
What are some problems with the retina?
- Dry Eye. After the age of 40, our tear production tends to decline. ...
- Floaters. ...
- Glaucoma. ...
- Macular Degeneration. ...
- Cataracts. ...
- Diabetic retinopathy. ...
- Detached retina. ...
- Trichiasis. ...
- Eyestrain. ...
- Blepharitis. ...
How to improve the health of the retina?
Keep Your Eyes Healthy
- Get a comprehensive dilated eye exam. Getting a dilated eye exam is simple and painless — and it’s the single best thing you can do for your eye health!
- Find out if you’re at risk for eye diseases. Getting older increases your risk of some eye diseases. ...
- Take care of your health. ...
- Protect your eyes. ...
How to heal your retina?
- Make sure to take frequent breaks from your television, computer, and cell phone. ...
- Avoid reading in dim light to reduce strain on your eye muscles.
- Make sure to always keep your eyeglass prescription current. ...
- When out in the sun, always wear sunglasses to protect your eyes. ...
- Wear protective eye gear around chemicals.
- Never wear old eye makeup.
What are the diseases of the retina?
- Sudden vision loss
- Loss of peripheral vision
- Light flashes
- Color perception changes
- Floaters
- Eye pain
- Redness
- Night blindness
- Vision loss in a particular vision field
- Trouble adjusting to light changes
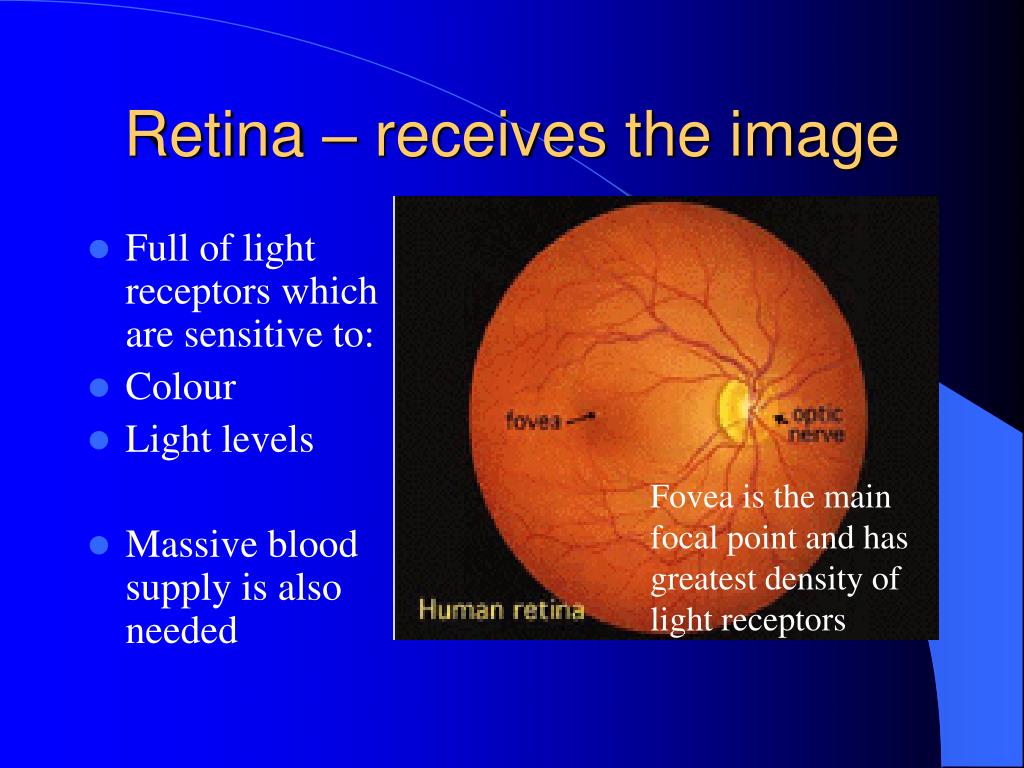
Does the retina contain rods and cones?
Distribution of rods and cones in the human retina. Graph illustrates that cones are present at a low density throughout the retina, with a sharp peak in the center of the fovea. Conversely, rods are present at high density throughout most of the retina, (more...)
Which one is found in retina?
There are five types of neurons in the retina: photoreceptors, bipolar cells, ganglion cells, horizontal cells, and amacrine cells.
What is the retina made of and what does it do?
