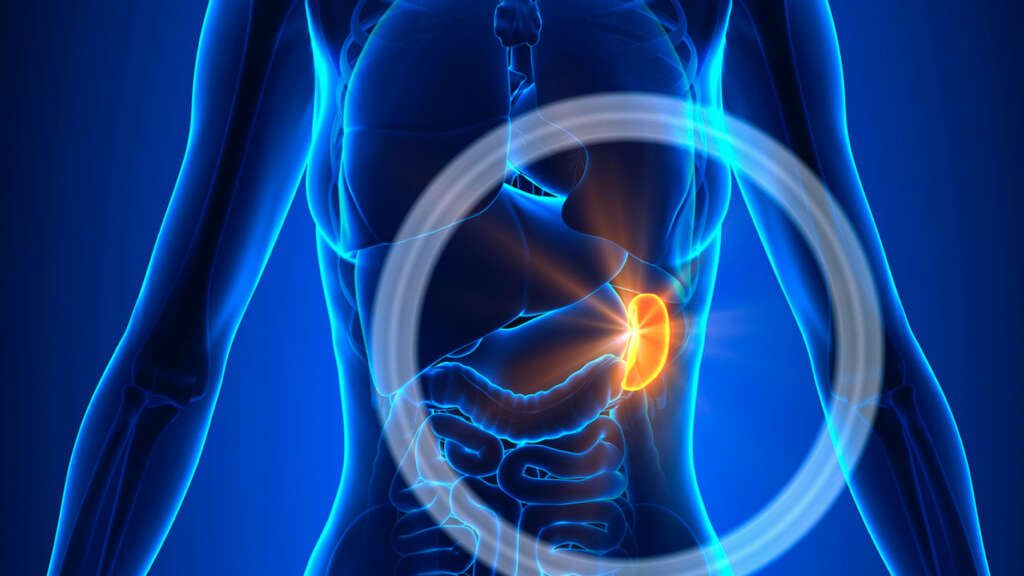
It affects the number of red blood cells that carry oxygen throughout your body, and the number of platelets, which are cells that help your blood to clot. It does this by breaking down and removing cells that are abnormal, old, or damaged. The spleen also stores red blood cells, platelets, and infection-fighting white blood cells.
What does the spleen do in the immune system?
The spleen has some important functions:
- it fights invading germs in the blood (the spleen contains infection-fighting white blood cells)
- it controls the level of blood cells (white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets)
- it filters the blood and removes any old or damaged red blood cells
What role does the spleen play in the immune system?
The cellular initiators and effectors of the adaptive splenic immune response
- Innate immune cell function and organization. Recognition of infection or host damage in the spleen activates a plethora of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) on myeloid cells, which in turn induce ...
- Adaptive immune cell function and organization. ...
- Hybrid Cells: Innate-like lymphocytes. ...
What are the functions of the spleen?
- This is the main function of the spleen
- Healthy blood cells pass through the spleen and circulate throughout the bloodstream
- Red blood cells that are old, malformed, or damaged can't pass through and are broken down in the spleen by macrophages, which are large white blood cells that destroy unhealthy ...
What are the symptoms of a spleen?
Signs and symptoms of a ruptured spleen include:
- Pain in the upper left abdomen
- Tenderness when you touch the upper left abdomen
- Left shoulder pain
- Confusion, lightheadedness or dizziness
See more
What is the function of the spleen to old red blood cells?
Your spleen's main function is to act as a filter for your blood. It recognizes and removes old, malformed, or damaged red blood cells. When blood flows into your spleen, your spleen performs "quality control"; your red blood cells must pass through a maze of narrow passages.
Does the spleen destroy red blood cells?
Red blood cells that are damaged or dying are trapped by your spleen and liver, which destroy the cells.
Does the spleen have red blood cells?
The spleen is the largest filter of RBCs in the body where the smallest openings for RBC passage are located (1). Splenic parenchyma is made of white pulp nodules and sheaths—that contain mainly T and B lymphocytes—interspersed into the red pulp, a spongy tissue that accounts for 75% of the splenic volume.
