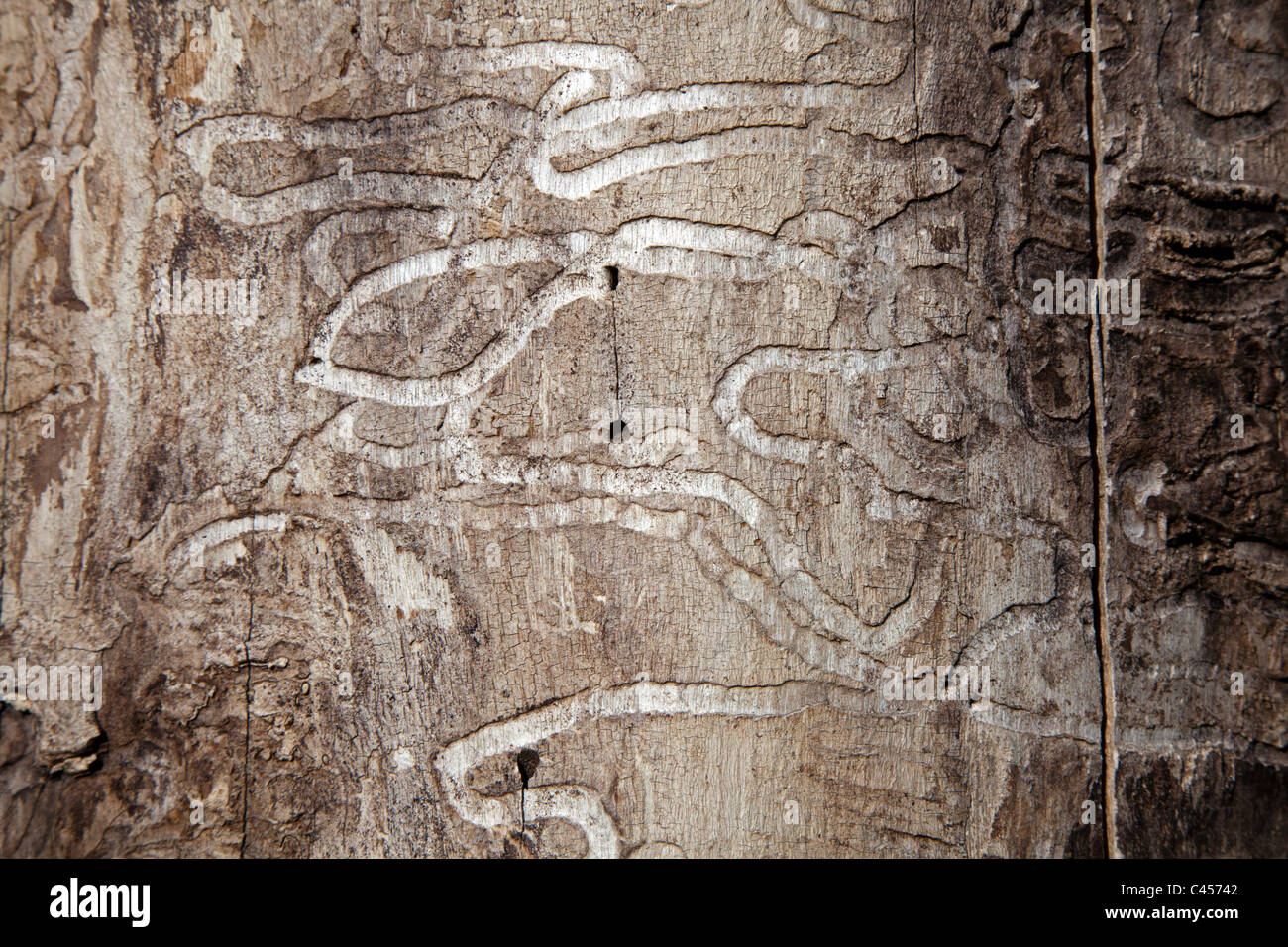
The larvae of the Emerald Ash Borer feed between two different layers within the tree.
- These layers are the sapwood and bark sections.
- The Larvae feed along the entire length of the tree’s trunk and also on the branches.
- It’s said they feed on branches that generally have a diameter of over 0.8 inches.
- Some trees can have hundreds or even thousands of larvae underneath the bark.
What is the natural predator for emerald ash borer?
Within its native range in Asia, emerald ash borer is attacked by a variety of predators including several species of parasitoid wasps that specialize on the beetle’s eggs or larvae.
