
What are the four functions of a cell membrane?
What are the six functions of the plasma membrane?
- A Physical Barrier. ...
- Selective Permeability. ...
- Endocytosis and Exocytosis. ...
- Cell Signaling. ...
- Phospholipids. ...
- Proteins. ...
- Carbohydrates. ...
- Fluid Mosaic Model.
What does the cell membrane protect against?
The nuclear membrane is a two-layered structure that protects the nucleus, keeps DNA separate from the rest of the cell and manages what materials enter the nucleus. It is made up of four main parts: outer membrane, inner membrane, perinuclear space and nuclear pores.
What are the parts and functions of the cell membrane?
What are the 6 functions of the cell membrane?
- Molecule Transport. Helps MOve food, water, or something across the membrane.
- Act as enzymes. Controls metabolic processes.
- Cell to cell communication and recognition. so that cells can work together in tissues.
- Signal Receptors.
- intercellular junctions.
- Attatchment to the cytoskeleton and ECM.
What is controlled by the cell membrane?
The cell membrane is made of two layers of lipid films (oil molecules) with many kinds of proteins inserted. These proteins control the movement of molecules such as water, ions, nutrients, and oxygen in and out of the cell. [In this figure] The anatomy of an animal cell with organelles labeled.
Does the cell membrane control everything?
The function of the plasma membrane is to control what goes in and out of the cell. Some molecules can go through the cell membrane to enter and leave the cell, but some cannot. The cell is therefore not completely permeable. "Permeable" means that anything can cross a barrier.
What are the 4 main functions of the cell membrane?
The four main functions of the plasma membrane include identification, communication, regulation of solute exchange through the membrane, and isolation of the cytoplasm from the external environment.
What are 3 main functions of the cell membrane?
Biological membranes have three primary functions: (1) they keep toxic substances out of the cell; (2) they contain receptors and channels that allow specific molecules, such as ions, nutrients, wastes, and metabolic products, that mediate cellular and extracellular activities to pass between organelles and between the ...
Which of the following is controlled by the cell membrane?
The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles, being selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules.
What are the 5 main roles of membranes within cells?
Enzymes can be attracted to membranes.Separates DNA.Vesicle and lysome formation.RER membrane allows attachment of ribosmones.Intercellular transport.Tonoplast surrounds and controls contents of vacuoles.Reactions take place on membranes.Prevents disruption of reactions.More items...•
What is the most important function of cell membrane?
The most important function of the cell membrane is that it controls the entry and exit of materials from cells. Hence it is also called semipermeable membrane.
Is the cell membrane the control center?
The nucleus is like the remote control center of the cell. It acts as the cell's brain by telling it what to do, how to grow, and when to reproduce. The nucleus is home to the cell's genes. A membrane, a thin layer that allows chemicals to pass in and out to the rest of the cell, surrounds the nucleus.
What are the 6 functions of the cell membrane?
Terms in this set (6)Molecule Transport. Helps MOve food, water, or something across the membrane.Act as enzymes. Controls metabolic processes.Cell to cell communication and recognition. so that cells can work together in tissues. ... Signal Receptors. ... intercellular junctions. ... Attatchment to the cytoskeleton and ECM.
What is the main control of cell?
NucleusNucleus is known as the control center of the cell as it performs the following functions: The nucleus contains the hereditary material of the cell, the DNA. It sends signals to the cells to grow, mature, divide and die.
What are the 4 parts of the membrane?
There are four main components of the cell membrane:Phospholipids.Proteins.Carbohydrates.Cholesterol.
What are the 4 structures of cell membranes?
The fluid mosaic model describes the plasma membrane structure as a mosaic of components—including phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates—that gives the membrane a fluid character.
What are the 6 functions of the cell membrane?
Terms in this set (6)Molecule Transport. Helps MOve food, water, or something across the membrane.Act as enzymes. Controls metabolic processes.Cell to cell communication and recognition. so that cells can work together in tissues. ... Signal Receptors. ... intercellular junctions. ... Attatchment to the cytoskeleton and ECM.
