What is true about the P waves?
The P wave represents electrical activity (in volts) that causes cardiac muscle contraction in the atria – the upper two heart chambers. When a P wave definition says it represents atrial contraction, this is not entirely incorrect. What a P wave depicts is the voltage (over time) that specifically triggers atrial muscle cell contraction.
What is the difference from P waves and S waves?
P waves travel faster than S waves, and are the first waves recorded by a seismograph in the event of a disturbance. P waves travel at speeds between 1 and 14 km per second, while S waves travel significantly slower, between 1 and 8 km per second. The S waves are the second wave to reach a seismic station measuring a disturbance.
What is the normal duration of a P wave?
Normal P Wave Size. Duration <120ms (3mm) Amplitude <2.5mm. The P wave is directed inferiorly and therefore should be positive in leads I and II. It is often biphasic in lead V1.
What do P waves and QRS waves represent?
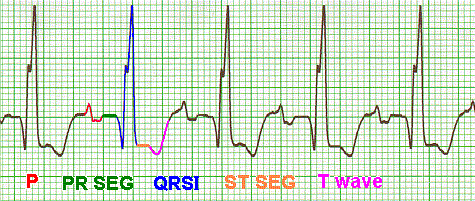
There are three main components to an ECG: the P wave, which represents the depolarization of the atria; the QRS complex, which represents the depolarization of the ventricles; and the T wave, which represents the repolarization of the ventricles.

What does the P wave represent quizlet?
The P wave represents the impulse that causes the atria to contract. In medical terminology , the P wave represents the atrial depolarization.
What do the P QRS and T waves represent?
The P wave in an ECG complex indicates atrial depolarization. The QRS is responsible for ventricular depolarization and the T wave is ventricular repolarization.
What does the QRS wave represent?
The QRS complex represents the depolarization of ventricles. It shows the beginning of systole and ventricular contraction. The QRS complex or wave starts with a small deflection downwards, represented by the point Q. It follows the P wave.
What happens to heart at P wave?
The first wave (p wave) represents atrial depolarisation. When the valves between the atria and ventricles open, 70% of the blood in the atria falls through with the aid of gravity, but mainly due to suction caused by the ventricles as they expand.
What is the difference between P wave and T wave?
'P' wave is the first wave in an ECG and is a positive wave. It indicates the activation of the SA nodes. 'T' wave too is a positive wave and is the final wave in an ECG though sometimes an additional U wave may be seen. It represents ventricular relaxation.
What does no P wave mean?
Absence of P waves suggests either. No normal atrial depolarization, e.g., atrial fibrillation, atrial standstill. The P waves are hidden within the QRS complexes, e.g., ventricular tachycardia, junctional tachycardia.
What does a large S wave indicate?
This vector is determined by electrical activation of the basal region of both ventricles and by depolarisation of the RVOT. A prominent S-wave in lead I is typically present in cases of congenital heart disease, valvular heart disease, and cor pulmonale that cause right ventricular enlargement and fibrosis.
Why are Q and S waves negative?
As septal depolarization moves from left to right, the depolarization vector is directed towards the - electrode of lead II (RA), and therefore a negative-going deflection (Q-wave) is produced.
What causes the T wave?
Normally, the T wave is formed at the end of the last phase of ventricular repolarization. Ventricular repolarization is the process by which the ventricular myocytes return to their negative resting potential so they can depolarize again.
What does high P wave mean?
P Pulmonale The presence of tall, peaked P waves in lead II is a sign of right atrial enlargement, usually due to pulmonary hypertension (e.g. cor pulmonale from chronic respiratory disease).
How do you read P waves on ECG?
1:207:16ECG for Beginners. Understanding the waves of ECG, P wave ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWell normal P waves should be upright in leads one two and upside-down or inverted and lead AVR.MoreWell normal P waves should be upright in leads one two and upside-down or inverted and lead AVR. Let's take a closer look at lead to a great lead to look at P wave morphology.
What does a long P wave mean?
Prolonged P wave duration signifies conduction delay between right and left atrium due to impulse slowing or blockage, probably most often but not exclusively in the Bachmann bundle. On the ECG this conduction delay is referred to as interatrial block (IAB) [14–16].
