
A cold war
Cold War
The Cold War was a period of geopolitical tension between the Soviet Union with its satellite states, and the United States with its allies after World War II. The historiography of the conflict began between 1946 and 1947. The Cold War began to de-escalate after the Revolutions of 1989. The co…
What is the true definition of the Cold War?
Cold War definition A state of political tension and military rivalry b/w nations that stops short of full-scale ware, that existed between the US and Soviet Union and their allies following WWII. It was marked with a great deal of mistrust, spying, threats, and manipulation b/w the 2 super power.
What is meant by 'Cold War'?
What is meant by cold War? (Important) 1) The term 'Cold War' was frequently used by Prof. Walter Lippmann to describe the conflict between Western power led by America and the communist group led by soviet Russia.
What is the Cold War best described as?
What is the best description of the Cold War? Cold War, the open yet restricted rivalry that developed after World War II between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies. The Cold War was waged on political, economic, and propaganda fronts and had only limited recourse to weapons.
What is Cold War and its history?
The Cold War was a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc, which began following World War II.Historians do not fully agree on its starting and ending points, but the period is generally considered to span the 1947 Truman Doctrine (12 March 1947) to the 1991 dissolution of the Soviet Union ...
What did the term Cold War refer to?
A cold war is a state of conflict between nations that does not involve direct military action but is pursued primarily through economic and political actions, propaganda, acts of espionage or proxy wars waged by surrogates. This term is most commonly used to refer to the American-Soviet Cold War of 1947–1991.
What was the term Cold War referring to quizlet?
"The Cold War" refers to the period following WWII until the collapse of the Soviet Union in the 1990s. This was a period when much of the world was divided by the communist/non-communist battle for military and political superiority.
What does the term Cold War refer to Mcq?
The Cold War (1945-1991) was a period of geopolitical tension between the Soviet Union and its satellite states (the Eastern European countries), and the United States with its allies (the Western European countries) after World War II.
Why do we use the term cold war?
The term cold war is used because there was no large-scale fighting directly between the two superpowers, but they each supported major regional conflicts known as proxy wars.
When was the Cold War quizlet?
You just studied 23 terms! The Cold War was a twentieth century conflict between the United States of America (US), the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, over political, economic and military issues, often described as a struggle between capitalism and communism.
Why did the Cold War occur quizlet?
The Cold War began because the Soviet Union was increasing their military power. The United States was trying to contain communism and began paying attention to the Soviets military. Because of this, the United States, also began supplying for a war.
Who first used the word Cold War?
Bernard BaruchOn this day in 1947, Bernard Baruch, the multimillionaire financier and adviser to presidents from Woodrow Wilson to Harry S. Truman, coined the term “Cold War” to describe the increasingly chilly relations between two World War II Allies: the United States and the Soviet Union.
Who called cold war a long twilight struggle Class 12?
question. John F. Kennedy, the 35th president of United States of America called the cold war as "Long Twilight struggle". He took as the office of President of United States of America in 1960 and called the cold war as Long Twilight Struggle in his inaugural speech.
What is the state of war Mcq?
What is the state of war? a) A state that is aggressive and always building up its military.
When did the term Cold War begin?
1945The term 'cold war' first appeared in a 1945 essay by the English writer George Orwell called 'You and the Atomic Bomb.
What was the Cold War fought over quizlet?
What was the cold war fought over? It was ideological battle between the United States and the Soviet Union, who had emerged as superpowers following World War II. The ideologies they were fighting over were Capitalism vs. Communism.
What are other names for the Cold War?
Words that mention cold-war in the Dictionarywitch-hunt.Union of Soviet Socialist Republics.east.eastern-bloc.four-minute warning.domino theory.iron curtain.khrushchevian.More items...
What is containment Cold War quizlet?
Containment. According to this policy, the US and its allies would do all in their power to 'contain' or stop the spread of communism to non-communist nation. They would not, however, attempt to overthrow existing communist nations (such as the USSR) Division of Europe after WWII and Soviet Control over Eastern Europe.
