
Do Plant Cells Have Cytoplasm?
- Cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the thick, jelly-like liquid present in all cells. ...
- Functions of cytoplasm. The primary function of the cytoplasm is to provide a medium for the chemical reactions of the plant to happen.
- Cytosol. The cytosol is the part of the cytoplasm not present within the membrane-bound organelles. ...
- Protoplasm. ...
What does the cytoplasm do for a plant cell cell?
Cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance that is found in animal and plant cells. It acts as a transport system and prevents the cell from collapsing.It allows gases to pass in and out of the cell.Cytoplasm acts as a transport system and lets things move freely it is in both plant and animal cells. thanked the writer. blurted this.
Do plant cells have more cytoplasm than animal cells?
animal cells have more cytoplasmic content in general but there can be variations depending upon the type of cell. Also you can identify non- membranous structures called centrosomes or centrioles in animal cells,whereas they are absent in the plant cell cytoplasm. more lysosomes have been observed in animal cells as well.
What is the main function of cytoplasm?
■ One of the important functions of cytoplasm is that it provides proper shape to cells. It fills the cells thus allowing the organelles to remain in place. ■ The cytoplasm acts as a regulator and protects the cell's genetic material as well as cellular organisms from damage by motion and collision with other cells.
What are functions of the cytoskeleton in plant cells?
Cytoskeleton Functions. The important cytoskeleton functions are mentioned below: It provides shape and support to the cell. It helps in the formation of vacuoles. It holds different cell organelles in place. It assists in cell signalling. It supports intracellular movements like the migration of cell organelles, transportation of vesicles in ...
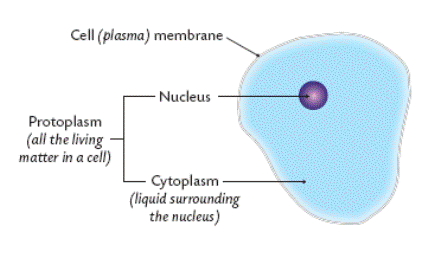
What is the function of the cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm Functions. The cytoplasm functions to support and suspend organelles and cellular molecules. Many cellular processes also occur in the cytoplasm, such as protein synthesis, the first stage of cellular respiration (known as glycolysis ), mitosis, and meiosis. The cytoplasm helps to move materials, such as hormones, ...
What is the cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm consists of all of the contents outside of the nucleus and enclosed within the cell membrane of a cell. It is clear in color and has a gel-like appearance. Cytoplasm is composed mainly of water but also contains enzymes, salts, organelles, and various organic molecules.
Why do plants use cyclosis?
Plants employ cyclosis to shuttle chloroplasts to areas receiving the most available sunlight. Chloroplasts are the plant organelles responsible for photosynthesis and require light for the process. In protists, such as amoebae and slime molds, cytoplasmic streaming is used for locomotion. Temporary extensions of the cytoplasm known as pseudopodia are generated that are valuable for movement and capturing food. Cytoplasmic streaming is also required for cell division as the cytoplasm must be distributed among daughter cells formed in mitosis and meiosis.
What is the structure that separates the cytoplasm from the extracellular fluid?
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is the structure that keeps cytoplasm from spilling out of a cell. This membrane is composed of phospholipids, which form a lipid bilayer that separates the contents of a cell from the extracellular fluid. The lipid bilayer is semi-permeable, meaning that only certain molecules are able to diffuse across the membrane to enter or exit the cell. Extracellular fluid, proteins, lipids, and other molecules may be added to a cell's cytoplasm by endocytosis. In this process, molecules and extracellular fluid are internalized as the membrane turns inward forming a vesicle. The vesicle encloses the fluid and molecules and buds off from the cell membrane forming an endosome. The endosome moves within the cell to deliver its contents to their appropriate destinations. Substances are removed from the cytoplasm by exocytosis. In this process, vesicles budding from Golgi bodies fuse with the cell membrane expelling their contents from the cell. The cell membrane also provides structural support for a cell by serving as a stable platform for the attachment of the cytoskeleton and cell wall (in plants).
What are the two parts of the cytoplasm?
The cytoplasm can be divided into two primary parts: the endoplasm ( endo -,- plasm) and ectoplasm ( ecto -,-plasm). The endoplasm is the central area of the cytoplasm that contains the organelles. The ectoplasm is the more gel-like peripheral portion of the cytoplasm of a cell.
What are the three types of inclusions in the cytoplasm?
Three types of inclusions found in the cytoplasm are secretory inclusions, nutritive inclusions, and pigment granules . Examples of secretory inclusions are proteins, enzymes, and acids. Glycogen (glucose storage molecule) and lipids are examples of nutritive inclusions.
What are some examples of organelles?
Examples of organelles include mitochondria, ribosomes, nucleus, lysosomes, chloroplasts, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus. Also located within the cytoplasm is the cytoskeleton, a network of fibers that help the cell maintain its shape and provide support for organelles.
What is the cytosol made of?
It is made up of a complex mixture of cytoskeleton filaments, water, and dissolved molecules.
Why is the cytoplasm important?
Thus, we can see that the cytoplasm forms an important part of the plant cell. It helps in providing a medium for the chemical reactions of the plant cell to occur.
What is the thick jelly-like liquid that is present in all cells?
The cytoplasm is the thick, jelly-like liquid present in all cells. It is enclosed by the plasma membrane and the cell wall in plants.
What is the primary component of the protoplasm?
The protoplasm is a colorless, jelly-like substance present in the cell. The primary component of the protoplasm is the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm regulates the cellular environment and helps the cell stay in shape.
What is the function of the cytoplasm?
The primary function of the cytoplasm is to provide a medium for the chemical reactions of the plant to happen. Processes such as cell division and glycolysis happen in the cytoplasm.
What are the elements that are found in the cytoplasm?
About 80% of the cytoplasm is usually made up of water. Due to this, the cytoplasm is colorless. It also comprises cytosol, which is an element of the cytoplasm.
What is the secondary component of a plant cell?
The secondary component is the nucleus which stores the genetic material of the cell. These two together form the protoplasm. It also contains dissolved proteins, fats, enzymes, and hormones which are necessary for the plant.

Divisions
Components
- Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria and archaeans, do not have a membrane-bound nucleus. In these cells, the cytoplasm consists of all of the contents of the cell inside the plasma membrane. In eukaryotic cells, such as plant and animal cells, the cytoplasm consists of three main components. They are the cytosol, organelles, and various particles and granules called cytopla…
Cytoplasmic Streaming
- Cytoplasmic streaming, or cyclosis, is a process by which substances are circulated within a cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs in a number of cell types including plant cells, amoeba, protozoa, and fungi. Cytoplasmic movement may be influenced by several factors including the presence of certain chemicals, hormones, or changes in light or temperat...
Cell Membrane
- The cell membrane or plasma membrane is the structure that keeps cytoplasm from spilling out of a cell. This membrane is composed of phospholipids, which form a lipid bilayer that separates the contents of a cell from the extracellular fluid. The lipid bilayer is semi-permeable, meaning that only certain molecules are able to diffuse across the membrane to enter or exit the cell. Extracell…
Sources
- “Cytoplasmic inclusions.” The Free Dictionary, Farlex,
- “Ectoplasm.” The Free Dictionary, Farlex,
- “Endoplasm.” The Free Dictionary, Farlex, .
- Goldstein, Raymond E., and Jan-Willem van de Meent. “A physical perspective on cytoplasmic streaming.” Interface Focus 5.4 (2015):20150030.