What does each part of an ECG represent?
Each will be explained individually in this tutorial, as will each segment and interval. The P wave indicates atrial depolarization. The QRS complex consists of a Q wave, R wave and S wave and represents ventricular depolarization. The T wave comes after the QRS complex and indicates ventricular repolarization.
What is a normal P QRS T axis?
Baseline ECG axes were automatically measured with normal values defined as follows: P-wave axis 0° to 75°, QRS axis -30° to 90°, and T axis 15° to 75°.
What events generate the P wave QRS complex and T wave?
The P wave results from atrial depolarization. The QRS complex is a result of ventricular depolarization and indicates the start of ventricular contraction. The T wave results from ventricular repolarization and signals the beginning of ventricular relaxation.
What events generate the P wave QRS complex and T wave quizlet?
What events generate the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave? The P wave is generated by depolarization of the atrial cardiac muscle, the QRS complex is generated by the depolarization of the ventricular cardiac muscle, and the T wave is generated by the repolarization of the ventricles.
What does "no P wave" mean?
The absence of P waves implies any of these possibilities. There is no typical atrial depolarization, such as atrial fibrillation or atrial standst...
What is the significance of the P wave QRS complex and T wave?
The ECG depicts atrial and ventricular depolarization and repolarization as a succession of waves: the P wave, followed by the QRS complex and the...
What does "absent P wave" mean?
Absence of P Waves: A lack of visible P waves preceding QRS complexes suggests a lack of sinus beats; this may occur with sinus dysfunction or in t...
What is a first wave?
An ECG complex is made up of a PQRST complex. In an ECG complex, the P wave signals atrial depolarization. The QRS is in charge of ventricular depo...
What does the P wave represent in atrial depolarization?
Tarek Ajam, MD, MS; Terrence X O'Brien, MD, MS, FACC; and more... Atrial depolarization is represented by the P wave. In leads I, II, and aVF, the...
What does "P" mean in ECG?
The P wave indicates the depolarization of the left and right atriums, as well as atrial contraction. The atrium contracts a fraction of a second a...
What does it mean when there are no P waves?
A lack of visible P waves preceding QRS complexes suggests a lack of sinus beats; this may occur with sinus dysfunction or in the presence of fibrillation or flutter waves. The P wave may also be hidden within the QRS complex.
What is bifid P wave?
Bifid P waves are also referred to as P mitrale. Their presence indicates dyssynchrony between right and left atrial depolarisation; this may be normal, or suggestive of left atrial enlargement.
What is the P wave in ECG?
The P wave and PR segment is an integral part of an electrocardiogram (ECG). It represents the electrical depolarization of the atria of the heart. It is typically a small positive deflection from the isoelectric baseline that occurs just before the QRS complex. It can sometimes have abnormalities in morphology or timing that can be indicative of significant clinical pathology.[1] An understanding of the normal and abnormal P wave morphology is, therefore, a crucial part of ECG interpretation. This article will review the basics of P wave interpretation, including characteristics of both the normal P wave and its pathologic abnormalities.
What is the PR interval?
The PR interval represents the time between atrial depolarization and ventricular depolarization. Abnormalities in the timing of the PR segment can indicate pathology.
Why is it important to alert clinicians of an abnormal rhythm or electrical conduction defect on ECG?
Early identification by nursing staff to alert clinicians of an abnormal rhythm or electrical conduction defect on ECG can lead to rapid management and decreased morbidity and mortality of patients. It is in the patients' best interest for all healthcare team members to have the ability and confidence to point out P wave abnormalities and PR segment prolongations or heart blocks.
What is the role of ECG interpretation?
ECG interpretation and identification of pathology on electrocardiograms should be an integral part of monitoring any patient placed on telemetry or who presents with signs and symptoms of abnormal cardiac function. The healthcare team, including physicians, nurses, and technicians, should be able to quickly recognize common abnormal ECG patterns and intervene or notify a healthcare member, such as a cardiologist, that can treat the pathology found on the electrocardiogram rhythm.
