What stimulates the flexor reflex?
This is called the flexor reflex. In its classic form, the flexor reflex is elicited most powerfully by stimulation of pain endings, such as by a pinprick, heat, or a wound, for which reason it is also called a nociceptive reflex, or simply a pain reflex. Stimulation of touch receptors can also elicit a weaker and less prolonged flexor reflex.
What is another name for flexor reflex?
This is called the flexor reflex. In its classic form, the flexor reflex is elicited most powerfully by stimulation of pain endings, such as by a pinprick, heat, or a wound, for which reason it is also called a nociceptive reflex, or simply a pain reflex.
What is the function of flexor reflex and withdrawal reflex?
Flexor Reflex and the Withdrawal Reflexes. In the spinal or decerebrate animal, almost any type of cutaneous sensory stimulus from a limb is likely to cause the flexor muscles of the limb to contract, thereby withdrawing the limb from the stimulating object. This is called the flexor reflex.
What is the flexor reflex and shoulder pain?
The Flexor Reflex and Chronic Pain. You’re diagnosed with a torn rotator cuff, a result of years of wear and tear from weight lifting. As the pain increases, you use your shoulder less and less in order to avoid the pain. You also develop the tendency to hold your right arm against your body to limit the movement in your shoulder.
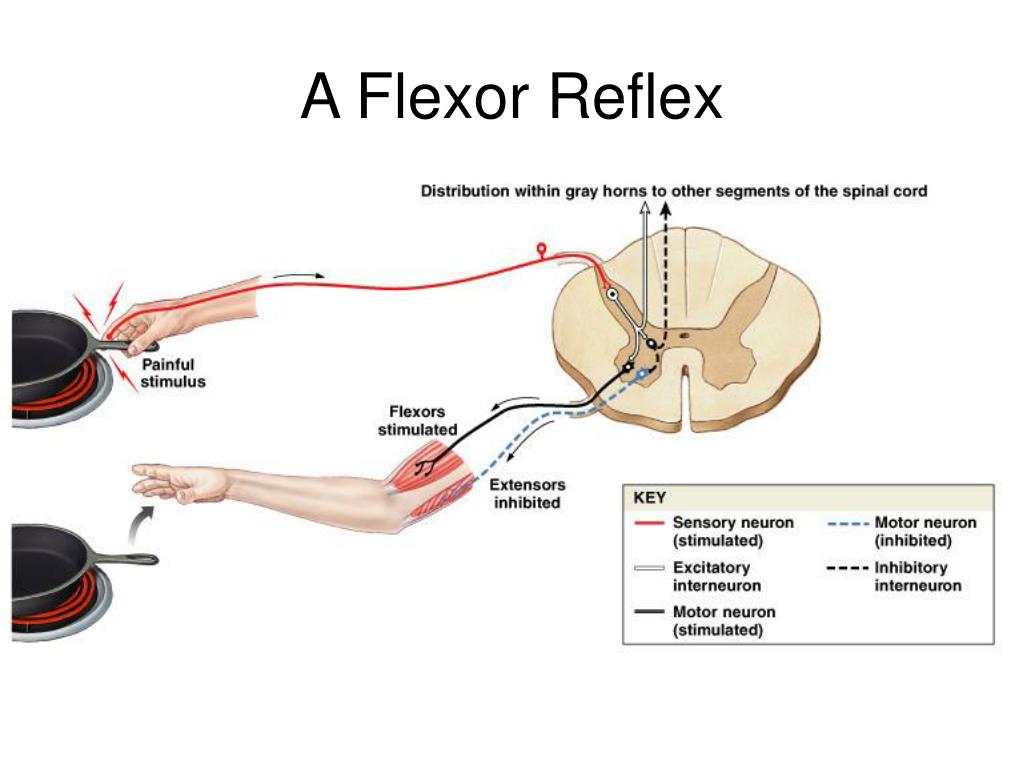
How does the flexor withdrawal reflex work?
The reflex rapidly coordinates the contractions of all the flexor muscles and the relaxations of the extensors in that limb causing sudden withdrawal from the potentially damaging stimulus. Spinal reflexes are often monosynaptic and are mediated by a simple reflex arc.
What happens in the flexor reflex?
A flexion reflex (or “flexion (or flexor) withdrawal reflex”) is a contraction of limb flexor muscles that is evoked by a nociceptive stimulus and that withdraws the limb from the stimulus. A flexion reflex is entirely spinally mediated.
Why is the flexor withdrawal reflex important?
This reflex protects humans against tissue necrosis from contact with noxious stimuli such as pain or heat. It can occur in either the upper or lower limbs.
What is a flexor reflex quizlet?
