Full Answer
How do you calculate the law of Conservation of mass?
Formula of Law of Conservation of Mass
- is the density
- is the time
- is the velocity
- is the divergence
Why is the law of Conservation of mass so important?
Why is the law of conservation important? The law of conservation of mass is very important to the study and production of chemical reactions. If scientists know the quantities and identities of reactants for a particular reaction, they can predict the amounts of products that will be made.
What is meant by the law of Conservation of mass?
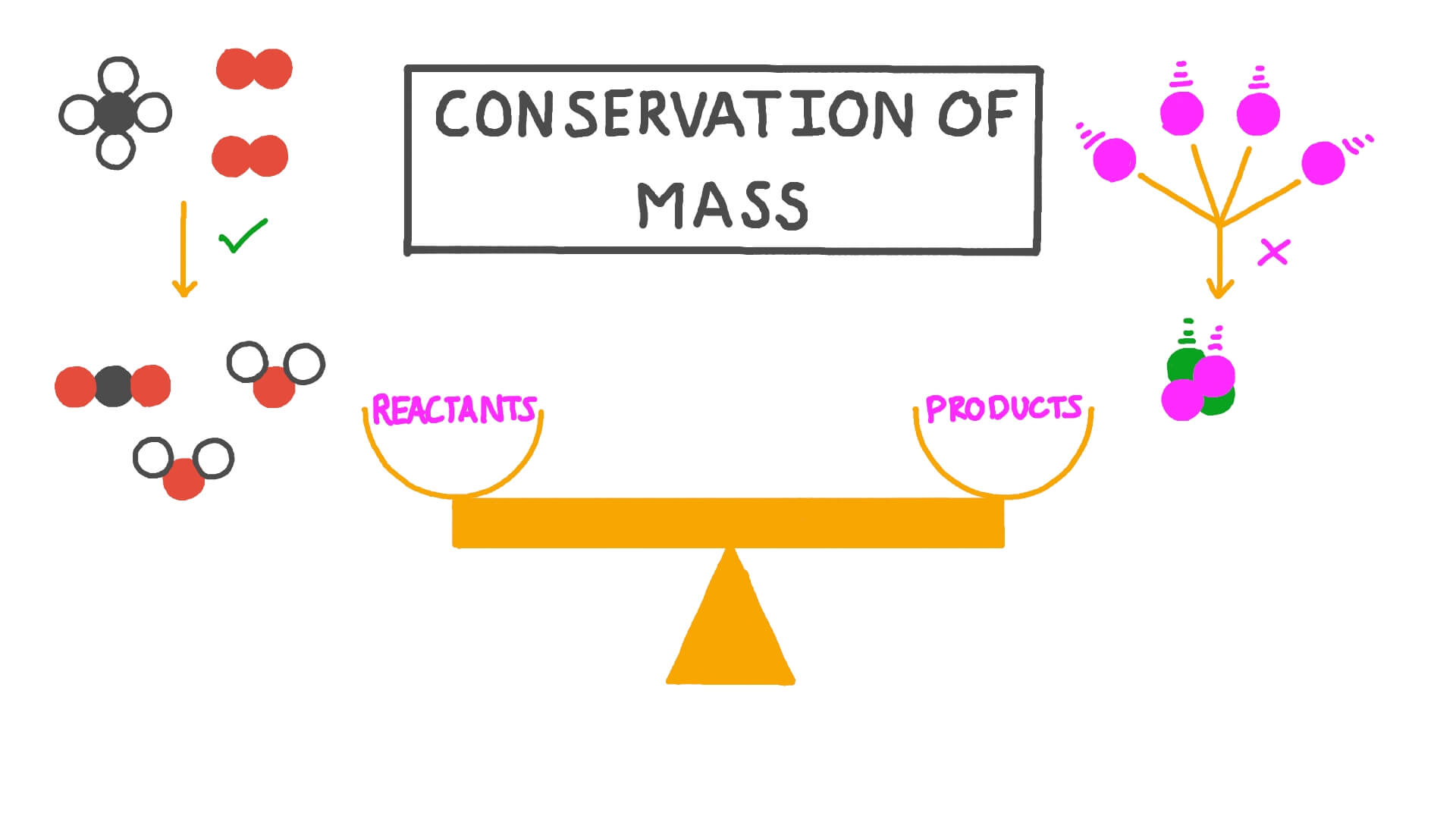
The law of conservation of mass states that mass in an isolated system is neither created nor destroyed by chemical reactions or physical transformations. According to the law of conservation of mass, the mass of the products in a chemical reaction must equal the mass of the reactants.
How do you prove the law of Conservation of mass?
