The modulation index in FM is stated as the ratio of maximum carrier frequency deviation to the modulating signal (input message signal) frequency and it is denoted with β. The equation of modulation index is Β = ∆f/fi FM Bandwidth
What is modulation index formula?
- Equation for FM: V= A sin [ wct +Δf / fm sin wmt ] = A sin [ wct + mf sin wmt ]
- Equation for AM = Vc ( 1 + m sin ωmt ) sin ωct where m is given by m = Vm / Vc
- In FM, the Modulation Index can have any value greater than 1 or less than one
- In AM, the Modulation Index will be between 0 and 1
- In FM, carrier amplitude is constant.
What is the maximum modulation frequency?
the L-R signal centered on a 38 kHz pilot carrier (which is suppressed) that ranges from 23 to 53 kHz . So, the information signal actually has a maximum modulating frequency of 53 kHz, requiring a reduction in the modulation index to about 1.0 to keep the total signal bandwidth about 200 kHz.
How to measure FM deviation?
How do I measure FM Deviation with a DSA?
- Set the center frequency of the analyzer to the carrier frequency of the FM signal. ...
- Set the Span to cover the expected frequency deviation of the input signal. Press SPAN > press Span > set using the scroll wheel or keypad
- Set the resolution bandwidth (RBW) to provide the resolution that is required for the test. ...
What are the types of modulation?
Types:-Fig:-Types of Modulation. Mainly Two Types of Modulation. 1.Continuous Wave Modulation. Amplitude Modulation; Angular Modulation; 2.Pulse Digital Modulation. Digital Modulation; Analog Modulation; Continuous Wave Modulation:-
What is the modulation index in FM?
The modulation index of FM is defined as the ratio of the frequency deviation of the carrier to the frequency of the modulating signal. mf = Modulation Index of FM = ∆f/fm.
What is the effect of increasing modulation index in FM?
As the modulation index increases for frequency modulation (FM), the number of significant sidebands increases, but the sidebands' total average power remains constant.
What does modulation index mean?
Definition of modulation index : a measure of the degree of frequency modulation expressed numerically for a pure tone modulation as the ratio of the frequency deviation to the frequency of the modulating signal.
What does a modulation index of 0.5 indicate?
In an amplitude modulation with modulation index 0.5 the ratio of the carrier wave to that of side band in the modulated wave is. 642750662.
What is the effect of decreasing modulation index in FM?
FM modulation is at a fixed amplitude. Therefore, any amplitudes above this fixed amplitude can be filtered out as noise. In general, FM signals have better signal to noise ratios. For a given transmitted signal quality, FM is usually more power efficient than AM.
What happens when modulation index is greater than 1?
If the modulation index is greater than 1, then we call this condition over modulation. In such cases, the baseband signal is not preserved in the envelope of the AM signal and therefore, the recovered signal is distorted at the output of the receiver. Was this answer helpful?
What does A modulation index of 1 mean?
A modulation index of 1 is the maximum level of modulation that can normally be applied and occurs when the envelope increases by a factor of 1, i.e. twice the steady state value, and falls to zero.
When modulation index is less than 1 then it is called as?
For instance, if this value is less than 1, i.e., the modulation index is 0.5, then the modulated output would look like the following figure. It is called as Under-modulation. Such a wave is called as an under-modulated wave.
What will happen if modulation index is greater than 100%?
What will happen if modulation index is greater than 100 %? When the modulation index is greater than 100 %, the message intended to be transferred will not be communicated properly. The over modulation of signal damages the signal and deteriorates the signal strength and quality. Was this answer helpful?
What should be the value of the modulation index for an ideal AM?
The ideal value of modulation index in AM. Solution: 462.
What is the effect of modulation index on bandwidth?
Increasing modulating frequency increases the frequency separation between sidebands. Increasing modulating frequency for a given level of deviation reduces modulation index. As a result, it reduces the number of sidebands with significant amplitude. This has the result of reducing the bandwidth.
What factors determine the modulation index of an FM signal?
The FM modulation index is equal to the ratio of the frequency deviation to the modulating frequency. From the formula and definition of the modulation index, it can be seen that there is no term that includes the carrier frequency and this means that it is totally independent of the carrier frequency.
What is the relationship between phase modulation and frequency modulation?
Frequency Modulation is the process of varying the frequency of the carrier signal linearly with the message signal. Phase Modulation is the process of varying the phase of the carrier signal linearly with the message signal.
