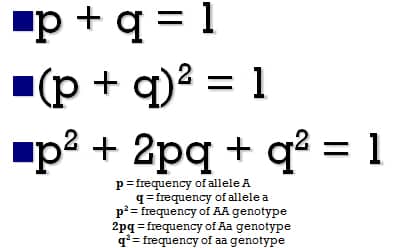
What does 2pq mean in the Hardy Weinberg formula?
In the Hardy Weinberg formula, what does 2pq represent? In the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium equation, the term 2pq represents the genotype frequency of heterozygotes in a population in equilibrium (where p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 ).
What does p2+2pq+q2 mean in the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium equation?
Explanation: In the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium equation ( p2+2pq+q2 = 1 ), the term 2pq represents the genotype frequency of heterozygotes (Aa) in a population in equilibrium. The term p2 represents the frequency of dominant homozygotes (AA) and the term q2 represents the frequency of recessive homozygotes (aa).
What does p2 2pq and Q2 mean?
The Hardy-Weinberg equation used to determine genotype frequencies is: p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1. Where ‘p2’ represents the frequency of the homozygous dominant genotype (AA), ‘2pq’ the frequency of the heterozygous genotype (Aa) and ‘q2’ the frequency of the homozygous recessive genotype (aa). What do P Q p2 2pq and q2 represent?
What are the 4 ways in which Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium can be affected?
assertive mating. inbreeding. genetic drift. founder effect. bottleneck effect. natural selection. How does inbreeding affect the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? It results in a higher level of either dominant or recessive homozygotes. It results in a higher level of heterozygotes. It has no effect on the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.

What is 2pq in Hardy-Weinberg?
p = frequency of the dominant allele in the population. q = frequency of the recessive allele in the population. p2 = percentage of homozygous dominant individuals. q2 = percentage of homozygous recessive individuals. 2pq = percentage of heterozygous individuals.
What does each term in the Hardy Weinberg equation represent?
The terms of this equation are defined as follows: p = the frequency of the dominant allele in a population. q = the frequency of the recessive allele in a population. 2 p q 2pq 2pq = the frequency of the heterozygous dominant genotype.
What does p2 q2 2pq represent?
The frequency of genotypes in a population may be calculated using the formula p2 + q2 + 2pq = 1, where p2 represents the frequency of homozygous dominant genotype, q2 represents the frequency of recessive genotype, and 2pq represents the frequency of heterozygous genotype.
What does q2 represent within the Hardy Weinberg equation?
According to the Hardy-Weinberg equation, what does 'q2' represent? Frequency of homozygous recessive individuals.
What does 2pq represent in the equation apex?
Answer and Explanation: The term "2pq" in the Hardy-Weinberg theorem represents option C. The frequency of the heterozygous individuals in the population. In the Hardy-Weinberg principle, p stands for the dominate allele while q stands for the recessive allele.
What are the 5 Hardy-Weinberg principles?
Key points: When a population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium for a gene, it is not evolving, and allele frequencies will stay the same across generations. There are five basic Hardy-Weinberg assumptions: no mutation, random mating, no gene flow, infinite population size, and no selection.
What is the value of the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium equation p2 2pq q2?
Summary: The Hardy-Weinberg principle is written as the equation p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 = 1. p represents the allele A frequency.
What do the variables in the Hardy-Weinberg equation represent P p2 q q2 2pq?
The frequency of genotypes in a population can be represented by p2+2pq+q2= 1, with p2 equal to the frequency of the homozygous dominant genotype, 2pq equal to the frequency of the heterozygous genotype, and q2 equal to the frequency of the recessive genotype.
What does this Hardy-Weinberg equation represent p2 2pq q2 1 hint think genotypes?
p 2+ 2pq + q 2 = 1.0 Thus p squared is the frequency of homozygous dominant genotypes, q squared is the frequency of homozygous recessive genotypes, and 2pq is the frequency of heterozygous genotypes. The sum of all three frequencies represents all individuals in the population and has to be 1.0 by definition.
What do P and q stand for in the Hardy-Weinberg equation quizlet?
What does p stand for in the Hardy-Weinberg equation? The dominant allele. What does q stand for in the Hardy-Weinberg equation? The recessive allele.
Which of the following statements best explains the need for the 2 in the 2pq term in the Hardy-Weinberg equation?
Which of the following statements best explains the need for the "2" in the 2pq term in the Hardy-Weinberg equation? Heterozygotes can come about in two ways. In a Hardy-Weinberg population with two alleles A1 and A2 that are in equilibrium, the frequency of the allele A2 is 0.3.
What the terms p2 2pq and q2 represent in the population of fruit flies?
The p^2 is the frequency of homozygous dominant traits, which in the fruit flies would be the number of flies with homozygous, not heterozygous, straight wings. The 2pq in the Hardy-Weinberg question is the frequency of heterozygous traits, which would be all of the heterozygous, straight winged flies.
What does the Hardy-Weinberg equation describe quizlet?
The Hardy-Weinberg equation can be used to: -Determine probable frequencies of genotypes in a population. -Track changes of genotypes from generation to generation. Genotype frequency: the percentage of a specific genotype within a population.
What does this Hardy-Weinberg equation represent p2 2pq q2 1 hint think genotypes?
p 2+ 2pq + q 2 = 1.0 Thus p squared is the frequency of homozygous dominant genotypes, q squared is the frequency of homozygous recessive genotypes, and 2pq is the frequency of heterozygous genotypes. The sum of all three frequencies represents all individuals in the population and has to be 1.0 by definition.
What do P and q stand for in the Hardy-Weinberg equation quizlet?
What does p stand for in the Hardy-Weinberg equation? The dominant allele. What does q stand for in the Hardy-Weinberg equation? The recessive allele.
What does 2pq mean in equilibrium?
In the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium equation, the term 2pq represents the genotype frequency of heterozygotes in a population in equilibrium (where p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 ).
What does p2 mean in biology?
The term p2 represents the frequency of dominant homozygotes (AA) and the term q2 represents the frequency of recessive homozygotes (aa). p represents the allele frequency of allele A, and q represents the allele frequency of the allele a.
