
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant males and females will sexually reproduce and have offspring together.
What is selective breeding and what is it used for?
Selective breeding, also known as artificial selection, is a process used by humans to develop new organisms with desirable characteristics. Selective breeding can be used to produce tastier fruits and vegetables, crops with greater resistance to pests, and larger animals that can be used for meat.
What are the pros and cons of selective breeding?
List of Advantages of Selective Breeding
- It requires no company patent. Any person who works in agriculture can start selective breeding whenever he wants. ...
- It allows for higher profit. Selective breeding allows the encouragement of plant and animal characteristics that are more beneficial to farmers. ...
- It can create new varieties of good crops. ...
- It does not have any issue of safety. ...
What are some reasons humans use selective breeding?
Selective breeding is a process that humans use to select parents from plants or animals that have specific characteristics of interest. The hope of making this selection is that the offspring will inherit the desirable traits, allowing future generations to benefit from the chosen changes. This practice has been in place for thousands of years.
Is selective breeding good or bad?
the method of selective breeding can produce fitter and stronger animals that provide higher yields of meat, milk or eggs. This should also be good as farmers can produce animals that are better suited to survive in marginal conditions or poor climates, preserving human food supplies and saving life.

What does selective breeding mean?
: the process of modifying the characteristics of living things especially to enhance one or more desirable traits by selection in breeding controlled by humans After about three years of selective breeding, their company, Cavendish Game Birds, was able to deliver quail that consistently dressed out to seven or eight ...
What is selective breeding answer in one word?
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant males and females will sexually reproduce and have offspring together.
What are 4 examples of selective breeding?
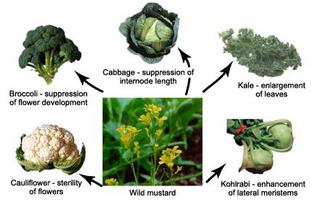
The meats sold today are the result of the selective breeding of chickens, cattle, sheep, and pigs. Many fruits and vegetables have been improved or even created through artificial selection. For example, broccoli, cauliflower, and cabbage were all derived from the wild mustard plant through selective breeding.
What is meant by selective breeding What is its purpose?
The purpose of selective breeding is to develop livestock whose desirable traits have strong heritable components and can therefore be propagated.
What is selective breeding quizlet?
Selective Breeding. A method of breeding that allows only those individual organisms with desired characteristics to produce the next generation. Hybridization. A breeding technique that involves crossing dissimilar individuals to bring together the best characteristics of both organisms.
How do you use selective breeding in a sentence?
This domestication is due to selective breeding, resulting in more tame and dog-like foxes. Both groups have worked hard to ensure the appearance and type of breed are standardized through careful selective breeding. Development of rainbow trout broodstock by selective breeding.
What are the 2 types of selective breeding?
The three methods of selective breeding are outcrossing, inbreeding and line breeding.
What are benefits of selective breeding?
List of Advantages of Selective BreedingAnyone can work on selective breeding. ... It provides improvements to the plants or animals. ... New plant and animal varieties can be created. ... Selective breeding can replicate what GMO work provides. ... Future generations of plants and animals maintain the improvements.More items...•
How does selective breeding lead to evolution?
Selective breeding leads to future generations of selectively bred plants and animals, all sharing very similar alleles which will reduce variation. Genes and their different alleles within a population are known as its gene pool .
Which is a result of selective breeding?
Artificial selection/selective breeding has resulted in an increase in the efficiency of the animals and plants we breed, such as increasing milk yield from cows by continuously breeding selected cows with one another to produce a hybrid.
Which statement about selective breeding is correct?
The correct answer: The true statement about selective breeding and genetically modified organisms is (a) Farmers have been able to produce new... See full answer below.
How is selective breeding done in animals?
Method of selective breeding It is carried out in the following way: A male and female organism are selected which display the desired characteristic (e.g. high meat production) The parents are bred together to produce offspring. The offspring which also display the desired characteristic are selected and bred together ...
What is selective breeding class 7th?
The process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotype traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant males and females will sexually reproduce and have offspring together is called selective breeding.
What is the definition for selective?
