
How to improve lymph circulation?
Here are some ways to increase lymph flow in your body:
- Breathe deeply and regularly. Breathing fully in through your nose and inhaling air down into the lower lobes of your lungs followed by a brisk exhalation massages the thoracic duct ...
- Exercise Regularly. ...
- Avoid Over-Exercise. ...
- Drink plenty of water. ...
- Eat a Healthy Diet. ...
- Get a massage. ...
- Dry Brush Your Skin. ...
- Try Rebounding and Vibration Therapy. ...
What merges to form the right lymphatic duct?
The right lymphatic duct is a terminating vessel of the lymphatic system and forms from the confluence of the right jugular, right subclavian and right bronchomediastinal lymphatic trunks. It has a short 2 cm course, usually draining into the systemic venous system at the junction of the right internal jugular and subclavian veins.
What are the functions of the lymphatic system?
What does the lymphatic system do?
- Definition. Lymph nodes, or “glands” may swell as the body responds to a threat. ...
- Anatomy. The lymphatic system consists of lymph vessels, ducts, nodes, and other tissues. ...
- Function. The lymphatic system helps maintain fluid balance. ...
- Diseases. ...
- News from MNT. ...
Which lymphatic duct will drain the abdomen?
The thoracic duct is the large lymphatic vessel, and the principal lymphatic vessel, which drains most of the body, including chyle from the abdomen, begins from the abdomen just below the diaphragm in the form of saccular dilation, the Cisterna Chyli (Chyle Cistern). [13] Surgical Considerations
What would happen if the right lymphatic duct was blocked?
If the lymph vessels or nodes are blocked, removed or damaged, it can cause a build up of fluid. This can cause swelling, known as lymphoedema.
What does the left lymphatic duct do?
It is also called the left lymphatic duct or the alimentary duct. A large portion of the body's lymph is collected by this duct and then drained into the bloodstream near the brachiocephalic vein between the internal jugular and the left subclavian veins.
Does the right lymphatic duct drain the right leg?
The right lymph duct drains the right arm, shoulder area, and the right side of the head and neck. The left lymph duct, or thoracic duct, drains everything else, including the legs, GI tract and other abdominal organs, thoracic organs, and the left side of the head and neck and left arm and shoulder.
Does the right lymphatic duct drain?
The right lymphatic duct drains lymph from the right upper limb, right side of thorax and right halves of head and neck. The thoracic duct drains lymph into the circulatory system at the left brachiocephalic vein between the left subclavian and left internal jugular veins.
Which duct drains the most lymph?
Thoracic ductThe thoracic duct is the largest lymphatic vessel in the human body. Around 75% of the lymph from the entire body (aside from the right upper limb, right breast, right lung and right side of the head and neck) passes through the thoracic duct.
Which lymphatic duct drains the right side?
The right lymphatic duct receives lymph from the right side of the head, neck and thorax and right upper limb. It drains into the systemic venous system at the junction of the right internal jugular and right subclavian vein or right brachiocephalic vein within the neck.
How do you know if your lymphatic drainage is blocked?
Lymphedema signs and symptoms include:Swelling of part or all of the arm or leg, including fingers or toes.A feeling of heaviness or tightness.Restricted range of motion.Recurring infections.Hardening and thickening of the skin (fibrosis)
How do you unblock lymphatic system in leg?
Place one hand on your shin and the other hand on the back of your lower leg, just below your knee. Gently stretch the skin towards your upper leg and release. Shift your hands down and repeat this upward motion until you reach your ankle. Remember to stretch and release the skin up towards your knee.
How do I clear my lymphatic system in my legs?
Examples include:Exercises. Gentle contraction of the muscles in the arm or leg can help move the excess fluid out of the swollen limb.Manual lymph drainage. ... Compression bandages. ... Compression garments. ... Sequential pneumatic compression.
Why is my right lymph node swollen?
Swollen lymph nodes usually occur as a result of infection from bacteria or viruses. Rarely, swollen lymph nodes are caused by cancer. Your lymph nodes, also called lymph glands, play a vital role in your body's ability to fight off infections.
How much does the right lymphatic duct drain?
