
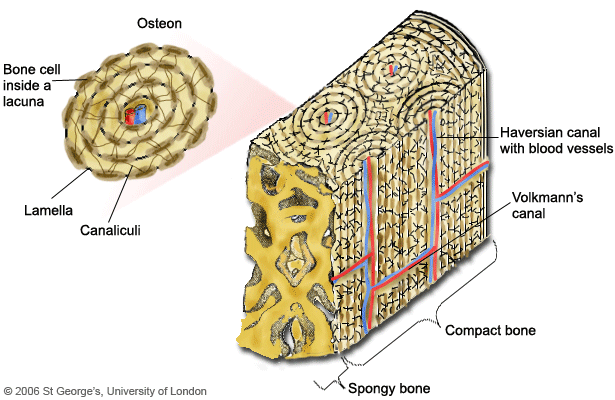
Osteon
The osteon or haversian system is the fundamental functional unit of much compact bone. Osteons are roughly cylindrical structures that are typically several millimeters long and around 0.2 mm in diameter. They are present in many bones of most mammals and some bird, reptile, and amphibian species.
What does the haversian system transport?
What does the haversian system do? The haversian canals surround blood vessels and nerve cells throughout bones and communicate with bone cells (contained in spaces within the dense bone matrix called lacunae) through connections called canaliculi.
What is the haversian system or osteon?
Mar 28, 2022 · A Haversian system, also known as an osteon, is a series of concentric circles, called lamellae, found in the compact bone of humans. Down the middle of each of these systems is a hollow tube that holds a blood vessel. Each compact bone in the human body has many Haversian systems that line up next to each other, creating a dense structure.
What is the function of haversian canal?
The Haversian system is conducive to the deposition and storage of mineral salts that. gives bone tissue its strength. Internal marrow called trabecular bone. Porous bone (cancelled). Used to communicate with other osteocytes to exchange nutrients and signals through the canaliculi.
What are haversian spaces in bone?
The Haversian system or osteone has been traditionally adopted as a universal unit of structure in compact bone. The basic functions and the structural signifi- cance of primary and secondary Haversian tissue, however, are poorly understood. Two explanations on the functional mean- ing of the secondary Haversian system

What is the function of a haversian system or Osteon?
It provides protection and strength to bones. Compact bone tissue consists of units called osteons or Haversian systems. Osteons are cylindrical structures that contain a mineral matrix and living osteocytes connected by canaliculi, which transport blood. They are aligned parallel to the long axis of the bone.
What are haversian systems What is their function quizlet?
The haversian system is conductive to mineral salt deposits and storage which. gives bone tissue it strength. Inner trabeculae bone of marrow called. Spongy (cancellous) bone. Used to communicate with other osteocytes to exchange nutrients and signals via canaliculi.
What are haversian systems?
Haversian system. (Science: anatomy) The basic unit of structure of compact bone, comprising a haversian canal and its concentrically arranged lamellae, of which there may be 4 to 20, each 3 to 7 microns thick, in a single haversian system.Jun 24, 2021
What is Haversian canal quizlet?
haversian canal. Where is an osteon found. cortical compact bone. Layers of connective tissue between concentric rings of osteocytes that surround the central canal. Lamellae.
Who was the first person to see the microscopic canal system in bones?
Though the Haversian canals are named after Clopton Havers, as he described them in detail, a Dutch scientist named Antonie van Leeuwenhoek (1678) was the first person to notice the microscopic canal system in bones.
Who was the first person to describe Sharpey's fibers?
The ‘Haversian system’ gets its name from an English physician named Clopton Havers (1657-1702), who is known for his seminal research in the analysis of the microscopic structure of bones and joints. He was the first person to describe Sharpey’s fibers.
Why do osteocytes need nutrients?
It must be noted that osteocytes are living cells, which is why they need nutrition. The osteon comprises several channels which facilitate waste disposal , as well as the supply of nutrients. These canaliculi also help the cells stay connected, as they can make contact with the cytoplasmic processes of other osteocytes through the canaliculi. Thus, the main function of this system is to facilitate the supply of oxygen, as well as nutrients to the bone cells. It is the central canal that is responsible for the nerve supply, as well as the vascular supply to the bone.
What makes bone hard?
It is the presence of mineral salts such as calcium and phosphates in the matrix that makes the bone hard, whereas collagen fibers strengthen the matrix. ✦ Between the lamellae are small spaces called lacunae. Osteocytes are located within these small spaces. ✦ Tiny channels called canaliculi connect the lacunae.
What happens to the osteoblasts after they are laid down?
After the osteoid layers are laid down, inorganic salts get deposited in the layers, thereby forming hardened, mineralized bone. The osteoblasts then turn into mature bone cells called osteocytes, when a new bone is being formed. Osteocytes get embedded within the bone matrix, and help maintain the structure of the bone.
Which axis of the bone is the epiphysis?
The osteons run parallel to the long axis of a bone. While the diaphysis is the shaft that makes up the long axis of the bone, epiphysis refers to the ends of the bone. The ends are covered by a thin layer of compact bone. The ends are wider than the shaft.
Which canal is parallel to the long axis of the bone?
The long axis of the osteon is parallel to the long axis of the bone. ✦ Haversian canals are located at the center. Small blood vessels that are present in the central canal perform the function of supplying blood to the osteocytes. The central canal also contains nerve filaments.
What are haversian systems and what is their function?