How long was the Cold War?
about 45 yearsThe Cold War lasted about 45 years. There were no direct military campaigns between the two main antagonists, the United States and the Soviet Union. Yet billions of dollars and millions of lives were lost in the fight. The United States became the leader of the free-market capitalist world.
16th Century England and Spain
In his 1964 article of Francis Drake's New Albion claim, Adolph S. Oko Jr. described certain 16th century tensions between England and Spain as a cold war.
Second Cold War
The Second Cold War, also called Cold War II, Cold War 2.0, or the New Cold War, is a term describing post- Cold-War era of political and military tensions between the United States and China or Russia .
Middle East
Malcolm H. Kerr first coined the term "Arab Cold War" to refer to a political conflict inside the Arab world between Nasserist republics defending Arab socialism, Pan-Arabism, and Arab nationalism led by Nasser's Egypt, against traditionalist monarchies led by Saudi Arabia.
South Asia
A commentator Ehsan Ahrari, a writer Bruce Riedel, a political commentator Sanjaya Baru and a Princeton University academic Zia Mian have used the term "cold war" since 2002 to refer to long-term tensions between India and Pakistan, which were part of the British India until its partition in 1947 .
East Asia
A Naval Postgraduate School academic Edward A. Olsen, a British politician David Alton, a York University professor Hyun Ok Park, and a University of Southern California professor David C. Kang used the term to refer to tensions between North Korea and South Korea, which have been divided since the end of World War II in 1945.
China and the Soviet Union
British writer Edward Crankshaw used the term to also refer to the relationship between China and the Soviet Union after the Sino-Soviet split.
China and India
Imran Ali Sandano of the University of Sindh, Arup K. Chatterjee of the Jindal Global Law School, journalist Bertil Lintner, writer Bruno Maçães, politician-lawyer P. Chidambaram, politician and journalist Sanjay Jha, and some others use the terms like "new cold war" to refer to growing tensions between China and India .
What was the Cold War?
The Cold War was a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc, which began following World War II.
How did the Cold War start?
While most historians trace the origins of the Cold War to the period immediately following World War II, others argue that it began with the October Revolution in Russia in 1917 when the Bolsheviks took power. In World War I, the British, French and Russian Empires had composed the Allied Powers from the start, and the U.S. joined them in April 1917. The Bolsheviks seized power in Russia in November 1917 and fulfilled their promise to withdraw from WWI, and German armies advanced rapidly across the borderlands. The Allies responded with an economic blockade against all of Russia. In early March 1918, the Soviets followed through on the wave of popular disgust against the war and accepted harsh German peace terms with the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk. In the eyes of some Allies, Russia now was helping Germany to win the war by freeing up a million German soldiers for the Western Front and by
What countries did the Soviet Union force to invade?
After signing the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact and German–Soviet Frontier Treaty, the Soviet Union forced the Baltic countries —Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania —to allow it to station Soviet troops in their countries. Finland rejected territorial demands, prompting a Soviet invasion in November 1939. The resulting Winter War ended in March 1940 with Finnish concessions. Britain and France, treating the Soviet attack on Finland as tantamount to its entering the war on the side of the Germans, responded to the Soviet invasion by supporting the USSR's expulsion from the League of Nations.
How did the US influence the Korean War?
The US initially seemed to follow containment when it first entered the war. This directed the US's action to only push back North Korea across the 38th Parallel and restore South Korea's sovereignty while allowing North Korea's survival as a state. However, the success of the Inchon landing inspired the US/UN forces to pursue a rollback strategy instead and to overthrow communist North Korea, thereby allowing nationwide elections under U.N. auspices. General Douglas MacArthur then advanced across the 38th Parallel into North Korea. The Chinese, fearful of a possible US invasion, sent in a large army and defeated the U.N. forces, pushing them back below the 38th parallel. Truman publicly hinted that he might use his "ace in the hole" of the atomic bomb, but Mao was unmoved. The episode was used to support the wisdom of the containment doctrine as opposed to rollback. The Communists were later pushed to roughly around the original border, with minimal changes. Among other effects, the Korean War galvanised NATO to develop a military structure. Public opinion in countries involved, such as Great Britain, was divided for and against the war.
