
What would happen if carbonic anhydrase was inhibited?
Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase reduces aqueous production. This may be a direct effect of enzyme inhibition or secondary to the altered intracellular pH and blockade of the sodium/potassium ATPase ion channel.
What effects does carbonic acid have on the human body?
- Visual hallucinations.
- Amplification of sensations like sounds and smells.
- Distorted sense of time.
- Blending of senses, such as “seeing” sounds or “hearing” colors.
- Sensation of the mind leaving the body.
- Impulsive behavior.
- Quickly shifting emotions.
- Mystical or religious sensations.
What are the most common uses of carbonic acid?
- Give your hair a fuller, thicker, and more bouncy appearance
- Increase hair strength and increase its volume
- This product can help unclog your hair pores
- Lessen excess sebum production
- Hair follicles are repaired by increasing blood circulation.
- Hairstyling can be improved
- Enhance the overall look and feel of your hair
What are the effects of carbonic acid on limestone?
Limestone is one familiar form of calcium carbonate. Acids in acid rain promote the dissolution of calcium carbonate by reacting with the carbonate anion. This produces a solution of bicarbonate. Because surface waters are in equilibrium with atmospheric carbon dioxide there is a constant concentration of carbonic acid, H 2 CO 3, in the water.
See more
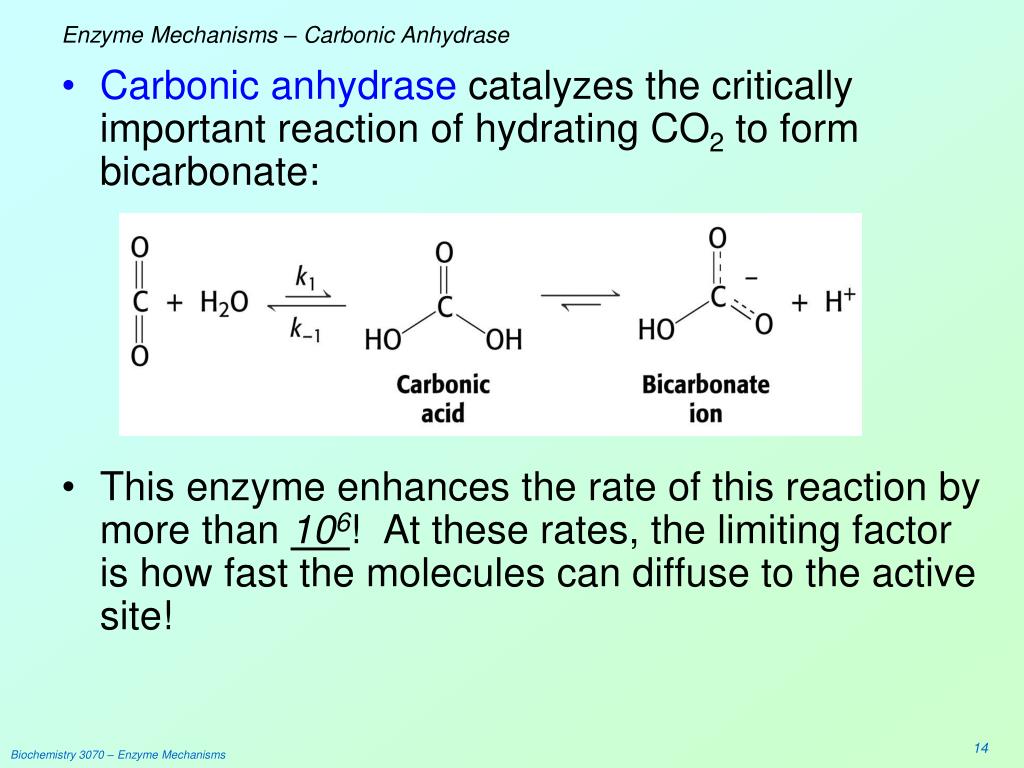
What is carbonic anhydrase and why is it important?
Carbonic anhydrases (CA) are a large family of zinc metallo-enzymes that reversibly catalyze a very important biochemical step in metabolism: These enzymes catalyze this specific chemical reaction and intervene in a great variety of biological processes.
What reaction does carbonic anhydrase catalyze?