Are your trees protected from the emerald ash borer?
Less than an inch long and metallic green, it was an emerald ash borer (EAB), an invasive beetle that has ... Midwestern sites have shown that as wasp populations build and seed-producing trees are protected with insecticide, young ash are surviving. “
Will emerald ash borer survive the winter?
Winter temperatures of approximately −38 °C (−36 °F) limit range expansion., and overwintering emerald ash borer survive down to average temperatures of −30 °C (−22 °F) because of antifreeze chemicals in the body and insulation provided by tree bark.
What does emerald ash borer damage look like?
Ash borers usually attack a tree first in the upper parts of the canopy, so damage is usually far advanced by the time emergence holes or damage are seen on the lower trunk of the tree. The first sign of EAB attack is vertical cracks in the bark, usually accompanied by woodpecker damage.
See more

What happens to a tree with emerald ash borer?
EAB chews through the tree's water and nutrient-conducting tissues, strangling the tree. If there is a high population of EAB in the tree, the leafy canopy in ash trees will start to die. A third to a half of the branches may die in one year.
What damage does the emerald ash borer do?
The emerald ash borer's larval stage is responsible for the damage that leads to the death of its host. The larvae's feeding under the tree bark, eventually damaging the tree's ability to transport moisture and nutrients from the soil to the tree's leaves, causes ash tree decline and death.
Can a tree recover from emerald ash borer?
Can ash trees be saved from emerald ash borer? In many cases, yes. Ash conservation efforts are stronger than ever, and treatment options are available to protect trees. In fact, when applied correctly, EAB treatment is 85 to 95 percent effective.
What trees are affected by the emerald ash borer?
What trees are susceptible to emerald ash borer? EAB gravitates towards really any ash tree—healthy or unhealthy, young or old! All ash trees are potential targets, even if EAB may prefer to lay eggs or feed on stressed trees.
What does a tree infested with ash borer look like?
Signs of infestation include thinning and yellowing leaves, D-shaped holes in the bark, and canopy and bark loss. Scientists are working to find ways to stop the beetle. It's been proven that efforts to save trees can be improved by identifying infested trees in their first year.
What eats emerald ash borer?
In addition to the introduced biocontrol agents, some native wasps have also been shown to parasitize emerald ash borer larvae, and birds – especially woodpeckers – eat the larvae and pupae.
Do woodpeckers eat emerald ash borer?
Their results proved that woodpeckers were indeed preying on emerald ash borers — eating 85 percent of the emerald ash borer in an infested tree.
What kills the emerald ash borer?
There are four active ingredients used to control emerald ash borer: imidacloprid, dinotefuran, emamectin benzoate, and azadirachtin. Imidacloprid. Imidacloprid is the most easily applied and usually least expensive of the insecticides used to control emerald ash borer.
Should I cut my ash tree down?
Some homeowners might be hesitant to remove dead ash trees because they provide valuable habitat for a range of woodland animals and mushrooms. However, we do not recommend keeping them standing unless you can guarantee that no people, domesticated animals, or property will ever be in their path if they fall.
Do wasps eat emerald ash borers?
For several years, the U.S. Department of Agriculture's Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) has used the emerald ash borer's (EAB) natural enemies— tiny stingless wasps known as parasitoids—as biological control agents to help manage infestations.
Can you stop emerald ash borer?