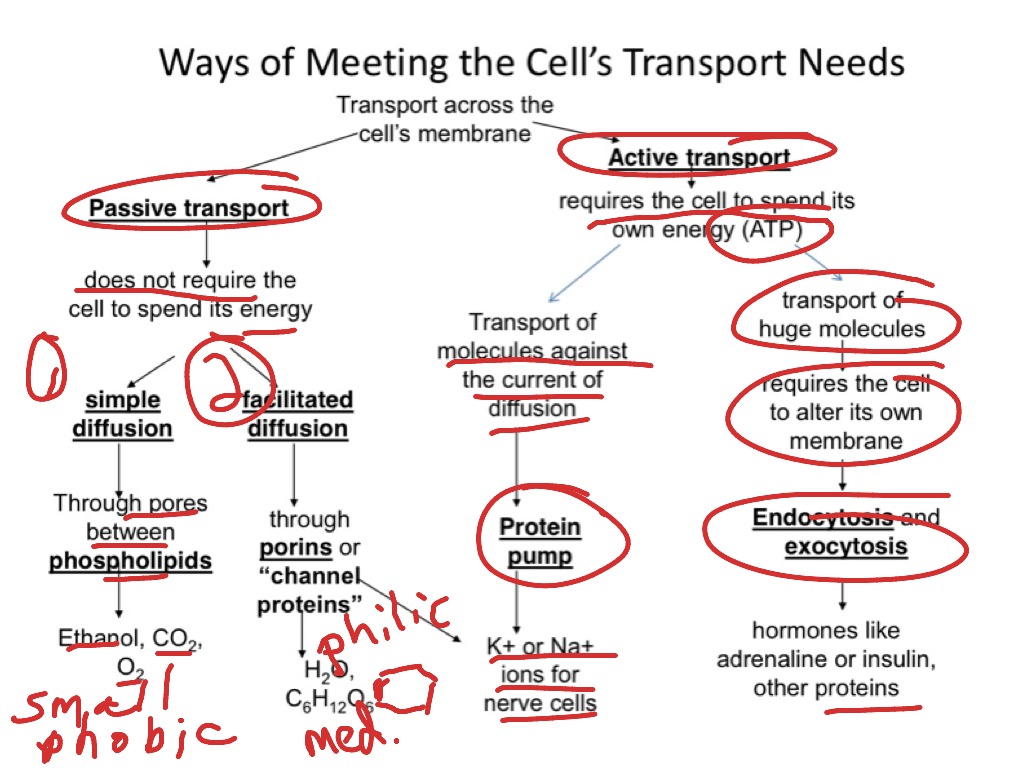
What are the 4 types of membrane transport?
Particles move across membranes by simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis and active transport.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out. It also serves as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some organisms and ...
What is the role of cholesterol in animal cell membranes?
Cholesterol molecules are selectively dispersed between membrane phospholipids. This helps to keep cell membranes from becoming stiff by preventing phospholipids from being too closely packed together. Cholesterol is not found in the membranes of plant cells.
What is the cell membrane made of?
Cell Membrane Structure. The cell membrane is primarily composed of a mix of proteins and lipids. Depending on the membrane’s location and role in the body, lipids can make up anywhere from 20 to 80 percent of the membrane, with the remainder being proteins.
What are the functions of cell membrane receptor proteins?
Cell membrane receptor proteins help cells communicate with their external environment through the use of hormones, neurotransmitters, and other signaling molecules.
Why is the cell membrane important?
Thus the cell membrane also serves to help support the cell and help maintain its shape.
What is the function of the nucleus?
The nucleus and mitochondria are two examples. Another function of the membrane is to regulate cell growth through the balance of endocytosis and exocytosis. In endocytosis, lipids and proteins are removed from the cell membrane as substances are internalized. In exocytosis, vesicles containing lipids and proteins fuse with ...
Which bilayer of lipids is hydrophobic?
Phospholipids form a lipid bilayer in which their hydrophilic (attracted to water) head areas spontaneously arrange to face the aqueous cytosol and the extracellular fluid, while their hydrophobic (repelled by water) tail areas face away from the cytosol and extracellular fluid.
What is the cell membrane?
Cell membrane, also called plasma membrane, thin membrane that surrounds every living cell, delimiting the cell from the environment around it. Enclosed by this cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane) are the cell’s constituents, often large, water-soluble, highly charged molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, ...
What is the innermost layer of a cell?
The innermost layer is a plasma membrane similar to the ones that surround most cells. The plasma membrane consists of a lipid bilayer with proteins embedded in it. Some of the proteins are embedded entirely within the lipid layer, others extend to one or the other surface, and still others…
What repels water soluble molecules?
Lipid-soluble molecules and some small molecules can permeate the membrane, but the lipid bilayer effectively repels the many large, water-soluble molecules and electrically charged ions that the cell must import or export in order to live.
What is the membrane of a neuron?
The neuron is bound by a plasma membrane, a structure so thin that its fine detail can be revealed only by high-resolution electron microscopy. About half of the membrane is the lipid bilayer, two sheets of mainly phospholipids with a space between. One…
What are the two types of lipids in membranes?
Membrane lipids are principally of two types, phospholipids and sterols (generally cholesterol ). Both types share the defining characteristic of lipids—they dissolve readily in organic solvents—but in addition they both have a region that is attracted to and soluble in water.
How thick is the lipid bilayer?
Intrinsic proteins penetrate and bind tightly to the lipid bilayer, which is made up largely of phospholipids and cholesterol and which typically is between 4 and 10 nanometers (nm; 1 nm = 10 −9 metre) in thickness.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane, therefore, has two functions: first, to be a barrier keeping the constituents of the cell in and unwanted substances out and , second, to be a gate allowing transport into the cell of essential nutrients and movement from the cell of waste products. Intrinsic proteins penetrate and bind tightly to the lipid bilayer, ...
