
Explore
The Anatomy of the Ilium
- Anatomy. As part of the hip bone, the ilium, alongside the ischium and pubis, are fused to one another, and, via the sacroiliac ligaments, are attached to the sacrum (the ...
- Function. ...
- Associated Conditions. ...
- Rehabilitation. ...
What is the main function of the sacrum?
- Sacrum and Lumbosacral Spine. The sacrum is located in between the right and left iliac bones (hips) and forms the back of the pelvis.
- Coccyx’s Role and Function. The coccyx, or tailbone, is located just below the sacrum. ...
- Sacral and Coccygeal Nerves. ...
- Sacrum and Tailbone Injury Prevention Tips. ...
What is the purpose of the sacrum and coccyx?
- upslip: the hip bone has moved straight upwards, relative to the sacrum
- anterior/ posterior rotation: the hip bone has rotated forwards or backwards, relative to the sacrum
- inflare/outflare: the hip bone has moved either inwards towards the center of the body, or outwards away from the sacrum
What causes sacrum to be out of alignment?
The interosseous ligament:
- Connects the outer surface of the sacrum (triangular part of the lower spine) to the inner surface ilium (hip bone)
- Receives the greatest stresses of the ligaments associated with the sacroiliac joint. ...
- Forms the major connection between the sacrum and the ilium.
- Prevents forward and downward movement of the sacrum. ...
What muscles are attached to the sacrum?

What does the sacrum control?
The sacral region is home to the control center for pelvic organs such as the bladder, bowel, and sex organs. Sexual function is a concern, especially in men who experience sacral spinal nerve injuries.
Why is the sacrum important?
Regarded as the keystone of the human body, the sacrum is important because it forms a link between the spine and the iliac bones, and also has an important part to play in hip stability.
What happens when your sacrum is out of place?
The most common symptoms of a sacral or SI problem are: low back pain, sciatic nerve pain, stiffness, inflammation, and muscle spasms in the buttocks, hips, down the legs, and even the bladder and reproductive organs.
What part of the body does the sacrum control?
The sacrum serves several important functions in the skeletal, muscular, nervous, and female reproductive systems. Acting as the keystone of the pelvis, the sacrum locks the hip bones together on the posterior side and supports the base of the spinal column as it intersects with the pelvis.
Why is sacrum called holy bone?
The os sacrum was so named by the Romans as a direct translation from the older Greek hieron osteon, which translates to “sacred” or “holy.” It was used in sacrificial rites and in protecting the genitalia (which in ancient times were considered sacred).
What causes the sacrum to hurt?
Sacroiliac pain can be aggravated with prolonged sitting or standing, standing on one leg, stair climbing, going from sit to stand, and with running. Potential causes of sacroiliac pain include arthritis, traumatic injury, pregnancy and post-partum, systemic inflammatory conditions, and infection.
How do you know if your sacrum is out of alignment?
Common presenting symptoms include low back pain often found on only one side, that is worsened with prolonged sitting/standing or specific mechanical movements. Other symptoms include buttock pain or radiating pain, numbness, or tingling in the hips, groin, or legs.
How do you reset your sacrum?
Start by slowly rotating your knees toward one side stopping where you feel a change in sensation, pull, tightness (restriction) and hold until you feel the softening (release). After you feel the release allow the knees to rotate a little further until you reach the next restriction.
How do you fix a sacral misalignment?
Keep the leg on the side of your sacrum that isn't injured on the ground. Raise the leg of the injured side up into the air and place it against the wall. Keep your knee as straight as possible. Hold the stretch for 20 to 30 seconds; then switch sides.
What nerves are affected by the sacrum?
Sacral PlexusNerve (Low Form)Prefixed Plexus (High Form)Postfixed PlexusLumbosacral trunkL4L4Nerve to quadratus femorisL4, L5L5, S1Nerve to obturator internusL4, L5, S1, S2S1, S2, S3TibialL3, L4, L5, S1, S2L5, S1, S2, S3, S411 more rows
What are the symptoms of S1 nerve damage?
S1 NERVE ROOT DAMAGE: A pinched nerve in the S1 section of the vertebral column usually results in radiating pain down the backside of the leg and into the outside of the foot. This pain can come in the form of numbness, tingling, weakness and shooting.
Can you damage your sacrum?