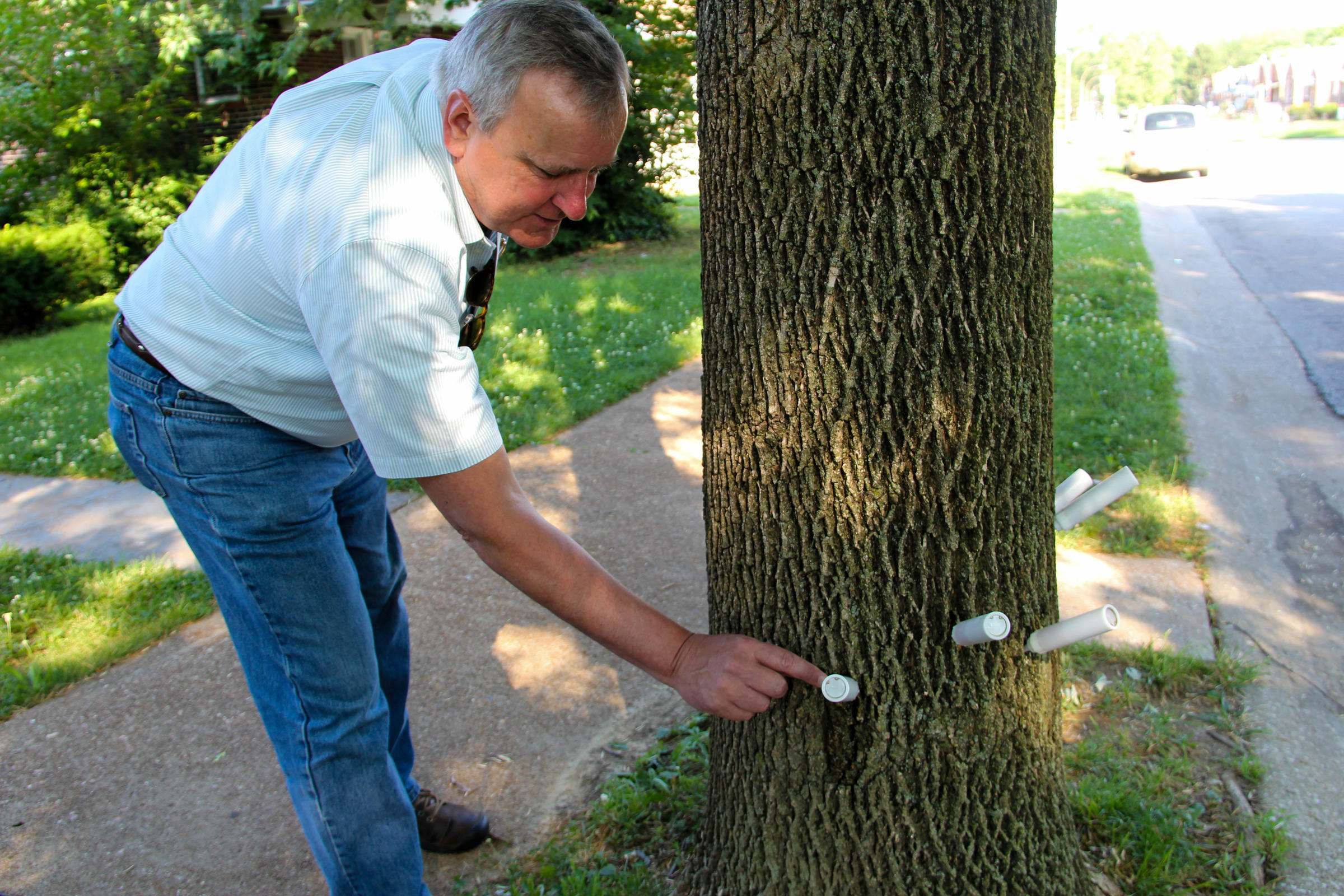
Homeowners can protect ash trees against EAB with the systemic insecticide imidacloprid, applied to the soil at the base of the tree. It is most effective when applied in spring but can also be applied in fall. It is less effective on trees over 50 inches in circumference.
Is emerald ash borer still a threat?
UPDATE: As of late June, 2022, emerald ash borer has been found in Forest Grove, Oregon. This is the farthest west the insect has been found in North America.
What kills the emerald ash borer?
There are four active ingredients used to control emerald ash borer: imidacloprid, dinotefuran, emamectin benzoate, and azadirachtin. Imidacloprid. Imidacloprid is the most easily applied and usually least expensive of the insecticides used to control emerald ash borer.
What does an ash borer do?
The Emerald Ash Borer (Agrilus planipennis or EAB) is responsible for the destruction of tens of millions of ash trees in 30 states. Native to Asia, it likely arrived in the United States hidden in wood packing materials.
Is emerald ash borer still a threat?
UPDATE: As of late June, 2022, emerald ash borer has been found in Forest Grove, Oregon. This is the farthest west the insect has been found in North America.
How many trees has the emerald ash borer killed?
Ash trees are one of the most valuable and abundant North American woodland trees: estimates of total number of ash trees in the United States alone range between seven and nine billion. The emerald ash borer has destroyed 40 million ash trees in Michigan alone and tens of millions throughout other states and Canada.
How much damage does the ash borer do to trees?
It is estimated that the borer will have caused $10 billion in economic damage by 2019. The borers attack trees by laying eggs on the bark. The serpentine feeding galleries of the larvae inside the bark disrupt the flow of nutrients and water and starve the tree. There are efforts to try to save ash trees from the borer.