What does the spleen have to do with white blood cells?
The spleen has a few important functions: It fights any invading germs in the blood (the spleen contains infection-fighting white blood cells). It controls the level of blood cells. The spleen controls the level of white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets (small cells that form blood clots)
Where do dead red blood cells go?
Old or damaged RBCs are removed from the circulation by macrophages in the spleen and liver, and the hemoglobin they contain is broken down into heme and globin. The globin protein may be recycled, or broken down further to its constituent amino acids, which may be recycled or metabolized.
How are red blood cells destroyed?
Red blood cells may be destroyed due to: An autoimmune problem in which the immune system mistakenly sees your own red blood cells as foreign substances and destroys them. Genetic defects within the red cells (such as sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, and G6PD deficiency)
What is the spleen responsible for?
The spleen has some important functions: it fights invading germs in the blood (the spleen contains infection-fighting white blood cells) it controls the level of blood cells (white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets) it filters the blood and removes any old or damaged red blood cells.
What are the four functions of the spleen?
FunctionStores blood.Filters blood by removing cellular waste and getting rid of old or damaged blood cells.Makes white blood cells and antibodies that help you fight infection.Maintains the levels of fluid in your body.Produces antibodies that protect you against infection.
Can you live without your spleen?
You can be active without a spleen, but you're at increased risk of becoming sick or getting serious infections. This risk is highest shortly after surgery. People without a spleen may also have a harder time recovering from an illness or injury.
Can you drink without a spleen?
You should not eat or drink anything the morning of surgery. Your doctor will give you complete instructions. Before surgery, you will be given drugs or a vaccine to prevent bacterial infections from developing after the spleen is removed.
Does the spleen store iron?
The body also uses the spleen as a place to store blood and iron for future use.
Which organ is the graveyard of RBC?
SpleenSo, the correct answer is 'Spleen'.
What are the four functions of the spleen?
FunctionStores blood.Filters blood by removing cellular waste and getting rid of old or damaged blood cells.Makes white blood cells and antibodies that help you fight infection.Maintains the levels of fluid in your body.Produces antibodies that protect you against infection.
Does the spleen destroy white blood cells?
The spleen is part of your lymphatic system, which fights infection and keeps your body fluids in balance. It contains white blood cells that fight germs. Your spleen also helps control the amount of blood in your body, and destroys old and damaged cells. Certain diseases might cause your spleen to swell.
What happens to red blood cells after splenectomy?
cases of acquired hemolytic anemia splenectomy will remove the major site of red cell destruction and in turn increase the hemoglobin concentration and abolish the need for an accelerated rate of red cell production.
Why spleen is known as Graveyard of RBC?
Answer: (4) The spleen plays an important role in the red blood cells also known as aserythrocytes and the digestive system. Old and damaged RBC's are destroyed in the spleen and It is known as the RBCs Graveyard.
What is the purpose of the spleen?
Nerthuz/iStock/Thinkstock. The spleen helps keep harmful microorganisms out of the bloodstream. It holds key components of the body’s immune system. The spleen also removes unhealthy, old, and misshapen red blood cells from circulation.
Where is the spleen located?
The findings may provide insights into conditions that lead to anemia, such as certain hereditary disorders, infectious diseases, and cancers. The spleen is located under the rib cage.
What does a healthy red blood cell look like?
Healthy red blood cells are disc-shaped and look like doughnuts without holes in the center. rasslava/iStock/Thinkstock. The analyses revealed the limits of surface area and volume within which red blood cells can cross the spleen. The work showed how the splenic slit determines the size and shape distributions of healthy red blood cells.
Can a spleen be enlarged?
In addition, some diseases — such as malaria, leukemia, and lymphomas — may cause enlargement of the spleen and lead it to filter out not only abnormal cells but also healthy red blood cells.
Can red blood cells pass through the spleen?
They can only reenter the bloodstream if they’re able to pass through a tiny splenic structure called the interendothelial slit. When the red blood cells’ size, shape, or ability to deform is altered, they can’t pass through.