In some cases, an injury to the sacrum can affect the nerves that control the bladder, bowel, or legs. Home treatment may be all that is needed for some sacral fractures. If a fracture is severe or affects nerves, you may need surgery. Bones heal best when you take good care of yourself.
How do you relieve sacrum pain?
Sacrum pain is typically treated with rest, physical therapy, and over-the-counter pain medications and anti-inflammatory medications. In severe ca...
Is the sacrum a strong bone?
The sacrum must support the weight of the body and spinal cord that sits atop it. Because of this, the sacrum is a thick, strong bone capable of su...
What is sacrum in human body?
In the human body, the sacrum is a triangular bone at the inferior portion of the spine that supports the weight of the spine superior to it. The s...
What is the function of the sacrum?
The main function of the sacrum is to support the weight of the spinal cord superior to it. The sacrum also provides multiple surfaces for muscle a...
Is the sacrum the tailbone?
The sacrum is the second to last inferior portion of the spine. It is not called the tailbone. The final inferior portion of the spine, the coccyx,...
What causes pain in sacrum?
The sacrum is a sturdy bone that rarely breaks unless an underlying bone diseases is present. If pain is felt near the sacrum it likely comes from...
The Spine
Humans are vertebrates, meaning that they have a skeletal back bone that encases the spinal cord. The spine is composed of individual bones called vertebrae. There are multiple portions of the spine, each composed of skeletal elements that are shaped differently to serve different structural and functional needs.
What Is the Sacrum?
Romans referred the second to last section of the spine as sacrum meaning ''holy bone.'' This name comes from the sacrum location within the pelvic cavity, as it appears to reside within a temple. The sacrum is a bone in the body that makes up a structurally important portion of the spinal cord.
Function of the Sacrum
The main sacrum function within the body is to offer support. As humans are upright, bipedal organisms, most of the the body's weight is supported by an upright spine. Gravity pulls the body downward, and thus a supportive base is needed to maintain a vertical posture.
What is the Sacrum
Sacrum, alternatively known as sacral vertebra or sacral spine, is a large, flat, triangular-shaped, irregular bone. It is composed of five fused vertebrae (S1-S5), located at the base of the vertebral column or spine. The bone links the spine with the hip, thus helping in hip stability.
Where is the Sacrum Bone Located
As stated, the sacrum bone is positioned at the base of the vertebral column or spine. More specifically, it is located between the right and left iliac bones of the hip and below the last lumbar vertebra (L5).
Functions
Locks the hip bones together on the posterior side, thus supporting the base of the spine.
Anatomy: Parts and Structure of Sacrum
The sacrum is a concave, irregular bone, resembling an inverted triangle. The widest part, called the base, is present at the top, and the pointy end, called the apex, is at the bottom. It also has three surfaces – dorsal, lateral, and pelvic.
Muscule Attachments
Several lower limb and back muscles originate or get inserted on the sacrum.
Nerves
As mentioned, the cauda equina, long sacral roots of spinal nerves, pass through the sacrum via the sacral canal.
FAQs
Q.1. Is the sacrum part of the axial skeleton or the appendicular skeleton?
What is the name of the projection on the lumbar plexus?
On either side of the base is a large projection known as an ala of sacrum and these alae (wings) articulate with the sacroiliac joints. The alae support the psoas major muscles and the lumbosacral trunk which connects the lumbar plexus with the sacral plexus.
What are the two projections of the sacrum called?
The two projections at the sides of the sacrum are called the alae (wings), and articulate with the ilium at the L-shaped sacroiliac joints. The upper part of the sacrum connects with the last lumbar vertebra (L5), and its lower part with the coccyx (tailbone) via the sacral and coccygeal cornua.
How many vertebrae are in the sacrum?
In dogs the sacrum is formed by three fused vertebrae. The sacrum in the horse is made up of five fused vertebrae. In birds the sacral vertebrae are fused with the lumbar and some caudal and thoracic vertebrae to form a single structure called the synsacrum. In the frog the ilium is elongated and forms a mobile joint with the sacrum that acts as an additional limb to give more power to its leaps.
What is the sacrum in anatomy?
FMA. 16202. Anatomical terms of bone. The sacrum (plural: sacra or sacrums ), in human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1–S5) between ages 18 and 30. The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, between the two wings of the pelvis.
What does the Greek word "os sacrum" mean?