The right lymphatic duct drains the right 25% of the body, while the thoracic or left lymphatic duct drains the rest (75%) of the body. There are two lymphatic collecting ducts: the right lymphatic duct (RLD) and the thoracic (left) lymphatic duct (TLD).
Which lymph nodes drain what?
Posterior cervical: drains scalp and neck, thorax, cervical and axillary nodes. Tonsillar: drains tonsils and posterior pharynx. Submental: drains lower lip, floor of mouth, tip of tongue and cheeks. Submandibular: drains floor of mouth, submandibular gland, tongue, lips, conjunctivae.
Where does the left lymphatic duct empty?
In the majority of cases, the duct terminates on the left side. In 2% to 3% of cases, the duct empties on the right, and bilaterally in up to 1.5% of cases. In over 95% of cases, the thoracic duct terminates in the internal jugular vein, the subclavian vein, or the angle between the two.
Which duct receives lymph from the left side?
thoracic lymph ductThe thoracic lymph duct, the largest lymph vessel in the body, takes lymph from the lower and left halves of the body. Because the thoracic lymph duct drains the intestinal lymph trunks, it carries a mixture of lymph and emulsified fatty acids called chyle back to the bloodstream.
What are the areas drained by the right and left lymphatic ducts?
The right lymphatic duct receives fluid from the right head and neck region, right upper torso, and right upper extremity, whereas the thoracic duct receives fluid from the left head and neck region, left upper section of torso, left upper extremity, bilateral lower sections of the torso, and bilateral lower ...
What are the 2 lymphatic ducts?
The two major lymphatics of the body include the right lymphatic duct and the thoracic duct. The right duct drains most of the right upper quadrant whereas the thoracic duct drains the lower body including the extremities and abdomen.
Where does the lymphatic system drain?
The thoracic duct drains all lymph from the lower half of the body. The pre- and para-aortic lymphatics drain into the cisterna chyli which is an elongated sac-like vessel that lies over the body of L1 and L2 behind the inferior vena cava and between the aorta and the azygous vein.
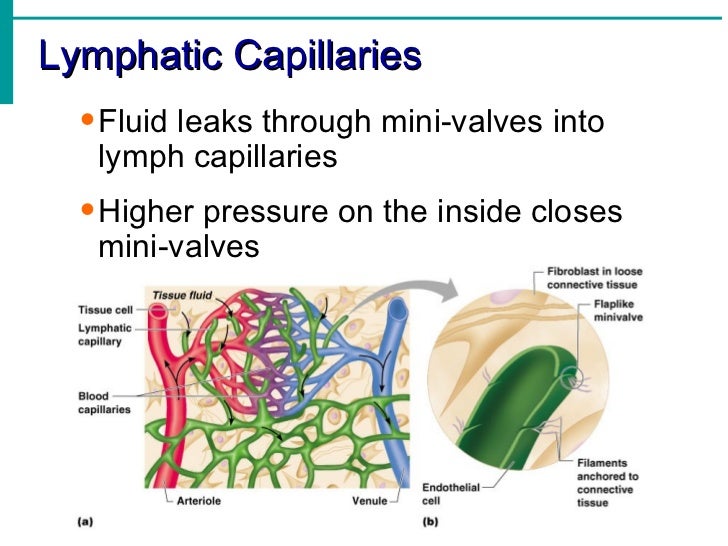
What is the function of the lymphatic capillaries?
The extracellular tissues of the body are constantly gaining fluid and debris (from capillary leakage, cell death, etc.) and the function of the lymphatics is to remove this and return it to the venous circulation. The lymphatic capillaries have the same basic structure as vascular capillaries but their distribution is not uniform throughout the body. The lymphatics in the limbs tend to be superficial, while those of the viscera tend to drain via channels on the posterior abdominal and thoracic walls.
What are the characteristics of lymphatic vessels?
