What happens if the genitofemoral nerve is damaged?
If the femoral branch of the genitofemoral branch is affected, the muscles at the front of the abdominal wall become weak since the nerve is responsible for both sensation and motion.
What muscles does genitofemoral nerve innervate?
Specifically, it supplies the mons pubis and labia majora in females, and the skin of the anterior scrotum in males. In addition, the genitofemoral nerve carries motor fibers to innervate the cremaster muscle in males.
What are the signs and symptoms of genitofemoral nerve entrapment?
The symptoms include groin pain, paresthesias, and burning sensation spreading from the lower abdomen to the medial aspect of the thigh. It may present with scrotal pain in male, while females experience symptoms radiating to the labia majora and mons pubis.
What causes genitofemoral pain?
Genitofemoral neuralgia is caused by compression of the genitofemoral nerve anywhere along its path. The most common causes of compression of this nerve are from trauma, especially blunt trauma to the nerve, as well as damage to the nerve during pelvic surgery. Genitofemoral neuralgia will rarely occur by itself.
Can the genitofemoral nerve heal?
Most cases of genitofemoral neuropathy are resolved with nerve blocks and time, though sometimes the pain may persist. Persistent pelvic nerve pain is one of the many types of chronic pelvic pain.
How long does Genitofemoral block last?
Nerve block injections are used to effectively “turn off” such nerves, and thus reduce any associated inflammation. The effect of these injections lasts between one and four weeks and can be repeated as required.
How do you stretch the genitofemoral nerve?
More videos on YouTube Kneeling on one knee, with your foot resting on a chair behind you. Tuck your bottom under and lunge slightly forwards into hip extension. Once you feel a gentle stretch slowly curl your head an upper back down to intensify the stretch for a few seconds then repeat.
How does the genitofemoral nerve get injured?
The genitofemoral nerve can be injured during surgery in several ways: It can be lacerated during injury to the groin. This can occur with penetrating trauma, a knife wound, or surgical exploration of the groin.
Where do you feel femoral nerve pain?
Symptoms of Femoral Nerve pain: Pain over the front of the thigh. Loss of power of knee extension and hip flexion. Lower extremity muscle weakness. Numbness, pain, burning, or tingling sensation in the medial aspect of the lower leg and anteromedial thigh.
What is a genitofemoral nerve block?
Genitofemoral nerve blocks are minimally invasive injections intended to relieve chronic pain in the groin or pelvic region. These nerve blocks can help in the diagnosis of chronic groin, testicular, penile, and pelvic pain conditions.
How do you get rid of groin nerve pain?
Do daily stretches to relieve pressure on your groin nerves. Apply a cold pack to reduce swelling or a hot pack to relax muscles. Consider using a standing desk or posture corrector to reduce pressure on your hips and groin and prevent nerve pinching. Take over-the-counter pain medications like ibuprofen (Advil).
Can you have neuropathy in your groin area?
Medical conditions that damage the nerves (neuropathy) can cause numbness in different parts of the body, including the groin.
What muscle does the genitofemoral nerve Pierce?
The genitofemoral nerve typically pierces and passes through the psoas major muscle before bifurcating into a genital branch and a femoral branch midway along its anterior surface.
What nerve controls the groin area?
Your obturator nerve is in your groin. It enables sensation and muscle movement in your inner thigh. Sports injuries and medical procedure complications can damage the nerve (obturator neuropathy).
What is the root value of the genitofemoral nerve?
L1 and L2The genitofemoral nerve originates from the lumbar plexus, having the root value L1 and L2 from ventral rami of spinal cord and is formed within the substance of psoas major muscle.
What does the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve innervate?
They include the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (L2-L3), posterior femoral cutaneous nerve (S1–S3) and the anterior femoral cutaneous nerves (L2–L4). The main function of these nerves is to provide cutaneous innervation to most of the skin of the thigh, knee, and proximal leg.
What are the two branches of the genital ramus?
At this point, it splits into its two eponymous branches (or rami): the genital ramus and the femoral ramus. In women, the genital ramus terminates in sensory branches that supply the labia majora (part of the external genital organs). In men, the branch constitutes part of the spermatic cord and acts additionally as a motor for ...
What is the function of the femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve?