Definition of selective 1 : of, relating to, or characterized by selection : selecting or tending to select. 2 : highly specific in activity or effect selective pesticides selective absorption.
What is breeding in biology?
Breeding is sexual reproduction that produces offspring, usually animals or plants. It can only occur between a male and a female animal or plant. Breeding may refer to: Animal husbandry, through selected specimens such as dogs, horses, and rabbits.
What are the types of selective breeding?
The three methods of selective breeding are outcrossing, inbreeding and line breeding.
What is selective breeding?
Selective breeding is the process by which humans control the breeding of organisms in order to exhibit or eliminate a particular characteristic. Selective breeding uses artificial selection to direct the genetic transfer of desirable traits. As opposed to natural selection, selective breeding focuses on traits which ...
What animals are selectively bred for food?
The same process occurred with domesticated animals such as sheep (bred for thicker wool), chickens (considerably larger than their wild ancestors), and cattle (bred for more muscle mass or increased milk yield). One of the oldest and most widely documented examples of selective breeding for food is the selection of tall growing ...
What is culling in biology?
Culling is a form of selective breeding. Rather than breeding two animals that display favorable traits, animals with undesirable traits (such as aggressive behavior) are removed from a population. Culling can be performed either by killing the individual or by spaying/neutering in order to prevent reproduction.
How do phenotypic traits pass from parents to offspring?
The desirable phenotypic traits are passed from parents to offspring via their genes. Although selective breeding can increase the prevalence ...
Why are dogs bred?
All modern dogs have been selectively bred by humans over thousands of years. Dogs were first bred from a common ancestor of the gray wolf (Canis Lupus), which was domesticated by humans with whom it lived in close proximity. It is widely speculated that these animals were first domesticated by humans for hunting and protection, although modern dogs have been bred for a variety of reasons, such as companionship, performing particular tasks, entertainment, or for aesthetic purposes. Today there are over 400 breeds of dog, meaning they have the widest phenotype range of any mammal.
Why is wheat bred?
Today, the breeding of wheat is a more scientific process; individuals with specific genes are identified and bred to create plants that have improved nutritional content, more intense flavors, and require less fertilizer or pesticide applications.
Is selective breeding good for humans?
Selective breeding is not always beneficial to humans. Outside of biology, selective breeding is accidentally practiced. Poachers, who hunt and kill rhinoceros and elephants for valuable rhino-horn and ivory, have in recent years caused unintentional selection for animals with smaller horns and tusks. As the males with the largest horns are the ...
What is selective breeding?
Selective breeding involves choosing parents with particular characteristics to breed together and produce offspring with more desirable characteristics. dogs with particular physiques and temperaments, suited to do jobs like herd sheep or collect pheasants. Selective breeding aims to adapt an organism’s characteristics in a way ...
Why are inbred populations more likely to suffer from genetic conditionscaused by recessivegene variants?
Inbred populations are more likely to suffer from genetic conditionscaused by recessivegene variants because they are more likely to inherit two copies of the recessive variants, one from each parent.
Why are some of the offspring taller than their parents?
Some of the offspring may even be taller than both of their parents, because they may inherit a combination of different “tall” gene variants from each parent and together these make the offspring taller. With repeated selective breeding over multiple generations this population will get taller and taller.
What breed of dog is a Labradoodle?
The Labradoodle is a crossbred dog resulting from breeding a Labrador with a poodle
What happens to an organism after many generations of inbreeding?
After many generations of inbreeding, the offspring will be almost genetically identical, and will produce identical offspring. When this happens, an organism is described as inbred or purebred.
Why are the offspring of plants that self pollinate not identical to the parent plant?
The offspring of plants that self-pollinate are not identical to the parent plant, because their genes are shuffled during reproduction. Plant breeders can use self-pollination as a type of inbreeding, creating plants that are genetically more identical and that produce identical offspring after many generations.
What are the factors that determine natural selection?
Natural selection is driven by environmental factors that limit survival and reproduction, such as harsh environments or competition for mates.
What is selective breeding?
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant males and females will sexually reproduce and have offspring together.
Who was the first to use selective breeding?
The notion of selective breeding was later expressed by the Persian Muslim polymath Abu Rayhan Biruni in the 11th century. He noted the idea in his book titled India, which included various examples. The agriculturist selects his corn, letting grow as much as he requires, and tearing out the remainder.