Summary: Carbonic anhydrase is an enzyme that balances the pH of the blood and enables the breathing out of carbon dioxide. In red blood cells carbonic anhydrase catalyzes the reaction to convert carbon dioxide into carbonic acid, which further breaks down into bicarbonate ions and protons (H+).
What is the function of carbonic anhydrase quizlet?
What is the function of Carbonic Anhydrase? Carbonic Anhydrase catalyzes a reaction that joins carbon dioxide and water to form carbonic acid that generates bicarbonate ions and transfers CO2 into the blood plasma.
Why is carbonic anhydrase necessary?
Its role is to prevent the depletion of intracellular bicarbonate which accompanies the cyanase-catalyzed bicarbonate-dependent hydrolysis of cyanate (16). CynT rehydrates the CO2 which is produced and thus prevents its loss by rapid diffusion from the cell.
What would happen without carbonic anhydrase?
What would happen if no carbonic anhydrase were present in red blood cells? Without carbonic anhydrase, carbon dioxide would not be hydrolyzed into carbonic acid or bicarbonate. Therefore, very little carbon dioxide (only 15 percent) would be transported in the blood away from the tissues.
How does carbonic anhydrase inhibitor work?
Mechanism of Action Acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. That means this drug works to cause an accumulation of carbonic acid by preventing its breakdown. The result is lower blood pH (i.e., more acidic), given the increased carbonic acid, which has a reversible reaction into bicarbonate and a hydrogen ion.
Which reaction does carbonic anhydrase catalyze quizlet?
The enzyme, carbonic anhydrase, catalyses the reaction of carbon dioxide and water.
How does carbonic anhydrase change the reaction between carbon dioxide and water quizlet?
Carbonic anhydrase (CA) catalyzes a reversible reaction converting carbon dioxide and water to carbonic acid (H2CO3). As soon as bicarbonate is inside the red blood cell, bicarbonate spontaneously combines with hydrogen ions that are released from the hemoglobin to form carbonic acid.
How would a deficiency in carbonic anhydrase affect the buffering of blood?
How would a deficiency in carbonic anhydrase affect the buffering of blood? Carbonic anhydrase is the enzyme that catalyzes the forward and backward reaction for CO₂+H₂O. When there is a deficiency in this enzyme, the activation energy is greater for the reaction. This slows down the buffering of blood.
Which drug is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor?
Acetazolamide, dichlorphenamide, and methazolamide are carbonic anhydrase inhibitors.
Which reaction does carbonic anhydrase catalyze quizlet?
The enzyme, carbonic anhydrase, catalyses the reaction of carbon dioxide and water.
What is the nucleophile in the reaction catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase?
The bottom panel shows the reaction with hydroxide (OH-) as the nucleophile. Since the OH- is a stronger nucleophile, HCO3- formation is faster when OH- is the nucleophile. Between H2O and OH-, formation of HCO3- occurs faster when OH- is the nucleophile.
How carbonic Anhydrases facilitate their turn over?
Carbonic anhydrase facilitates uptake of carbon dioxide by catalyzing the hydration of CO2 dissolved in blood to the more soluble bicarbonate ( ). A zinc ion (Zn2+), coordinated by three histidine ligands and a water (H2O), centers the catalytically active site (Fig. 4.1).
What is the result of the reaction between hemoglobin and carbon dioxide?
When carbon dioxide binds to hemoglobin, a molecule called carbaminohemoglobin is formed. Binding of carbon dioxide to hemoglobin is reversible. Therefore, when it reaches the lungs, the carbon dioxide can freely dissociate from the hemoglobin and be expelled from the body.
1. Explain the Similarities of Cadmium-Containing Carbonic Anhydrase to Other Carbonic Anhydrases?
Answer: The mechanism of the Cadmium Carbonic Anhydrase (CDCA) is importantly similar to that of other carbonic anhydrases in its conversion of car...
2. What are CDCA-Like Proteins?
Answer: The other phytoplankton from various water sources has been tested for the CDCA presence. It was also found that a major count of them have...
3. Give the Transport of Cadmium?
Answer: Still, cadmium is considered lethal to the phytoplankton in higher amounts. Studies have also shown that T. weissflogii contains an initial...
