
What are the interspinous ligaments?
The interspinous ligaments (interspinal ligaments) are thin and membranous ligaments, that connect adjoining spinous processes of the vertebra in the spine. They extend from the root to the apex of each spinous process. They meet the ligamenta flava in front and blend with the supraspinous ligament behind.
Why does the interspinous ligament cause lower back pain?
The lumbar interspinous ligaments receive an innervation from the medial branches of the lumbar dorsal rami and experimental stimulation of interspinous ligament produces low back pain and referred pain in the lower limbs.This renders the interspinous ligament as an attractive source of low back ache.
What is the function of intertransverse ligament?
Intertransverse Ligament. The intertransverse ligaments connect these processes together and help limit the action of side bending ( lateral flexion ). They also form a sort of border between the bodies in front and the bony rings in the back of the vertebrae.
What is the structure of the spinous ligament?
This ligament is composed of thin sheets connecting the spinous processes (from roots to apexes) from C1-S1 one segment at a time. Anteriorly, Its fibres connect with ligamentum flavum, whilst posteriorly its fibres connect with the supraspinous ligamen t.
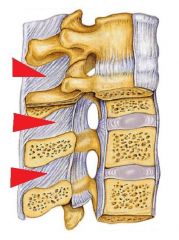
What movement does the interspinous ligament limit?
FlexionThe Anterior Longitudinal Ligament attaches to the front (anterior) of each vertebra....Ligaments.LigamentSpinal RegionLimits…InterspinousLumbarFlexionIntertransverseLumbarLateral flexionIliolumbarSacroiliac jointsStability & some motionSacroiliacSacroiliac jointsStability & some motion10 more rows
What does the interspinous ligament connect?
The interspinous ligaments (interspinal ligaments) are thin and membranous ligaments, that connect adjoining spinous processes of the vertebra in the spine. They extend from the root to the apex of each spinous process. They meet the ligamenta flava in front and blend with the supraspinous ligament behind.
What does the interspinous ligament resist?
The interspinous ligament interconnects the spinous processes, from root to apex of adjacent processes. Sometimes described together as the interspinous/supraspinous ligament complex, they weakly resist spinal separation and flexion.
What does the supraspinous ligament do?
The supraspinous ligament helps maintain the upright position of the head. It's stretched in flexion, it`s fibers resist separation of spinous processes during forward flexion, during hyperflexion interspinous ligament and supraspinous ligament are the first to fail.
What is interspinous ligament injury?
Damage to interspinous ligaments, most commonly caused by whiplash, negatively impacts the stability of the spine as well as the body's ability to move properly. The recovery period for a neck sprain injury can last from several weeks to several months.
What is the interspinous ligament made of?
collagen fibresHistologically, these ligaments are mainly composed of collagen fibres, whereas the elastic fibres are ubiquitous, although mostly concentrated in the ventral part, which is closely linked to the yellow ligament.
What is the strongest ligament in the spine?
Ligamentum FlavumLigamentum Flavum This yellow ligament is the strongest. It runs from the base of the skull to the pelvis, in front of and between the lamina, and protects the spinal cord and nerves. The ligamentum flavum also runs in front of the facet joint capsules.
What are the 3 more important ligaments of the spine?
The three major ligaments of the spine are the ligamentum flavum, anterior longitudinal ligament (ALL), and posterior longitudinal ligament (PLL) (Fig.
What is the difference between interspinous ligament and supraspinous ligament?
Vertebral Column and Ligaments: Beneath the skin and subcutaneous tissue, the supraspinous ligament runs between the tips of the spinous processes. The interspinous ligament connects adjacent spinous processes, blending posteriorly with the supraspinous ligament and anteriorly with the ligamentum flavum.
What are the 5 ligaments of the spine?