To verify the law of conservation of mass in a chemical reaction - Science Practicals
- The spring balance should be held vertical while taking measurements.
- Before making use of the spring balance it must be ensured that its pointer is at zero mark. If not then ask your teacher to help.
- The readings of the spring balance should be noted only when its pointer comes to rest.
What are the principle of conservation of mass?
The principle of conservation of mass states that the mass of a body is constant during its motion. This can be stated in the rate form, as the time rate of change of the mass of a body is zero. It is obvious that this statement must be expressed mathematically for a material system.
What does the conservation of mass mean?
conservation of mass, principle that the mass of an object or collection of objects never changes, no matter how the constituent parts rearrange themselves.
What does the conservation of mass means in a chemical reaction?
The law of conservation of mass states that. “The mass in an isolated system can neither be created nor be destroyed but can be transformed from one form to another”. According to the law of conservation of mass, the mass of the reactants must be equal to the mass of the products for a low energy thermodynamic process.
What is conservation of mass in short?
The law of conservation of mass states that mass in an isolated system is neither created nor destroyed by chemical reactions or physical transformations. According to the law of conservation of mass, the mass of the products in a chemical reaction must equal the mass of the reactants.
Why is the conservation of mass so important?
The law of conservation of mass was crucial to the progression of chemistry, as it helped scientists understand that substances did not disappear as result of a reaction (as they may appear to do); rather, they transform into another substance of equal mass.
How does the law of conservation of mass apply to everyday life?
The law of conservation of mass states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. For example, when wood burns, the mass of the soot, ashes, and gases equals the original mass of the charcoal and the oxygen when it first reacted. So the mass of the product equals the mass of the reactant.
What is the law of conservation of mass describe with an activity?
The law of conservation of mass states that matter cannot be created nor destroyed, only it's form changed. Take the example of burning a piece of paper. It seems that the mass shrinks as the paper burns. However, what is really happening is that the paper is changing form to ash, carbon dioxide, and water vapor.
How does the law of conservation of mass apply to a chemical change?
The Law of Conservation of Matter states that matter cannot be created or destroyed. In a physical change, substances can change form, but the total mass remains the same. In a chemical change, the total mass of the reactants always equals the total mass of the products.
Which one is the best example of law of conservation of mass?
A sample of air increases in volume when heated at constant pressure but its mass remains unaltered.
What is conservation of momentum simple definition?
conservation of momentum, general law of physics according to which the quantity called momentum that characterizes motion never changes in an isolated collection of objects; that is, the total momentum of a system remains constant.
Is the law of conservation of mass always true?
Conservation of mass The total amount of mass in an isolated system, in which we can account for all mass, is always conserved. Mass can neither be created from nothing nor destroyed, except when converted directly to energy in very special circumstances.
How many law of conservation of mass are there?
The following two laws of the chemical combination were established after many experimentations by Lavoisier and Joseph Proust: Law of conservation of mass. Law of constant proportions. Law of multiple proportions.
Why is the law of conservation of mass important?
The law of conservation of mass was crucial to the progression of chemistry, as it helped scientists understand that substances did not disappear as result of a reaction (as they may appear to do); rather, they transform into another substance of equal mass. History credits multiple scientists with discovering the law of conservation of mass.
Who discovered the law of conservation of mass?
History credits multiple scientists with discovering the law of conservation of mass. Russian scientist Mikhail Lomonosov noted it in his diary as a result of an experiment in 1756. In 1774, French chemist Antoine Lavoisier meticulously documented experiments that proved the law. The law of conservation of mass is known by some as Lavoisier's Law.
Which law states that a balanced chemical equation has the same mass of reactants and products?
According to the Law of Conservation of Mass, a balanced chemical equation has the same mass of reactants and products.
Is mass constant in an isolated system?
Therefore, the mass contained in that isolated system will remain constant, regardless of any transformations or chemical reactions that occur—while the result may be different than what you had in the beginning, there can't be any more or less mass than what you had prior to the transformation or reaction. The law of conservation of mass was ...
What is the principle of mass conservation?
The principle of mass conservation states that matter is neither created nor destroyed. This principle like many physics laws is empirical; that is, its validity rests on experimental observations. In every process, it is necessary to obey the law of mass conservation.
What is the net change in the mass of a system?
(1.2) states that in a transient process taking place over a given time period, t, the net change in the mass of the system, Δ msys, is equal to the sum of the masses entering the system through n inlet port minus the sum of the masses leaving the system through m outlet ports.
What is the general form of the continuity equation for modeling subsurface pollutant transport?
Eq. (7.15) is the general form of the continuity equation for modeling subsurface pollutant transport. With the linear sorption isotherm and the assumption of local equilibrium, the bulk concentration of a pollutant can be expressed as:
What is the mass flux vector?