4. What is Meant By Carbon Capture?
Answer: Carbonic anhydrase could prove relevant to carbon capture in principle. A few carbonic anhydrases can withstand temperatures around 107 °C...
What is carbonic anhydrase?
What is a Carbonic Anhydrase? Carbonic anhydrase is defined as an enzyme. It is found in red blood cells, pancreatic cells, gastric mucosa, and the renal tubules that catalyze the interconversion of carbonic acid (H2CO3) and carbon dioxide (CO2). Carbonic anhydrase plays an essential role in respiration by influencing CO2 transport in the blood.
What is the role of carbonic anhydrase in respiration?
Carbonic anhydrase plays an essential role in respiration by influencing CO2 transport in the blood. This enzyme also functions in the hydrochloric acid formation by the stomach.
What is the reaction that is catalyzed by the carbonic anhydrase?
The reaction, which is catalyzed by the carbonic anhydrase is given by: HCO-3 + H+ ⇋ CO2 + H2O. Since carbonic acid has a pKa of up to 6.36 (depending on the medium), a lower percentage of the bicarbonate can be protonated at pH 7. Carbonic anhydrase is the fastest enzyme, and its rate is normally limited by the rate at which its substrates diffuse.
How does carbonic anhydrase help plants?
Carbonic anhydrase in plants helps to increase the carboxylation rate of the RuBisCO enzyme by increasing the concentration of CO2 within the chloroplast. This reaction integrates CO2 into the organic carbon sugars during the photosynthesis process and can use only CO2 form of carbon, but not carbonic acid or bicarbonate.
What is the catalysis of carbonic anhydrase in the lungs?
The following reaction illustrates the catalysis of carbonic anhydrase in our tissues: Catalyzation of the carbonic anhydrase in the lungs is represented by: The reaction's reason being in the opposite directions for lungs and tissues is because of the variable pH levels found in them. Without the carbonic anhydrase catalyst, however, ...
What is the name of the enzyme that removes water from a compound?
An anhydrase can be defined as an enzyme, which catalyzes the water molecule removal from a compound, and so, it is the "reverse" reaction, which gives the carbonic anhydrase its name because it removes water a molecule from the carbonic acid. Carbonic anhydrase in the lungs transforms bicarbonate into carbon dioxide, which is ideal for exhalation.
What are the three residues of carbonic anhydrase?
Many forms of carbonic anhydrase take place in nature. The zinc ion can be coordinated by the imidazole rings of three histidine residues, His94, His96, and His119, in the best-studied, -carbonic anhydrase shape, which is present in animals.
What is the active site of carbonic anhydrases?
bicarbonate and hydrogen ions ). The active site of most carbonic anhydrases contains a zinc ion. They are therefore classified as metalloenzymes.
Where is carbonic anhydrase found?
Carbonic anhydrase was initially found in the red blood cells of cows.
What is the name of the ion that contains carbonic anhydrase?
T. weissflogii, a species of phytoplankton common to many marine ecosystems, was found to contain carbonic anhydrase with a cadmium ion in place of zinc.
How hot can carbonic anhydrase be?
Carbonic anhydrase could in principle prove relevant to carbon capture. Some carbonic anhydrases can withstand temperatures up to 107 °C and extreme alkalinity (pH > 10). A pilot run with the more stable CA on a flue stream that consisted of 12–13% mol composition CO₂ had a capture rate of 63.6% over a 60-hour period with no noticeable effects in enzyme performance. CA was placed in a N-methyldiethanolamine (MDEA) solution where it served to increase the concentration difference (driving force) of CO 2 between the flue stream of the power plant and liquid phase in a liquid-gas contactor.
How does carbonic anhydrase help with glaucoma?
For example, carbonic anhydrase produces acid in the stomach lining. In the kidney, the control of bicarbonate ions influences the water content of the cell. The control of bicarbonate ions also influences the water content in the eyes. Inhibitors of carbonic anhydrase are used to treat glaucoma, the excessive build up of water in the eyes. Blocking this enzyme shifts the fluid balance in the eyes of the patient to reduce fluid build up thereby relieving pressure.
Why are carbonic anhydrase reactions in opposite directions?
