The lateral and medial cords innervate the muscles of the anterior (flexor) compartment of the forearm, whereas the posterior cord innervates the muscles of the posterior (extensor) compartment of the forearm. Each of the cords gives off one or more preterminal branches. The lateral cord gives rise to the lateral pectoral nerve.
What nerve innervates the posterior posterior cord?
Posterior cord has as an initial branch, the thoracodorsal innervating latissimus dorsi and subscapularis branches. Its major outflow, though, is to all the radial-innervated muscles including triceps through extensor communis. The other major branch or nerve goes to the axillary nerve innervating the deltoid.
What is the posterior cord?
The posterior cord is a part of the brachial plexus. It consists of contributions from all of the roots of the brachial plexus. The posterior cord gives rise to the following nerves:
What nerve innervates the axillary nerve?
The axillary nerve derives from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus with the radial nerve, and lies in close proximity to the surgical neck of the humerus. The major branches of the axillary nerve include the lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm and motor branches to the deltoid and teres minor muscles (C5–C6).
What is the function of the posterior interosseous nerve?
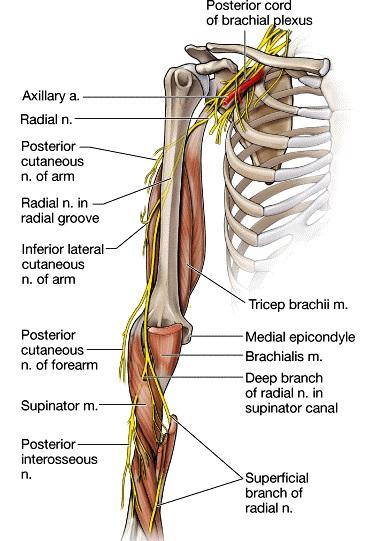
This nerve descends inferiorly through the posterior aspect of the forearm where it penetrates the supinator muscle and emerges as the posterior interosseous nerve. Its main function is to supply the muscles located in the posterior compartment of the forearm (the wrist extensors and the long muscles of the thumb).

What does the posterior cord of the brachial plexus supply?
The posterior cord of the brachial plexus gives off the upper subscapular nerve, thoracodorsal nerve and lower subscapular nerve.
What arises from the posterior cord?
The radial nerve arises from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus and travels to the upper arm via the axilla. It travels under the triceps and wraps around the posterior humerus in close approximation to the spiral groove.
Which of the following muscles is supplied by a branch from posterior cord?
It supplies the triceps brachii muscle, anconeus muscle, brachioradialis muscle, and the lateral half of the brachialis muscle. The posterior interosseous nerve originates in the level of the elbow and then passed under the arcade of Frohse, the proximal edge of the superficial head of the supinator muscle.
What does the medial cord innervate?
The median nerve is derived from the medial and lateral cords of the brachial plexus from the C5–C8 nerve roots (Fig. 38.5). The nerve innervates forearm flexors and some of the hand intrinsics in the thenar eminence.
What nerve innervates the posterior deltoid?
Axillary nerveOriginPosterior cord of brachial plexus (C5-C6)InnervationMotor - deltoid muscle, teres minor muscle, lateral head of the triceps brachii muscle Sensory - glenohumeral joint, skin of the deltoid region/upper armClinical relationsNeuropathy, quadrangular space syndrome1 more row
What muscles do C5 and C6 innervate?
The lower subscapular nerve (C5-C6) innervates teres major; and both the upper and lower subscapular nerves innervate the subscapularis, the third muscle of the rotator cuff apparatus.
What nerve innervates the biceps?
the musculocutaneous nerveThe biceps brachii muscle receives its innervation from the C5 and C6 fibers of the musculocutaneous nerve. The brachialis muscle originates on the distal portion of the anterior humerus, and inserts on both the coronoid process and tuberosity of the ulna.
What does brachial plexus innervate?
The brachial plexus is a major network of nerves transmitting signals responsible for motor and sensory innervation of the upper extremities, including the shoulder, arm, and hand.
What does the lumbar plexus innervate?
The lumbar plexus provides innervation to several important muscles. Notable muscles include the psoas muscle, quadratus lumborum, lumbar transverse muscles, quadriceps femoris, transversus abdominis, and internal oblique muscles.
What is innervated by the ulnar nerve?
The ulnar nerve innervates the flexor muscles of the forearm including the flexor carpi ulnaris and flexor digitorum profundus. It also innervates the intrinsic muscles of the hand including the palmaris brevis, lumbricals, hypothenar and interossei muscles.
What Innervates medial forearm?
medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve[1] Specifically, the medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve provides sensory innervation of the medial forearm as well as the skin overlying the olecranon. [2] It emerges from the medial cord of the brachial plexus and has sensory cell bodies located in C8 and T1.
Which nerve arises from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus quizlet?
-The thoracodorsal nerve arises from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus.
Which nerve arises from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus quizlet?
-The thoracodorsal nerve arises from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus.
Where does the brachial plexus start and end?
The brachial plexus is a network (plexus) of nerves formed by the anterior rami of the lower four cervical nerves and first thoracic nerve (C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1). This plexus extends from the spinal cord, through the cervicoaxillary canal in the neck, over the first rib, and into the armpit.
What is the main outflow of the posterior cord?
