What are the five major functions of the cell membrane?
protects the cell by acting as a barrier. 2. regulates the transport of substances in and out of the cell. 3. receives chemical messengers from other cell. 4. acts as a receptor. 5. cell mobility, secretions, and absorptions of substances.
What are the parts and functions of the cell membrane?
What are the 6 functions of the cell membrane?
- Molecule Transport. Helps MOve food, water, or something across the membrane.
- Act as enzymes. Controls metabolic processes.
- Cell to cell communication and recognition. so that cells can work together in tissues.
- Signal Receptors.
- intercellular junctions.
- Attatchment to the cytoskeleton and ECM.
What is the main function of cell membrane?
The function of a cell membrane, also referred to as the plasma membrane, is to protect the structures within the cell, give shape to the cell and support its structure. The cell membrane is composed of a double layer of lipids and proteins.
What are the 5 components of the cell membrane?
Cell Membrane Structure
- Phospholipids. Phospholipids are referred to as glycerophospholipids, these phospholipids are part of the cell membrane of living beings as well as a group of lipid compounds; i.e. ...
- Protein. This protein itself is derived from the Greek word “Protos” which means “most importantly”. ...
- Glycolipids and glycoproteins. ...
- Oligosaccharides. ...
- Cholesterol. ...
What are 3 functions of the cell membrane?
Biological membranes have three primary functions: (1) they keep toxic substances out of the cell; (2) they contain receptors and channels that allow specific molecules, such as ions, nutrients, wastes, and metabolic products, that mediate cellular and extracellular activities to pass between organelles and between the ...
What are the 4 main functions of the cell membrane?
The four main functions of the plasma membrane include identification, communication, regulation of solute exchange through the membrane, and isolation of the cytoplasm from the external environment.
What is the most important function of cell membrane?
The most important function of the cell membrane is to maintain cellular integrity and transport of molecules inside and outside the cell. It is selectively permeable. Many molecules can move across the membrane passively, polar molecules require carrier protein to facilitate their transport.
What is the purpose of the cell membrane quizlet?
To protect the cell from its surroundings.It also recognizes certain chemicals and molecules that can or can't go into the cell.
What are 5 functions of the cell membrane?
Terms in this set (5)protects the cell by acting as a barrier.regulates the transport of substances in and out of the cell.receives chemical messengers from other cell.acts as a receptor.cell mobility, secretions, and absorptions of substances.
What are the 6 functions of the cell membrane?
Functions of the Plasma MembraneA Physical Barrier. ... Selective Permeability. ... Endocytosis and Exocytosis. ... Cell Signaling. ... Phospholipids. ... Proteins. ... Carbohydrates. ... Fluid Mosaic Model.
What are the main functions of a cell?
They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialized functions. Cells also contain the body's hereditary material and can make copies of themselves.
What are the 7 functions of the cell wall?
What Are The 7 Functions Of The Cell Wall?Renders mechanical strength.Serve as food reservoir.It maintains the shape of the cell.It regulates the intercellular transport.It regulates the expansion of cells.Provides protection against pathogens.More items...•
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane, therefore, has two functions: first, to be a barrier keeping the constituents of the cell in and unwanted substances out and , second, to be a gate allowing transport into the cell of essential nutrients and movement from the cell of waste products. Intrinsic proteins penetrate and bind tightly to the lipid bilayer, ...
What is the cell membrane?
Cell membrane, also called plasma membrane, thin membrane that surrounds every living cell, delimiting the cell from the environment around it. Enclosed by this cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane) are the cell’s constituents, often large, water-soluble, highly charged molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, ...
What is the innermost layer of a cell?
The innermost layer is a plasma membrane similar to the ones that surround most cells. The plasma membrane consists of a lipid bilayer with proteins embedded in it. Some of the proteins are embedded entirely within the lipid layer, others extend to one or the other surface, and still others…
What repels water soluble molecules?
Lipid-soluble molecules and some small molecules can permeate the membrane, but the lipid bilayer effectively repels the many large, water-soluble molecules and electrically charged ions that the cell must import or export in order to live.
