2.3 Between-species carbon balance differences
| Sponge | Host type | I − Epartial | P | R |
| Tectitethya crypta | LMA | 0.93 | 0.03 | 0.46 |
| Mycale laxissima | LMA | 1.45 | 0.11 | 1.67 |
| Verongula reiswigi | HMA | 0.63 | 0.02 | 2.48 |
What is the function of flagella and choanocyte in sponge?
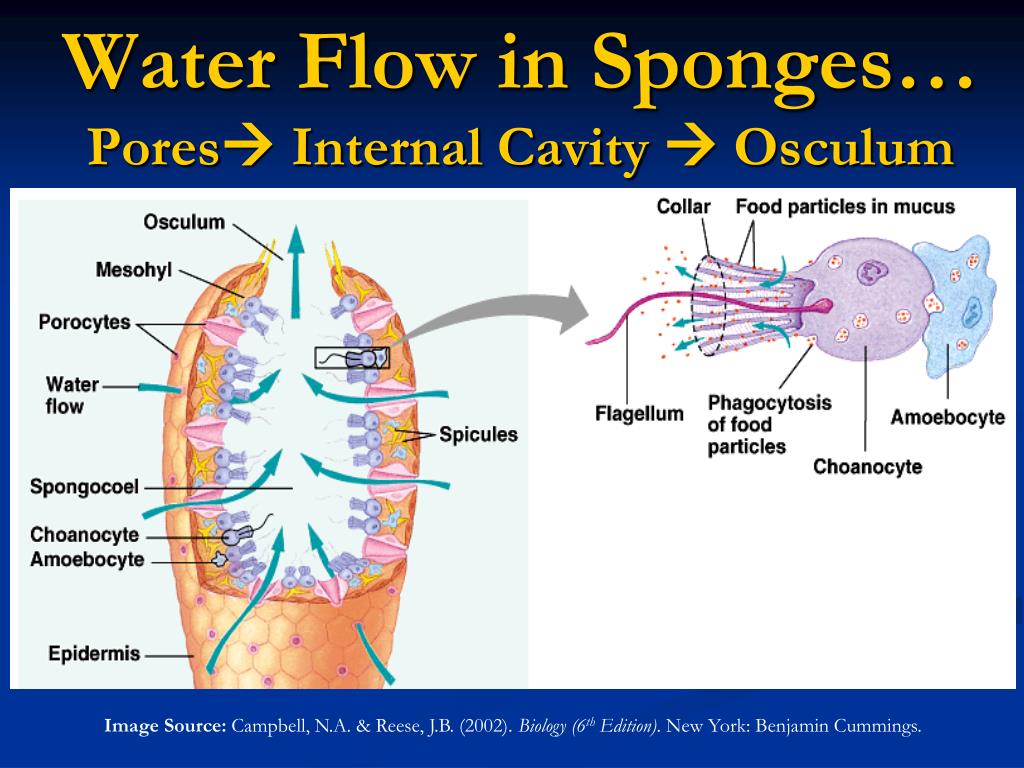
The flagella help in creating a unidirectional flow of water around the body of sponge. Choanocyte also has a collar made of microvilli. These cells capture microcopic food particles. Digestion is also intracellular, taking place within choanocyte.
What is the function of choanocyte?
Choanocyte. The cell has the closest resemblance to the choanoflagellates which are the closest related single celled protists to the animal kingdom (metazoans). The flagellae beat regularly, creating a water flow across the microvilli which can then filter nutrients from the water taken from the collar of the sponge.
Where are choanocytes found in a sponge?
Choanocytes are cells located on the whip-like appendages, called flagella, located in the sponge. Click to see full answer. Similarly one may ask, what is the role of Choanocytes and Amoebocytes in a sponge?
What are the functions of sponges'specialized cells?
What are the functions of sponges' specialized cells: archaeocytes, choanocytes, porocytes? There are several cells in body of sponges and they are responsible to perform different functions. Archaeocytes are totipotent cells which can differentiate into other cell types within the body of sponge.

What is a choanocyte and what does it do?
Choanocytes are specialized cells that have a single flagellum surrounded by a net-like collar of microvilli (Figure 3). Choanocytes join together creating the choanoderm, where they perform two major functions. The first is to create a flow of water and the second is to capture food items as they pass by these cells.