How wide is the P wave?
The combined depolarisation wave, the P wave, is less than 120 ms wide and less than 2.5 mm high
What does it mean when you have a P wave in lead II?
The presence of tall, peaked P waves in lead II is a sign of right atrial enlargement, usually due to pulmonary hypertension (e.g. cor pulmonale from chronic respiratory disease).
What does it mean when there are multiple P wave morphologies?
The presence of multiple P wave morphologies indicates multiple ectopic pacemakers within the atria and/or AV junction . If ≥ 3 different P wave morphologies are seen, then multifocal atrial rhythm is diagnosed:
What does the separation of right and left atrial electrical forces in lead V1 mean?
This separation of right and left atrial electrical forces in lead V1 means that abnormalities affecting each individual atrial waveform can be discerned in this lead. Elsewhere, the overall shape of the P wave is used to infer the atrial abnormality.
Which direction do the right and left atrial waveforms move?
However, in lead V1 the right and left atrial waveforms move in opposite directions. This produces a biphasic P wave with the initial positive deflection corresponding to right atrial activation and ...
What is the first positive deflection on the ECG?
The P wave is the first positive deflection on the ECG
Is the P wave biphasic?
The P wave is typically biphasic in V1, with similar sizes of the positive and negative deflections.
What are the P waves?
P waves. P waves, or Primary waves, are the first waves to arrive at a seismograph. P waves are the fastest seismic waves and can move through solid, liquid, or gas. They leave behind a trail of compressions and rarefactions on the medium they move through. P waves are also called pressure waves for this reason.
How to understand P waves?
To understand P waves, we have to first look into the basics of seismology and seismic waves. The waves of energy that travel through the earth and cause earthquakes and related phenomena are seismic waves. There are two types of seismic waves : 1 Body waves 2 Surface waves
What are the two types of seismic waves?
There are two types of seismic waves : Body waves. Surface waves. Body waves are the waves that can travel through the layers of the earth. They are the fastest waves and as a result, the first waves that seismographs can record. Body waves can move through all states of matter including rocks and molten lava.
Can shear waves move through solids?
They are compression waves. They are shear waves. Can move through solids and liquids. Can only move through solids. Shake the medium in the direction in which they are propagating. Shake the medium in the direction perpendicular to which they are moving.
Which wave progression follows the same rules as R wave progression?
T-wave progression follows the same rules as R-wave progression (see earlier discussion).
Why is Q wave important?
The Q-wave. It is crucial to differentiate normal from pathological Q-waves, particularly because pathological Q-waves are rather firm evidence of previous myocardial infarction. However, there are numerous other causes of Q-waves, both normal and pathological and it is important to differentiate these.
What is ECG interpretation?
ECG interpretation includes an assessment of the morphology (appearance) of the waves and intervals on the ECG curve. Therefore, ECG interpretation requires a structured assessment of the waves and intervals. Before discussing each component in detail, a brief overview of the waves and intervals is given.
Why are R waves high?
It is important to assess the amplitude of the R-waves. High amplitudes may be due to ventricular enlargement or hypertrophy. To determine whether the amplitudes are enlarged, the following references are at hand:
Which direction do vectors resulting from activation of the ventricular free walls go?
The vectors resulting from activation of the ventricular free walls are directed to the left and downwards ( Figure 7 ). The explanation for this is as follows:
Where is the T wave vector?
The T-wave vector is directed to the left, downwards and to the back in children and adolescents . This explains why these individuals display T-wave inversions in the chest leads. T-wave inversions may be present in all chest leads. However, these inversions are normalized gradually during puberty. Some individuals may display persisting T-wave inversion in V1–V4, which is called persisting juvenile T-wave pattern. If all T-waves persist inverted into adulthood, the condition is referred to as idiopathic global T-wave inversion.
Is lead II positive or negative?
The P-wave is always positive in lead II during sinus rhythm. This is rather easy to understand because lead II is angled alongside the P-wave vector, and the exploring electrode is located in front of the P-wave vector ( Figure 2, right-hand side). The P-wave vector is slightly curved in the horizontal plane.