The function of the femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve is exclusively for sensory perception in both genders. It connects to the area of skin below the inguinal ligament, which extends from the hip to the pubic bone in the groin. Last medically reviewed on January 23, 2018.
What is the genitofemoral nerve?
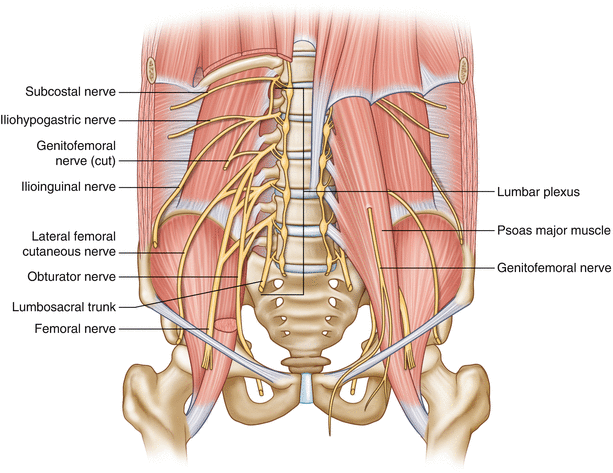
The genitofemoral nerve is a branch of the lumbar plexus, one of three components of the larger lumbosacral plexus (a network of intersecting nerves in the lower vertebral column).
Which nerve in the genital branch stimulates the motor fibers of the genital branch?
Sensory fibers in the upper male thigh respond to gentle touch, stimulating the motor fibers of the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve and causing the cremaster to contract, raising the testes on the same side.
What nerve is the genital branch?
Genital Branch. Main article: Genital branch of genitofemoral nerve. The genital branch passes through the deep inguinal ring and enters the inguinal canal. In men, the genital branch supplies the cremaster and scrotal skin. In women, the genital branch accompanies the round ligament of uterus, terminating in and innervating the skin ...
Which nerve is responsible for the sensory and motor portions of the cremasteric reflex?
The genitofemoral nerve is responsible for both the sensory (femoral branch) and motor portions (genital branch) of the cremasteric reflex, which describes contraction of the cremasteric muscle when the skin of the superior medial part of the thigh is touched.
Where is the genitofemoral nerve located?
The genitofemoral nerve refers to a nerve that is found in the abdomen. Its branches, the genital branch and femoral branch supply sensation to the upper anterior thigh, as well as the skin of the anterior scrotum in males and mons pubis in females.
Which nerve passes through the psoas major muscle?
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (November 2013) The genitofemoral nerve typically pierces and passes through the psoas major muscle before bifurcating into a genital branch and a femoral branch midway along its anterior surface.
Where is the lumbar plexus?
The lumbar plexus and its branches. (Genitofemoral nerve visible at upper left.) The genitofemoral nerve refers to a nerve that is found in the abdomen. Its branches, the genital branch and femoral branch supply sensation to the upper anterior thigh, as well as the skin of the anterior scrotum in males and mons pubis in females. ...
Which nerve divides into two branches?
It passes downwards, pierces the psoas major and emerges from its anterior surface. The nerve divides into two branches, the genital branch and the lumboinguinal nerve also known as the femoral branch, both of which then continue downwards and medially to the inguinal and femoral canal respectively.
Where does the femoral branch go?
The femoral branch passes underneath the inguinal ligament, travelling through the lateral muscular compartment of the femoral canal where it innervates skin of the upper leg. Passing through the cribriform fascia of the saphenous opening of the fascia lata of the thigh, it then supplies the skin of the upper, anterior and medial side of thigh.
What is genitofemoral neuralgia?
Genitofemoral neuralgia is one of the most common causes of pain in the lower abdomen and pelvis. There are many possible causes for nerve pain:
What is the function of the genitofemoral nerve?
Functions of genitofemoral nerve. In women, the genital branch of genitofemoral nerve supply the sensory fibers to labia majora and pubic mound. In men, the branch supplies motor fibers to cremaster and dartos muscles, which elevates and lowers the testes. The sensory fibers from the nerve in upper male thigh react to gentle stimulation ...
What is the function of the spermatic cord?
In men, it goes along with the spermatic cord and supplies motor fibers to cremaster and dartos muscles. It supplies the sensory fibers to the spermatic fascia and tunica vaginalis of the testis. It also provides skin sensation to the upper anterior portion of the scrotum.