What were the three worlds of the Cold War?
Second World: Eastern Bloc led by the USSR, China, and their allies. Third World: Non-Aligned and neutral countries.
Which country received the bulk of its arms and economic assistance from the USSR?
Egypt, which received the bulk of its arms and economic assistance from the USSR, was a troublesome client, with a reluctant Soviet Union feeling obliged to assist in both the 1967 Six-Day War (with advisers and technicians) and the War of Attrition (with pilots and aircraft) against pro-Western Israel.
When was the Cold War first used?
Main article: Cold war (general term) At the end of World War II, English writer George Orwell used cold war, as a general term, in his essay "You and the Atomic Bomb", published 19 October 1945 in the British newspaper Tribune.
Answer
A cold war is a state of conflict between nations that does not involve direct military action but is pursued primarily through economic and political actions, propaganda, acts of espionage or proxy wars waged by surrogates.
New questions in English
Read the passage and study the image from Sugar Changed the World. Slaves were given long, sharp machetes, which would be their equipment—but for some …
What does "cold war" mean?
Princeton's WordNet (2.00 / 1 vote) Rate this definition: cold war noun. a state of political hostility between countries using means short of armed warfare. Cold War noun. a state of political hostility that existed from 1945 until 1990 between countries led by the Soviet Union and countries led by the United States.
What countries did the US and USSR fight in?
The US and USSR became involved in political and military conflicts in the Third World countries of Latin America, Africa, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia. To alleviate the risk of a potential nuclear war, both sides sought relief of political tensions through détente in the 1970s.
What is the Cold War?
(Government, Politics & Diplomacy) a state of political hostility and military tension between two countries or power blocs, involving propaganda, subversion, threats, economic sanctions, and other measures short of open warfare, esp that between the American and Soviet bloc s after World War II (the Cold War) ...
What is the difference between a cold war and a hot war?
cold war - a state of political hostility between countries using means short of armed warfare. antagonism, enmity, hostility - a state of deep-seated ill-will. hot war - actual fighting between the warring parties. 2. Cold War - a state of political hostility that existed from 1945 until 1990 between countries led by the Soviet Union ...
What is the definition of a state of rivalry?
2. A state of rivalry and tension between two factions, groups, or individuals that stops short of open, violent confrontation.
What was the most important event that brought the USSR and Russia to the brink of a nuclear war?
At the height of the Cold War, one incident that brought USSR (now Russia) and the US to the brink of a nuclear war was the Cuban Missile Crisis.
What is the purpose of the book Cold War?
This book's purpose is to fill the historiographical gap in the study of the Cold Warin Southeast Asia by providing a general political history of the Cold Warin Southeast Asia (3).
What does "cold warrior" mean?
2. A state of rivalry and tension between two factions, groups, or individuals that stops short of open, violent confrontation. cold warrior n. American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition.
What is the book "We were soldiers too" about?