The mass flux vector, J, is the mass crossing a unit area per unit time, and includes advective, diffusive, and dispersive mass transport ( Mohamed and Paleologos, 2018 ). The reaction term accounts for radioactive decay, biodegradation of organic pollutants, precipitation and redox chemical reactions that may mobilize a pollutant, and others. It is expressed by the symbol S + with units of mass per unit volume per unit time. For an arbitrary control volume, the conservation of mass equation is given by Eq. (7.14):
What is the second term of the control volume?
where the first term from the left-hand side represents the time rate of increase in the total mass within the control volume, the second term is the net flux of mass into the volume across the control surface with n v the outward unit normal vector to the control surface, and the last term is the mass increase due to sources located within the volume ( Mohamed and Paleologos, 2018 ). Because the control volume is arbitrary, Eq. (7.14) can be rewritten as per ( Eq. 7.15 ):
Is mass conserved in a chemical reaction?
Mass is also conserved in chemical reactions. For example, consider oxidation of hydrogen. The product of reaction is water. The reactants (O 2 and H 2) no longer exist after the reaction and a new product (H 2 O) is formed. The conservation of mass requires that the sum of the masses of oxygen and hydrogen be equal to the mass of water. In general, the total mass of reactants should equal the total mass of products in a chemical reaction in accordance with the law of mass conservation.
Is there mass differential in steady flow?
For a steady flow system, there is no mass differential, hence it can be written as follows:
How is conservation of mass expressed?
The law can be formulated mathematically in the fields of fluid mechanics and continuum mechanics, where the conservation of mass is usually expressed using the continuity equation, given in differential form as
What is the law of conservation of mass?
In physics and chemistry, the law of conservation of mass or principle of mass conservation states that for any system closed to all transfers of matter and energy, the mass of the system must remain constant over time, as the system's mass cannot change, so quantity can neither be added nor be removed. Therefore, the quantity of mass is conserved ...
Why is mass conservation important?
The idea of mass conservation plus a surmise that certain "elemental substances" also could not be transformed into others by chemical reactions, in turn led to an understanding of chemical elements, as well as the idea that all chemical processes and transformations (such as burning and metabolic reactions) are reactions between invariant amounts or weights of these chemical elements.
What did Einstein say about mass?
This theory implied several assertions, like the idea that internal energy of a system could contribute to the mass of the whole system, or that mass could be converted into electromagnetic radiation.
Why can't rest masses be added?
The reason that rest masses cannot be simply added is that this does not take into account other forms of energy, such as kinetic and potential energy, and massless particles such as photons, all of which may (or may not) affect the total mass of systems.
What is the continuity equation for mass?
The interpretation of the continuity equation for mass is the following: For a given closed surface in the system, the change in time of the mass enclosed by the surface is equal to the mass that traverses the surface, positive if matter goes in and negative if matter goes out.
Why did mass change in the 19th century?
The change in mass of certain kinds of open systems where atoms or massive particles are not allowed to escape, but other types of energy (such as light or heat) are allowed to enter, escape or be merged, went unnoticed during the 19th century, because the change in mass associated with addition or loss of small quantities of thermal or radiant energy in chemical reactions is very small. (In theory, mass would not change at all for experiments conducted in isolated systems where heat and work were not allowed in or out.)

Overview
In physics and chemistry, the law of conservation of mass or principle of mass conservation states that for any system closed to all transfers of matter and energy, the mass of the system must remain constant over time, as the system's mass cannot change, so quantity can neither be added nor be removed. Therefore, the quantity of mass is conserved over time.
Formulation and examples
The law of conservation of mass can only be formulated in classical mechanics, in which the energy scales associated to an isolated system are much smaller than , where is the mass of a typical object in the system, measured in the frame of reference where the object is at rest, and is the speed of light.
The law can be formulated mathematically in the fields of fluid mechanics and continuum mecha…
History
As early as 520 BCE, Jain philosophy, a non-creationist philosophy based on the teachings of Mahavira, stated that the universe and its constituents such as matter cannot be destroyed or created. The Jain text Tattvarthasutra (2nd century CE) states that a substance is permanent, but its modes are characterised by creation and destruction.
Generalization
In special relativity, the conservation of mass does not apply if the system is open and energy escapes. However, it does continue to apply to totally closed (isolated) systems. If energy cannot escape a system, its mass cannot decrease. In relativity theory, so long as any type of energy is retained within a system, this energy exhibits mass.
Also, mass must be differentiated from matter, since matter may not be perfectly conserved in is…
See also
• Charge conservation
• Conservation law
• Fick's laws of diffusion
• Law of definite proportions
• Law of multiple proportions