The reason for the reactions being in opposite directions for the tissues and lungs is because of the different pH levels found in them. Without the carbonic anhydrase catalyst, the reaction is very slow, however with the catalyst the reaction is 10 7 times faster. The reaction catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase is:
What is the pH of carbonic acid?
Carbonic acid has a pK a of around 6.36 (the exact value depends on the medium), so at pH 7 a small percentage of the bicarbonate is protonated. Carbonic anhydrase is one of the fastest enzymes, and its rate is typically limited by the diffusion rate of its substrates.
What are carbonic anhydrases?
Carbonic anhydrases are a group of enzymes with the ability to modify intra and extracellular pH and therefore influence proliferation, migration and invasion, and contribute significantly to the pH gradient inversion. The family of carbonic anhydrases (CAs), also known as carbonic dehydratases, are a group of metallo-enzymes known ...
Why inhibit membrane carbonic anhydrases?
Inhibiting membrane carbonic anhydrases became a goal in order to curb growth and development of malignancies. 3, 12 In the experimental environment the inhibition of CAs has shown encouraging results in osteosarcoma, 13 glioblastoma, 14 breast, 15 cervical, 16 prostate, 17, 18 lung, 19, 20 colon, renal 21 cancers, T-cell lymphoma 22 and many other cancers.
What is CA in the nephron?
Carbonic anhydrase (CA) facilitates acid–base transport in the distal nephron, just as in the proximal tubule and the thick ascending limb discussed previously.157,158,659 Both histochemical methods (e.g. Hanson's technique) and immunocytochemical methods, and more recently molecular techniques, have been used to localize CA along the distal nephron. Principal cells either do not stain for CA or stain weakly. In contrast, intercalated cells along the distal nephron have intense cytoplasmic CA staining, 375,377,660,661 probably representing Type II CA. 377,662–665 CA II may be important in the development of the IC phenotype. 530 In addition to cytosolic CA, mouse and rabbit IC have membrane associated CA staining, particularly on the apical membrane. 375,453 In the rat, IC do not have membrane associated CA staining 660 or immunoreactivity for CA type IV, the predominant renal membrane associated with CA. 666 In the human kidney, in contrast to other species, all distal convoluted tubule cells are reportedly positive for CA, 377,664,667 in the rat, distal convoluted tubule cells have basolateral membrane staining. 661 In the rabbit OMCD is, staining for CA is predominantly in the apical membrane but there is variability along the length of the segment, the number of positive cells increasing from outer to inner zone of OMCD is, 453 rabbit OMCD is and IMCD i have CA type IV by RT-PCR. 668 Although the IMCD i has predominantly membrane staining as in the OMCD is, the IMCD t does not have CA staining at least in the rabbit, 453 mouse, 375 and probably the rat. 661 Cells in the human kidney IMCD do stain for both CA II and IV. 664,669 Studies of rat IMCD also demonstrate CA activity. 514,670 Another isozyme of membrane associated CA, CA XII, has been shown in the basolateral membranes of the TAL, the distal tubule, and principal cells of the collecting duct. 671–673 Obviously, variations in species, cell types, and techniques prevent a cohesive understanding of the role of CA along the distal nephron. However, CA is present in most, if not all, distal nephron cells involved in acid–base transport. Despite the membrane staining in some cells, functional studies discussed below demonstrate no luminal CA in most distal nephron segments.
How many carbonic anhydrase isoforms are there in fish?
By virtue of its ability to increase the rates of the CO 2 reactions up to 25 000-fold, carbonic anhydrase plays key roles in many physiological processes, ranging from calcification through metabolism, gas transfer, ionic regulation, and acid–base balance. At least 20 carbonic anhydrase isoforms exist in fish.
What is the name of the enzyme that catalyzes the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide?
Stephen Warrillow, in Critical Care Nephrology (Second Edition), 2009. Carbonic anhydrase is a zinc-complexed enzyme found in tissues of all animal species and photosynthesizing organisms, in which it catalyzes the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide (CO2 ).
Where is carbonic anhydrase 2 located?