How does the spleen affect blood?
It does this by breaking down and removing cells that are abnormal, old, or damaged. The spleen also stores red blood cells, platelets, and infection-fighting white blood cells.
What is the function of the spleen?
The spleen also stores red blood cells, platelets, and infection-fighting white blood cells. The spleen plays an important role in your immune system response. When it detects bacteria, viruses, or other germs in your blood, it produces white blood cells, called lymphocytes, to fight off these infections.
Why is the spleen important?
Though your spleen isn’t a large organ, it plays many important roles in your body. It helps remove old and damaged blood cells, and it produces infection-fighting cells to protect your health. The spleen also makes certain substances that have an important role in inflammation and healing.
What causes a spleen to be enlarged?
Other conditions that cause an enlarged spleen include: bacterial, viral, and parasitic infections such as syphilis, tuberculosis, endo carditis, mononucleosis (mono), and malaria. blood cancers such as Hodgkin’s disease, leukemia, and lymphoma. liver diseases like cirrhosis. hemolytic anemia.
What is the lymphatic system?
The lymphatic system helps remove cellular waste, maintain fluid balance, and make and activate infection-fighting white blood cells for the immune system. It’s also responsible for making substances that play an important role in inflammation and healing. Trusted Source. .
Why can't my spleen filter blood?
metabolic disorders like Gaucher’s disease and Niemann-Pick disease. When your spleen enlarges, it can’t filter your blood as efficiently as it once did. It may accidentally filter out normal red blood cells and platelets, leaving fewer healthy blood cells in your body.
Why does the spleen enlarge?
Many different conditions can cause the spleen to enlarge, especially diseases that cause blood cells to break down too quickly. An excess destruction of blood cells, for example, can overwork the spleen, and cause it to enlarge.
Why is the spleen important?
Your spleen is a small but important organ. It works hard to fight infection, remove old or damaged blood cells and keep fluids moving through your body. Many disorders, infections, injuries and diseases can cause problems in the spleen.
What is the spleen?
The spleen is a small organ inside your left rib cage, just above the stomach. It’s part of the lymphatic system (which is part of the immune system). The spleen stores and filters blood and makes white blood cells that protect you from infection. Many diseases and conditions can affect how the spleen works. A ruptured (torn) spleen can be fatal.
Why does my spleen feel so big?
Splenomegaly is a dangerous condition because the spleen can rupture (tear) or bleed.
Why is splenomegaly dangerous?
Splenomegaly is a dangerous condition because the spleen can rupture (tear) or bleed. The spleen can become enlarged from: Blood cancers, such as leukemia and Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and cancer in other parts of the body that metastasize (spread) to the spleen. Blood clots in the spleen or the liver.
Why do they remove the spleen?
Sometimes, healthcare providers perform surgery to remove the spleen (splenectomy) because it’s damaged or diseased. Without the spleen, the liver takes over many of the spleen’s duties. Splenectomy is also a treatment for different types of thrombocytopenia, including immune thrombocytopenia (ITP).
What are the two parts of the spleen?
There are two parts of the spleen. They each do different jobs. The types of tissue in the spleen are: White pulp: As part of the immune system, the white pulp produces white blood cells. These blood cells make antibodies. Antibodies fight infection. Red pulp: The red pulp acts like a filter.
What happens when your spleen doesn't work?
Protein disorders like amyloidosis. Functional asplenia: This condition happens when your spleen doesn’t work as it should. It may overreact (hypersplenism) and destroy healthy red blood cells. Destroying too many blood cells can increase the risk of infection and lead to bruising and bleeding.
What is the function of the spleen?
Functions of the spleen. The spleen’s primary job is to filter the blood. As blood flows into the spleen, it performs a quality control service, detecting any red blood cells that are old or damaged. Blood flows through a maze of passages in the spleen. Healthy cells flow straight through, but those considered to be unhealthy are broken down by ...
Why is the spleen important?