What is frequency deviation in FM?
Frequency deviation in FM is defined as the way to describe the difference between the minimum and maximum extent of a frequency modulated signal and the carrier frequency.
How to calculate modulation index?
Modulation index can be calculated by knowing modulating voltage and carrier voltage. But it is very common to measure the modulation index from the modulated waveform. The same can be viewed in the CRO (i.e. Oscilloscope).
What is the percentage of modulation?
When modulation index is multiplied by 100, the degree of modulation is expressed as a percentage. This is known as percentage of modulation.
What is the difference between AM and FM?
AM is the short form of Amplitude Modulation and FM is the short form of Frequency Modulation. In AM, carrier amplitude is varied in accordance to modulating signal amplitude. In FM, carrier frequency is varied in accordance to modulating signal frequency.
What is FM modulation?
Overview. Frequency Modulation (FM) is a form of modulation in which changes in the carrier wave frequency correspond directly to changes in the baseband signal. FM is considered an analog form of modulation because the baseband signal is typically an analog waveform without discrete, digital values. Contents.
What is FM radio?
Frequency modulation (FM) is most commonly used for radio and television broadcast. The FM band is divided between a variety of purposes. Analog television channels 0 through 72 utilize bandwidths between 54 MHz and 825 MHz. In addition, the FM band also includes FM radio, which operates from 88 MHz to 108 MHz.
What is the Modulation Index of Frequency Modulation?
The modulation index of FM is defined as the ratio of the frequency deviation of the carrier to the frequency of the modulating signal
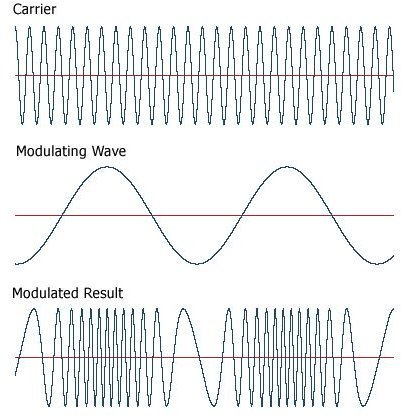
What is frequency modulation?
The frequency modulation can be defined as; the frequency of the carrier signal is varied proportional to (in accordance with) the Amplitude of the input modulating signal. The input is a single tone sine wave. The carrier and the FM waveforms also are shown in the following figure.
What is the amount of change in the carrier frequency produced by the amplitude of the input modulating signal called?
The amount of change in the carrier frequency produced, by the amplitude of the input modulating signal, is called frequency deviation.
What is 98% of FM signal power?
As a rule of thumb, often termed as Carson’s Rule, 98% of the signal power in FM is contained within a bandwidth equal to the deviation frequency, plus the modulation frequency-doubled.
What is demodulation method?
The demodulation method directly detects these modulation frequencies, so it is used for recovering the data from the modulated carrier signal.
What are the two types of modulation techniques used in telecommunications?
In telecommunications, there are two types of frequency modulation techniques used like analog frequency modulation & digital frequency modulation.
What is amplitude modulation?
Sometimes, amplitude modulation signals are capable of bouncing off the ionosphere. As compared to FM, the distance traveled through the AM is high. In frequency modulation, the carrier wave frequency can be changed based on the signal that holds data. The radio signals include high BW as compared to AM radio signals.
What is modulation index?
As in other modulation systems, the modulation index indicates by how much the modulated variable varies around its unmodulated level. It relates to variations in the carrier frequency :
How to achieve FM modulation?
Direct FM modulation can be achieved by directly feeding the message into the input of a voltage-controlled oscillator.
How to approximate a baseband modulating signal?
Mathematically, a baseband modulating signal may be approximated by a sinusoidal continuous wave signal with a frequency fm. This method is also named as single-tone modulation. The integral of such a signal is:
How to generate FM signals?
FM signals can be generated using either direct or indirect frequency modulation: 1 Direct FM modulation can be achieved by directly feeding the message into the input of a voltage-controlled oscillator. 2 For indirect FM modulation, the message signal is integrated to generate a phase-modulated signal. This is used to modulate a crystal-controlled oscillator, and the result is passed through a frequency multiplier to produce an FM signal. In this modulation, narrowband FM is generated leading to wideband FM later and hence the modulation is known as indirect FM modulation.
How to find the bandwidth of a sideband?