What is the membrane of a neuron?
The neuron is bound by a plasma membrane, a structure so thin that its fine detail can be revealed only by high-resolution electron microscopy. About half of the membrane is the lipid bilayer, two sheets of mainly phospholipids with a space between. One…
What are the two types of lipids in membranes?
Membrane lipids are principally of two types, phospholipids and sterols (generally cholesterol ). Both types share the defining characteristic of lipids—they dissolve readily in organic solvents—but in addition they both have a region that is attracted to and soluble in water.
What type of bond is used to attach membrane proteins?
Membrane proteins are also of two general types. One type, called the extrinsic proteins, is loosely attached by ionic bond s or calcium bridges to the electrically charged phosphoryl surface of the bilayer. They can also attach to the second type of protein, called the intrinsic proteins.
What is the cell membrane?
The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The cell membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell.
What is the function of the plasma membrane?
One is to transport nutrients into the cell and also to transport toxic substances out of the cell.
What are the proteins that interact with other cells?
Another is that the membrane of the cell, which would be the plasma membrane, will have proteins on it which interact with other cells. Those proteins can be glycoproteins, meaning there's a sugar and a protein moiety, or they could be lipid proteins, meaning that there's a fat and a protein.
Is the cell wall tougher than the plasma membrane?
In fact, they have a cell wall outside of them, and that cell wall is much tougher and is structurally more sound than a plasma membrane is. William Gahl, M.D., Ph.D.
Is cholesterol in the plasma membrane?
And there are different types of plasma membranes in different types of cells, and the plasma membrane has in it in general a lot of cholesterol as its lipid component. That's different from certain other membranes from within the cell.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Function of the Cell Membrane. The cell membrane gives the cell its structure and regulates the materials that enter and leave the cell. It is a selectively permeable barrier, meaning it allows some substances to cross, but not others. Like a drawbridge intended to protect a castle and keep out enemies, the cell membrane only allows certain ...
What is the cell membrane?
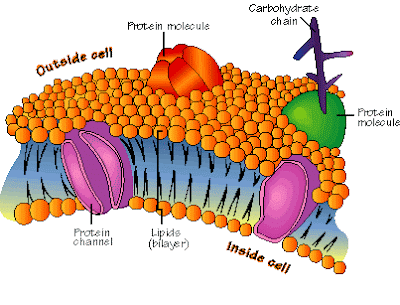
Definition. The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a double layer of lipids and proteins that surrounds a cell. It separates the cytoplasm (the contents of the cell) from the external environment. It is a feature of all cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic. a 3D diagram of the cell membrane.
What is the technical term for this double layer of phospholipids that forms the cell membrane?
The technical term for this double layer of phospholipids that forms the cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer. Structure of the cell membrane and its associated components.
What is the phospholipid bilayer?
Phospholipid Bilayer. The cell membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer. Phospholipids are lipid molecules made up of a phosphate group head and two fatty acid tails. Importantly, the properties of phospholipid molecules allow them to spontaneously form a double-layered membrane. The phosphate group head of a phospholipid is hydrophilic, ...
How does the cell control the rate of diffusion of substances?
Another way the cell membrane can bring molecules into the cytoplasm is through endocytosis. The reverse process, where the cell delivers contents outside the membrane barrier, is called exocytosis. Endocytosis includes phagocytosis (“cell eating”) ...
What is the process of endocytosis?
Endocytosis includes phagocytosis (“cell eating”) and pinocytosis (“cell drinking”). During these processes, the cell membrane forms a depression, surrounding the particle that it is engulfing. It then “pinches off” to form a small sphere of membrane called a vesicle that contains the molecule and transports it to wherever it will be used in ...
Why is cholesterol important in the cell membrane?
The amount of cholesterol in the membrane helps maintain its permeability so that the right amount of molecules can enter the cell at a time. The cell membrane also contains many different proteins. Proteins make up about half of the cell membrane.
