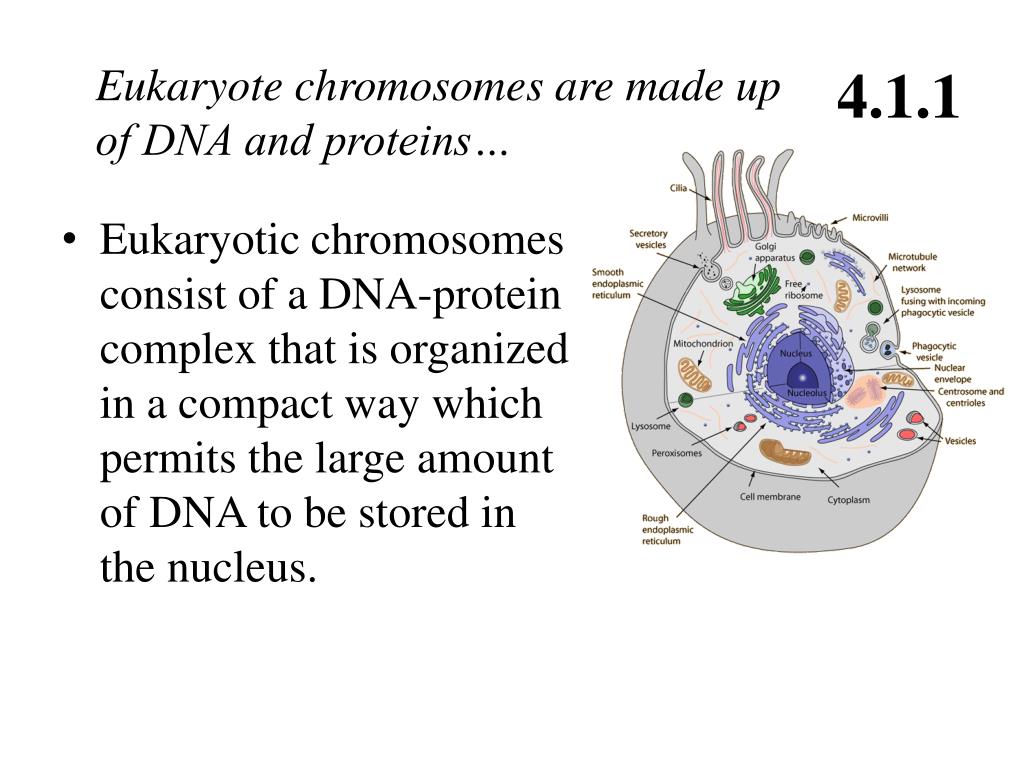
The Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance states that the theory of linkage is the inheritance of features in a way that defies Mendel
Gregor Mendel
Gregor Johann Mendel was a scientist, Augustinian friar and abbot of St. Thomas' Abbey in Brno, Margraviate of Moravia. Mendel was born in a German-speaking family in the Silesian part of the Austrian Empire and gained posthumous recognition as the founder of the modern scienc…
Why does each chromosome have only one chromatid?
Then during mitosis, when the DNA is transferred to the two daughter cells, one of each of those chromatids is transferred to each of the two cells. So a chromatid is one copy of a chromosome after DNA replication.
What is the chromosome theory?
The chromosome theory of heredity, developed in 1902–1904, became one of the foundation stones of twentieth-century genetics. It is usually referred to as the Sutton–Boveri theory after Walter ...
Why are chromosomes important to inheritance?
Why are chromosomes important to heredity? Chromosomes are the carriers of genetic information. During cell division, each DNA helix in the cell coils up to form a chromosome which then acts as a package carrying genetic information from the parent cell to the daughter cell.
What is the role that the chromosomes play in inheritance?
What role do chromosomes play in inheritance? Each gene occupies a specific position on a chromosome . Because genes provide instructions for making proteins, and proteins determine the structure and function of each cell in the body, it follows that genes are responsible for all the characteristics you inherit .

What does chromosome theory of inheritance explain?
The chromosomal theory of inheritance explains how genetic material is passed from parents to offspring through chromosomes. Chromosomes are large structures of DNA found in the nucleus of each cell.
What is the chromosome theory of inheritance quizlet?
The chromosome theory of inheritance states that inherited traits are controlled by genes residing on chromosomes faithfully transmitted through gametes, maintaining genetic continuity from generation to generation. Both the chromosome theory of inheritance and Mendel's findings are the same.
Which best describes the chromosomal theory of inheritance?
a. The theory was proposed by Charles Darwin. It describes the units of inheritance between parents and offspring as well as the processes by which those units control offspring development.
Who described the chromosomal theory of inheritance?