There are five main ligamentous structures seen throughout the spinal column:Anterior Longitudinal Ligament (ALL)Posterior Longitudinal Ligament (PLL)Ligamentum Flavum.Interspinous ligaments.Supraspinous ligament[1]
What ligament prevents hyperextension of the spine?
The anterior longitudinal ligamentThe anterior longitudinal ligament attaches to both the vertebra and the intervertebral discs. This ligament helps to prevent hyperextensions of the spine.
What ligament prevents hyperflexion?
posterior longitudinal ligamentThe posterior longitudinal ligament is a ligament connecting the posterior surfaces of the vertebral bodies of all of the vertebrae. It weakly prevents hyperflexion of the vertebral column. It also prevents posterior spinal disc herniation, although problems with the ligament can cause it.
What are the interspinous ligaments?
The interspinous ligaments (ISLs) are thin and short structures connecting adjacent spinous processes. The ISLs are well vascularized and contain sensory nerves, particularly on their dorsal and lateral surfaces.
Where are the interspinous ligaments?
→ The interspinal ligaments are located between spinal processes of the lower thoracic and lumbar spine.
Where do the intertransverse ligaments attach?
The intertransverse ligaments are sheets of connective tissue that connect the transverse processes of adjoining vertebrae. They extend from the upper border of the transverse process of one vertebra to the lower border of the transverse process above.
What is the difference between interspinous ligament and supraspinous ligament?
Vertebral Column and Ligaments: Beneath the skin and subcutaneous tissue, the supraspinous ligament runs between the tips of the spinous processes. The interspinous ligament connects adjacent spinous processes, blending posteriorly with the supraspinous ligament and anteriorly with the ligamentum flavum.
What is the function of the interspinous ligaments?
In the neck they are often considered part of the nuchal ligament. The function of the interspinous ligaments is to limit flexion of the spine.
What is the interspinal ligament?
The interspinous ligaments ( interspinal ligaments) are thin and membranous ligaments, that connect adjoining spinous processes of the vertebra in the spine. They extend from the root to the apex of each spinous process.
Where do the ligaments meet?
They meet the ligamenta flava in front and blend with the supraspinous ligament behind. The ligaments are narrow and elongated in the thoracic region, broader, thicker, and quadrilateral in form in the lumbar region, and only slightly developed in the neck. In the neck they are often considered part of the nuchal ligament.
What is the name of the ligament that connects the vertebrae?
Interspinous ligament. The interspinous ligaments ( interspinal ligaments) are thin and membranous ligaments, that connect adjoining spinous processes of the vertebra in the spine.
What are the 3 more important ligaments of the spine?
The three major ligaments of the spine are the ligamentum flavum, anterior longitudinal ligament (ALL), and posterior longitudinal ligament (PLL) (Fig.
What causes thickening of ligaments?
Other studies support the hypothesis that a facet degeneration alone without disc space narrowing can lead to physiologic ligament thickening. Furthermore, thickening occurs as a result of inflammation and fibrocartilaginous transformation can cause hypertrophy of the ligament.
What motion do ligaments?
Ligaments often connect two bones together, particularly in the joints: Like strong, firmly attached straps or ropes, they stabilize the joint or hold the ends of two bones together. This ensures that the bones in the joint don't twist too much or move too far apart and become dislocated.
Where are the Denticulate ligaments?
Denticulate ligaments arise from the pia mater on the lateral edge of the spinal cord and fuse to the overlying dura mater and the filum terminale extends from the conus medullaris to the end of the dural sac in order to anchor the inferior tip of the spinal cord.
Where are the interspinous ligaments found?
The interspinous ligaments (interspinal ligaments) are thin and membranous ligaments, that connect adjoining spinous processes of the vertebra in the spine. They extend from the root to the apex of each spinous process.
Can you tear ligaments in your back?
Excess stress on your back can stretch or tear the ligaments. This is called a sprain. A strain is a stretching or tearing of muscle or tendon. It doesn't really matter whether you have a strain or a sprain.
What is the function of the Intertransverse ligament?
The intertransverse ligaments often blend with the intertransverse muscles. The function of the intertransverse ligaments is to limit lateral flexion of the spine.
Where are the Denticulate ligaments?
Denticulate ligaments arise from the pia mater on the lateral edge of the spinal cord and fuse to the overlying dura mater and the filum terminale extends from the conus medullaris to the end of the dural sac in order to anchor the inferior tip of the spinal cord.
Can you tear ligaments in your back?
Excess stress on your back can stretch or tear the ligaments. This is called a sprain. A strain is a stretching or tearing of muscle or tendon.
What are the 3 more important ligaments of the spine?
Three of the more important ligaments in the spine are the Ligamentum Flavum, Anterior Longitudinal Ligament and the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament.
Does your spine have ligaments?
Ligaments. The ligaments are strong fibrous bands that hold the vertebrae together, stabilize the spine, and protect the discs. The three major ligaments of the spine are the ligamentum flavum, anterior longitudinal ligament (ALL), and posterior longitudinal ligament (PLL) (Fig. 7).
What ligament prevents hyperextension of the spine?
The anterior longitudinal ligament attaches to both the vertebra and the intervertebral discs. This ligament helps to prevent hyperextensions of the spine.
What ligaments attach to the spinous processes?
The interspinous ligaments (interspinal ligaments) are thin and membranous ligaments, that connect adjoining spinous processes of the vertebra in the spine. They extend from the root to the apex of each spinous process.
How thick is the interspinous ligament?
The mean thicknesses presented as: Upper (0.22 mm); Middle (0.37 mm) and L5-S1 (0.72 mm). Ligaments in the females were slightly thinner in comparison to the males. Fibres of inter-spinous ligaments were also found to attach to the inner aspects of the supraspinous ligament.
Where does the interspinous ligament connect to the spinous process?
The interspinous ligaments connect the whole of each spinous process vertically. The interspinous ligament starts at the root of the spinous process, where it emerges from the ring of bone located at the back of the body of its respective vertebra, and extends all the way out to the tip.
What is the intertransverse ligament?
Intertransverse ligaments go from a superior (remember, superior refers to an above location, relatively speaking) transverse process of a vertebra to the transverse process of the vertebra below it . The intertransverse ligaments connect these processes together and help limit the action of side bending (lateral flexion). They also form a sort of border between the bodies in front and the bony rings in the back of the vertebrae.
What ligaments provide stability to the column?
Spinal ligaments also provide stability to the column. They do this by limiting the degree of movement in the direction opposite their location. For example, your anterior longitudinal ligament (see below for details) is located in front of your vertebral bodies. When you arch back, it prevents you from going too far.
What is ligamentum flavum?
The phrase ligamentum flavum means "yellow ligament". The ligamentum flavum is made of a (pale) yellow-colored elastic tissue. This tissue is similar to the type of connective tissue that comprises the other spinal ligaments, except there’s a degree of elasticity to it.
Which ligaments are more fibrous?
In the thoracic (mid-back) area, the intertransverse ligaments are tougher and more fibrous. Now you know your ligament ABCs. These are the spinal ligaments that affect all or at least large portions of the spine. Other spinal ligaments are specific to an area such as the neck or the sacrum and sacroiliac joints.
Where is the ligament flavum located?
It is located between the laminae of the vertebra. At each vertebral level, fibers originate from a superior lamina (the term superior refers to a location above, relatively speaking) and connect to the inferior lamina (i.e. the lamina just below). The ligamentum flavum limits spinal flexion (bending forward), especially abrupt flexion. This function enables the ligamentum flavum to protect your discs from injury.
Which ligaments limit forward bending?
The supraspinous and interspinous ligaments both limit flexion (forward bending). Located in back, the supraspinous ligament is a strong rope like tissue that connects the tips of the spinous processes from your sacrum up to C7 (otherwise known as the base of the neck).
