.
What is the purpose of the ACTH test?
The ACTH test measures the amount of ACTH in the blood. This test is often performed alongside a cortisol test to help identify problems with the adrenal glands or pituitary glands.
What is the normal range of ACTH?
However, the levels of these two hormones can vary throughout the day [ 4 ]. Generally speaking, the normal range of ACTH in adults is about 6 to 76 pg/ml.
When to do adrenal blood test?
ACTH levels can vary throughout the day, so blood tests are typically performed in the morning when levels are highest. A doctor may request that the patient fast overnight before the test.
What is the name of the drug that measures the levels of both ACTH and cortisol in the blood?
corticotropin. cosyntropin , which is a drug form of ACTH. An ACTH test measures the levels of both ACTH and cortisol in the blood and helps your doctor detect diseases that are associated with too much or too little cortisol in the body. Possible causes of these diseases include:
What is the function of the adrenal gland?
The function of ACTH is to regulate levels of the steroid hormone cortisol, which released from the adrenal gland. An ACTH test measures the levels of both ACTH and cortisol in the blood and helps your doctor detect diseases ...
Why do you need an acth test?
Why the ACTH test is performed. Your doctor may order an ACTH blood test if you have symptoms of too much or too little cortisol. These symptoms can vary widely from person to person and are often a sign of additional health problems. If you have a high cortisol level, you may have: obesity. a rounded face.
What is the normal range of acth?
Normal values of ACTH are 9 to 52 picograms per milliliter. Normal value ranges may vary slightly depending on the laboratory. Your doctor will explain your test results to you.
How to test ACTH levels?
Your doctor will likely schedule your test for very early in the morning. ACTH levels are tested using a blood sample. A blood sample is taken by drawing blood from a vein, usually from the inside of the elbow. Giving a blood sample involves the following steps:
What are the symptoms of low cortisol?
diabetes. The symptoms of low cortisol include: weak muscles. fatigue. weight loss. increased skin pigmentation in areas not exposed to the sun. a loss of appetite.
When is the ACTH test done?
These can affect the accuracy of the results. The test is usually done first thing in the morning. ACTH levels are highest when you’ve just woken up.