1: Sutton and Boveri: (a) Walter Sutton and (b) Theodor Boveri are credited with developing the Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance, which states that chromosomes carry the unit of heredity (genes).
How does the chromosome theory of inheritance provide a physical explanation for Mendelian inheritance quizlet?
The chromosomal theory of inheritance holds that the separation of maternal and paternal chromosomes during gamete formation is the physical basis of Mendelian inheritance.
What are the differences between genes and chromosomes?
Chromosomes are structures within cells that contain a person's genes. Genes are contained in chromosomes, which are in the cell nucleus. A chromosome contains hundreds to thousands of genes. Every normal human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes.
Which of the following statements correctly describes the chromosome theory of inheritance as it was understood in the early 20th century?
Which of the following statements correctly describes the chromosome theory of inheritance as it was understood in the early 20th century? Mendelian genes are at specific loci on the chromosome and, in turn, segregate during meiosis.
When was the chromosome theory of inheritance?
" The chromosome theory of inheritance is credited to papers by Walter Sutton in 1902 and 1903, as well as to independent work by Theodor Boveri during roughly the same period. Boveri was studying sea urchins, in which he found that all the chromosomes had to be present for proper embryonic development to take place.
When was the chromosomal theory of inheritance?
1902: Chromosome Theory of Heredity.
What is the chromosome theory of inheritance Chapter 15?
1. What is the chromosome theory of inheritance? According to the chromosome theory of inheritance, Mendelian genes have specific loci (positions) along chromosomes, and it is the chromosomes that undergo segregation and independent assortment, accounting for inheritance patterns.
How does the chromosome theory of inheritance provide a physical explanation for Mendelian inheritance?
Answer and Explanation: The chromosome theory of inheritance explains Mendelian inheritance because the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis can account for the laws. The chromosome theory of inheritance is the theory by Theodor Boveri and Walter Sutton which said genetic information is carried on chromosomes.
What is law of segregation simple definition?
Law of segregation is the second law of inheritance. This law explains that the pair of alleles segregate from each other during meiosis cell division (gamete formation) so that only one allele will be present in each gamete.
What is the probability (%) of having a child that is affected by a autosomal recessive disorder if both parents are carriers?
If you are born to parents who both carry the same autosomal recessive gene, you have a 25% (1 in 4) chance of inheriting the abnormal gene from both parents and developing the disease. You have a 50% (1 in 2) chance of inheriting one abnormal gene. This would make you a carrier.
Who proposed the chromosomal theory of inheritance?
The chromosomal theory of inheritance was proposed by Sutton and Boveri independently in 1902. It was experimentally proved by Morgan and his colleagues.
Who studied the behaviour of chromosomes and found that it was parallel to the behaviour of genes?
Sutton, along with Boveri, studied the behaviour of chromosomes and found that it was parallel to the behaviour of genes. They used chromosome movements to explain Mendel’s laws. Together they proposed a theory that the chromosomes were the carriers of Mendel’s factors. They observed two important things:
How many homologous chromosomes does a zygote have?
The homologous chromosomes from two parents fuse during fertilisation, and thus, the zygote has one homologous chromosome from each parent. Mendel held the opinion that paternal and maternal characters mix up in the progeny.
What are the Mendelian factors?
Sutton and Boveri recognised close parallelism between the Mendelian factor and behaviour of chromosomes during sexual reproduction, like: 1 Chromosomes occur in homologous pairs. Therefore, Mendel also assumed that factors exist in pairs. 2 Synapsed chromosomes segregate during gametogenesis, precisely, meiosis-I. Mendel also suggested the segregation of paired factors during gametogenesis.#N#(a) This is Mendel’s law of segregation. 3 The chromosomes of the various homologous pairs are assorted at random, and chromosomes of each pair segregate independently. This is the same behaviour of factors, as Mendel suggested.#N#(a) This is Mendel’s law of Independent assortment. 4 The homologous chromosomes from two parents fuse during fertilisation, and thus, the zygote has one homologous chromosome from each parent. Mendel held the opinion that paternal and maternal characters mix up in the progeny. 5 The chromosomes retain their structures and individuality throughout the life cycle of an individual. Mendel also suggested that the characters are not lost, even if they are not expressed.
What are gametes formed during?
The gametes formed during gametogenesis (i.e., sperms and ova) form a bridge between one generation and the next generation. The sperms and ova carry all the hereditary traits.
Which type of chromosomes synapse during meiosis?
Homologous chromosomes synapse during meiosis and then segregate independently into different cells, which establish the quantitative basis of segregation and independent assortment of hereditary characters.
Where are the genes located in the chromosomes?
The chromosomal theory of inheritance states that the genes (or Mendelian Factors) are located at specific loci on the chromosomes, and it is the chromosomes that segregate (or separate) and assort (distribute into groups of the same kind) independently during meiosis and recombine at the time of fertilisation in the zygote.