Since the sidebands are on both sides of the carrier, their count is doubled , and then multiplied by the modulating frequency to find the bandwidth. For example, 3 kHz deviation modulated by a 2.2 kHz audio tone produces a modulation index of 1.36. Suppose that we limit ourselves to only those sidebands that have a relative amplitude of at least 0.01. Then, examining the chart shows this modulation index will produce three sidebands. These three sidebands, when doubled, gives us (6 × 2.2 kHz) or a 13.2 kHz required bandwidth.
How does FM improve SNR?
FM provides improved signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), as compared for example with AM. Compared with an optimum AM scheme, FM typically has poorer SNR below a certain signal level called the noise threshold, but above a higher level – the full improvement or full quieting threshold – the SNR is much improved over AM. The improvement depends on modulation level and deviation. For typical voice communications channels, improvements are typically 5–15 dB. FM broadcasting using wider deviation can achieve even greater improvements. Additional techniques, such as pre-emphasis of higher audio frequencies with corresponding de-emphasis in the receiver, are generally used to improve overall SNR in FM circuits. Since FM signals have constant amplitude, FM receivers normally have limiters that remove AM noise, further improving SNR.
What is frequency modulation used for?
Frequency modulation is widely used for FM radio broadcasting. It is also used in telemetry, radar, seismic prospecting, and monitoring newborns for seizures via EEG, two-way radio systems, sound synthesis, magnetic tape-recording systems and some video-transmission systems. In radio transmission, an advantage of frequency modulation is that it has a larger signal-to-noise ratio and therefore rejects radio frequency interference better than an equal power amplitude modulation (AM) signal. For this reason, most music is broadcast over FM radio .
What is the modulation index of NBFM wave?
If NBFM wave whose modulation index β is less than 1 is applied as the input of frequency multiplier, then the frequency multiplier produces an output signal, whose modulation index is ‘n’ times β and the frequency also ‘n’ times the frequency of WBFM wave.
What is the direct method of FM wave generation?
This method is called as the Direct Method because we are generating a wide band FM wave directly. In this method, Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) is used to generate WBFM. VCO produces an output signal, whose frequency is proportional to the input signal voltage. This is similar to the definition of FM wave. The block diagram of the generation of WBFM wave is shown in the following figure.
What is the modulating signal of a VCO?
Here, the modulating signal m ( t) is applied as an input of Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO). VCO produces an output, which is nothing but the WBFM.
Why do we need multiple stages of frequency multiplier and mixers?
Sometimes, we may require multiple stages of frequency multiplier and mixers in order to increase the frequency deviation and modulation index of FM wave.
How many inputs does a summer block have?
The summer block has two inputs, which are nothing but the two terms of NBFM equation. Positive and negative signs are assigned for the carrier signal and the other term at the input of the summer block. Finally, the summer block produces NBFM wave.
Why is the indirect method called the indirect method?
This method is called as Indirect Method because we are generating a wide band FM wave indirectly. This means, first we will generate NBFM wave and then with the help of frequency multipliers we will get WBFM wave. The block diagram of generation of WBFM wave is shown in the following figure.
What is FM in radio?
Frequency Modulation (FM) requires that the amplitude changes in a message signal are converted into carrier frequency changes.
What is the result of an increase in message amplitude?
b. An increase in message amplitude, Am, results in an increase in occupied frequency bandwidth.
What is the frequency range of a signal?
A signal has a frequency range from 300Hz to 3.4kHz. What is the frequency bandwidth in Hz?
What happens if the AM index is greater than 1?
a. If the AM Index is greater than 1 (i.e., µAM>1), then over modulation occurs leading to signal distortion
What is the importance of viewing the signal in both the time and frequency domains?
All signals that contain information/messages have an associated frequency bandwidth. Therefore, viewing the signal in both the time and frequency domains is critical.
Which frequency range can support high data throughput?
b. Optical signal operate in the THz frequency range, which can support high data throughput.
What is an ideal isotropic antenna?
An ideal isotropic antenna is a theoretical antenna that propagates signal energy from a single point antenna.
FM History
Frequency Deviation
- The amount of change in the carrier frequency produced, by the amplitude of the input modulating signal, is called frequency deviation.
- The Carrier frequency swings between fmax and fmin as the input varies in its amplitude.