What is cryo nerve ablation?
Cryo-nerve ablation. Psychotherapy, in case the pain is secondary to mental disturbances. Relaxation techniques. In case medications do not treat the pain properly, the next step is to perform genitofemoral nerve block. It can ensure dramatic pain relief.
Where does the femoral nerve go?
Femoral branch descends further down and enters the femoral sheath beneath the inguinal ligament. There it lies anterolateral from the femoral artery.
Which nerve divides into genital and femoral?
Genitofemoral nerve divides into genital nerve and femoral nerve. Genital branch further goes in the inguinal canal and goes through the inguinal ring. In men, it goes along with the spermatic cord and supplies motor fibers to cremaster and dartos muscles.
Where is the genitofemoral nerve located?
Genitofemoral nerve is a branch of the lumbar plexus. it is formed from branches of L1 and L2 spinal nerves. The nerve forms in the substance of the psoas major muscle. The nerve passes down in the substance of psoas major muscle and emerges on its anterior surface, deep in the fascia. Afterwards it descends in the retroperitoneum.
What nerve is located in the lower lumbar plexus?
Genitofemoral nerve. The genitofemoral nerve is a branch of the lumbar plexus, one of three components of the larger lumbosacral plexus (a network of intersecting nerves in the lower spinal column). Originating from this source, it pierces the anterior surface of the psoas major — the muscle stabilizing the spine that controls rotational movements ...
Which nerve is responsible for raising testes on the same side?
Sensory fibers in the upper male thigh respond to gentle touch, stimulating the motor fibers of the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve and causing the cremaster to contract, raising the testes on the same side. The function of the femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve is exclusively sensory in both genders.
What muscle is responsible for rotational movements of the hips?
Originating from this source, it pierces the anterior surface of the psoas major — the muscle stabilizing the spine that controls rotational movements of the hips. At this point, it splits into two branches (or rami): the genital ramus and the femoral ramus.
Where does the genital ramus terminate?
In women, the genital ramus terminates in sensory branches that supply the labia majora (part of the external genital organs).
Where is the femoral nerve located?
It connects to the area of skin below the inguinal ligament, which extends from the hip to the pubic bone in the groin. Last medically reviewed on January 23, 2018.
What should be given to patients who do not respond to genitofemoral nerve block?
For patients who do not rapidly respond to genitofemoral nerve block, consideration should be given to epidural steroid injection of the L1-L2 segment s.
How to block genitofemoral nerve?
The femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve is blocked by identifying the middle third of the inguinal ligament. After preparation of the skin with antiseptic solution, 3 to 5 mL of 1% lidocaine is infiltrated subcutaneously just below the ligament (see Fig. 81.2 ). Care must be taken not to enter the femoral artery or vein or to block the femoral nerve inadvertently. The needle must be kept in a subcutaneous position to avoid entering the peritoneal cavity and perforating the abdominal viscera. If the patient has an inflammatory component to the pain, the local anesthetic is combined with 80 mg methylprednisolone and injected in incremental doses. Subsequent daily nerve blocks are carried out in a similar manner, by substituting 40 mg methylprednisolone for the initial 80-mg dose. Because of overlapping innervation of the ilioinguinal and iliohypogastric nerves, it is usually not necessary to block branches of each nerve during genitofemoral nerve block. After injection of the solution, pressure is applied to the injection site to decrease the incidence of ecchymosis and hematoma formation, which can be quite dramatic, especially in anticoagulated patients. Ultrasound needle guidance will help increase the accuracy of needle placement as well as decrease the incidence of needle-related complication when blocking the femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve.
What are the mechanisms of injury to the genitofemoral nerve?
Mechanisms of injury to the genitofemoral nerve include iatrogenic injury, specifically hysterectomy and herniorrhaphy, and blunt trauma.
What is the treatment for genitofemoral neuralgia?
Initial treatment of genitofemoral neuralgia consists of simple analgesics, nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs, or cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Avoidance of repetitive activities thought to exacerbate the pain (e.g., squatting or sitting for prolonged periods) may also ameliorate the patient's symptoms. Pharmacologic treatment is usually ...
Which nerve is responsible for the cremasteric reflex?