Haversian canals are microscopic tubes or tunnels in cortical bone that house nerve fibers and a few capillaries. This allows bone to get oxygen and nutrition without being highly vascular. These canals also communicate with bone cells using special connections, or canaliculi.
Where is Haversian system present?
bone Haversian canals (sometimes canals of Havers) are a series of microscopic tubes in the outermost region of bone called cortical bone. They allow blood vessels and nerves to travel through them to supply the osteocytes.
What is Haversian system?
Haversian system. (Science: anatomy) The basic unit of structure of compact bone, comprising a haversian canal and its concentrically arranged lamellae, of which there may be 4 to 20, each 3 to 7 microns thick, in a single haversian system.
What is haversian Canal System Class 11?
Haversian canals are a series of tubes around narrow channels that are formed by the lamellae in the bones. The Haversian canal (osteonic canal) contains the bone’s blood vessels and nerve fibers. Haversian canal surrounded by concentric rings of lamellar bone in which osteocytes are embedded in their lacunae.
What do lamellae do in bone?
Each osteon consists of lamellae, which are layers of compact matrix that surround a central canal called the Haversian canal. The Haversian canal (osteonic canal) contains the bone’s blood vessels and nerve fibers (Figure 1).
What is hermitian Canal?
Haversian canals are found in the bone matrix of the long bone of mammals (Rabbit, rat, etc). These canals surround blood vessels and nerve cells throughout bones and facilitate communication within bone cells.
What is haversian Canal System Class 9?
Haversian canal system : Haversian system is the functional unit of a compact bone. It has a cylindrical, column like structure arranged parallel to the axis of the bone. These canals are surrounded by blood vessels and nerve cells for communication. Each haversian canal consists of several layers or lamellae.
Where is the Haversian system found?
This system is found in the bone matrix of long bones like femur, humerus and others. The haversian canals consists of veins, arteries, areolar tissues, nerves and lymph.
What are the parts of the Haversian system?
Each unit consists of four parts: the Haversian canal, lamellae, lacunae, and canaliculi.
What is the purpose of the haversian canal?
The haversian canals surround blood vessels and nerve cells throughout bones and communicate with bone cells (contained in spaces within the dense bone matrix called lacunae) through connections called canaliculi. Subsequently, question is, what is the purpose of the trabecular bone?
How many capillaries are in the Haversian canal?
Each haversian canal contains one or two capillaries and nerve fibres. They surround blood vessels and nerve cells throughout bones and communication with bone cells. Haversian canals are contained within osteons , which are arranged along the long axis of the bone, parallel to the surface.
What are the parts of compact bone?
The basic unit of compact bone is the Haversian system which is also called osteon. Each unit consists of four parts: the Haversian canal, lamellae, lacunae, and canaliculi. The Haversian system compromises several channels that facilitate waste disposal, as well as the supply of nutrients. Click to see full answer.
What is the structure of a haversian canal?
Haversian canal. The structure of bone is an important consideration for the size, type, and surface of dental implants. Haversian canals are microscopic tubes or tunnels in cortical bone that house nerve fibers and a few capillaries. This allows bone to get oxygen and nutrition without being highly vascular.
How are Haversian canals formed?
Haversian canals are formed by lamellae, or concentric layers of bone , and are contained inside osteons. Osteons are cyndrylical structures that transport oxygenated blood to bone, and they are arranged parallel to the surface of the bone, along the long axis.
What is the percentage of cortical bone in the haversian canal?
Osteons that have intact Haversian canals comprise about 45% of cortical bone, or a little less than half. Haversian canals and osteons are part of the Haversian system, which allows nutrients to pass between the blood and bone. Post navigation. Gingiva. Iliac graft.
What are the structures of the bone that are used to make dental implants?
The structure of bone is an important consideration for the size, type, and surface of dental implants. Haversian canals are microscopic tubes or tunnels in cortical bone that house nerve fibers and a few capillaries. This allows bone to get oxygen and nutrition without being highly vascular. These canals also communicate with bone cells using special connections, or canaliculi. This connection facilitates the deposit and storage of mineral salts, which essentially gives bones their strength. Haversian canals are formed by lamellae, or concentric layers of bone, and are contained inside osteons. Osteons are cyndrylical structures that transport oxygenated blood to bone, and they are arranged parallel to the surface of the bone, along the long axis. Osteons that have intact Haversian canal s comprise about 45% of cortical bone, or a little less than half. Haversian canal s and osteons are part of the Haversian system, which allows nutrients to pass between the blood and bone.
Did You Know?
Structure of A Long Bone
- Only compact bones have osteons as a basic structural unit; spongy bones don’t have osteons. With the exception of the kneecap, wrist, and ankle bones, all the bones of the limbs are long bones. They are called long bones, as their length is more than their width. They are composed of a shaft and two ends. The osteons run parallel to the long axis of a bone. The long bones are co…
Haversian System Structure and Function
- It must be noted that osteocytes are living cells, which is why they need nutrition. The osteon comprises several channels which facilitate waste disposal, as well as the supply of nutrients. These canaliculi also help the cells stay connected, as they can make contact with the cytoplasmic processes of other osteocytes through the canaliculi. Thus,...
Components of A Haversian System
- An osteon comprises a long, hollow central canal that is surrounded by concentric layers called lamallae. This central canal is referred to as the Haversian canal. The long axis of the osteon is parallel to the long axis of the bone. Each osteon has a cylindrical structure that consists of the following components: ✦ Haversian canals are located at the center. Small blood vessels that ar…