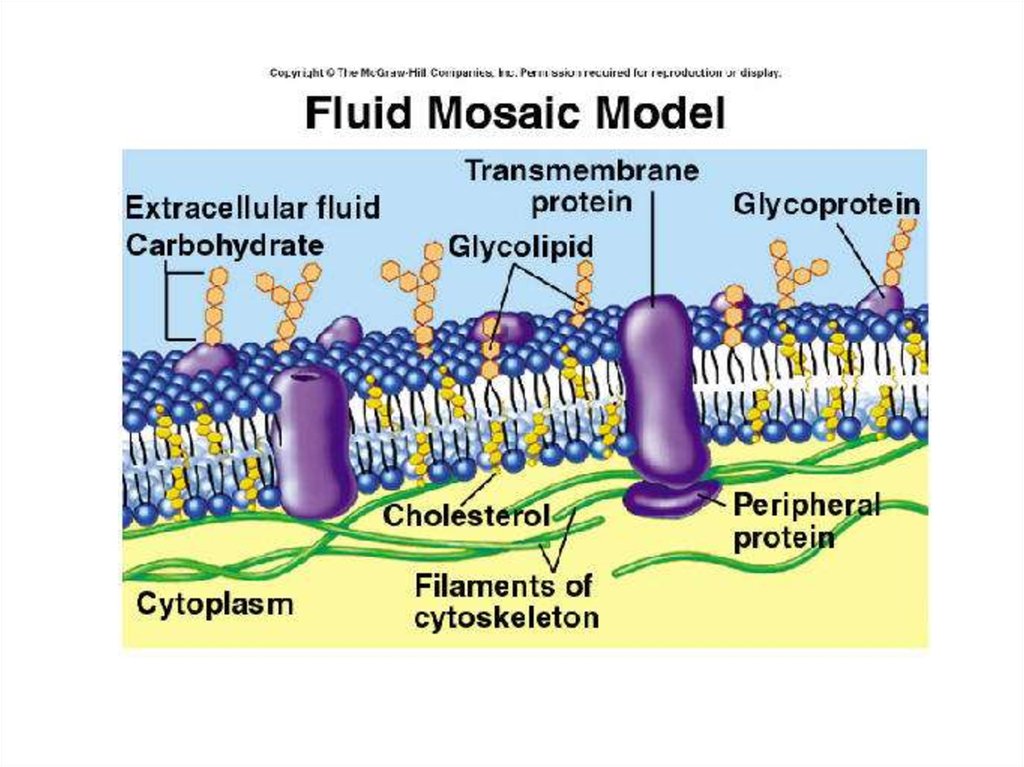
How do scientists explain the cell membrane?
To better describe the properties of the cell membrane, scientists explain the cell membrane appearance and functions using the fluid mosaic model.#N#If you zoom in on the cell membrane, you will see the ocean of lipid molecules decorated with membrane proteins, cholesterols, and carbohydrates. These molecules are constantly moving in two dimensions, in a fluid fashion, similar to icebergs floating in the ocean. There is no consistent pattern or arrangement of these molecules; they are more like a mosaic.
What is the cell membrane made of?
The cell membrane is made of two layers of lipid films (oil molecules) with many kinds of proteins inserted. These proteins control the movement of molecules such as water, ions, nutrients, and oxygen in and out of the cell. [In this figure] The anatomy of an animal cell with organelles labeled.
What does cell membrane look like under a microscope?
Under a compound light microscope, the cell membrane (only 5-10 nm) may be too thin to be seen. However, you can easily tell the boundary of cells if stained with proper dyes. That is where the cell membrane is.
What is the backbone of a cell?
Phospholipid bilayer as a versatile biological barrier. The backbone structure of the cell membrane is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules, called lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer ).
How do membrane proteins control the cell?
Membrane proteins control the traffic of biomolecules in and out the cells. Cells eat and excrete by changing the cell membrane. Cells talk to each other via direct or indirect contacts on their cell membranes. Signal transduction along the cell membrane of nervous cells.
Why are lipid bilayers important?
The lipid bilayers are ideally suited to keeps ions, proteins, and other charged molecules from diffusing across the membrane, even though they are only a few nanometers in width. At the same time, uncharged molecules and gases can easily cross the cell membrane.