In a flexor reflex, pain receptors are stimulated to cause what. increased frequency of action potentials to be generated and conducted along the axon of a sensory neuron. The additional spinal cord segments are caused from the. excitation of several association neurons from sensory impulses.
Where is the flexor reflex?
the spinal cordSince a flexor reflex involves the entire limb, the pathway is spread over several segments of the spinal cord. This includes the motor neurons that innervate all of the flexor muscles of the limb.
What is the purpose of the flexor reflex quizlet?
What is the function of the flexor reflex? In both UE and LE, it causes movement of the flexor muscles, to move a limb away from a harmful stimulus.
What reflex is triggered by pain?
The nociceptive flexion reflex (NFR) is a physiological, polysynaptic reflex allowing for painful stimuli to activate an appropriate withdrawal response.
What complements the flexion reflex?
-Lower motor neurons. Which of the following complements the flexion (withdrawal) reflex? -Stretch reflex.
How do you test for flexor withdrawal reflex?
0:000:51Flexor Withdrawl Reflex - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo the next reflex we're going to test is the flexor withdraw reflex. This one has an onset of 28MoreSo the next reflex we're going to test is the flexor withdraw reflex. This one has an onset of 28 weeks and an integration of 1 to 2 months this one also can be irritating to an infant. So if you're
What are the 4 types of reflexes?
There are different types of reflexes, including a stretch reflex, Golgi tendon reflex, crossed extensor reflex, and a withdrawal reflex.
Which reflex occurs in response to excessive tension on a tendon?
The Golgi tendon reflex is a response to extensive tension on a tendon. It helps avoid strong muscle contractions which could tear the tendon from either the muscle or bone. In sports, quick movements can damage the tendon before the reflex can occur.
What is an example of a flexor reflex?
The motor pathways of flexor reflexes are more complex than those of myotatic reflexes because motor neurons for all flexor muscles in the affected limb are activated and the entire limb is flexed. An example is a flexor reflex of the pelvic limb of a dog, which causes flexion of the hock, stifle, and hip.
What is the reflex that complements the withdrawal reflex by making adjustments on the opposite side of the body?
The reflex that complements a withdrawal reflex by making compensatory adjustments on the opposite side of the body receiving the stimulus is the ANSWER: crossed extensor reflex.
What are the flexor muscles?
flexor muscle, any of the muscles that decrease the angle between bones on two sides of a joint, as in bending the elbow or knee. Several of the muscles of the hands and feet are named for this function.
What is the difference between a flexor and an extensor?
Flexor vs Extensor Muscles The muscles that decrease the angle between bones are called flexor muscles. The muscles that increase the angles between bones are called extensor muscles. These muscles decrease the angles between two body parts. These muscles increase the angle between two body parts.
Is the flexor reflex ipsilateral or contralateral?
As a result of activity in this circuitry, stimulation of nociceptive sensory fibers leads to excitation of ipsilateral flexor muscles and reciprocal inhibition of ipsilateral extensor muscles.
Why do reflexes occur quizlet?
Reflexes are automatic responses to sensory input that occur without our intent or often even our awareness unlike other motor actions. Also other fibres: intra-fusal fibres that form the muscle spindle apparatus. Golgi tendon organs monitor tension in tendons produced by muscle stretch or contraction.
What is a withdrawal reflex quizlet?
Terms in this set (3) Withdrawal reflex. Causes flexor muscles to contract in response to a painful or discomforting stimulus. This helps to withdraw part of the body from a painful stimulus to avoid damage.
What are the three kinds of neurons involved in reflexes quizlet?
MatchSensory neurons- receive information about stimulus and transfer it to interneurons.Interneurons- choose the reaction.Motor neurons- execute the reaction.
Is flexor reflex controlled by brain or spinal cord?
spinalRelaxation of the extensor muscles and contraction of the flexor muscles allow complete flexion of the limb. The flexor reflex is a spinal reflex and does not require any activation of the brain.
In which reflex is there a quick contraction of flexor muscles in response to a painful stimulus?
The flexor reflex is a polysynaptic reflex that results in flexor muscle contraction. It is elicited by afferent stimuli collectively known as flexor reflex afferents (FRAs).
What is the response of a Golgi tendon reflex?
The Golgi tendon reflex operates as a protective feedback mechanism to control the tension of an active muscle by causing relaxation before the tendon tension becomes high enough to cause damage.
What is the function of crossed extensor reflex?
The crossed extensor reflex is a contralateral reflex that allows the body to compensate on one side for a stimulus on the other. For example, when one foot steps on a nail, the crossed extensor reflex shifts the body's weight onto the other foot, protecting and withdrawing the foot on the nail.
Why is the Flexor Reflex important?