As the Greek adjective ἱερός may also mean "strong", it has also been suggested that os sacrum is a mistranslation of a term intended to mean "the strong bone". This is supported by the alternative Greek name μέγας σπόνδυλος by the Greeks, translating to "large vertebra", translated into Latin as vertebra magna.
What is the lateral surface of the sacrum?
Lateral surface. The lateral surface of the sacrum is broad above, but narrows into a thin edge below. The upper half presents in front an ear-shaped surface, the auricular surface, covered with cartilage in the immature state, for articulation with the ilium.
What is the sacrum?
The sacrum is a complex structure providing support for the spine and accommodation for the spinal nerves. It also articulates with the hip bones. The sacrum has a base, an apex, and three surfaces – a pelvic, dorsal and a lateral surface.
What muscles are involved in sacrum pain?
Other muscles that result in pain to this area include the deep lateral rotators, hamstrings, hip flexors, and pelvic floor muscles. A vertical fracture of the pelvic area may also result in sacrum pain. This fracture typically runs parallel to your spine. However, fractures going horizontally across the sacrum are also a possible cause ...
What is the lower back?
The lower back has a diverse set of muscles involved in postural stability and other flexor and extension actions. This makes lower back pain or sacrum pain a complicated diagnosis, as many variables are at play. Various connecting muscles may refer the pain away from the actual site of injury, requiring medical professionals to examine all ...
How to treat sacrum pain?
Luckily, treatment for sacrum pain usually does not require surgery, as getting adequate rest, taking pain relieving medication, and staying active is often enough to fully resolve the pain over time. Your doctor may recommend you wear a medical brace or corset to help support the bone structure, but this is seldom needed. Water exercises may help maintain flexibility while limiting tension on the back muscles. In severe cases where a fracture has occurred, a sacroplasty procedure may be required, where bonding material is injected into the joint site for faster fusion of the fracture.
Why does my sacrum hurt?
What causes pain in the sacrum? Pain in the area of the sacrum can be due to the ligaments becoming too loose or too tight. This may be caused by a fall injury, work injury, car accident, pregnancy, or hip/spine surgery (laminectomy, lumbar fusion). Many diseases may also lead one to experience pain in this region.
What is the sacral region?
The sacral region is composed of five segments, S1 to S5, that are fused together. The sacrum is part of the pelvic girdle and contributes to the formation of joints at the hip bone called the sacroiliac joints. The sacral region contains a serious of four openings on each side through which the sacral nerves and blood vessels run.
What is the best treatment for sacrum pain?
If sacrum pain is due to bone weakness, vitamin D and calcium supplementation may be appropriate.
Why does my muscle feel tight?
This lack of movement for extended periods of time causes the muscles to become tighter and hold tension. This creates pressure on the nerves running through the muscle leading to a pain sensation.
What is the sacral canal?
The sacral canal runs down the center of the sacrum, representing the end of the vertebral canal. The five segments of the sacral vertebrae affect nerve communication to the lower part of the body. There, numerical levels are often mentioned in imaging studies of the spine. S1 refers to the first sacral bone, S2 to the second sacral bone, and so on.
What is the name of the wing of the sacrum?
The first three vertebrae of the sacral region form the wide lateral wings called the alae. The alae (also called the ala or wing of sacrum) connect with the blades of pelvis—called the ilium . The sacrum also forms the back wall of the pelvis and the joints at ...
What causes sacral vertebrae to be damaged?
Common causes of injuries related to the sacral vertebrae include car accidents, sports injuries, trauma, falls, birth defects, osteoporosis, and joint degeneration . Injuries and damage to S1, S2, S3, S4, or S5 can still leave a person functional, but they primarily affect bowel and bladder function.
How many bones are in the sacral vertebrae?
Treatment. The sacral vertebrae—also called the sacral spine—consists of five sacral vertebrae bones. These bones fuse together to form the sacrum, the shield-shaped bony structure located at the base of the lumbar vertebrae (the five cylindrical bones forming the spine of the lower bank) and connected to the pelvis.
What is the sacrum?
The sacrum also form s the back wall of the pelvis and the joints at the hip bones called the sacroiliac joints . There are a series of four openings on each side of the sacrum where the sacral nerves and blood vessels run. The sacral canal runs down the center of the sacrum, representing the end of the vertebral canal.
What is the function of sacral vertebrae?