The retina is a thin layer of tissue that lines the back of your eye. This tissue is composed of cells called photoreceptor cells. The role of photoreceptor cells is to receive the light that passes through your eye. The photoreceptors then translate the light into impulses.
What cells are found in each layer of the retina?
In peripheral retina, the ganglion cell layer consists of only a single layer of cells whereas in central retina they form a layer comprise of up to 10 cells....Layers of Retina:Name of the layersContentInner plexiform layerSynapses between bipolar, amacrine, and ganglion cells9 more rows•Apr 1, 2021
What are the main features of the retina?
What is the primary function of the retina? The retina contains millions of cells that work together to detect light, turn it into electrical signals and communicate with the brain to produce vision. These tiny photoreceptor cells are called cones and rods.
What layer contains rods and cones?
Answer and Explanation: Of the above choices, the layer of the eye that contains both rod and cone cells is the J. retina. The retina is a thin membrane-like layer of rod...
What are the 4 layers of retina?
The cellular layers of the retina are as follows: 1) The pigmented epithelium, which is adjacent to the choroid, absorbs light to reduce back reflection of light onto the retina, 2) the photoreceptor layer contains photosensitive outer segments of rods and cones, 3) the outer nuclear layer contains cell bodies of the ...
How many cells are in the retina?
Function. There are about 0.7 to 1.5 million retinal ganglion cells in the human retina. With about 4.6 million cone cells and 92 million rod cells, or 96.6 million photoreceptors per retina, on average each retinal ganglion cell receives inputs from about 100 rods and cones.
Which layer of the retina contains the photoreceptors?
outer nuclear layerSurgical Retina The outer nuclear layer contains the cell bodies of the photoreceptor cells. These cells extend a process toward the outer plexiform layer, where they form the characteristic synaptic terminals of rods (spherules) and cones (pedicles).
What are the 3 parts of the retina?
The optic vesicle gives rise to three structures: the neural retina, the retinal pigmented epithelium, and the optic stalk. The neural retina contains the retinal progenitor cells (RPCs) that give rise to the seven cell types of the retina.
What are the 3 major cell layers of the retina?
There are three primary layers in the retina that are made up of nerve cells or neurons. These are the photoreceptor cell layer, ganglion cell layer and bipolar cell layer.
Does the retina contain blood vessels?
Throughout the retina the major blood vessels of the retinal vasculature supply the capillaries that run into the neural tissue. Capillaries are found running through all parts of the retina from the nerve fibre layer to the outer plexiform layer and even occasionally as high as in the outer nuclear layer.
What is the retina?
Posted on August 14, 2018 by Austin Retina Associates in Retina. The retina is an essential part of the eye that enables vision. It’s a thin layer of tissue that covers approximately 65 percent of the back of the eye, near the optic nerve. Its job is to receive light from the lens, convert it to neural signals and transmit them to ...
What are the parts of the eye that work together to produce clear vision?
The eye has many parts that must work together in order to produce clear vision. The retina is made up of ten layers of cells that work together to detect light and turn it into electrical impulses. These special cells are called cones and rods and are known as photoreceptors: Cones.
How to repair retinal detachment?
Retinal tears and detachments can be repaired with procedures and surgeries such as: Laser. A laser makes small burns around the retinal tear. The resulting scar seals the retina to the underlying tissue, which helps prevent further damage, like retinal detachment. Freezing treatment (cryotherapy)
What is the function of the optic nerve?
Its job is to receive light from the lens, convert it to neural signals and transmit them to the brain for visual recognition. Because the retina and optic nerve originate as outgrowths of the developing brain, they are both considered part of the central nervous system and brain tissue.
Where are cones located?
Cones are located in the central, or macula, part of the retina. These cells help detect color and detail. Similarly, the macula allows us to perform fine functions like reading, writing, typing and clearly recognizing people’s facial details (e.g., freckles).
What is the retina?
58301. Anatomical terminology. The retina (from Latin: rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which translates that image into electrical neural impulses to ...
What is the retina in the human eye?
The retina (from Latin: rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs.
How does the retina work?
The retina translates an optical image into neural impulses starting with the patterned excitation of the colour-sensitive pigments of its rods and cones, the retina's photoreceptor cells. The excitation is processed by the neural system and various parts of the brain working in parallel to form a representation of the external environment in the brain.
What is the structure of the retina that is not directly associated with vision?