Carbonic anhydrase II is located in the cytosol of all acidifying renal tubules, and comprises 95% of carbonic anhydrase activity in the kidney. 120 Carbonic anhydrase IV comprises approximately 5% of total renal carbonic anhydrase activity, and is located on the apical and basolateral membrane of the proximal tubule and on the apical membrane of acid-secreting cells in the distal nephron. 192,194,195,245 Carbonic anhydrase XII is present on the basolateral membrane of acidifying segments. 156 In rodents, carbonic anhydrase XIV is also expressed on the apical membrane of the proximal tubule and thick ascending limb. 161 Carbonic anhydrase II protein abundance, normalized per millimeter of tubular length, increases approximately 10-fold in rat proximal convoluted tubules, cortical collecting tubules, and outer medullary collecting tubules between one and twelve weeks of age. 120 In the rabbit, carbonic anhydrase II increases only two-fold during postnatal maturation compared to carbonic anhydrase IV, which undergoes a ten-fold increase in mRNA and protein abundance with cortical maturation. 195,245 Thus, the developmental increase in carbonic anhydrase may be a factor in the postnatal increase in renal acidification.
Which step catalyzes the dissociation of carbonic acid into bicarbonate and a proton?
Fig. 1. Carbonic anhydrase catalyzes step 1 in a reversible manner. Step 2, the dissociation of carbonic acid into bicarbonate and a proton, is a spontaneous phenomenon. This chemical reaction is essential for the life of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Hence, they are widely distributed and can be found in mammals, plants and bacteria.
What is carbonic anhydrase?
These are zinc-containing metalloenzymes that act as catalysts in the dehydration of bicarbonates, as well as the hydration of carbon dioxide. The reversible reaction for this process is as follows: In spite of being one of the fast-reacting enzymes, the rate of carbonic anhydrase is inhibited by the rate ...
What is the role of carbonic anhydrase in exhalation?
As carbonic anhydrase converts bicarbonates to hydrogen ions, it helps in exhalation in the lungs.
What is enzyme activation energy?
Enzyme activation energy. Reactions driven by carbonic anhydrases are extremely crucial in several tissues. In the parietal cells in the stomach, there is a huge amount of acid secretion in the form of hydrogen ions and protons, in the lumen, as well as bicarbonate ions into the blood.
What are the different types of carbonic anhydrase?
There are five recognized distinct carbonic anhydrase families. However, they do not have any similarity in their amino acid sequence and we believe it to be an example of convergent evolution. Carbonic anhydrase is classified as follows: 1 Alpha-CA or α-CA 2 Beta-CA or β-CA 3 Gamma-CA or γ-CA 4 Delta-CA or δ-CA 5 Zeta-CA or ζ-CA
How many families of carbonic anhydrase are there?
Families of Carbonic Anhydrase. There are five recognized distinct carbonic anhydrase families. However, they do not have any similarity in their amino acid sequence and we believe it to be an example of convergent evolution. Carbonic anhydrase is classified as follows: Alpha-CA or α-CA. Beta-CA or β-CA. Gamma-CA or γ-CA. Delta-CA or δ-CA.
What is the role of an enzyme in the regulation of pH?
Other than helping in the transport of carbon dioxide, the enzyme also maintains acid-base balance, aids in the regulation of pH, and helps maintain fluid balance. However, the exact role of the enzyme depends primarily on its location. For instance, in the stomach lining, carbonic anhydrase produces acid.
How does the body produce carbon dioxide?
It produces carbon dioxide in all cells by metabolism. Also, the red blood cells remove it from the body. With the help of the enzyme, the red blood cells convert a majority of it to bicarbonate for transport. After that, it again exhales the carbon dioxide again in the lungs.
What is the role of enzymes in biochemistry?
The main role of enzymes is to make biochemical reactions happen more quickly (1st, 5:34).
Why do enzymes bring molecules closer together?
1. Enzymes can bring two molecules closer together so that collisions happen more often and more quickly.
Why would covalent catalysis help this reaction go faster?
A covalent catalysis would help this reaction go faster because the enzyme would act as an electron carrier (electron sink) by covalently binding to its target molecule thus helping transfer electrons (1st, 3:41).
Why would acid/base catalysis go faster?