The spleen is an important organ involved in cleaning out old blood cells and helping to mount the immune response. Although it is relatively small, it carries out a variety of roles. Despite this, if it is removed, a person can carry on without it.
Why do people need to have their spleen removed?
Most commonly, this is due to a ruptured spleen, but it can also be because of an enlarged spleen, certain blood disorders, some cancers, infection, or noncancerous growths.
Why does the spleen burst after a spleen rupture?
Certain diseases, such as malaria and infectious mononucleosis, make a ruptured spleen more likely because they cause the spleen to swell and the protective capsule to become thinner.
How much blood is stored in the spleen?
The spleen also stores blood — the blood vessels of the spleen can expand significantly. In humans, around 1 cup of blood is kept in the spleen, ready to be released if there is a significant loss of blood, after an accident, for instance. Interestingly, when a racehorse is at rest, up to half. Trusted Source.
How much does a spleen weigh?
Although it varies in size between individuals, a spleen is typically around 3–5.5 inches long and weighs 5.3–7.1 ounces ( oz). The spleen is a soft organ with a thin outer covering of tough connective tissue, called a capsule.
How many people have an additional spleen?
There are some conditions that can involve the spleen, these include: Accessory spleen: An estimated 10–15 percent of people have an additional spleen. The second spleen is usually much smaller — around 1 centimeter (cm) in diameter. Generally, it causes no health problems.
Spleen and Red Blood Cells Definition
The spleen is known as the largest lymphoid organ. It is a significant organ that works by keeping balance in the bodily fluids. However, a person can survive without them. The spleen plays vital roles concerning red blood cells as well as the defense system.
Overview of Spleen And Red Blood Cells
Spleen shows its role by identifying as well as eliminating old and disrupted red blood cells. When blood inclines to flows into the spleen, the spleen undertakes the quality control. The red blood cells subsequently show movement via the narrow passages.
Graveyard of the Cells
Spleen is demonstrated as the graveyard of the cells. It is situated under the ribcage and above the stomach in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen. It is a type of soft organ. The significant function of the spleen is filtering the blood.
Symptoms Can Be Seen is Spleen and Associated Problems Arise
The size of the spleen become enlarged and can cause huge problems like:
Red Blood Cells
Red blood cells (RBCs) are formed in the bone marrow of bones. They work by transporting oxygen from the lungs to different tissues throughout your body. A high red blood cell count can lead to a condition that will limit the supply of oxygen. It can also result in a condition that directly raises the production of a red blood cell.
Composition of Red Blood Cells
Red blood cells make up approximately 45 percent of the blood. The other leftover 55% is plasma and less than 1% comprises of other cells like thrombocytes as well as leukocytes.
When does the spleen produce hemoglobin?
In utero, the spleen is partially responsible for hemoglobin synthesis from the 10th through the 25th week of pregnancy. After birth, the primary function of the spleen shifts to the following major roles:
How does the spleen respond to sympathetic stimulation?
As a reservoir for blood, the spleen weights about 100 g. The organ can respond to sympathetic stimulation by contracting its fibroelastic capsule and trabeculae to increase systemic blood supply. In particular, this vital function takes place during hemorrhage. About 25% to 30% of red blood cells (RBCs) are stored in the spleen, along with about 25% of platelets normally sequestered in the spleen.
Why do people have splenic dysfunction?
There are a variety of causes for splenic dysfunction ranging from extravascular hemolysis to sickle cell disease and trauma. Due to the spleen playing a large role in the immune system, recognizing splenic dysfunction or preparing to lose the spleen is critical in preventing death secondary to asplenic sepsis. For any patient with splenic dysfunction, they must receive prophylactic vaccination against encapsulated organisms, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitides,and Haemophilus influenzae. Due to the increased risk of a Streptococcus pneumoniaeinfection following infection from the influenza virus, a- or hypo-splenic patients should receive yearly influenza vaccinations as well. Because vaccinations do not cover all serotypes of the organism, many patients receive either daily prophylactic antibiotics, usually penicillin, or an emergency supply should they develop a fever. The timing of implementation for these practices depends on the reason for splenic dysfunction. In patients with functional asplenia or hyposplenism, such as in sickle cell disease, prophylaxis should begin as soon as possible. In cases of elective spleen surgery, prophylaxis should begin two weeks before surgery. In emergency surgery, it should commence two weeks after surgery. [25]
What is the fibrous capsule that covers the spleen?