The function of the sacral vertebrae is to secure the pelvic girdle, the basin-like bone structure connect ing the truck and the legs, supporting and balancing the trunk, and containing the intestines, bladder, bowel, and internal sex organs.
What is the S1 nerve?
S1 refers to the first sacral bone, S2 to the second sacral bone, and so on. S1 is at the top and S5 is towards the bottom. Each number corresponds with the nerves in that part of the spinal cord. S1 nerves affect the hips and groin. S2 nerves affect the back of the thighs. S3 nerves affect the medial buttock area.
What are the symptoms of a sacral fracture?
Symptoms of a sacral fracture include bruising and swelling in the low back. Pain in the back, hips, and buttocks also occurs.
Why does Michael have a sacrum fracture?
Sacral fractures most often occur due to motor vehicle accidents, direct force to the sacrum, and falls.
What is the sacrum made of?
It is made up of five vertebrae that are fused together to form a single bone. The sacrum connects to other bones to form a strong pelvis. Below the sacrum is the coccyx, which is often called the tailbone. Michael had the classic symptoms of a sacral fracture.
How many vertebrae are in the sacrum?
It's composed of five vertebrae that are fused together to make a single bone. The sacrum connects to the pelvis to support the body and protect internal organs. Fractures of the sacrum most often occur in motor vehicle accidents, direct force to the sacrum, or falls.
Where is the sacrum located?
The sacrum is a bone located in your lower back. In this lesson, we'll learn how you can break that bone and explore what happens when you do, including symptoms, treatment, and recovery. Create an account.
How old was Michael when he planned his birthday party?
Michael was planning a birthday party for his 8-year-old daughter. He thought it would be fun to have the party at the roller-skating rink. The party was a big success and lots of family and friends showed up. As kids do, his daughter begged him to go roller-skating with her.
Is Michael's recovery time longer?
Since Michael's health is compromised, it may take longer but full recovery is expected. If the fracture would have caused bone fragments to be displaced, surgery would have been indicated. In surgery, the bones would be placed back in their normal position and be stabilized with hardware.
What is the sagittal plane motion at the SI joint called?
Sagittal plane motion at the SI joint is called either nutation or counternutation . The word nutation means to nod and is similar to the concept of the slight tilting or nodding of the earth on its axis as described in astronomy. Counternutation is simply movement in the opposite direction.
Why is it important to rotate the ilium anteriorly?
These motions are essential for proper movement because of the unique demands placed on the pelvis during locomotion. For example, during walking one leg is in flexion and the other is in extension.
What is counternutation in anatomy?
Counternutation is simply movement in the opposite direction. Nutation is defined as a relative anterior tilt of the sacral base (upper flat surface of the sacrum that articulates with L5) in relation to the ilium (Figure 1).
Which muscles pull the sacrum?
The erector spinae pull on the lower sacrum so that the upper portion is rotating anteriorly. The hamstrings pull the ischial tuberosities inferiorly so that the innominates rotate posteriorly in relation to the sacrum. All these combined motions will lead to increased nutation and may help stabilize the SI joint.
What is the most important motion of the SI joint?
There is very little motion that occurs at the SI joint, but the most important motion that does occur is a slight back and forth rocking motion of the sacrum in the sagittal plane. The importance of this motion will be explained shortly. Most motions that occur in the sagittal plane are called flexion or extension.
Why is it important to understand the sacroiliac joint?
Yet, it is still important to comprehend how the joint works in order to accurately evaluate function or pathological problems.
Is there nutation on one side of the SI joint?
Therefore there may be some degree of relative nutation on one side and counternutation on the other. There is a delicate balance between stability and movement at the SI joint. While a small amount of nutation and counternutation are desirable, too much movement at this joint can lead to pain and biomechanical dysfunction.