Acid/base catalysis would help this reaction go faster because the enzyme acts like an acid or base. Acids/bases are good proton carriers and it would help move that proton around (1st, 2:56).
When are enzymes not consumed?
Enzymes are NOT consumed when they catalyze a reaction and the same enzyme can catalyze reactions over and over again (2nd, 5:28).
Why does electrostatic catalysis help DNA replication?
Electrostatic catalysis from a metal cation would help DNA polymerase during DNA replication because it stabilizes all the negatively charged phosphate groups on the backbone of DNA (1st, 3:58).
Which stage of the enzyme is most tightly bound to its substrate?
The enzyme is most tightly bound to its substrate during the transition state (induced fit stage) because it is when the enzyme and substrate change their shape a little bit so that they mold together to bind really tightly and it is also when the enzyme is catalyzing the reaction at full force (3rd, 3:59).
Why are carbonic anhydrase inhibitors used in emergency situations?
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are applicable during emergencies because they are able to rapidly reduce the pressure that has built up inside the eye by 40% to 60%. The less fluid that is allowed to build up yields less pressure behind the eye.
What type of bond does oxygen form with Zn2+?
Anionic oxygen forms a bond with Zn2+
Overview
The carbonic anhydrases (or carbonate dehydratases) (EC 4.2.1.1) form a family of enzymes that catalyze the interconversion between carbon dioxide and water and the dissociated ions of carbonic acid (i.e. bicarbonate and hydrogen ions). The active site of most carbonic anhydrases contains a zinc ion. They are therefore classified as metalloenzymes. The enzyme maintains acid-base balance and he…
Background
An enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms which helps to speed up chemical reactions. Carbonic anhydrase is one important enzyme that is found in red blood cells, gastric mucosa, pancreatic cells, and even renal tubules. It was discovered in the year 1932 and it has been categorized into three general classes. Class one being alpha carbonic anhydrase which is found in mammals, class two being beta carbonic anhydrase which is found in bacteria and pl…
Reaction
The reaction that shows the catalyzation of carbonic anhydrase in our tissues is:
CO2 + H2O H 2CO 3 H + HCO 3
The catalyzation of carbonic anhydrase in the lungs is shown by:
H + HCO 3 H 2CO 3 CO2 + H2O
The reason for the reactions being in opposite directions for the tissues and lu…
Mechanism
A zinc prosthetic group in the enzyme is coordinated in three positions by histidine side-chains. The fourth coordination position is occupied by water. A fourth histidine is close to the water ligand, facilitating formation of Zn-OH center, which binds CO2 to give a zinc bicarbonate. The construct is an example of general acid – general base catalysis (see the article "Acid catalysis"). The a…
Families
Carbonic anhydrase was initially found in the red blood cells of cows.
At least five distinct CA families are recognized: α, β, γ, δ and ζ. These families have no significant amino acid sequence similarity and in most cases are thought to be an example of convergent evolution. The α-CAs are found in humans.
Structure and function
Several forms of carbonic anhydrase occur in nature. In the best-studied α-carbonic anhydrase form present in animals, the zinc ion is coordinated by the imidazole rings of 3 histidine residues, His94, His96, and His119.
The primary function of the enzyme in animals is to interconvert carbon dioxide and bicarbonate to maintain acid-base balance in blood and other tissues, and to help transport carbon dioxide ou…
Cadmium-containing carbonic anhydrase
Marine diatoms have been found to express a new form of ζ carbonic anhydrase. T. weissflogii, a species of phytoplankton common to many marine ecosystems, was found to contain carbonic anhydrase with a cadmium ion in place of zinc. Previously, it had been believed that cadmium was a toxic metal with no biological function whatsoever. However, this species of phytoplankton appears to have adapted to the low levels of zinc in the ocean by using cadmium when there is n…
Carbon capture and sequestration
Carbonic anhydrase could in principle prove relevant to carbon capture. Some carbonic anhydrases can withstand temperatures up to 107 °C and extreme alkalinity (pH > 10). A pilot run with the more stable CA on a flue stream that consisted of 12–13% mol composition CO₂ had a capture rate of 63.6% over a 60-hour period with no noticeable effects in enzyme performance. CA was placed in a N-methyldiethanolamine (MDEA) solution where it served to increase the conce…