Who cleared out the Chromosome theory of inheritance?
However, in 1915, the controversy has finally been cleared out by the works of Thomas Morgan on the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster.
What is the relationship between chromosomes and Mendel's observations?
1. Chromosomes Come in Pairs. This observation is closely related to Mendel’s observations in genes that come in pairs. Just like in Mendelian factors, the origin of one copy of the chromosome comes from both parents. 2.
What is linkage in genetics?
This phenomenon is known as the “ linkage “. In general, genes that exhibit linkage tend to affect the expression of genes in the next generations. In conclusion, the postulation of the Chromosome Theory of Inheritance had served as the vehicle for chromosomes to be viewed of great importance regarding heredity.
What is it called when two genes are located on a single chromosome?
This phenomenon is known as the “ linkage “.
Which law of inheritance does the Boveri and Sutton theory obey?
With great similarities, it can be inferred that the Boveri and Sutton’s theory obey Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance. It is just quite interesting how despite the absence of any evidence about chromosomes, the Chromosome Theory of Inheritance was correctly postulated.
Which part of the cell is responsible for carrying genetic material?
Chromosomes are known to carry the genetic material in living organisms. But did you ever wonder who first discovered that genes are located on the chromosomes? And what is this Chromosome theory of inheritance all about? Find out below.
Who discovered that chromosomes contain genetic material?
In 1902 and the following year, scientists Theodor Boveri and Walter Sutton independently published works that together pointed out that the chromosome could contain the genetic material. At present, it is called as the “ Chromosome Theory of Inheritance “.
Who discovered that genes are located on chromosomes?
The chromosome theory of inheritance, or the idea that genes are located on chromosomes, was proposed based on experiments by Thomas Hunt Morgan using Drosophila melanogaster, or fruit flies. Drosophila are like humans in that an individual with two X chromosomes is female and an individual with one X and one Y chromosome is male ...
Why do sex-linked traits show interesting inheritance patterns?
Sex-linked traits show interesting inheritance patterns in part because females have two copies of each X chromosome, but males only have one . This inheritance pattern means that a male with the recessive allele will always show the recessive trait, because he only has one copy of the allele. In contrast, most genes are located on ...
How does genetic linkage occur?
Genetic linkage occurs when the genes controlling two different traits are located near each other on the same chromosome . The basic idea is that if two genes are on the same chromosome, and you inherit the whole chromosome, then you have to inherit those two genes (and whatever alleles they have) together.
What happens when you cross over two genes?
A crossover event between the locations of two genes on a chromosome results in genetic recombination, or new combinations of alleles on a chromosome. Crossing over between genes A and B results in recombinant chromosomes with new allele combinations a, b and A, B, in addition to the original parental combinations A, b and a, B.
Where are most genes located?
In contrast, most genes are located on the autosomes, or non sex chromosomes, where both males and females have two copies of each gene. Recall that all the patterns of inheritance observed by Mendel, including the principle of segregation and the principle of independent assortment are explained by the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis. ...
Why did Mendel's independent assortment violate the principle of independent assortment?
This result seemed to violate Mendel’s principle of independent assortment, because two different traits (gender and eye color) seemed to be linked. The only way to explain these results was if the gene that caused eye color was located on (linked to) the X chromosome.
Do both parents carry alleles?
both parents must carry allele. parents may not display trait (carriers) ~1/4 of children affected (if both parents are carriers) Autosomal dominant. affects males and females equally. only one parent must carry alllele. if child displays trait, at least one parent must also display trait.
Which direction do chromosomes align in the metaphase plate?
chromosomes align on metaphase plate and pulled toward opposite direction
Why are PARs called pseudoautosomal regions?
PARs (pseudoAutosomal regions) because identical regions/genes are present at the ends of X chromosomes
How does the cytoplasm divide?
cytoplasm divides by contractile ring and splits into 2 daughter cells with identical nuclues/organelles
Where is the centromere located?
centromere is in the middle of the chromosome
Which cells make up the majority of tissues in an organism?
cells who have mitotically split and make up majority of tissues in organism

Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance: Who Proposed It?
Features of Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
Parallelism Between Mendelian Factor and Chromosome
Law of Segregation
Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance: Law of Independent Assortment
Chromosomal Theory of Linkage
Summary
- Thus, chromosomal theory of inheritance explains that the genes (or Mendelian Factors) are located at specific loci on the chromosomes, and it is the chromosomes that segregate (or separate) and assort (distribute into groups of the same kind) independently during meiosis and recombine at the time of fertilisation in the zygote. Since Mendel’s fact...
FAQs About Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance