What is L-lysine decarboxylase test?
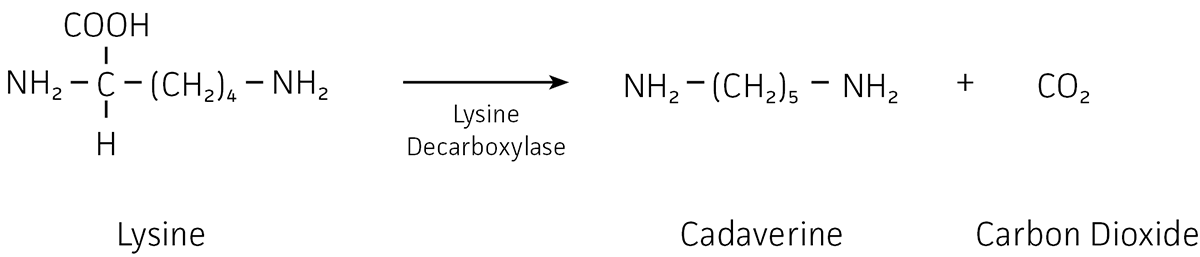
Lysine decarboxylase test relies on the capability of certain bacteria to degrade L-lysine into caverine after the release of carbon dioxide. What is Lysine decarboxylase test? Lysine decarboxylase test relies on the capability of certain bacteria to degrade L-lysine into caverine after the release of carbon dioxide.
What is the purpose of the lysine test?
The purpose is to see if the microbe can use the amino acidlysineas a source of carbon and energy for growth. Use oflysineis accomplished by the enzymelysine decarboxylase.
How does lysine decarboxylase work?
The lysine decarboxylase is an enzyme that targets the carboxylic component in the amino acid, lysine and results in the formation of amine cadaverine. The sugar inside the medium gets fermented by enterobacteria and results in a color change of the indicator system, from purple to yellow.
What does the decarboxylation test measure?
This test measures the enzymatic ability (decarboxylase) of an organism to decarboxylate (or hydrolyze) an amino acid to form an amine. Decarboxylation, or hydrolysis, of the amino acid results in an alkaline pH and a color change from orange to purple.

What does a decarboxylation test determine?
This simple test is able to measure the ability of bacteria to produce decarboxylase or dihydrolase that are used to remove carboxyl group from amino acids resulting in the formation of amines.
What is the purpose of the enzyme lysine decarboxylase?
Lysine decarboxylase converts L-lysine into cadaverine (1,5-pentanediamine), which is an acid neutralizer (through deamination) and superoxide radical scavenger; MnSOD is also involved in acid neutralization and reduction of oxidative stress (Kim et al., 2005).
What would a positive test for lysine decarboxylase show in the results?
The final results are then obtained by observing the tube at 48 hours. Change back to purple from yellow indicates a positive test for lysine decarboxylase. Failure to turn yellow at 24 hours or to revert back to purple at 48 hours indicates a negative result.
What does a negative lysine decarboxylase test mean?
Lysine decarboxylation results in cadaverine. These byproducts are sufficient to raise the pH of the media so that the broth turns purple. If the inoculated medium is yellow, or if there is no color change, the organism is decarboxylase-negative for that amino acid.
How does lysine decarboxylase media work?
Lysine decarboxylase (CadA) removes carbon dioxide from lysine, thus producing cadaverine, an amine which protonates to generate OH−.
What is amino acid decarboxylation?
Decarboxylation is the reduction of carbon, while transamination is the exchange within the amino group of an amino acid to a keto acid (the introduction or removal of nitrogen).
What does a positive and negative reaction for decarboxylase test mean?
A positive test is a turbid purple to faded-out yellow-purple color (alkaline). A negative test is a bright clear yellow color (acid) or no change (nonfermenting rods). The control tube must retain its original color or turn yellow. The turbidity and alkaline or purple color in the control tube invalidate the test.
What does lysine decarboxylase do to lysine?