How many ash trees have been killed by the ash borer?
So far, the insect has spread in all directions, killed tens of millions of ash trees and threatens to kill most of the 8.7 billion ash trees throughout North America. It is estimated that the borer will have caused $10 billion in economic damage by 2019.
What happens if an ash borer destroys a white fringe tree?
Cipollini said that if the emerald ash borer destroys white fringetree, the birds, insects, and other wildlife dependent on the tree’s leaves and fruit may also be threatened. “It’s one of these unexpected consequences of biological invasions,” he said.
What is the name of the agency that inspects ash borer?
He then sent photos of the larvae and a larval specimen to experts at the Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS), an arm of the U.S. Department of Agriculture. Cipollini was told the larvae in the photos appeared to match those of emerald ash borer. The same is being done with the adult specimen in order to confirm its identity.
What is destroying ash trees?
The emerald ash borer, which is destroying ash trees in a large swath of the nation, has apparently spread to a different tree, according to a researcher at Wright State University. Professor Don Cipollini has found that the invasive green beetle has apparently begun to attack white fringetree ( Chionanthus virginicus ).
What is the threat to white fringetree?
Cipollini said the threat to white fringetree is the latest example of the narrowing of the plant ecosystem, which provides humans with such things as fuel, water purification, and erosion control.
When did Borers attack White Fringetree?
He discovered that borers were also attacking white fringetree in August when he acted on a hunch.
What is the closest threat to the EAB?
Without a natural predator and the Woodpecker being the closest known threat to the EAB, the population has been able to thrive with plentiful amounts of food and an abundance of hosts in the form of different Ash tree species across North America.
How many larvae are there in a tree?
Some trees can have hundreds or even thousands of larvae underneath the bark.
Is the EAB a natural predator?
No natural predators in North America#N#Without a natural predator and the Woodpecker being the closest known threat to the EAB, the population has been able to thrive with plentiful amounts of food and an abundance of hosts in the form of different Ash tree species across North America. With our ten years of experience, we’ve seen the population rapidly increase throughout the Twin Cities and beyond which is why it’s important to spread awareness about this problem.#N#Larvae are the real problem#N#There have been many studies conducting research into just how the EAB can kill a tree.
How to control Emerald Ash Borer?
Controlling the spread of emerald ash borer begins with keeping ash trees healthy and unstressed. The insect is usually spread through human activities, such as moving infested firewood. Prevent ash borer by inspecting firewood closely before purchasing and buy locally when possible. Do not transport firewood if you live in an area that has an ash borer population.
What is an ash borer?
Emerald Ash Borer Characteristics. The emerald ash borer is so named for its emerald green color. The insect is about ½ inch (1.5 cm.) long and leaves D-shaped holes when exiting the ash trees interior. The pest lays eggs and leaves the larvae to hatch inside the valuable ash trees, where they create serpentine tunnels that interfere with ...
What is the best treatment for ash tree borer?
For the homeowner who spots ash borer damage and wishes to do their own ash tree borer treatment, a soil application of imidacloprid can be applied (such as Bayer Advanced). Most chemicals to control ash borer damage require a pesticide applicator license for purchase.
How far away can you see ash tree borer?
Ash tree borer treatment is not needed until the emerald ash bor er is spotted within a 15 mile (24 km.) radius, unless symptoms are visible on your ash trees. Symptoms include canopy dieback, D-shaped exit holes, and bark splitting on your ash trees . If you see what appears to be ash tree borer damage, you may contact a certified arborist about ...
What is an EAB?
Printer Friendly Version. Image by Donald Bilski. The Emerald ash tree borer (EAB) is an invasive, non native insect discovered in the U.S. during the last decade. Ash borer damage is significant in all species of North American ash trees that become infected.
When to scout for ash borer?
Susceptible trees include white, green, and black ash. Know where your ash trees are located and scout for the pest in June and July as the first step to prevent ash borer from causing serious or deadly damage.
Can you transport firewood to ash borers?
Do not transport firewood if you live in an area that has an ash borer population. Identifying ash trees is another step to lessen ash borer damage. Insecticidal treatments may slow damage to trees that are valued for shade or historic purposes. Ash tree borer treatment should be applied in May before the adult insects emerge.
What is an Emerald Ash Borer?
