Where is the sphenoid bone and what does it do?
The sphenoid bone is one of the most complex bones of the human body. Due to its shape, it is also referred to as the 'wasp bone'. It makes up most of the middle part of the base of the skull and contributes to the floor of the middle cranial fossa of the skull.
What is unique about the sphenoid?
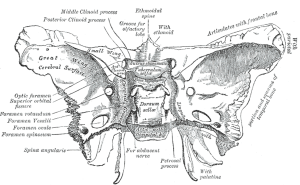
What's particularly unique about the sphenoid bone, is that on its cranial surface, the body has a deeply concave surface called the sella turcica. It is bordered by the anterior, middle and posterior clinoid processes, which are points of attachment for the dura mater of the brain.
What gland does the sphenoid bone protect?
the pituitary glandSphenoid bone primarily consists of a centrally positioned body, which surrounds and protects the pituitary gland, and two sets of lateral, wing-like extensions called the greater and lesser wings.
Does the sphenoid protect the brain?
The sphenoid is an interesting bone in that while it doesn't actively protect the brain like the bones of the calvaria, it does have a multitude of functions, particularly in creating tunnels through which various nerves pass.
Why is sphenoid bone called the Keystone?
A prominent, irregular, wedge-shaped bone at the base of the skull. The sphenoid bone has been called the “keystone” of the cranial floor since it is in contact with all of the other cranial bones.
Why is the sphenoid bone a tricky bone to learn?
The sphenoid bone is extremely complex! It extends all the way from one side of the skull to the other. The sphenoid bone forms important parts of the underside, and outside of the skull; and it forms part of the orbit. The sphenoid bone also forms this large and complicated part of the floor of the cranium.
Does the sphenoid bone move?
On expiration, the spheno-basilar articulation relaxes as the pressure created by the inhaled air is exhaled. This release of pressure causes the spheno-basilar junction to move slightly anterior and superior. These movements of the spheno-basilar junction are believed to drive the cranial-sacral rhythm.
Can you break your sphenoid bone?
Abstract. Fractures of the sphenoid bone occur following injury to the orbit and base of the skull. Such fractures are important since they can cause loss of vision and damage to various neural and muscular tissues. Ocular injury is also commonly associated.
What makes the sphenoid bone different?
The sphenoid bone has articulations with twelve other paired and unpaired bones – this makes it the most complex bone in the human body. While the sphenoid bone is unpaired, it stretches from one side of the skull to the other.
What is the strongest bone in the skull?
jawboneYour mandible, or jawbone, is the largest, strongest bone in your face.
What is a sphenoid fracture?
Sphenoid Fractures When fracture of the sphenoid bone occurs, the orbit or base of the skull are impacted. Given its function, this can lead to numerous dangerous complications, including damage to cranial nerves and eyes as well as loss of color vision.
What is the weakest part of the skull?
pterionThe pterion is known as the weakest part of the skull. The anterior division of the middle meningeal artery runs underneath the pterion. Consequently, a traumatic blow to the pterion may rupture the middle meningeal artery causing an epidural haematoma.
Anatomical Structure
The sphenoid bone is said to be ‘ butterfly-shaped ‘. It consists of a body, paired greater wings and lesser wings, and two pterygoid processes.
Muscular Attachments
The lateral and medial pterygoid muscles which form some of the muscles of mastication originate from the lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone.
Articulations
The sphenoid is an unpaired bone. It sits anteriorly in the cranium, and contributes to the middle cranial fossa, the lateral wall of the skull, and the floor and sides of both orbits.
Clinical Significance - Transsphenoidal Surgery
The sphenoid bone shares a close anatomical relationship with the pituitary gland. Indeed, the pituitary can be accessed surgically by passing instruments through the sphenoid bone and sinus.
The sphenoid bone (wasp bone) is part of the base of the skull
Mark Gurarie is a freelance writer, editor, and adjunct lecturer of writing composition at George Washington University.
Anatomy
The sphenoid bone has a butterfly-like structure, with four major components—body, lesser wings, greater wings, and pterygoid processes. 1
Function
Working in concert with the orbital floor, the primary function of the sphenoid bone is to help form the base and sides of the skull. 2 Portions of this bone are also components of the facial skeleton.