Why is choanocyte important?
Functions of Choanocytes The primary function of choanocytes is to assist with circulation. The flagellum on each choanocyte whips back and forth, which creates water movement. This water current helps circulate seawater within and through the sponge.
What is a choanocyte chamber?
Choanocytes (or 'collar-cells'), are grouped within chambers. They are the main 'pumping stations' for sponge survival. These collar cells have a microscopic central hair-like whip (flagellum) that actively beats to create a water current.
Where is the choanocyte in a sponge?
Location. Choanocytes are found dotting the surface of the spongocoel in asconoid sponges and the radial canals in syconoid sponges, but they comprise entirely the chambers in leuconoid sponges.
What role does the choanocyte play in filter feeding?
Choanocytes help sponges to filter out nutrients from the water. In some species they are also capable of transforming into spermatocytes used to fertilize ova from other sponges.
How a sponge utilizes choanocytes to move water and nutrients?
The beating of flagella from all choanocytes moves water through the sponge. Food particles are trapped in mucus produced by the sieve-like collar of the choanocytes and are ingested by phagocytosis. This process is called intracellular digestion.
What is the structure of a choanocyte?
The choanocytes of Demosponges are small and arranged in a hollow sphere around each flagellated chamber. Each choanocyte possesses on its free end a single flagellum and a collar, which encircles the flagellum. The structure of the collar has been considered to be a continuous cylindrical cytoplasmic projection.
What are choanocytes quizlet?
choanocyte. specialized cells that use flagella to move a steady current of water through the sponge. osculum.
Do choanocytes produce eggs?
The sperm floating in the water reach the “female” sponge (one that is producing eggs at the time of reproduction) by the pumping action of choanocytes.
What features do choanoflagellates have in common with choanocytes in sponges?
Choanoflagellates are almost identical in shape and function with the choanocytes, or collar cells, of sponges; these cells generate a current that draws water and food particles through the body of a sponge, and they filter out food particles with their microvilli.
What do amoebocytes do?
Amoebocytes or archaeocytes are totipotent cells found in sponges. They have varied functions such as transport of digested food from choanocytes to other cells, delivering sperm to egg and can transform into specific cells. The egg cell is formed from amoebocytes for sexual reproduction.
Do choanocytes mitochondria?
Choanocytes also do not possess glycogen reserves and devote significantly less of their cell volume (9.25 ± 0.39%) than choanoflagellates (single: 12.92 ± 0.58% and colonial: 11.56 ± 0.27%) to the nucleus, and less to mitochondria (2.5% ± 0.3% versus single: 5.08 ± 1.14% and colonial: 6.63 ± 0.42%) (Figure S6A).
Classification of Sponges
Taxonomy represents a branch of science that classifies living organisms based upon their evolutionary and genetic relatedness. Sponges are classified as follows:
Sponge Anatomy
Although sponges are multicellular, these animals do not possess tissue-level organization, resulting in the absence of organs. As such, the body of a sponge is relatively simple in structure and designed to basically facilitate the flow of water through the body.
Choanocytes Structure and Location
As briefly touched upon earlier, the internal surfaces of the sponge's body consist of one or more chambers through which water travels. These chambers are lined by choanocytes, which serve as the main water pump for the animal.
How do choanocytes work in a sponge?
By cooperatively moving their flagella, choanocytes filter particles out of the water and into the spongocoel, and out through the osculum. This improves both respiratory and digestive functions for the sponge, pulling in oxygen and nutrients and allowing a rapid expulsion of carbon dioxide and other waste products. Although all cells in a sponge are capable of living on their own, choanocytes carry out most of the sponge's ingestion, passing digested materials to the amoebocytes for delivery to other cells.
What is the cell layer of a sponge?
Choanocyte. They make up the choanoderm, a type of cell layer found in sponges. The cell has the closest resemblance to the choanoflagellates which are the closest related single celled protists to the animal kingdom (metazoans).
What are the main cell types of Porifera?
