
What is the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient?
The Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient is a measure of the linear relationship between two questions/measures/variables, X and Y. The Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient is a measure of the linear relationship between two questions/measures/variables, X and Y.
What is a correlation coefficient?
A correlation coefficient is a number between -1 and 1 that tells you the strength and direction of a relationship between variables. In other words, it reflects how similar the measurements of two or more variables are across a dataset.
What is correlation in R?
In this sense, a correlation allows to know which variables evolve in the same direction, which ones evolve in the opposite direction, and which ones are independent. In this article, I show how to compute correlation coefficients, how to perform correlation tests and how to visualize relationships between variables in R.
What is the correlation coefficient in a scatter plot?
The correlation coefficient tells you how closely your data fit on a line. If you have a linear relationship, you’ll draw a straight line of best fit that takes all of your data points into account on a scatter plot.
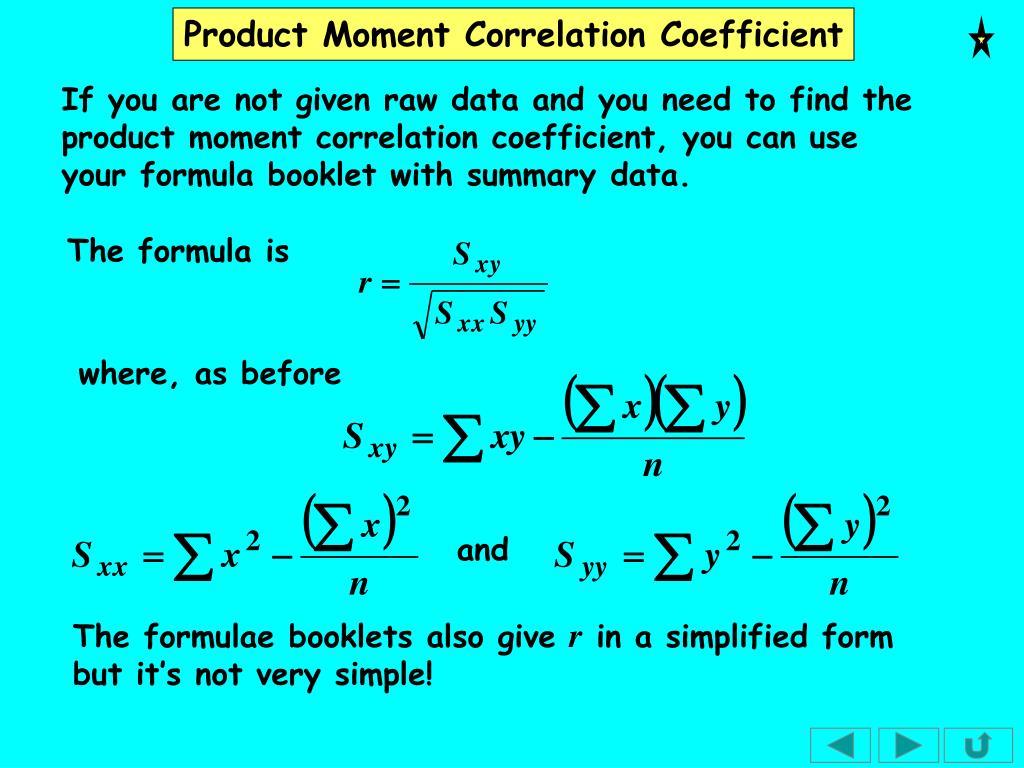
What does product moment correlation measure?
Pearson's Product Moment Correlation Coefficient measures the degree of correlation there may be between two variables. It is best used when results have already been plotted on a scatter graph and there is an indication of a linear relationship between the two factors.
What does the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient tell you?
The Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient (Pearson's correlation, for short) is a measure of the strength and direction of association that exists between two variables measured on at least an interval scale.
What is the r value correlation coefficient?
What is r? Put simply, it is Pearson's correlation coefficient (r). Or in other words: R is a correlation coefficient that measures the strength of the relationship between two variables, as well as the direction on a scatterplot. The value of r is always between a negative one and a positive one (-1 and a +1).
What is Pearson product moment coefficient of correlation r?
The Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient (or Pearson correlation coefficient, for short) is a measure of the strength of a linear association between two variables and is denoted by r.
How do you interpret a correlation r equal to?
The magnitude of the correlation coefficient indicates the strength of the association. For example, a correlation of r = 0.9 suggests a strong, positive association between two variables, whereas a correlation of r = -0.2 suggest a weak, negative association.
How do you interpret a correlation coefficient?
The strength of relationship can be anywhere between −1 and +1. The stronger the correlation, the closer the correlation coefficient comes to ±1. If the coefficient is a positive number, the variables are directly related (i.e., as the value of one variable goes up, the value of the other also tends to do so).
What does the R value represent?