A thin, fibrous capsule covers the spleen from which trabeculae arise. Trabeculae are fibrous bands transporting blood vessels to and from the splenic pulp. [5]
What are the two major units of the spleen?
The spleen contains two major units: white pulp and red pulp .[2] The white pulp is composed of lymphatic tissue surrounding a central arteriole and contains mainly white blood cells that are involved in the initiation of the adaptive immune response. The innermost area of the white pulp, the germinal center, contains B-cells while the surrounding marginal zone contains T-cells.[3] The marginal zone is surrounded by a periarteriolar lymphoid sheath (PALS), which also contains T-cells. White pulp throughout the spleen is surrounded by red pulp. The red pulp is composed of splenic cords (Cords of Billroth) and a large volume of venous sinuses, which gives the structure its characteristic red appearance under a microscopic. The splenic cords provide the organ structure through reticulin and fibrils. The cords also contain a reservoir of monocytes to aid in wound healing. Splenic cords lead to splenic sinuses where macrophages respond to antigens and filter abnormal or aging erythrocytes out of blood flow. [4]
Where is the spleen located?
It is an intraperitoneal organ located in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen posterior and lateral to the stomach.[1] The spleen is situated anatomically behind the 9 and 11 ribs on the left side of the body.
Can CBC be used to test for splenomegaly?
While not highly sensitive or specific, the clinician can perform a physical exam to test for splenomegaly. Laboratory work that can help assess splenic activity is a complete blood count (CBC) complimented by a peripheral blood smear. Abnormalities in quantity or quality of cell types can provide evidence of pathology involving the spleen. In addition to the physical exam and laboratory testing, there is a variety of imaging modalities to visualize the spleen. [17]
When the spleen destroys red blood cells so rapidly that severe anemia develops, what happens?
When the spleen destroys red blood cells so rapidly that severe anemia develops. When the spleen so depletes stores of white blood cells that infection is likely. When the spleen so depletes stores of platelets that bleeding is likely.
What happens when the spleen is enlarged?
An enlarged spleen may outgrow its own blood supply. When parts of the spleen do not get enough blood, they may become damaged, causing them to bleed or die.
What is the best way to determine how large the spleen is?
Ultrasonography or computed tomography (CT) is usually needed to determine how large the spleen is and whether it is pressing on other organs. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provides similar information and also traces blood flow through the spleen.
Why does my spleen feel full?
An enlarged spleen usually does not cause many symptoms, and the symptoms that it does cause may be mistaken for many other medical conditions. Because the enlarged spleen lies next to the stomach and sometimes presses against it, people may feel full after eating a small snack or even without eating. People may also have abdominal or back pain in the area of the spleen in the upper left part of the abdomen or the left side of the back. The pain may spread to the left shoulder, especially if parts of the spleen do not get enough blood and start to die.
Why do people with enlarged spleens need to avoid contact sports and weight lifting?
People with an enlarged spleen need to avoid contact sports and weight-lifting because the spleen is at risk of tearing, causing uncontrollable bleeding.
What tests can be used to determine if a spleen is enlarged?
Blood protein measurement can determine whether other conditions are present that can cause the spleen to enlarge, such as amyloidosis, sarcoidosis, malaria, visceral leishmaniasis, brucellosis, and tuberculosis. Liver tests help determine whether the liver is also diseased.
What is the condition where the bone marrow produces red blood cells that are large and abnormal?
Deficiencies of vitamin B12 and folate (folic acid) cause a condition called megaloblastic anemia. In patients with megaloblastic anemia the bone marrow produces red blood cells that are large and abnormal (megaloblasts). Which of the following is NOT a cause of Vitamin B12 or folate deficiency?