What animals were selectively bred?
Selective breeding of both plants and animals has been practiced since early prehistory; key species such as wheat, rice, and dogs have been significantly different from their wild ancestors for millennia, and maize , which required especially large changes from teosinte, its wild form, was selectively bred in Mesoamerica.
How many generations of selection for rainbow trout?
Rainbow trout ( S. gairdneri) was reported to show large improvements in growth rate after 7–10 generations of selection. Kincaid et al. (1977) showed that growth gains by 30% could be achieved by selectively breeding rainbow trout for three generations. A 7% increase in growth was recorded per generation for rainbow trout by Kause et al. (2005).
How are animals bred?
Animals with homogeneous appearance, behavior, and other characteristics are known as particular breeds or pure breeds, and they are bred through culling animals with particular traits and selecting for further breeding those with other traits. Purebred animals have a single, recognizable breed, and purebreds with recorded lineage are called pedigreed. Crossbreeds are a mix of two purebreds, whereas mixed breeds are a mix of several breeds, often unknown. Animal breeding begins with breeding stock, a group of animals used for the purpose of planned breeding. When individuals are looking to breed animals, they look for certain valuable traits in purebred stock for a certain purpose, or may intend to use some type of crossbreeding to produce a new type of stock with different, and, it is presumed, superior abilities in a given area of endeavor. For example, to breed chickens, a breeder typically intends to receive eggs, meat, and new, young birds for further reproduction. Thus, the breeder has to study different breeds and types of chickens and analyze what can be expected from a certain set of characteristics before he or she starts breeding them. Therefore, when purchasing initial breeding stock, the breeder seeks a group of birds that will most closely fit the purpose intended.
Why did Charles Darwin coin the term "selective breeding"?
Charles Darwin coined the term 'selective breeding'; he was interested in the process as an illustration of his proposed wider process of natural selection. Darwin noted that many domesticated animals and plants had special properties that were developed by intentional animal and plant breeding from individuals that showed desirable characteristics, and discouraging the breeding of individuals with less desirable characteristics.
Is selective breeding intentional?
Selective breeding can be unintentional, e.g., resulting from human cultivation; it may also produce unintended – desirable or undesirable – results. For example, in some grains, an increase in seed size may have resulted from certain plowing practices rather than from the intentional selection of larger seeds.
Are we missing a good definition for selective breeding? Don't keep it to yourself..
The ASL fingerspelling provided here is most commonly used for proper names of people and places; it is also used in some languages for concepts for which no sign is available at that moment.
Definitions & Translations
Get instant definitions for any word that hits you anywhere on the web!
What Does Selective Breeding Mean?
Selective breeding is the practice of intentionally reproducing living species with the goal of attaining desirable and heritable traits. This is done with both animal and plant species by amateurs, hobbyists, professionals, and researchers alike. It is the cause and practice behind many familiar animals such as the family dog, and plants like common corn.
Why do growers use selective breeding?
In cannabis cultivation, growers often use selective breeding to create new strains, carry on successful ones, an ensure maximum yield and uniformity in the grow room in order to please patients and ensure profits.
How long has selective breeding been around?
While it is impossible to say with any certainly the exact date selective breeding by man began, it is known that it has been done for thousands of years.
What is a hybrid breed?
The products of successful selective breeding are known as hybrids, which presumably display a combination of some or all of the desired traits of both of its parents. Some hybrids are capable of reproducing, others are sterile, such as with the mule, a hybrid of a horse and a donkey.
Why are marijuana plants selectively bred?
Some of the stated reasons for selective breeding in marijuana plants include improvement in a plant’s appearance, taste, storage, potency, and resistance to insect and disease threats.
How Does Selective Breeding Work?
Understanding what selective breeding is and why people do it is rather straightforward, but how exactly does it work? We will have to take a brief biology lesson to find out. If you have ever taken a biology course, some of these words and phrases may sound familiar.
What are the downsides of selective breeding?
Selective breeding can have downsides even when the breeders are fully responsible and ethical. One such downside is that the gene pool closes. This happens a lot for purebreds because only a limited amount of genes can go into the pool for the dog to still be considered purebred.