Additional structures, not directly associated with vision, are found as outgrowths of the retina in some vertebrate groups. In birds, the pecten is a vascular structure of complex shape that projects from the retina into the vitreous humour; it supplies oxygen and nutrients to the eye, and may also aid in vision.
What are the two types of cells that are found in the retina?
The primary light-sensing cells in the retina are the photoreceptor cells, which are of two types: rods and cones .
Which area of the retina is avascular?
Some vertebrates, including humans, have an area of the central retina adapted for high-acuity vision. This area, termed the fovea centralis, is avascular (does not have blood vessels), and has minimal neural tissue in front of the photoreceptors, thereby minimizing light scattering.
How thick is the retina?
In section, the retina is no more than 0.5 mm thick. It has three layers of nerve cells and two of synapses, including the unique ribbon synapse.
Which type of retina has the highest concentration of cones?
There are two main types of photoreceptors, rods and cones, in the retina. The fovea in the macula , which is a central space of the retina, has the highest concentration of cones but not one single rod. 2 Cones deliver a better resolution of images.
Which part of the retina is responsible for visual processing?
It is made of millions of nerve fibers and transmits visual information to the brain for processing. Macula: The macula is a specialized pigmented part of the retina in the very center of the retina that gives us central vision. In the center of the macula is the fovea. The fovea has the region of best visual acuity.
What is the condition where the central retina develops a cyst and central vision becomes distorted?
Central Serous Retinopathy: Central serous retinopathy is a relatively common condition in which the central retina develops a cyst and central vision becomes distorted. Macular Degeneration: Macular degeneration is a disease of the macula in which there is a loss in the center of the field of vision.
What is the layer of the eye that absorbs light?
The retina is a light-sensitive layer that lines the back of the eye. It is only 0.2 mm thick and is about the size of a silver dollar. The retina is made up of 200 million neurons, many of which are photoreceptors. Photoreceptors absorb light and then convert and transmit those signals through the optic nerve to the brain. 1 .
What is retinal tear?
Retinal Tear or Detachment: A retinal tear or detachment is considered an ocular emergency where the light-sensitive retina is torn or detached away from the back of the eye that feeds in oxygen and nourishment.
Which region of the retina has the best visual acuity?
The fovea has the region of best visual acuity. Equator and Mid Peripheral Retina: This is the area of the retina as it extends from the posterior pole. Ora Serrata: The ora serrata is the serrated area between the retina and the ciliary body.
What is the fundus of the eye?
The fundus includes the retina as well as the following parts: Posterior Pole: The posterior pole in the back portion of the retina and includes the optic nerve and macula. Optic Nerve Head: The optic nerve head is the face of the optic nerve as it enters the back of the eye.
What is the retina?
Retina Definition. The retina is the sensory membrane that lines the inner surface of the back of the eyeball. It's composed of several layers, including one that contains specialized cells called photoreceptors. There are two types of photoreceptor cells in the human eye — rods and cones. Rod photoreceptors detect motion, provide black-and-white ...
What is retinal detachment?
A retinal detachment — a pulling away of the retina from the underlying choroid layer of the eye that provides its nourishment — is a medical emergency. If the retina is not surgically reattached as soon as possible, permanent and worsening vision loss can occur. [Read more about retinal detachment .]
What are the most common retinal problems?
There is a wide variety of retina problems, conditions and diseases. Here is a short list of the more common retina problems: Macular degeneration. Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the most common serious, age-related eye disease, affecting 9.1 million Americans. And the prevalence of AMD — which affects one in 14 Americans over age 40 ...
What are the consequences of diabetic retinopathy?
One of the devastating consequences of diabetes is damage to the blood vessels that supply and nourish the retina, leading to significant vision loss. [Read more about diabetic retinopathy .] Macular edema. This is an accumulation of fluid and swelling of the macula, causing distortion and blurred central vision.
What are the two main functions of rod photoreceptors?
Rod photoreceptors detect motion, provide black-and-white vision and function well in low light. Cones are responsible for central vision and color vision and perform best in medium and bright light. Rods are located throughout the retina; cones are concentrated in a small central area of the retina called the macula.
Which cell converts light into chemical and nervous signals?
Retina Function. Photoreceptor cells take light focused by the cornea and lens and convert it into chemical and nervous signals which are transported to visual centers in the brain by way of the optic nerve. [See eye illustration .]
Where does vision begin?