What are the proteins that interact with other cells?
Another is that the membrane of the cell, which would be the plasma membrane, will have proteins on it which interact with other cells. Those proteins can be glycoprotein, meaning there's a sugar and a protein moiety, or they could be lipid proteins, meaning there's a fat and a protein.
What is the membrane of a cell called?
Plasma Membrane (Cell Membrane) Plasma Membrane (Cell Membrane) =. The plasma membrane , also called the cell membrane, is the membrane found in all cells that separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. In bacterial and plant cells, a cell wall is attached to the plasma membrane on its outside surface.
Which membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell?
The plasma membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The plasma membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell.
Is cholesterol in the plasma membrane?
And there are different types of plasma membranes in different types of cells, and the plasma membrane has in it in general a lot of cholesterol as its lipid component. That's different from certain other membranes within the cell.
Can you add videos to your watch history?
Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations. To avoid this, cancel and sign in to YouTube on your computer.
What is the technical term for this double layer of phospholipids that forms the cell membrane?
The technical term for this double layer of phospholipids that forms the cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer. Structure of the cell membrane and its associated components.
What is the difference between hydrophobic and hydrophilic phospholipids?
When in water or an aqueous solution (including inside the body) the hydrophobic heads of phospholipids will orient themselves to be on the inside, as far away from the water as possible. In contrast, the hydrophilic heads will be on the outside, making contact with the water. The result is that a double layer of phospholipids is formed, with the hydrophobic heads clustering together in the center, and the hydrophilic tails forming the outside of the structure. The technical term for this double layer of phospholipids that forms the cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer.
What is the phospholipid bilayer?
Phospholipid Bilayer. The cell membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer. Phospholipids are lipid molecules made up of a phosphate group head and two fatty acid tails. Importantly, the properties of phospholipid molecules allow them to spontaneously form a double-layered membrane. The phosphate group head of a phospholipid is hydrophilic, ...
How does the cell control the rate of diffusion of substances?
Another way the cell membrane can bring molecules into the cytoplasm is through endocytosis. The reverse process, where the cell delivers contents outside the membrane barrier, is called exocytosis. Endocytosis includes phagocytosis (“cell eating”) ...
What is the process of endocytosis?
Endocytosis includes phagocytosis (“cell eating”) and pinocytosis (“cell drinking”). During these processes, the cell membrane forms a depression, surrounding the particle that it is engulfing. It then “pinches off” to form a small sphere of membrane called a vesicle that contains the molecule and transports it to wherever it will be used in ...
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Function of the Cell Membrane. The cell membrane gives the cell its structure and regulates the materials that enter and leave the cell. It is a selectively permeable barrier, meaning it allows some substances to cross, but not others. Like a drawbridge intended to protect a castle and keep out enemies, the cell membrane only allows certain ...
Why is cholesterol important in the cell membrane?
The amount of cholesterol in the membrane helps maintain its permeability so that the right amount of molecules can enter the cell at a time. The cell membrane also contains many different proteins. Proteins make up about half of the cell membrane.
What does cell membrane look like under a microscope?
Under a compound light microscope, the cell membrane (only 5-10 nm) may be too thin to be seen. However, you can easily tell the boundary of cells if stained with proper dyes. That is where the cell membrane is.
What is the backbone of a cell?
Phospholipid bilayer as a versatile biological barrier. The backbone structure of the cell membrane is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules, called lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer ).
What is the cell membrane made of?
The cell membrane is made of two layers of lipid films (oil molecules) with many kinds of proteins inserted. These proteins control the movement of molecules such as water, ions, nutrients, and oxygen in and out of the cell. [In this figure] The anatomy of an animal cell with organelles labeled.
How do membrane proteins control the cell?
Membrane proteins control the traffic of biomolecules in and out the cells. Cells eat and excrete by changing the cell membrane. Cells talk to each other via direct or indirect contacts on their cell membranes. Signal transduction along the cell membrane of nervous cells.
Why are lipid bilayers important?
The lipid bilayers are ideally suited to keeps ions, proteins, and other charged molecules from diffusing across the membrane, even though they are only a few nanometers in width. At the same time, uncharged molecules and gases can easily cross the cell membrane.
What is the membrane of a balloon?
This soft but tough balloon is made from the cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane). The cell membrane is a thin biological membrane that separates the interior of cells from the outside space and protects the cells from the surrounding environment. The cell membrane is made of two layers of lipid films (oil molecules) ...
Why do ions and molecules have different concentrations on the membrane?
Because the membrane acts as a barrier for charged molecules and ions, they can occur in different concentrations on the two sides of the membrane. The difference in total charge between the inside and outside of the cell is called the membrane potential.