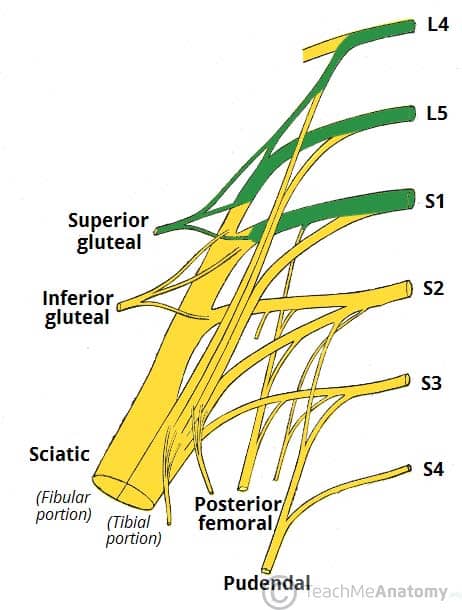
Bony Landmarks
- Base
The top part of the sacrum, lying just below the spinal base, is referred to as the base of the scarum. It is the widest portion of the bone. The first one of the five fused sacral vertebrae, S1, is located here. The S1 vertebra is the biggest one, having concave superior articular facets that project posteromedially to articulate with the fifth l… - Apex
It is the pointy part of the sacrum, directing downwards. The fifth sacral vertebra lies in this most inferior segment of the bone. The apex projects posteriorly to increase the size of the pelvic cavity. This region features an oval facet for articulation with the coccyx.
Articulations
- Lumbosacral joint: The base of the sacrum articulates with the fifth lumbar vertebrae (L5) superiorly via the L5/S1 intervertebral disc, forming this amphiarthrodial joint.
- Sacrococcygeal joint: Here, the apex of the bone articulates with the base of the coccyx, to form another amphiarthrodial joint.
- Sacroiliac joint: The sacral ala laterally articulates with the ilium of the pelvis, forming this synovial joint.
Anatomical Variations of The Sacrum
- Sometimes, the sacrum shows some anatomical variation, including variation in the number of vertebrae, its surface and curvature. 1. The most common anatomical variation of the bone is the variation in the number of sacral vertebrae. Commonly sacrum has five fused vertebrae, but four or six sacral vertebrae have also been documented. 2. Another anomaly of the sacrum is related to its surface and curvature. The curvature of the bon…
Sacrum in Females vs. in Males
- Sacrum is sexually dimorphic, meaning it has a slightly different appearance in females and males. The sacrum is wider in females than males. It is also more backwardly curved in females, increasing the size of the pelvic cavity. This wider pelvic cavity in females aids in enduring pregnancy, offers more space for the developing fetus, and houses r...
Overview
The sacrum (plural: sacra or sacrums ), in human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1–S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, between the two wings of the pelvis. It forms joints with four other bones. The two projections at the sides of the sacrum are called the alae (wings), and articulate with the ilium at the L-shaped sacroiliac joints. The upper …
Structure
The sacrum is a complex structure providing support for the spine and accommodation for the spinal nerves. It also articulates with the hip bones. The sacrum has a base, an apex, and three surfaces – a pelvic, dorsal and a lateral surface. The base of the sacrum, which is broad and expanded, is directed upward and forward. On either side of the base is a large projection known as an ala of sacrum and these alae (wings) articulate with the sacroiliac joints. The alae suppor…
Clinical significance
The congenital disorder, spina bifida, occurs as a result of a defective embryonic neural tube, characterised by the incomplete closure of vertebral arch or of the incomplete closure of the surface of the vertebral canal. The most common sites for spina bifida malformations are the lumbar and sacral areas.
Another congenital disorder is that of caudal regression syndrome also known as sacral agenesis. This is characterised by an abnormal underdevelopment in the embryo (occurring by the seventh week) of the lower spin…
Other animals
In dogs the sacrum is formed by three fused vertebrae. The sacrum in the horse is made up of five fused vertebrae. In birds the sacral vertebrae are fused with the lumbar and some caudal and thoracic vertebrae to form a single structure called the synsacrum. In the frog the ilium is elongated and forms a mobile joint with the sacrum that acts as an additional limb to give more power to its leaps.
History
English sacrum was introduced as a technical term in anatomy in the mid-18th century, as a shortening of the Late Latin name os sacrum "sacred bone", itself a translation of Greek ἱερόν ὀστέον, the term found in the writings of Galen. Prior to the adoption of sacrum, the bone was also called holy bone in English, paralleling German heiliges Bein or Heiligenbein (alongside Kreuzbein ) and Dutch heiligbeen.
The origin of Galen's term is unclear. Supposedly the sacrum was the part of an animal offered in sacrifice (sinc…
See also
• Bone terminology
• Pelvimetry
• Rump (croup)
External links
• Anatomy photo:43:st-0401 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Female Pelvis: Bones"
• pelvis at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)