Scientifically, it is named Agrilus planipennis. To the everyday person, the name is emerald ash borer. EAB is short for Emerald Ash Borer. The EAB is a green jewel-colored beetle that feeds on ash tree species. They reproduce inside the bark. EABs lay eggs in bark crevices, specifically on ash trees, and larvae feed underneath the bark of ash trees. These larvae take up to two years to turn into adults. This species was not very destructive in its land of origination. However, it's been noticed that outside its native range, it is an invasive species and is highly destructive to ash trees.
How fast does Emerald Ash Borer kill ash trees?
When EAB first becomes established, it is usually low in numbers and difficult to detect. But as populations build, external evidence of infestation may be present. As visible symptoms increase, it is often too late as EAB populations explode. This accelerates the damage and it is not uncommon for trees to die within a couple of years.
How does Emerald Ash Borer spread?
On occasion, a long-distance flight will occur with the right conditions. But typically, EAB is spread by human transport of firewood. It is also transported through ash materials harboring the live emerald ash borers.
How can I help prevent the spread of Emerald Ash Borer?
It is crucial to not remove any of the following items from infected and quarantined areas:
Can trees recover from Emerald Ash Borer attack?
A healthy tree that is controlled with insecticides, may be able to survive an EAB attack. If the leaf canopy has already sustained more than 30- 50% loss, it is probably too late to the save the tree.
Can I treat ash trees myself?
But pesticide applications must be done with great care. For large trees, you should certainly get in contact with a licensed professional. Also, you should get in touch with your city or county forester. Local requirements or prohibitions may exist for the treatment of EAB.
What treatments can be used to control Emerald Ash Borer?
In general, there are four control approaches considered for use in the management of EAB:
What trees survived the Emerald Ash Borer?
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — “Lingering ash." That’s what the U.S. Forest Service calls the relatively few green and white ash trees that survive the emerald ash borer onslaught. Those trees do not survive by accident, and that may save the species, according to Penn State researchers, who conducted a six-year study of ash decline and mortality.
How do ash trees resist insects?
There are three kinds of resistance to insects commonly exhibited by trees, Steiner explained, and more research will be needed to determine which ones the ash trees may be deploying. One is avoidance, when a tree doesn't attract the adult females that are flying between the trees as they look for a place to lay their eggs. A tree may accomplish this by not emitting a chemical signal the insects are homing in on.
When did Penn State plant ash trees decline?
Researchers began measuring the decline of ash trees in the Penn State plantation in 2012, shortly after emerald ash borers arrived there, and they measured it every year through 2017. The effect of the insect was devastating. Credit: Kim Steiner/Penn State. All Rights Reserved.
Why do some trees survive longer?
The fact that some trees survived longer means there are heritable genetic differences among trees from different populations and seed parents, Steiner added.
What is wiping out ash trees?
Four views of the emerald ash borer, the invasive insect that is wiping out green and white ash trees: adult beetle (top, left) pupa found under the bark (lower left) beetle peering out of a characteristic D-shaped hole that they bore, and a section of a dead ash tree, showing how the insects girdle and kill a tree by boring under the bark. Credit: David Cappaert/Bugwood.org, Greg Hoover/Penn State, Missouri Department of Conservation, Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources. All Rights Reserved.
Where is the largest collection of green ash germplasm in the world?
This little-known ash plantation off Porter Road near Penn State's Swine Research Facility — the largest collection of green ash germplasm in one location in the world — may play a role in saving the species.
What is the second insect attack?
The second is surviving attack. Adult insects lay eggs on a tree, the larvae hatch and the insects grow into adulthood, all the while causing damage, but the tree is vigorous enough to withstand that injury.
Why Do Some Ash Trees Survive the Emerald Ash Borer?
Forest Service, has discovered a new phenomenon they’re calling “lingering ash.” These ash trees are stubbornly holding on and surviving an emerald ash borer infestation. Because these trees endure and continue to thrive, this invasive species may not cause ash trees to become extinct in North America.
When did Emerald Ash Borer come to America?
Since this invasive species first came to North America in 2002, it has been chewing through local ash trees to a devastating effect. Find out how there may still be hope for the local ash trees and how Martin’s Tree Service can help you keep the trees throughout your property safe. Don’t let the emerald ash borer in Ontario infest ...
How Can I Protect My Ash Trees?
At Martin’s Tree Service, we’re committed to keeping your property safe. Contact us if you have additional questions about your ash trees. There may be some treatment options available or, if it’s too late, we can safely remove dead ash trees from your property. Enjoy a safe, beautiful view without dead or dying ash trees and the threat of the emerald ash borer.