The Retina: Where Vision Begins. The first step in the process of vision is the conversion of light into signals that can be interpreted in the brain. This takes place in the retina, which is located in the back of the eye.
What is the layer of the brain that stimulates the eye?
Retina, layer of nervous tissue that covers the inside of the back two-thirds of the eyeball, in which stimulation by light occurs, initiating the sensation of vision. The retina is actually an extension of the brain, formed embryonically from neural tissue and connected to the brain proper by the optic nerve. Read More on This Topic.
How does light pass through the photoreceptor cells?
Light must pass through the overlying layers to reach the photoreceptor cells, which are of two types, rods and cones, that are differentiated structurally by their distinctive shapes and functionally by their sensitivity to different kinds of light.
Why are cones important?
Cones are more prominent in humans and those animals that are active during the day and provide detailed vision (as for reading) and colour perception. In general, the more cones per unit area of retina, the finer the detail that can be discriminated by that area.
What happens when light enters the eye?
When light enters the eye, it passes through the cornea and the lens and is refracted, focusing an image onto the retina. Light-sensitive molecules in the rods and cones react to specific wavelengths of light and trigger nerve impulses.
Is the retina a transparent tissue?
It is now time to examine some of the elementary... The retina is a complex transparent tissue consisting of several layers, only one of which contains light-sensitiv e photo receptor cells.
What is the Retina?
Vision is a very important sense for humans. It is essential for connecting people with their surroundings and for safety, learning, and creating memories. Accessory structures of the eye, such as the pupil, retina, and lens, direct light entering the eye onto the optic nerve for signal transmission to the brain.
Retina Function
The retina has photoreceptor cells that process different light signals, such as color variations, and uses the optic nerve to transmit these signals to the brain. Everyone has a blind spot in their eyes where the optic nerve passes through the retina out of the eye.
Anatomy of Retina: Parts of Retina
Rods are photoreceptors in the retina that are specialized for functioning at low light levels. They are usually found around the edges of the retina and are essential for peripheral vision. They are very sensitive to light, operate over a wide range of light stimuli, and recognize size, shape, and brightness of images.

Overview
The retina (from Latin: rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which translates that image into electrical neural impulses to the brain to create visual perception. The retina serves a function analogous to that of the film or image sensor in a camera.
Structure
The vertebrate retina is inverted in the sense that the light sensing cells are in the back of the retina, so that light has to pass through layers of neurons and capillaries before it reaches the rods and cones. The ganglion cells, whose axons form the optic nerve, are at the front of the retina; therefore the optic nerve must cross through the retina en route to the brain. In this region there a…
Function
The retina translates an optical image into neural impulses starting with the patterned excitation of the colour-sensitive pigments of its rods and cones, the retina's photoreceptor cells. The excitation is processed by the neural system and various parts of the brain working in parallel to form a representation of the external environment in the brain.
Clinical significance
There are many inherited and acquired diseases or disorders that may affect the retina. Some of them include:
• Retinitis pigmentosa is a group of genetic diseases that affect the retina and cause the loss of night vision and peripheral vision.
• Macular degeneration describes a group of diseases characterized by loss of central vision because of death or impairment of the cells in the macula.
History
Around 300 BCE, Herophilos identified the retina from dissections of cadaver eyes. He called it the arachnoid layer, from its resemblance to a spider web, and retiform, from its resemblance to a casting net. The term arachnoid came to refer to a layer around the brain; the term retiform came to refer to the retina.
Between 1011 and 1021 CE, Ibn Al-Haytham published numerous experiments demonstrating tha…
Additional images
• The structures of the eye labeled
• Another view of the eye and the structures of the eye labeled
• Illustration of image as 'seen' by the retina independent of optic nerve and striate cortex processing.
See also
• Adeno associated virus and gene therapy of the human retina
• Charles Schepens – "the father of modern retinal surgery"
• Evolution of the eye
• Duplex retina
Further reading
• S. Ramón y Cajal, Histologie du Système Nerveux de l'Homme et des Vertébrés, Maloine, Paris, 1911.
• Rodieck RW (1965). "Quantitative analysis of cat retinal ganglion cell response to visual stimuli". Vision Res. 5 (11): 583–601. doi:10.1016/0042-6989(65)90033-7. PMID 5862581.
• Wandell, Brian A. (1995). Foundations of vision. Sunderland, Mass: Sinauer Associates. ISBN 978-0-87893-853-7.