What structures does the pretracheal fascia Enclose?
Function. The pretracheal fascia encloses the thyroid gland, and is responsible for its movement during deglutition.
What is the inferior attachment of the prevertebral fascia?
Inferiorly, the investing layer attaches to the manubrium of sternum, spine of the scapular, acromion of scapular and the clavicles.
What are the three layers of the deep cervical fascia?
Moving on, the deep cervical fascia consists of three fascial layers or sheaths called the investing, pretracheal and prevertebral fascia which serve to support the cervical viscera, muscles, vessels and lymph nodes.
Where is a prevertebral structure located?
Structure and Function The prevertebral muscles are located anterior to the cervical column and primarily function in motions of the head and neck at the craniocervical junction. The longus colli consists of a long, flat muscle that sits on the anterior surface of the spine.
Is alar fascia part of prevertebral fascia?
The alar fascia is a layer of fascia, sometimes described as part of the prevertebral fascia, and sometimes as in front of it.
What is the investing layer of fascia?
The investing layer of deep fascia of the neck is a tough layer of fibrous tissue arranged like a collar around the neck. It is attached below to the upper surface of the clavicle. It splits to enclose the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles on each side (Figure 4).
What are the 2 layers of fascia?
Subcutaneous fascia is the connective tissue under the skin that completely surrounds the individual in two layers known as superficial fascia and deep fascia, which adhere to each other.
How many layers of fascia are there?
What are the different layers of fascia? There are four different layers of fascia in your body: superficial, deep, visceral and parietal.
What is the difference between deep fascia and superficial fascia?
The superficial fascia (i.e. tela subcutanea, hypodermis, subcutaneous tissue) is used to describe the connective that separates the skin from the underlying muscle tissue. The deep fascia is a dense, organized, connective tissue located deep to the skin and subcutaneous tissue.
What is the difference between prevertebral and Paravertebral?
Unlike paravertebral ganglion neurons, which serve primarily as a relay, the prevertebral neurons integrate preganglionic inputs with inputs arising from primary visceral afferents with cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglia and afferents from sensory neurons of the enteric nervous system.
What does prevertebral mean?
Medical Definition of prevertebral : situated or occurring anterior to a vertebra or the spinal column prevertebral muscles.
What is the name of deep fascia interior layer?
The deep fasciae envelop all bone (periosteum and endosteum); cartilage (perichondrium), and blood vessels (tunica externa) and become specialized in muscles (epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium) and nerves (epineurium, perineurium, and endoneurium)....Deep fasciaDetailsLatinfascia profundaAnatomical terminology1 more row
What are the two layers of the superficial fascia?
One of these layers, the "superficial fascia" consists of two layers: a membranous Scarpa's fascia and an outer fatty layer, the Campers' fascia. Scarpa's fascia lies below the Camper's fascia and above the external oblique muscle. It is connected laterally to the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle.
Where is the superficial plate of the cervical fascia located?
The superficial cervical fascia is the subcutaneous connective tissue of the neck between the dermis and the deep cervical fascia.
What is the danger space in the neck?
The danger space or alar space, is a region of the neck. The common name originates from the risk that an infection in this space can spread directly to the thorax, and, due to being a space continuous on the left and right, can furthermore allow infection to spread easily to either side.
Which prevertebral muscles flex the atlanto occipital joint?
Rectus capitis lateralis originates from the transverse process of the atlas and inserts onto the jugular process of the occipital bone. It's innervated by branches from the loop between C1 and C2 spinal nerves and when it contracts, it stabilizes and flexes the atlanto-occipital joint.
Which muscle is associated with the prevertebral fascia?
The prevertebral fascia surrounds the vertebral co lumn and its associated muscles; scalene muscles, prevertebral muscles, and the deep muscles of the back.
Where is the superficial cervical fascia?
The superficial cervical fascia lies between the dermis and the deep cervical fascia. It contains numerous structures:
Why is the neck fascia important?
This is of clinical importance as a pathway for the spread of infection. The neck fascia compartmentalises structures within the neck. These layers of tough fascia can limit the spread of infection (for example, a superficial skin abscess may be prevented from spreading deeper into the neck by the investing fascia).
How many fascias are there in the neck?
There are two fascias in the neck – the superficial cervical fascia and the deep cervical fascia. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the fascial layers of the neck - their attachments, anatomical relationships and their clinical relevance. Superficial Cervical Fascia.
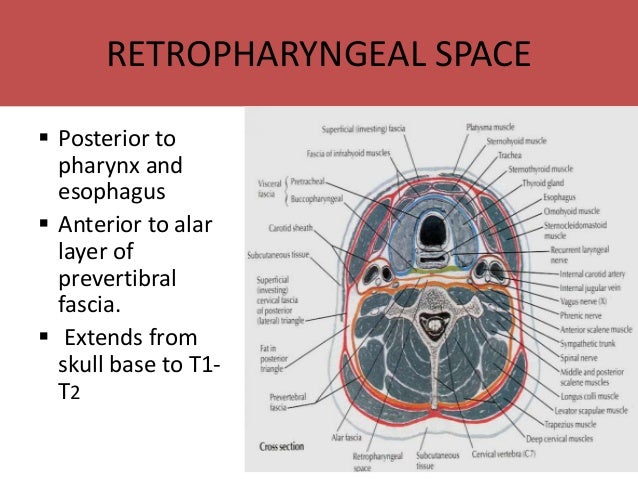
Where is the retropharyngeal space?