Although much variation exists, 1 the genitofemoral nerve often penetrates the psoas major muscle to then divide into a genital and femoral branch. The genital branch, or external spermatic branch, is in part responsible for the cremasteric reflex by supplying the cremaster muscle.
Which nerve is joined by the ventral ramus?
The ventral ramus of L1, which is frequently joined by a branch of T12, bifurcates into upper and lower portions (Fig. 29-1 ). The upper part divides into the iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves as the lower part unites with a branch of the L2 ramus to form the genitofemoral nerve.
Where is the nerve located in the iliac vessels?
The nerve commonly lies adjacent to the common iliac vessels, in the groove between the vessels and the medial aspect of the psoas muscle (Fig. 40-4 ). Dissection of the nodal tissue should start proximally at the para-aortic or paracaval nodes in an extended template.
What is the ISBN for Gray's anatomy for students?
3. FAAA RDP, FAAA AWVP, FRCR AWMMMBBSFRCS. Gray's anatomy for students. Churchill Livingstone. ISBN:0443066124. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Which nerve divides the psoas fascia?
Just above the inguinal ligament both left and right genitofemoral nerves perforate the psoas fascia and divide in to genital and femoral branches.
Where is the genitofemoral nerve located?
At its origin, the genitofemoral nerve is found on the anterior surface of the psoas major muscle from which it emerges. The nerve then courses in the retroperitoneum and lies posterior to the ureter, gonadal vessels and abdominal vessels. The nerve bifurcates above the inguinal ligament with the femoral branch passing under the ligament on the lateral aspect of the external iliac artery entering the femoral sheath lateral to the femoral artery. The genital branch passes through the deep inguinal ring along the inguinal canal accompanying the spermatic cord in men or the round ligament of the uterus in women.
Which nerve passes deep to the right ureter?
On the right the nerve passes deep to the right ureter and gonadal vessels and the ileocolic artery and vein. Just above the inguinal ligament both left and right genitofemoral nerves perforate the psoas fascia and divide in to genital and femoral branches.
Where does the psoas nerve pass?
The nerve passes downwards within the substance of the psoas major muscle, eventually emerging on the muscle's anterior surface, and possibly the psoas minor muscle when present, deep to the psoas fascia.
Where do nerves bifurcate?
20% of nerves bifurcate prematurely at the upper portion (rather than the mid-portion) of the anterior surface of the psoas major muscle. occasionally the genital and femoral branches do not merge into a common trunk within the substance of the psoas muscle and remain as distinct nerves as they travel into the pelvis.
Where do 20% of nerves bifurcate prematurely?
20% of nerves bifurcate prematurely at the upper portion (rather than the mid-portion) of the anterior surface of the psoas major muscle
What is nerve pain?
Nerve pain can be extremely uncomfortable and is often hard to describe to those who have not experienced the pain. Nerve pain is also referred to as " neuropathic pain ." Neuropathic pain may occur anywhere in which a nerve is injured. With the genitofemoral nerve, this pain occurs in the pelvis.
How to treat genitofemoral neuropathy?
Treatment options may include: 2 . Surgical intervention: Surgery can sometimes be helpful, but can also sometimes provoke the pain. Most cases of genitofemoral neuropathy are resolved with nerve blocks and time, though sometimes the pain may persist. Persistent pelvic nerve pain is one of the many types of chronic pelvic pain.
What is the pain in the lower back and abdomen?
Symptoms. Like many types of neuropathic pain, genitofemoral neuropathy is often described as burning, sharp, shooting or throbbing. This type of pelvic nerve pain may be felt in the abdomen, lower back or between the legs. It may come and go, or it may be more persistent.
How does genitofemoral neuropathy work?
The genitofemoral nerve first leaves the spine and makes its way through the psoas muscle. The psoas muscle is the only muscle which attaches the spine to the leg. It is a large muscle that attaches to the spine on one end ...
What is the pain caused by the pelvic nerve?
Pelvic nerve pain may be caused by damage or dysfunction of the genitofemoral nerve . This type of pelvic nerve pain is called genitofemoral neuralgia or genitofemoral neuropathy. BSIP/UIG / Universal Images Group.
Why does my genitofemoral nerve hurt?
Damage or compression to the genitofemoral nerve, as well as conditions which damage the lining of nerves in general (peripheral neuropathy) may lead to genitofemoral nerve pain. Some causes include: 2 . Abdominal or pelvic surgery: The genitofemoral nerve can be damaged during certain types of surgery.