What is the membrane of a balloon?
This soft but tough balloon is made from the cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane). The cell membrane is a thin biological membrane that separates the interior of cells from the outside space and protects the cells from the surrounding environment. The cell membrane is made of two layers of lipid films (oil molecules) ...
What is the membrane of a cell called?
Plasma Membrane (Cell Membrane) Plasma Membrane (Cell Membrane) =. The plasma membrane , also called the cell membrane, is the membrane found in all cells that separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. In bacterial and plant cells, a cell wall is attached to the plasma membrane on its outside surface.
Which membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell?
The plasma membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The plasma membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell.
What are the proteins that interact with other cells?
Another is that the membrane of the cell, which would be the plasma membrane, will have proteins on it which interact with other cells. Those proteins can be glycoprotein, meaning there's a sugar and a protein moiety, or they could be lipid proteins, meaning there's a fat and a protein.
Is cholesterol in the plasma membrane?
And there are different types of plasma membranes in different types of cells, and the plasma membrane has in it in general a lot of cholesterol as its lipid component. That's different from certain other membranes within the cell.
Chemical composition of the cell membrane
It has a heterogeneous chemical composition that varies according to the type of cell . Anyway and in general it is composed of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates.
Cell membrane structure
Scientists have been based on a model called ” model of the fluid mosaic “ that serves for their study and physiology of the membrane. This model was proposed by Singer and Nicolson in 972 and is made up of 3 layers, two external lines and two internal ones. In the middle of both is the lighter layer called the fluid mosaic pattern.
Attraction of molecules
The attractive force between the molecules allows them to slide from one side to the other.
Cell membrane wateriness
Prior to the fluid mosaic model , the membrane was considered to be a solid body , but later it was shown that it behaves like a liquid .
Selective permeability of the cell membrane
The cell membrane is characterized by being semi-permeable . In other words, it allows the membrane to select which molecules must enter and which must exit.
Processes carried out by the cell membrane
If endocytosis captures particles then the process is known as phagocytosis.
Cell membrane asymmetry
Another characteristic of the plasma membrane is that it has an asymmetric structure, since the composition of each layer that forms the cell membrane is different from one another. On the other hand, proteins also vary if they are found in one layer or another. This means that the functions of the layers are different.
What is the cell membrane?
The cell membrane of the cell is a phospholipid bilayer containing many different molecular components, including proteins and cholesterol, some with carbohydrate groups attached.
What molecules can pass through the cell membrane?
The structure of the lipid bilayer allows only small, non-polar substances such as oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass through the cell membrane, down their concentration gradient, by simple diffusion.
What are the two layers of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane consists of two adjacent layers of phospholipids. The lipid tails of one layer face the lipid tails of the other layer, meeting at the interface of the two layers. The phospholipid heads face outward, one layer exposed to the interior of the cell and one layer exposed to the exterior (Figure 3.3). Because the phosphate groups are polar and hydrophilic, they are attracted to water in the intracellular fluid. Intracellular fluid (ICF) is the fluid interior of the cell. The phosphate groups are also attracted to the extracellular fluid. Extracellular fluid (ECF) is the fluid environment outside the enclosure of the cell membrane. Interstitial fluid (IF) is the term given to extracellular fluid not contained within blood vessels. Because the lipid tails are hydrophobic, they meet in the inner region of the membrane, excluding watery intracellular and extracellular fluid from this space. The cell membrane has many proteins, as well as other lipids (such as cholesterol), that are associated with the phospholipid bilayer. An important feature of the membrane is that it remains fluid; the lipids and proteins in the cell membrane are not rigidly locked in place.
How does facilitated diffusion work?