Its major outflow, though, is to all the radial-innervated muscles including triceps through extensor communis. The other major branch or nerve goes to the axillary nerve innervating the deltoid. ...
Which nerves are located in the lateral and medial cords?
A few specific nerves emerge from the lateral and medial cords. The lateral pectoral nerve branches from the lateral cord superficial to the first part of the axillary artery and vein, sends a branch to the medial pectoral nerve, and continues on to innervate pectoralis major.
What nerves are involved in the lateral cutaneous nerve?
The major branches of the axillary nerve include the lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm and motor branches to the deltoid and teres minor muscles (C5–C6). Axillary nerve injuries cause weakness of arm abduction, deltoid muscle atrophy with severe axonal injuries, and sensory loss along the upper lateral arm.
Which nerve runs behind the axillary artery?
The lower subscapular nerve supplies the lower subscapularis and teres major by traveling downward behind the subscapular vessels. The thoracodorsal nerve arises between the two subscapular nerves, runs behind the axillary artery, and travels along with the thoracodorsal artery to innervate the latissimus dorsi.
Which nerve runs medially along the axillary vein and innervates the skin of the medial arm?
The medial brachial cutaneous nerve runs medially along the axillary vein and innervates the skin of the medial arm. The medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve arises between the axillary artery and vein and courses medial to the brachial artery.
What nerve is the pin?
The deep branch of the radial nerve is also known as the posterior interosseus nerve (PIN). The PIN winds around the neck of the radius to move distally between the superficial and deep muscles of the posterior compartment of the forearm and terminates at the wrist. View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter.
Where is the posterior cord incision?
The incision extends from the inferior border of the clavicle, within the deltopectoral groove, to the axilla. If exposure to the AN is necessary, the incision is extended into the axilla.
Which Of The Following Nerves Does Not Arise From The Brachial Plexus?
The two nerves that originate from the roots of brachial plexus are: 1) The dorsal scapular nerve which comes off near your shoulder blades; 2 )Long Thoracic Nerve – it courses through middle scalene muscle before piercing into lower neck area The best way I’ve found to understand this information is by doing an Internet search on ” Understanding Brains Through Developmental Disorders.”.
Posterior Cord Of Brachial Plexus
The posterior cord is a complex structure that consists of contributions from all the roots and branches.
What Does The Axillary Nerve Innervate
The axillary nerve is an important nerve that supplies three muscles in the arm: deltoid (a shoulder muscle), triceps (long head) and teres minor.
What Does The Radial Nerve Innervate
The radial nerve is a versatile and important structure in the human body. It supplies many muscles, including those that move our arms up toward us or outwards from their sides to make grasping movements at different objects- which means this area of your skin may be sensitive if you have any trouble bending it!
Which Nerve Arises From The Brachial Plexus
The two nerves that originate from the brachial plexus are often quite difficult to identify. The dorsal scapular nerve, for example, can be traced back to C5 in one direction and then proceeds into your shoulder blade as it courses through muscle before emerging on an arm or hand near where you would expect a vein!
Which Numbered Structure Carries The Efferent Signal?
All neuronal cell bodies are located in gray matter. The signal carrying structure, or axon as it’s known scientifically is sent from the CNS to an effector organ and can be found branching off into tiny fibers along its length called ‘dendrites’.
Which Of The Following Statements About Olfactory Receptors Is False?
Each of us has something called Jacob’s ladder on our brain. This is a bulb-like structure at the tip where olfactory nerves begin and helps with smell, taste or other senses like touch!
Which nerve is the lateral cord?
The lateral cord gives rise to the lateral pectoral nerve. The posterior cord gives rise to the upper subscapular nerve, thoracodorsal nerve and lower subscapular nerve. The medial cord gives rise to the medial pectoral nerve, medial cutaneous nerve of the arm and medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm.
Which cord innervates the muscles of the anterior (flexor) compartment of the forearm?
The lateral and medial cords innervate the muscles of the anterior (flexor) compartment of the forearm, whereas the posterior cord innervates the muscles of the posterior (extensor) compartment of the forearm. Each of the cords gives off one or more preterminal branches.
What nerve is the medial brachial nerve?
The medial brachial cutaneous nerve, also called the medial cutaneous nerve of the arm, arises from the medial cord carrying fibers of C8 and T1 spinal nerves. This nerve provides sensory innervation to the skin of the inferior portion of the medial side of the arm.
What are the branches of the medial cord?
The medial cord gives off the medial pectoral nerve, medial brachial cutaneous nerve, medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve, medial root of median nerve, as well as the ulnar nerve (another terminal branch of brachial plexus).
What is the lateral cord?
The lateral cord gives rise to a couple of preterminal branches; the lateral pectoral nerve and lateral root of median nerve. It also gives off one of the terminal branches of the brachial plexus, the musculocutaneous nerve.
How are the cords of the brachial plexus formed?
The cords of the brachial plexus are formed by the 3 anterior and 3 posterior divisions that merge in a specific way: The lateral cord is formed by the merger of the anterior division of the superior trunk and anterior division of the middle trunk.
What is the brachial plexus?
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that gives rise to all the motor and sensory nerves of the upper extremity . This plexus arises from the anterior rami of spinal nerves C5-T1 that undergo several mergers and splits into trunks and divisions, until they finally give rise to their terminal branches.