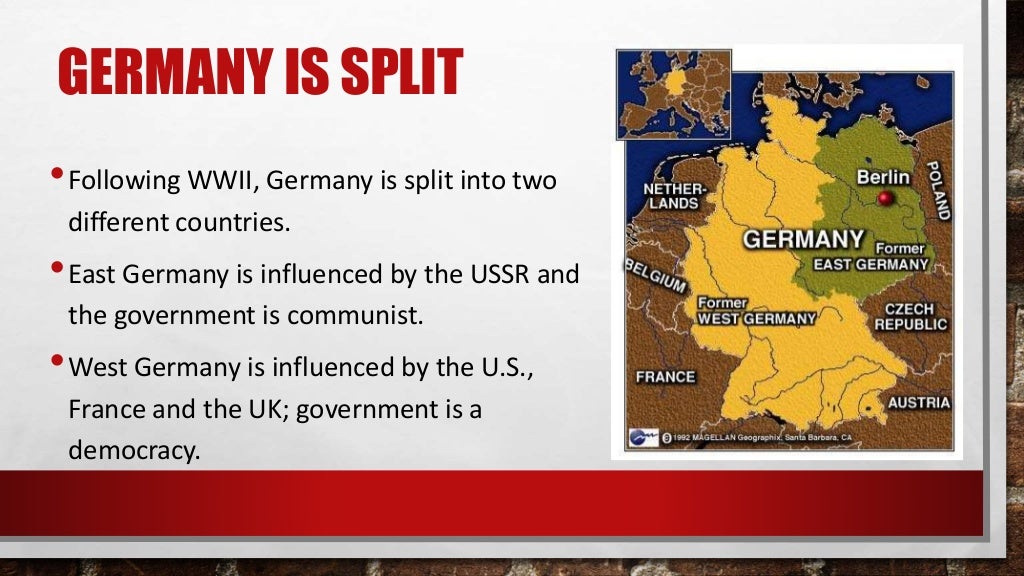
Book two in the series, We Were Soldiers Too: A Historical Look at Germany During the Cold WarFrom the US Soldiers Who Served There (ISBN-13: 9781523677528), covers the careers of seventeen veterans who served in Germany from 1960 to 1989.
How did the Cold War affect the US and USSR?
the cold war influences the US and USSR along with many other nations because most of the world was allied with a nation
How to help Germany prevent a war?
Encourage communism for worldwide worker's revolution, rebuild their economy ruined by war by using Europe's industrial equipment and raw materials, and Keep Germany divided to prevent them from waging war
What is the meaning of "struggle over political differences"?
a struggle over political differences carried out by means of short military action or war
What did the USSR want?
The US wanted to spread capitalism and democracy while the USSR wanted to spread communism (competing political philosophies)

Overview
A cold war is a state of conflict between nations that does not involve direct military action but is pursued primarily through economic and political actions, propaganda, acts of espionage or proxy wars waged by surrogates. This term is most commonly used to refer to the American-Soviet Cold War of 1947–1991. The surrogates are typically states that are satellites of the conflicting nations, i.e., nations allied to them or under their political influence. Opponents in a cold war will often pr…
Historiography
Origins of the term
Background
End of World War II (1945–1947)
As soon as the term "Cold War" was popularized to refer to post-war tensions between the United States and the Soviet Union, interpreting the course and origins of the conflict has been a source of heated controversy among historians, political scientists, and journalists. In particular, historians have sharply disagreed as to who was responsible for the breakdown of Soviet–US relations after the Second World War; and whether the conflict between the two superpowers wa…
Containment and the Truman Doctrine (1947–1953)
At the end of World War II, English writer George Orwell used cold war, as a general term, in his essay "You and the Atomic Bomb", published 19 October 1945 in the British newspaper Tribune. Contemplating a world living in the shadow of the threat of nuclear warfare, Orwell looked at James Burnham's predictions of a polarized world, writing:
Looking at the world as a whole, the drift for many decades has been not towards anarchy but to…
Crisis and escalation (1953–1962)
While most historians trace the origins of the Cold War to the period immediately following World War II, some argue that it began with the October Revolution in Russia in 1917 when the Bolsheviks took power. In World War I, the British, French and Russian Empires had composed the major Allied Powers from the start, and the US joined them as a self-styled Associated Power in April 19…
From confrontation to détente (1962–1979)
The Allies disagreed about how the European map should look, and how borders would be drawn, following the war. Each side held dissimilar ideas regarding the establishment and maintenance of post-war security. Some scholars contend that all the Western Allies desired a security system in which democratic governments were established as widely as possible, permitting countries to p…