As an example, even though sodium ions (Na +) are highly concentrated outside of cells, these electrolytes are polarized and cannot pass through the nonpolar lipid bilayer of the membrane. Their diffusion is facilitated by membrane proteins that form sodium channels (or “pores”), so that Na + ions can move down their concentration gradient from outside the cells to inside the cells. There are many other solutes that must undergo facilitated diffusion to move into a cell , such as amino acids, or to move out of a cell, such as wastes. Because facilitated diffusion is a passive process, it does not require energy expenditure by the cell. Water also can move freely across the cell membrane of all cells, either through protein channels or by slipping between the lipid tails of the membrane itself. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane (Figure 3.7).
What is the bilayer of phospholipids?
The phospholipid bilayer consists of two adjacent sheets of phospholipids, arranged tail to tail. The hydrophobic tails associate with one another, forming the interior of the membrane. The polar heads contact the fluid inside and outside of the cell.
What are the two proteins that are found in the cell membrane?
Two different types of proteins that are commonly associated with the cell membrane are the integral proteins and peripheral protein (Figure 3.4). As its name suggests, an integral protein is a protein that is embedded in the membrane. A channel protein is an example of an integral protein that selectively allows particular materials, such as certain ions, to pass into or out of the cell.
What color is the cell membrane in a newt?
A lung cell from a newt, commonly studied for its similarity to human lung cells, is stained with fluorescent dyes. The green stain reveals mitotic spindles, red is the cell membrane and part of the cytoplasm, and the structures that appear light blue are chromosomes. This cell is in anaphase of mitosis. (credit: “Mortadelo2005”/Wikimedia Commons)
Why is the cell membrane important?
The cell membrane is also important for cell movement and adhesion to the extracellular matrix and other cells. Integral proteins are embedded in the membrane that bind to both internal components of the cell, such as the cytoskeleton, and to external components like the extracellular matrix. These connections can be remodeled as cells need to grow, divide and move throughout the body.
What is a Cell Membrane?
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin, flexible barrier that separates the cell from its environment and regulates what enters and leaves the cell, called selective permeability. The cell membrane is important for creating a flexible, semi-permeable barrier around the cell. This allows the cell to create stable, internal conditions that are different from a changing environment. The cell membrane is made of two layers of phospholipids and also includes proteins, carbohydrates and cholesterol. Forming a barrier is the main function of the cell membrane, but it also has additional functions including:
What is the role of carbohydrates in the cell membrane?
Carbohydrates also play an important role in helping cells attach to the extracellular matrix in cellular adhesion. The collection of carbohydrates on the outside of the cell is called the glycocalyx. In addition to cell adhesion and cell recognition the glycocalyx also helps to cushion the plasma membrane.
What are the two types of proteins in the cell membrane?
There are two types of proteins in the cell membrane: integral and peripheral proteins. Integral proteins span the cell membrane and exist both outside and in it. These proteins have a hydrophobic core that allows them to interact with the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids. Peripheral proteins are located on the outside of the cell membrane. These proteins are hydrophilic and attach to the phospholipid heads.
What makes up the cell membrane?
What makes up the cell membrane? The basic structure of the cell membrane includes a two layers of phospholipids, called the phospholipid bilayer. The phospholipid bilayer also has additional macromolecules that help the membrane do its job. What is the structure of the cell membrane? The structure of the cell membrane can be described by the fluid mosaic model. The fluid mosaic model explains that the components of the cell membrane are fluid and can drift laterally in the bilayer. It also explains how the membrane is flexible and able to move with the cell. The fluid mosaic model also describes how the cell membrane is a mosaic, made of many different macromolecules including:
What is the role of the cell membrane in cell signaling?
The cell membrane is also crucial for cell signaling and acts like a transducer, converting chemical signals in the environment to changes inside the cell. Signaling molecules outside the cell bind to proteins which cause changes in protein activation inside the cell. This can lead to changes in cell behavior and trigger protein synthesis. For example, growth hormone is produced during times of growth and repair in the body. It binds to receptors on the outside of the cell which cause changes in signal transduction. These signaling systems ultimately create changes in gene transcription which promote cell growth and division.
How does glucose transport work?
These transporter proteins allow glucose to diffuse down its concentration gradient through a channel into the cell where it can be used to create energy. In this way, glucose transport is controlled and tightly regulated to align with the energy needs of the body.