The flexor reflex is extremely helpful during acute pain or injury because it helps us avoid pain and further damage to our body. However, when it is activated constantly by chronic pain or a prolonged healing process from an injury, we can easily develop muscular patterns that stay with us permanently. What begins as a protective postural mechanism becomes a habitual muscular pattern, causing misalignment, dysfunctional movement, and further pain.
What is the Flexor Reflex?
When one side of the body is injured or feels pain, such as when we step on a nail or touch a very hot pan, an automatic nervous system response called the flexor reflex is triggered. The flexor muscles on the injured side of the body contract to pull the affected area away from the source of pain. Then the crossed-extensor refle x immediately kicks in, activating the extensor muscles on the opposite side of the body so that our weight remains balanced and we don’t fall over.
Who developed the Flexor Reflex?
Thomas Hanna, who developed Clinical Somatic Education, observed the effects of the flexor reflex in his clients. They had tilted and often rotated posture, uneven hips and shoulders, and different patterns of muscular contraction on each side of the body. Many of these clients had scoliosis, sciatica, or pain in their hip, knee, and ankle joints, while others had frozen shoulder, bursitis, or carpal tunnel syndrome.
How do flexor reflexes work?
The pathways for eliciting the flexor reflex do not pass directly to the anterior motor neurons but instead pass first into the spinal cord interneuron pool of neurons and only secondarily to the motor neurons. The shortest possible circuit is a three- or four-neuron pathway; however, most of the signals of the reflex traverse many more neurons and involve the following basic types of circuits: (1) diverging circuits to spread the reflex to the necessary muscles for withdrawal; (2) circuits to inhibit the antagonist muscles, called reciprocal inhibition circuits; and (3) circuits to cause afterdischarge lasting many fractions of a second after the stimulus is over.
What is the flexor reflex?
In its classic form, the flexor reflex is elicited most powerfully by stimulation of pain endings, such as by a pinprick, heat, or a wound, for which reason it is also called a nociceptive reflex, or simply a pain reflex. Stimulation of touch receptors can also elicit a weaker and less prolonged flexor reflex.
How long does the flexor reflex hold the body?
Further, because of afterdischarge, the reflex can hold the irritated part away from the stimulus for 0.1 to 3 seconds after the irritation is over. During this time, other reflexes and actions of the central nervous system can move the entire body away from the painful stimulus.
What is the term for the muscle that pulls the limb from the stimulus?
In the spinal or decerebrate animal, almost any type of cutaneous sensory stimulus from a limb is likely to cause the flexor muscles of the limb to contract, thereby withdrawing the limb from the stimulating object. This is called the flexor reflex.
What is withdrawal of a reflex?
If some part of the body other than one of the limbs is painfully stimulated, that part will similarly be withdrawn from the stimulus, but the reflex may not be confined to flexor muscles, even though it is basically the same type of reflex. Therefore, the many patterns of these reflexes in the different areas of the body are called withdrawal ...
What is the afterdischarge of the anterior motor neuron?
These, in turn, transmit impulses to the anterior motor neurons, sometimes for several seconds after the incoming sensory signal is over.
Which muscle pulls the arm outward?
The pattern of withdrawal that results when the flexor reflex is elicited depends on which sensory nerve is stimulated. Thus, a pain stimulus on the inward side of the arm elicits not only contraction of the flexor muscles of the arm but also contraction of abductor muscles to pull the arm outward.
Learn about this topic in these articles
The flexor reflex, which removes a limb from a noxious stimulus, has a minimum of two interneurons and three synapses.
structure of nervous system
The flexor reflex, which removes a limb from a noxious stimulus, has a minimum of two interneurons and three synapses.
What does the flexor reflex do when you step on a tack?
Ex) When you step on a tack, the flexor reflex pulls the affected foot away while the crossed extensor reflex straightens the other leg to support your shifting weight
What is a tendon reflex?
A tendon reflex- monitors external tension produced during muscle contraction and prevents tearing of tendons.
What is the classification of reflexes?
Reflexes can be classified by their complexity, as Monosynaptic or Polysynaptic. Define these
Which reflex involves many segments that interact to produce a coordinated, highly variable response?
Polysynaptic spinal reflex that involves many segments that interact to produce a coordinated, highly variable response.
What is the route followed by nerve impulses to produce a reflex?
Reflex arc is the route followed by nerve impulses to produce a reflex.
How do higher centers reinforce spinal reflexes?
Higher centers reinforce spinal reflexes by stimulating excitatory neurons in brain stem or spinal cord
Which neuron innervates intrafusal fibers?
Gammamotor neurons innervate intrafusal fibers. Their axons are called gamma efferents which synapse onto intrafusal fibers to contract them