The term "R"-value represents how well insulation restricts heat flow. To test for R-value, a piece of insulation placed between two plates in a laboratory. Heat is then passed through the material to test the thermal conductivity, measured in BTUs per hour. The greater the "R"-value the better the insulation.
What does the R value mean in regression?
R-squared is a goodness-of-fit measure for linear regression models. This statistic indicates the percentage of the variance in the dependent variable that the independent variables explain collectively.
What is r in an equation?
'R' is the set of real numbers. The equation has infinite number of solutions, meaning any real number is a solution: loading.
What is the purpose of Pearson's r as a statistical technique?
Pearson's correlation coefficient is the test statistics that measures the statistical relationship, or association, between two continuous variables. It is known as the best method of measuring the association between variables of interest because it is based on the method of covariance.
How do you use Pearson r correlation?
You use Pearson's correlation when you're dealing with two quantitative variables. The three possible research hypotheses state whether or not there is a linear relationship between the two variables. 1) +r: There is a positive linear relationship (as one variable increases, so does the other).
What is the importance of Pearson r correlation in quantitative studies?
The Pearson correlation coefficient (also known as Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient) r is a measure to determine the relationship (instead of difference) between two quantitative variables (interval/ratio) and the degree to which the two variables coincide with one another—that is, the extent to which two ...
What is a good R value?
Depending on where you live and the part of your home you're insulating (walls, crawlspace, attic, etc.), you'll need a different R-Value. Typical recommendations for exterior walls are R-13 to R-23, while R-30, R-38 and R-49 are common for ceilings and attic spaces.
What does the R 2 value mean in statistics?
R-squared (R2) is a statistical measure that represents the proportion of the variance for a dependent variable that's explained by an independent variable or variables in a regression model.
What is the difference between r and r2?
R: The correlation between the observed values of the response variable and the predicted values of the response variable made by the model. R2: The proportion of the variance in the response variable that can be explained by the predictor variables in the regression model.
What does R 2 mean in correlation?
The R-squared value, denoted by R 2, is the square of the correlation. It measures the proportion of variation in the dependent variable that can be attributed to the independent variable.
What is the definition of the Pearson correlation coefficient?
The Pearson correlation coefficient ( r ) is the most common way of measuring a linear correlation. It is a number between –1 and 1 that measures...
When should I use the Pearson correlation coefficient?
You should use the Pearson correlation coefficient when (1) the relationship is linear and (2) both variables are quantitative and (3) normally dis...
How do I calculate the Pearson correlation coefficient in R?
You can use the cor() function to calculate the Pearson correlation coefficient in R. To test the significance of the correlation, you can use...
How do I calculate the Pearson correlation coefficient in Excel?
You can use the PEARSON() function to calculate the Pearson correlation coefficient in Excel. If your variables are in columns A and B, then cl...
What is positive correlation?
Positive correlation: Is when both the variables have the same type of moment and they both rise or fall together in the same direction. E.g sale of ice cream with change in temperature, if the temperature increases more ice cream is sold and as the temperature decreases less ice cream is sold. The expenditure of a family depends on their income.
What is a perfect negative correlation?
If the coefficient of correlation is -1. It is considered a perfect negative correlation and if the correlation is +1 then it is considered a perfect positive correlation. The closer the value is to -1 or +1 the stronger the relationship is considered to be. a) Find the correlation coefficient.
What is a good relation between variables?
A good relation between the variables means that the line of best fit will pass through maximum points. The interdependence of the two variables is known as as correlation.correlation is measured by coefficient of correlation which is denoted by ”r”. And its numerical value ranges from +1 to -1.
Is X and Y linear dependent?
Then in that case, both the variables X and Y are considered independent and are considered to have no linear dependency on each other.
What values can the Pearson correlation coefficient take?
The Pearson correlation coefficient, r, can take a range of values from +1 to -1. A value of 0 indicates that there is no association between the two variables. A value greater than 0 indicates a positive association; that is, as the value of one variable increases, so does the value of the other variable. A value less than 0 indicates a negative association; that is, as the value of one variable increases, the value of the other variable decreases. This is shown in the diagram below:
What is Pearson correlation?
Note: Pearson's correlation coefficient is a measure of the strength of a linear association between two variables. Put another way, it determines whether there is a linear component of association between two continuous variables. As such, linearity is not strictly an "assumption" of Pearson's correlation. However, you would not normally want to use Pearson's correlation to determine the strength and direction of a linear relationship when you already know the relationship between your two variables is not linear. Instead, the relationship between your two variables might be better described by another statistical measure (Cohen, 2013). For this reason, it is not uncommon to view the relationship between your two variables in a scatterplot to see if running a Pearson's correlation is the best choice as a measure of association or whether another measure would be better.
How can we determine the strength of association based on the Pearson correlation coefficient?