However, infections that reach the potential spaces between the neck fascia have a well-defined spread: Retropharyngeal space – located between the buccopharyngeal fascia (posterior aspect of the visceral pretracheal fascia) and the prevertebral fascia. Extends from the base of the skull to the posterior mediastinum.
Which part of the neck surrounds the brachial plexus?
The anterolateral portion of prevertebral fascia forms the floor of the posterior triangle of the neck. It also surrounds the brachial plexus as it leaves the neck and subclavian artery as it passes through the lower neck region – in doing so, it forms the axillary sheath.
Where is the platysma located?
The platysma is a broad superficial muscle which lies anteriorly in the neck. It has two heads, which originate from the fascia of the pectoralis major and deltoid. The fibres from the two heads cross the clavicle, and meet in the midline, fusing with the muscles of the face.
What is the prevertebral muscle?
Prevertebral muscles. The prevertebral muscles are a group of deep cervical muscles inside the neck located laterally at the upper vertebral column. They are enveloped by the prevertebral layer of the cervical fascia. Their main task is the bending forward of the skull (ventral flexion). Furthermore they cause a lateral flexion ...
What muscle group is the rectus capitis anterior?
Rectus capitis anterior and lateralis muscles. The rectus capitis anterior and the lateralis muscles make up the ventral group of the short neck muscles. The rectus capitis anterior muscle has its origin at the massa lateralis of the atlas, the rectus capitis lateralis muscle at the transverse process of the atlas.
Which muscle is the most important antagonist of the large cervical spine extensors?
The prevertebral muscles are - despite their small size - the most important antagonists of the large cervical spine extensors such as the trapezius muscle and levator scapulae muscle. They play an enormous role in the connection and stabilization of the cervical column and the skull.
Where is the longus colli muscle located?
Longus colli muscle. The longus colli muscle has several origins from the 3rd thoracic to 3rd cervical vertebrae. Its insertions are located at the upper cervical vertebrae, the transverse processes of the 5th and 6th cervical vertebrae and the anterior tubercle of the atlas.
Which spinal nerve innervates the short neck muscles?
In comparison to the dorsal group of the short neck muscles (suboccipital muscles) which are counted among the intrinsic back muscles they are innervated by the ventral branch of the first spinal nerve (C1). Therefore they are considered as secondary back muscles.
What is the function of the cervical fascia?
Cervical fascias. “An important function of the cervical fascia is to guide against the spread of pus and debris (abscesses) resulting from diseased or abnormal tissues, however, a potential pathway for spread of infection exists...”. As applies to most walls of several regions of the body, structures making up the neck are surrounded by a layer ...
Why is the cervical fascia important?
The most significant clinical importance of the cervical fascia is prevention of the spread of pus and debris. However, this function is mainly restricted to the deep cervical fascia which lies closer to the neck viscera and muscles. For example, if an infection occurs between the investing layer of deep cervical fascia and the muscular part ...
What is the name of the muscle that is swollen posterior to the sternocleidomastoi?
Pus from an abscess posterior to the prevertebral layer of deep cervical fascia may extend laterally in the neck and form a swelling posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Such pus may perforate the prevertebral layer and enter the retropharyngeal space, producing a bulge in the pharynx, a condition referred to as retropharyngeal abscess ...
What is the pretracheal layer?
Pretracheal layer. This layer of deep cervical fascia is a thin fascia limited to the anterior part of the neck. It is named after the trachea, to which it provides a slippery surface for up and down gliding during swallowing and neck movements.
What is the fourth part of the deep cervical fascia?
This is the fourth part or layer of the deep cervical fascia. It is a tubular fascial investment that extends from the cranial base to the root of the neck. Anteriorly, this sheath blends with the investing and pretracheal layers of the deep cervical fascia, posteriorly it is continuous with the prevertebral layer, and it contains the common carotid arteries, internal carotid arteries, internal jugular vein, the vagus nerve (CN X), some deep cervical lymph nodes, carotid sinus nerve, and sympathetic nerve fibres ( carotid periarterial plexuses ).
Which layer of the cervical fascia contains trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles?
This layer of the deep cervical fascia is a collar of fascia surrounding the whole neck and contains the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles.
Which layer of the cervical fascia supports the viscera of the neck?
The prevertebral layer of deep cervical fascia. These layers of the deep cervical fascia also function to support the viscera of the neck (e.g., the thyroid gland ), muscles, blood and lymphatic vessels, and deep lymph nodes. They also form the carotid sheath that wraps around vessels like the common carotid arteries, internal jugular veins, ...