- The difference between fmax and fc is known as frequency deviation. fd = fmax – fc
- Similarly, the difference between fc and fmin also is known as frequency deviation. fd = fc –f…
- The amount of change in the carrier frequency produced, by the amplitude of the input modulating signal, is called frequency deviation.
- The Carrier frequency swings between fmax and fmin as the input varies in its amplitude.
- The difference between fmax and fc is known as frequency deviation. fd = fmax – fc
- Similarly, the difference between fc and fmin also is known as frequency deviation. fd = fc –fmin
Frequency Modulationequation
- The FM equationinclude the following v = A sin [ wct + (Δf / fm) sin wmt ] = A sin [ wct + mf sin wmt ] A = Amplitude of the FM signal. Δf = Frequency deviation mf = Modulation Index of FM mf = ∆f/fm mf is called the modulation index of frequency modulation. wm = 2π fm wc = 2π fc
What Is The Modulation Index of Frequency Modulation?
- The modulation index of FMis defined as the ratio of the frequency deviation of the carrier to the frequency of the modulating signal mf = Modulation Index of FM = ∆f/fm
Difference Between Amplitude Modulation and Frequency Modulation
- The Amplitude Modulation Vs Frequency Modulation is discussed below. The key differences between AM and FMinclude the following. 1. Equation for FM: V= A sin [ wct +Δf / fm sin wmt ] = A sin [ wct + mf sin wmt ] 2. Equation for AM = Vc ( 1 + m sin ωmt ) sin ωct where m is given by m = Vm / Vc 3. In FM, the ModulationIndex can have any value greater than 1 or less than one 4. In A…
Advantages of Frequency Modulation
- The advantages of frequency modulation include the following. 1. Less noise and interference 2. Service areas are well defined for specified transmitter power. 3. As compared to amplitude modulation, FM includes low power consumption. 4. The radiated power is less. 5. Guard bands separate nearby FM channels. 6. Lesser geographical interference among adjacent stations. 7. E…
Disadvantages of Frequency Modulation
- The disadvantages of frequency modulation include the following. 1. High equipment cost is high 2. High bandwidth 3. The receiving area of the FM signal is small. 4. The antennas for FM systems should be kept close for better communication 5. Much more Bandwidth (as much as 20 times as much). 6. More complicated receiver and transmitter. 7. FM has poorer spectral efficiency than …
Overview
Frequency modulation (FM) is the encoding of information in a carrier wave by varying the instantaneous frequency of the wave. The technology is used in telecommunications, radio broadcasting, signal processing, and computing.
In analog frequency modulation, such as radio broadcasting, of an audio signal representing voice or music, the instantaneous frequency deviation, i.e. the diff…
Theory
If the information to be transmitted (i.e., the baseband signal) is and the sinusoidal carrier is , where fc is the carrier's base frequency, and Ac is the carrier's amplitude, the modulator combines the carrier with the baseband data signal to get the transmitted signal:
where , being the sensitivity of the frequency modulator and being the amplitud…
Noise reduction
FM provides improved signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), as compared for example with AM. Compared with an optimum AM scheme, FM typically has poorer SNR below a certain signal level called the noise threshold, but above a higher level – the full improvement or full quieting threshold – the SNR is much improved over AM. The improvement depends on modulation level and deviation. For typical voice communications channels, improvements are typically 5–15 dB. FM broadcasti…
Implementation
FM signals can be generated using either direct or indirect frequency modulation:
• Direct FM modulation can be achieved by directly feeding the message into the input of a voltage-controlled oscillator.
• For indirect FM modulation, the message signal is integrated to generate a phase-modulated signal. This is used to mod…
Applications
When an echolocating bat approaches a target, its outgoing sounds return as echoes, which are Doppler-shifted upward in frequency. In certain species of bats, which produce constant frequency (CF) echolocation calls, the bats compensate for the Doppler shift by lowering their call frequency as they approach a target. This keeps the returning echo in the same frequency range …
See also
• Amplitude modulation
• Continuous-wave frequency-modulated radar
• Chirp
• FM broadcasting
• FM stereo
Further reading
• Carlson, A. Bruce (2001). Communication Systems. Science/Engineering/Math (4th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-011127-8, ISBN 978-0-07-011127-1.
• Frost, Gary L. (2010). Early FM Radio: Incremental technology in twentieth-century America. Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-9440-4, ISBN 978-0-8018-9440-4.
External links
• Analog Modulation online interactive demonstration using Python in Google Colab Platform, by C Foh.