Main cell types of Porifera. Choanocytes (also known as "collar cells") are cells that line the interior of asconoid, syconoid and leuconoid body types of sponges that contain a central flagellum, or cilium, surrounded by a collar of microvilli which are connected by a thin membrane. Choanocyte. They make up the choanoderm, a type ...
Is choanoflagellate a sister cell?
Choanocytes bear a superficial resemblance to Choanoflagellates. Molecular phylogenies indicate that choanoflagellates and metazoans are sister groups. One can see some modern choanoflag ellates living in small colonies. The evolutionary relationship between the two cell types is debated.
What are the functions of choanocytes in sponges?
Choanocytes join together creating the choanoderm, where they perform two major functions. The first is to create a flow of water and the second is to capture food items as they pass by these cells. The flow of water is initiated through the coordinated beating of flagella. Once water enters the sponge through ostia ( Figure 1 ), it passes through a canal system of lesser or greater complexity, depending on the species, until it reaches the choanocytes. Once at the choanocyte, bacteria are captured in the microvillar net and passed to archaeocytes within the mesohyl. Water exits the sponge through the osculum ( Figure 1 ).
How are choanocytes organized?
The manner in which choanocytes are organized is dictated in part by the general structure of the sponge body. There are three basic categories for the structure of a sponge's aquiferous system and each describes a progressive increase in the complexity of the degree of folding found in the choanoderm.
Why are cytological features not used in sponge taxonomy?
They have never been introduced systematically in sponge descriptions because cytological techniques are considered difficult to apply in routine analysis and because histological slides and electron micrographs could be difficult to interpret ( Erpenbeck, 2004). But the use of cytological features of the aquiferous system for sponge taxonomy was proposed by several authors who focused on the different aspects of choanocytes chambers, choanocytes and apopylar cells (Minchin, 1896; Bidder, 1898; Dendy and Row, 1913; Lévi, 1979; Bergquist, 1980, 1995; Vacelet et al., 1989; Boury-Esnault et al., 1990; De Vos et al., 1990; Bergquist et al., 1998; Bergquist and Cook, 2002a ).
How big do syconoid sponges grow?
These sponges never achieve large sizes, typically growing to less than one centimeter in height, and are typical of the Calcarea. Syconoid sponges create an infolding of the choanocytic lining but these C-shaped choanocyte pockets still directly empty into, and abut, the atrium.
What is the action of the choanocyte flagellum in generating a low pressure to draw water through
The action of the choanocyte flagellum in generating a low pressure to draw water through the collar is well described by Simpson (1984) from Van Tright (1919) and Kilian (1952). Though the basics are quite clear, exactly how the water moves through the collar and chamber is not actually known.
What are spermatic cysts surrounded by?
The spermatic cysts are surrounded by the follicle cells deriving through the transformation of pinacocytes (pseudo-epithelial cells) or archaeocytes. In demosponges cell junctions between the follicle cells are simple (apposition) with no detectable membrane specialization.
How does water enter a sponge?
Once water enters the sponge through ostia ( Figure 1 ), it passes through a canal system of lesser or greater complexity, depending on the species, until it reaches the choanocytes. Once at the choanocyte, bacteria are captured in the microvillar net and passed to archaeocytes within the mesohyl.
What is the function of choanocytes in sponges?
They then push out both carbon dioxide and w. The function of a choanocyte is to create water flow through the body of a sponge. This allows nutrients to filter ...
How does the movement of water in a sponge affect the digestive system?
These flagella then constantly beat at the water, propelling water and nutrients through the pores in the sponge, which the choanocytes trap. The movement of water initiated by the choanocytes aids the digestive and respiratory systems of the sponge, because as well as pulling in water, they also pull in oxygen.
What is the cell wall that helps the movement of water within the plant without requirement of blood circulation?
Permeability : Cell wall though is tough and rigid is permeable to small molecules like water and carbon dioxide. This helps the movement of water within the plant without requirement of blood circulation. Of-course the main transport vessel for the conduction in plant is xylem and phloem.
Which transport vessel is responsible for the conduction of plant cells?
Of-course the main transport vessel for the conduction in plant is xylem and phloem. But cell wall permeability helps inter-cellular transport by diffusion and other processes. Also besides, in bacteria cell wall provides flagella and pili functions.