Where does genitofemoral pain occur?
With the genitofemoral nerve, this pain occurs in the pelvis. Genitofemoral neuralgia (genitofemoral pain) is often present for some time before a diagnosis is made, adding to the frustration that goes with this type of pain.
What is the pain in the lower back and abdomen?from verywellhealth.com
Symptoms. Like many types of neuropathic pain, genitofemoral neuropathy is often described as burning, sharp, shooting or throbbing. This type of pelvic nerve pain may be felt in the abdomen, lower back or between the legs. It may come and go, or it may be more persistent.
How to treat genitofemoral neuropathy?from verywellhealth.com
Treatment options may include: 2 . Surgical intervention: Surgery can sometimes be helpful, but can also sometimes provoke the pain. Most cases of genitofemoral neuropathy are resolved with nerve blocks and time, though sometimes the pain may persist. Persistent pelvic nerve pain is one of the many types of chronic pelvic pain.
Why does my genitofemoral nerve hurt?from verywellhealth.com
Damage or compression to the genitofemoral nerve, as well as conditions which damage the lining of nerves in general (peripheral neuropathy) may lead to genitofemoral nerve pain. Some causes include: 2 . Abdominal or pelvic surgery: The genitofemoral nerve can be damaged during certain types of surgery.
How does genitofemoral neuropathy work?from verywellhealth.com
The genitofemoral nerve first leaves the spine and makes its way through the psoas muscle. The psoas muscle is the only muscle which attaches the spine to the leg. It is a large muscle that attaches to the spine on one end ...
What is the pain caused by the pelvic nerve?from verywellhealth.com
Pelvic nerve pain may be caused by damage or dysfunction of the genitofemoral nerve . This type of pelvic nerve pain is called genitofemoral neuralgia or genitofemoral neuropathy. BSIP/UIG / Universal Images Group.
Why does my lower abdomen hurt?from londonpainclinic.com
Genitofemoral neuralgia is one of the most common causes of lower abdominal and pelvic pain. It’s main symptoms include burning pain and numbness over the lower abdomen that radiates to to the genitalia and into the inner thigh.
What is the treatment for genitofemoral neuralgia?from londonpainclinic.com
Initial treatment of genitofemoral neuralgia will usually consist of anti-neuropathic, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory and weak opioid medication. Qutenza patches can also be considered as a conservative method of localised treatment.
What is Genitofemoral neuralgia?
Genitofemoral neuralgia is a syndrome characterized by chronic pain and paresthesia in the region of genitofemoral nerve distribution. Genitofemoral nerve entrapment has been described after inguinal herniorrhaphy, appendectomy, and cesarean section.
What muscle does the genitofemoral nerve Pierce?
The genitofemoral nerve arises from the L1 and L2 ventral primary rami, which fuse in the psoas muscle. It pierces the anterior surface of the psoas major at the level of L3-4 and descends on the fascial surface of the psoas major past the ureter.
How do you know if you have a genitofemoral nerve?
The keys to avoiding inadvertent avulsion of the genitofemoral nerve are knowing its location and identifying it early. The nerve commonly lies adjacent to the common iliac vessels, in the groove between the vessels and the medial aspect of the psoas muscle (Fig. 40-4).
Where does the genitofemoral nerve divide?
It passes downwards, pierces the psoas major and emerges from its anterior surface. The nerve divides into two branches, the genital branch and the lumboinguinal nerve also known as the femoral branch, both of which then continue downwards and medially to the inguinal and femoral canal respectively.
What nerve affects the groin area?
The femoral nerve is one of the largest nerves in your leg. It's located near the groin and controls the muscles that help straighten your leg and move your hips. It also provides feeling in the lower part of your leg and the front of your thigh.
Are there nerves in your groin area?
There are many nerves in the groin, lower abdomen and proximal thigh that can be severed, damaged or irritated with routine surgery or trauma. This can result in either a Neuroma or a nerve compression. Post Surgery chronic groin pain may result from hernia repair, cesarean section or any abdominal surgery.
What promotes nerve healing?
Typically, damaged nerve fibres of the central nervous system (CNS) in the brain, the optic nerve and spinal cord don't have the ability to regenerate.