Lysine decarboxylase (CadA) removes carbon dioxide from lysine, thus producing cadaverine, an amine which protonates to generate OH−.
Is E coli lysine decarboxylase positive?
ESCHERICHIA COLI | Food Poisoning Similar to Shigella spp., EIEC are nonmotile, lactose negative, and lysine decarboxylase-negative.
What does arginine ornithine and lysine do?
The use of arginine, ornithine and lysine is one of the natural ways to increase the level of growth hormone, the use of which has a positive effect on our trainings, especially when we have deficiency of this hormone in our body. Growth hormone lowers fat levels, and this promotes an increase in muscle protein.
Is Salmonella lysine positive?
Typically, Salmonella spp. test positive for lysine-decarboxylase.
What is a decarboxylase enzyme?
Decarboxylases are a group of enzymes that remove carboxyl groups (CO2H) from acidic substrates and require pyridoxal phosphate or pyruvate as a co-factor. They are known for their various roles in metabolic pathways, non-oxidative decarboxylation of α- and β-keto acids and carbohydrate synthesis.
What is the basic principle of LDC?
Principle and Interpretation: Lysine decarboxylase test is based on the ability of some bacteria to cleave L-lysine to cadaverine under the liberation of carbon dioxide (1). Decarboxylase media were first described by Moeller (2-4) for detecting lysine and ornithine decarboxylase and arginine dihydrolase.
What is the purpose of the phenylalanine test?
Serum phenylalanine screening is a blood test to look for signs of the disease phenylketonuria (PKU). The test detects abnormally high levels of an amino acid called phenylalanine.
Which enzyme does the oxidase test check for?
cytochrome c oxidaseThe oxidase test is used to identify bacteria that produce cytochrome c oxidase, an enzyme of the bacterial electron transport chain. (note: All bacteria that are oxidase positive are aerobic, and can use oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor in respiration.
What is decarboxylation microbiology?
Decarboxylases are a group of substrate specific enzymes that are capable of reacting with the carboxyl (COOH) portion of amino acids, forming alkaline-reacting amines and byproduct carbon dioxide. Some microorganisms possess such an enzyme which allows their detection.
Where does lysine deamination occur?
Lysine deamination is an aerobic process which occurs on the slant of the media. Lysine decarboxylation is an anaerobic process which occurs in the butt of the media.
What happens if decarboxylase is not produced?
If the decarboxylase is not produced, the butt remains acidic (yellow). If oxidative deamination of lysine occurs, a compound is formed that, in the presence of ferric ammonium citrate and a coenzyme, flavin mononucleotide, forms a burgundy color on the slant. If deamination does not occur, the LIA slant remains purple.
What is the purpose of the H2S test?
This test is used to differentiate gram-negative bacilli based on decarboxylation or deamination of lysine and the formation of hydrogen sulfide (H2S).
What is lysine iron agar?
Lysine iron agar or LIA is a differential media used to distinguish bacteria that are able to decarboxylate lysine and/or produce hydrogen sulfide from those that cannot.
What tests are performed on colonies from pure culture?
It is recommended that biochemical, immunological, molecular, or mass spectrometry testing be performed on colonies from pure culture for complete identification.
Is dextrose a fermentable carbohydrate?
Dextrose is a source of fermentable carbohydrate. Ferric ammonium citrate and sodium thiosulphate are indicators of H 2 S formation. Cultures that produce hydrogen sulphide cause blackening of the medium due to ferrous sulphide production.
What is the purpose of decarboxylase test?
This test is commonly used to differentiate the members of the family Enterobacteriaceae on the basis of their ability to produce the enzyme decarboxylase.
What media is used to test for decarboxylase?
Media: Decarboxylase test medium Base is generally used for testing the amino acid decarboxylase activity. Where as the other medias like Motility-indole-ornithine medium and Lysine iron agar can also be used.
Why is the production of enzymes important?
The production of these enzymes is taken as an important parameter for differentiating the bacteria present in the family of Enterobacteriaceae.