A main characteristic is the discontinuity of the basement membrane at the interface between the lymphatic endothelium and the surrounding connective tissue that facilitates active fluid transport. In some tissues, including intestine, lung, and skin, lymphatic vessels completely lack a basement membrane. A second major characteristic is the tight connection of the lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) to the surrounding matrix through anchoring filaments (AFs). It has been proposed that tissue expansion due to excess interstitial fluid tightens the AFs, which pull on the lymphatic capillaries, thereby creating gaps between the LEC to increase the intake of fluid. A third characteristic of the lymphatic vessels is that valves in the vessel wall are already present at the level of capillaries, unlike in the venous blood system where they are found only in venules and larger vessels. These valves ensure unidirectional flow of the lymphatic fluid, which starts in the blind-ended capillaries. Furthermore, LECs are significantly larger than the blood endothelial cells; this enables elongation of the cells to accommodate the tissue stretch (see Table 1 for a list of differences between lymphatic vessels and blood vessels).
What is the color of the lymphatic system?
Figure 1. Schematic depicting the blood vascular system (red color) and the lymphatic system (green color) in the skin. Notice that the two systems are closely aligned but never mix. The blood vascular system is a closed circulatory system, with arteries leading to capillary loops (shown close to the epidermis) and draining to veins. The lymphatic capillaries are blind-ended, finger-like projections that begin near the epidermis and drain into larger collecting lymphatic vessels.
Which system is responsible for carrying lymph from the periphery of tissues to the venous system?
The lymphatic system forms a one-way route, carrying lymph from the periphery of tissues through the thoracic duct or the right lymphatic duct into the venous blood. These two main lymphatic ducts are connected with the venous system at the junction of the left internal jugular vein and the left subclavian vein and at the veins of the right jugulo-subclavian confluence, respectively. However, other potential lymphaticovenous communications (e.g., iliac and renal areas) may become functional when lymphatic pressure rises or in a pathological situation.
Which part of the body drains lymph?
The lymphatics in the limbs tend to be superficial, while those of the viscera tend to drain via channels on the posterior abdominal and thoracic walls. The lymphatic vessels return the lymph to the venous system via two main channels: The thoracic duct drains all lymph from the lower half of the body.
Which organ system lacks lymphatics?
Nearly all vascularized tissues, except the central nervous system (CNS), are invested with lymphatic vessels. The CNS lacks lymphatics since it has a blood-neural barrier that is less permeable than other tissues and is immune-privileged.
What is the right lymphatic duct?
Anatomical terminology. The right lymphatic duct is an important lymphatic vessel that drains the right upper quadrant of the body. It forms various combinations with the right subclavian vein and right internal jugular vein.
Where is the right lymphatic duct located?
The right lymphatic duct courses along the medial border of the anterior scalene at the root of the neck. The right lymphatic duct forms various combinations with the right subclavian vein and right internal jugular vein. It is approximately 1.25 cm long.
Which lymphatic duct enters directly into the junction of the internal jugular and subclavian vein?
A right lymphatic duct that enters directly into the junction of the internal jugular and subclavian veins is uncommon.
Which lymphatic duct is most likely to rupture in the thorax?
Along with the thoracic duct, the right lymphatic duct is one of the lymphatic structures most likely to be ruptured in the thorax. This can cause chylothorax.
Which part of the body is drained by the right jugular trunk?
the upper right section of the trunk, (right thoracic cavity, via the right bronchomediastinal trunk ), the right arm (via the right subclavian trunk ), and right side of the head and neck (via the right jugular trunk ), also, in some individuals, the lower lobe of the left lung. All other sections of the human body are drained by the thoracic duct.
Overview
The right lymphatic duct is an important lymphatic vessel that drains the right upper quadrant of the body. It forms various combinations with the right subclavian vein and right internal jugular vein.
Structure
The right lymphatic duct courses along the medial border of the anterior scalene at the root of the neck. The right lymphatic duct forms various combinations with the right subclavian vein and right internal jugular vein. It is approximately 1.25 cm long.
A right lymphatic duct that enters directly into the junction of the internal jugular and subclavian veins is uncommon.
Function
The right duct drains lymph fluid from:
• the upper right section of the trunk, (right thoracic cavity, via the right bronchomediastinal trunk ),
• the right arm (via the right subclavian trunk ),
• and right side of the head and neck (via the right jugular trunk),
Clinical significance
Along with the thoracic duct, the right lymphatic duct is one of the lymphatic structures most likely to be ruptured in the thorax. This can cause chylothorax.
History
The discovery of this structure has been credited to Niels Stensen.
Additional images
• Deep lymph nodes and vessels of the thorax and abdomen (diagrammatic).