Associated Conditions
There are several conditions that can affect the sphenoid bone; given its significance, these can have significant complications. Associated conditions include those below. 2
Treatment
Given the severity of the above-mentioned conditions, treatment needs to be timely and efficient. Luckily, today healthcare providers are better able than ever before to take on issues of the sphenoid bone.
Structure
Seven bones articulate to form the orbit. The sphenoid bone is shown as pink (directly in the middle of the orbital cavity)
Body of sphenoid
Articulates with ethmoid bone anteriorly and basilar part of occipital bone posteriorly. It shows:
Sphenoidal sinuses
These are asymmetrical air sinuses in the body of the sphenoid, closed by Sphenoidal conchae
Greater wings
This forms the floor of the middle cranial fossa. It presents (starting from the front):
Lesser wings
These are two triangular wings projecting laterally from anterosuperior part of the body. Each consists of:
Function
This bone assists with the formation of the base and the sides of the skull, and the floors and walls of the orbits. It is the site of attachment for most of the muscles of mastication.
Other animals
The sphenoid bone of humans is homologous with a number of bones that are often separate in other animals, and have a somewhat complex arrangement.
Importance of the Sphenoid
There are 22 bones that make up the skull, and the sphenoid (don't you just love saying it?) is one of the 8 bones of the neurocranium. It is situated at the base of the skull, acting as the keystone. A keystone in architecture is the piece at the apex of an arch; it locks all the other pieces together and bears the weight.
Sphenoid Landmarks
Our bat-shaped sphenoid is divided into a median body, two greater wings, two lesser wings, and two pterygoid plates.
Pathologies of the Sphenoid
The thing about the sphenoid is that it's located in such a place that injuries to it are not as common as injuries to bones at the forefront of the skull. That said, you can definitely injure it. Fracturing the bone following severe bumps, impacts, and whiplash can affect vision or cause nerve damage.
Definition
The sphenoid bone of the skull base is one of the most complex bones of the body. It is an unpaired bone with many foramina (holes) and grooves that allow nerves and blood vessels to pass through or along it. The form of the sphenoid bone is often referred to as bat-shaped, wasp-shaped, or butterfly-shaped.
Sphenoid Bone Location
The location of the sphenoid bone lies behind the top of the nasal cavity and stretches from the left side of the skull to the right. Each end meets the outer surface of the skull in front of the left and right parietal bones and under the frontal bone.
Sphenoid Bone Anatomy
Sphenoid bone anatomy is complex, not only because of its strange shape but also because of its many articulations with other bones. It is much easier to split this topic into four subheadings, each heading describing both the shape and position of a particular part.
Sphenoid Bone Function
The sphenoid bone has many functions. As we have already seen, each part has more than one task to fulfill, either in cooperation with other bones of the cranium and face, or alone.
Bibliography
Mesa J, Buchman SR, MacKay DR, Losee JE, Havlik RJ. (2019). Atlas of Operative Craniofacial Surgery. New York, Thieme

Overview
Structure
- Working in concert with the orbital floor, the primary function of the sphenoid bone is to help form the base and sides of the skull.2 Portions of this bone are also components of the facial skeleton. Its central position within this part of the body makes it essential for providing rigidity—thereby protecting brain and nerve structures—while it...
Body of sphenoid
Sphenoidal sinuses
Greater wings
The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that articulate to form the orbit. Its shape somewhat resembles that of a butterfly or bat with its wings extended.
Lesser wings
It is divided into the following parts:
• a median portion, known as the body of sphenoid bone, containing the sella turcica, which houses the pituitary gland as well as the paired paranasal sinuses, the sphenoidal sinuses
• two greater wings on the lateral side of the body and two lesser wings from the anterior side.
Function
Articulates with ethmoid bone anteriorly and basilar part of occipital bone posteriorly. It shows:
1. Jugum sphenoidale
2. Sulcus chiasmaticus
3. Tuberculum sellae
4. Sella turcica
Other animals
These are asymmetrical air sinuses in the body of the sphenoid, closed by Sphenoidal conchae