What to do if ash tree dies?
If it’s too late and one of your ash trees has died, you need professional tree removal services. Our team at Martin’s Tree Service can inspect trees on your property and recommend pruning or removal before these trees become a liability. You don’t need to remove all your ash trees if you’re concerned about an emerald ash borer infestation, but dead trees could cause significant property damage or personal injury if they blow over in a strong wind. Dead, standing ash trees should be safely removed both to reduce the risk of falling and to prevent the spread of emerald ash borers throughout Ontario.
What is a lingering ash tree?
Lingering ash trees are typically green and white ash. Not all of these species survive, but there are remnants that do. Researchers are looking at the specific genetic traits that may cause these rugged trees to cling to life.
Can ash borers survive?
They may be vigorous enough to survive having eggs laid, larvae hatch and adult emerald ash borers emerge. Another explanation is that some features of these trees make them unfavourable for adult females to lay their eggs. Finally, the trees may actively attack larvae or remove the necessary nutrition for them to grow into adults.
Is there hope for ash trees?
There is hope for ash trees in your area. Whether you currently have an ash tree that is dying or you’ve never had emerald ash borers on your property, this research may uncover the ways that we can better protect this at-risk tree species.
What is Ash Borer?
Ash Lumber and the Emerald Ash Borer. Ash is a great species of lumber to work with. Ash is known for its staining potential and ability to mimic oak. It has great shock resistance, and solid workability. To this point, it has been an economical wood that was always readily available.
What color is ash?
The light brown and creamy white colorations of ash look great with a simple clear finish and are strikingly beautiful.
Is ash lumber popular?
This resurgence in the popularity of ash is bittersweet. We will continue to celebrate and use ash lumber while it is available, while cheering on the parasitic wasps and hoping they will catch up to the emerald ash borer.
Can you save an ash tree?
Many woodworkers and designers are embracing ash, with a desire of paying homage to ash in its wood form, embracing the idea that even when you can’t save the ash tree, you can save its wood.
Do woodpeckers have stingers?
Woodpeckers are the wasps only natural competition. According to the USDA, the wasps are not attracted to pets or people and have no stingers. What looks like a stinger is actually their egg-laying organ. Currently, scientists are breeding and releasing them.
Can the Emerald Ash Borer be Stopped?
Research continues and (expensive) single-tree treatment is now available, but as of now, the infestation continues. In areas of the country already infected by emerald ash borer, quarantine efforts are underway to slow the spread of the emerald ash borer to new areas ( the latest quarantine map ).
How long does it take for an ash tree to die from ash borer?
Sadly, ash trees that are not treated against the jade green beetle from Northeast Asia die within five to ten years of the emerald ash borer being detected in an area. Part of the problem for municipalities and property owners is what to with all the dead trees that EAB leaves in its wake.
What to do if you suspect ash borer?
If you suspect that your ash tree is infested with emerald ash borer, contact Martin’ s Tree Service to safely remove the tree for you and advise you on what to do with the wood.
What is EAB in ash trees?
Published by Martins Tree. The dangers of emerald ash borer (EAB) are well known by now and the government, local municipalities, and homeowners are all doing their bit to curb the spread of this insidious little creature and save as many of the country’s ash trees as possible. Sadly, ash trees that are not treated against ...
What happens if you remove an ash tree?
Once the dead ash tree in your garden has been removed, you will be left with a pile of wood that is most likely infected with emerald ash borer and your next challenge is how to safely dispose of it and not aid the spread of EAB.
Can you chop down an ash tree?
Many gardeners and homeowners think that they can simply chop down the dead ash tree in their backyard or driveway, but this is not a good idea. The average homeowner will not have the correct equipment to safely remove a dead ash tree and the best way to deal with the problem is to have it removed by a professional tree removal company.
Can ash trees fall over?
Dead ash trees in forests can be left to rot and fall over in their own good time but this is not feasible in urban or populated areas. Ash trees that have been killed by EAB are unstable, unpredictable and downright dangerous and they need to be dealt with immediately.
Can you climb dead ash trees?
Because dead ash trees are brittle and unstable it is often not possible to climb them and cut them down branch by branch. Typically, the entire tree needs to be felled in one piece or removed with the aid of a crane or bucket truck. While this is an expensive exercise, it will most likely save you money in the long run.