The stronger the association of the two variables, the closer the Pearson correlation coefficient, r, will be to either +1 or -1 depending on whether the relationship is positive or negative, respectively . Achieving a value of +1 or -1 means that all your data points are included on the line of best fit – there are no data points that show any variation away from this line. Values for r between +1 and -1 (for example, r = 0.8 or -0.4) indicate that there is variation around the line of best fit. The closer the value of r to 0 the greater the variation around the line of best fit. Different relationships and their correlation coefficients are shown in the diagram below:
Do the two variables have to be measured in the same units?
No, the two variables can be measured in entirely different units. For example, you could correlate a person's age with their blood sugar levels. Here, the units are completely different; age is measured in years and blood sugar level measured in mmol/L (a measure of concentration). Indeed, the calculations for Pearson's correlation coefficient were designed such that the units of measurement do not affect the calculation. This allows the correlation coefficient to be comparable and not influenced by the units of the variables used.
Why is Pearson's correlation the incorrect test?
In many cases, Pearson’s correlation will be the incorrect statistical test to use because your data " violates/does not meet " one or more of these assumptions. This is not uncommon when working with real-world data, which is often "messy", as opposed to textbook examples.
What is the first step before using Pearson's correlation?
The first and most important step before analysing your data using Pearson’s correlation is to check whether it is appropriate to use this statistical test. After all, Pearson’s correlation will only give you valid/accurate results if your study design and data " pass/meet " seven assumptions that underpin Pearson’s correlation.
Is Pearson's correlation a statistical test?
If observations are not independent, they are related, and Pearson’s correlation is not an appropriate statistical test (although there are other measures of association that can be used when you have observations that are not independent).
How to calculate the significance of a hypothesis?
Steps for performing the test: 1 Set up the hypothesis. 2 Decide the level of significance. 3 Calculate the degree of freedom (df = N-2) and using that value determine the critical value of t from t-distribution table. 4 Calculate Pearson’s correlation coefficient and calculate the value of t from the formula above. 5 Determine whether to accept or reject the hypothesis
What is significance test?
A test of significance for the Pearson’s correlation coefficient may be used to find out if the computed Pearson correlation r could have significantly occurred in the population in which the two variables are significantly related or not. The test statistics follow t-distribution with N-2 degree of freedom. The significance is computed using the following formula
What is the value of the correlation coefficient?
The value of the correlation coefficient always ranges between 1 and -1, and you treat it as a general indicator of the strength of the relationship between variables.
What does a correlation coefficient tell you?
Correlation coefficients summarize data and help you compare results between studies.
What is the correlation of determination?
When you square the correlation coefficient, you end up with the correlation of determination ( r2 ). This is the proportion of common variance between the variables. The coefficient of determination is always between 0 and 1, and it’s often expressed as a percentage.
What is the difference between Spearman and Pearson correlation coefficients?
While the Pearson correlation coefficient measures the linearity of relationships, the Spearman correlation coefficient measures the monotonicity of relationships.
What does it mean when a variable has a high coefficient of alienation?
A high coefficient of alienation indicates that the two variables share very little variance in common. A low coefficient of alienation means that a large amount of variance is accounted for by the relationship between the variables.
What happens when you take away the coefficient of determination from unity?
When you take away the coefficient of determination from unity (one), you’ll get the coefficient of alienation. This is the proportion of common variance not shared between the variables, the unexplained variance between the variables.
What is the purpose of coefficient of determination?
The coefficient of determination is used in regression models to measure how much of the variance of one variable is explained by the variance of the other variable.
Why is the correlation coefficient biased?
The reason is that the correlation coefficient could be biased due to an outlier or due to the type of link between the two variables.
Why is correlation important in descriptive analysis?
Correlations between variables play an important role in a descriptive analysis. A correlation measures the relationship between two variables, that is, how they are linked to each other. In this sense, a correlation allows to know which variables evolve in the same direction, which ones evolve in the opposite direction, ...
How to visualize correlation between two variables?
A good way to visualize a correlation between 2 variables is to draw a scatterplot of the two variables of interest. Suppose we want to examine the relationship between horsepower ( hp) and miles per gallon ( mpg ):
What does it mean when a correlation is close to 0?
This also means that a correlation close to 0 indicates that the two variables are independent, that is, as one variable increases, there is no tendency in the other variable to either decrease or increase.
What is the function of rcorr?
Similar to the correlation matrix used to compute correlation for several pairs of variables, the rcorr () function (from the {Hmisc} package) allows to compute p -values of the correlation test for several pairs of variables at once. Applied to our dataset, we have:
What is the difference between a positive and negative correlation?
Regarding the direction of the relationship: On the one hand, a negative correlation implies that the two variables under consideration vary in opposite directions, that is , if a variable increases the other decreases and vice versa. On the other hand, a positive correlation implies that the two variables under consideration vary in the same direction, i. e., if a variable increases the other one increases and if one decreases the other one decreases as well.
What does negative correlation mean?
Regarding the direction of the relationship: On the one hand, a negative correlation implies that the two variables under consideration vary in opposite directions, that is, if a variable increases the other decreases and vice versa.