What is true breeding?
Some people practice true breeding, which is when the breeder mates two purebreds to create purebred puppies. True breeding normally happens when a buyer is either a fan of a specific breed or wants to show the dog at competitions.
What is the difference between dominant and recessive traits?
The dominant traits are those that will win out and show themselves in the offspring. Recessive traits, in contrast, are those that remain within the offspring, but they don’t show themselves. Even though the dominant trait is what you will see in the dog, the dog can still pass off recessive genes in its genetic profile.
Why do dogs breed?
Dogs naturally breed to fulfill an instinctual desire to produce, but selective breeding is normally done for a different purpose. As a result, selective breeding includes selecting a mate and controlling the timing with a particular purpose or trait in mind.
What is a bloodline dog?
Bloodline: A set of dogs that all share some blood and similar traits over more than one generation.
What happens when a dog is inbreeding?
When inbreeding happens, mated dogs will share much of the same genetic material, including illnesses and diseases. As a result, the offspring will often have the disease or illness, even if both parents are healthy. That’s because the offspring has an increased likelihood of getting the illness when both sets of their DNA express it.
Selective Breeding Definition
Selective Breeding Overview
- The procedure involves identifying certain desirable features and finding two members of a species that exhibit the particular feature. A series of matings or breedings is then performed between the individuals with favored features to produce offspring that exhibit the feature and that can be used for future matings. The desirable phenotypic traits are passed from parents to …
Selective Breeding Examples
- Dogs
All modern dogs have been selectively bred by humans over thousands of years. Dogs were first bred from a common ancestor of the gray wolf (Canis Lupus), which was domesticated by humans with whom it lived in close proximity. It is widely speculated that these animals were fir… - Plants and Livestock
Almost all of the food consumed by modern humans has been selectively bred over thousands of years. Around 10,000 years ago when humans began living in permanent or semi-permanent settlements, they started to cultivate their own cropsand herd flocks of livestock for the first tim…
Overview
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant males and females will sexually reproduce and have offspring together. Domesticated animals are known as breeds, normally bred by a professional br…
History
Selective breeding of both plants and animals has been practiced since early prehistory; key species such as wheat, rice, and dogs have been significantly different from their wild ancestors for millennia, and maize, which required especially large changes from teosinte, its wild form, was selectively bred in Mesoamerica. Selective breeding was practiced by the Romans. Treatises as much as 2,000 years old give advice on selecting animals for different purposes, and these anci…
Animal breeding
Animals with homogeneous appearance, behavior, and other characteristics are known as particular breeds or pure breeds, and they are bred through culling animals with particular traits and selecting for further breeding those with other traits. Purebred animals have a single, recognizable breed, and purebreds with recorded lineage are called pedigreed. Crossbreeds are a mix of two purebreds, whereas mixed breeds are a mix of several breeds, often unknown. Animal …
Plant breeding
Plant breeding has been used for thousands of years, and began with the domestication of wild plants into uniform and predictable agricultural cultigens. High-yielding varieties have been particularly important in agriculture.
Selective plant breeding is also used in research to produce transgenic animals that breed "true" (i.e., are homozygous) for artificially inserted or deleted genes.
Selective breeding in aquaculture
Selective breeding in aquaculture holds high potential for the genetic improvement of fish and shellfish. Unlike terrestrial livestock, the potential benefits of selective breeding in aquaculture were not realized until recently. This is because high mortality led to the selection of only a few broodstock, causing inbreeding depression, which then forced the use of wild broodstock. This was evident in selective breeding programs for growth rate, which resulted in slow growth and hi…
Advantages and disadvantages
Selective breeding is a direct way to determine if a specific trait can evolve in response to selection. A single-generation method of breeding is not as accurate or direct. The process is also more practical and easier to understand than sibling analysis. Selective breeding is better for traits such as physiology and behavior that are hard to measure because it requires fewer individuals to test than single-generation testing.
See also
• Animal breeding
• Animal husbandry
• Breed registry
• Breeding back
• Captive breeding
Bibliography
• Darwin, Charles (2004). The Origin of Species. London: CRW Publishing Limited. ISBN 978-1-904633-78-5.