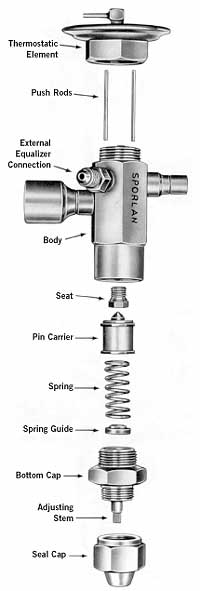
A thermal expansion valve or thermostatic
Thermostat
A thermostat is a component of which senses the temperature of a system so that the system's temperature is maintained near a desired setpoint. The thermostat does this by switching heating or cooling devices on or off, or regulating the flow of a heat transfer fluid as needed, to maintain the c…
Thermal expansion valve
A thermal expansion valve (often abbreviated as TEV, TXV, or TX valve) is a component in refrigeration and air conditioning systems that controls the amount of refrigerant flow into the condenser thereby controlling the superheating at the outlet of the evaporator. Thermal expansion …
How to test a TX valve?
To diagnose a bad TXV, look for:
- Low evaporator pressure
- High evaporator and compressor superheats
- Low compressor amp draw
- Short cycling on the low-pressure control
- Higher than normal discharge temperatures
- Low condensing pressure
- Low condenser split
- Normal to high condenser subcooling
How does a thermostatic expansion valve work?
Superheat and Pressure
- The superheat boils the refrigerant inside the bulb and as it boils it creates pressure. ...
- The expansion valve has a removable cartridge placed inside the inlet. This has an orifice, which works with the valve to control the refrigerant. ...
- The refrigerant comes from the condenser and enters the valve body through the inlet. ...
What valves are anti-compounding valves?
An Anti-Compounding valve is a relay valve with a double-check valve built into it . To see how anti-compounding works, let's use the example where a truck is stopped on a hill, and while the driver holds the foot brake, the driver also sets the parking brakes.
What is a TXV valve for heat pump?
TXV or Thermostatic Expansion Valve are used in air conditioners and heat pumps to meter refrigerant. The TXV or Thermostatic Expansion Valve is preferred over other refrigeration metering devices because it only allows a specified amount of refrigerant to flow based on demand. Any type of refrigeration metering device creates a pressure drop ...

What happens when TXV valve goes bad?
If the TXV fails closed it can be said to be “underfeeding,” which means not enough boiling refrigerant is fed through the evaporator coil and superheat will be too high at the evaporator outlet.
What are the symptoms of a bad TXV?
Bad TXV valve symptoms There is frost on the evaporator. Your unit is blowing warm air. The AC compressor is running constantly.
What happens when TXV is stuck open?
In some instances where the TXV is stuck, a lubricant additive like A/C ReNew may be added to the refrigerant system to help free the valve. Once the additive is added, it is still necessary to exercise the TXV by placing the bulb into hot and cold water several times.
How do I know if my TXV is working?
If possible, check the manufacturer's specification for the proper superheat for that particular model. As a rule of thumb 8° – 12° is considered normal. If you measure a superheat somewhere in this range, regardless of what is happening in the system, the TXV is most likely working.
How much does it cost to replace a TXV valve?
It costs an average of $400 to replace the TXV expansion valve on an AC unit. The average cost is $350 to $450, but it can range from $100 to $700. The labor and the valve are the only costs associated with this project.
How do I know if my expansion valve is clogged?
Usually a bad or failing AC expansion valve or orifice tube will produce a few symptoms that can alert the driver of a potential issue.AC system performing worse than usual and blowing warm air. ... Frost on AC evaporator or coming from the vents. ... AC compressor constantly running.
What happens when expansion valve clogged?
If the expansion valve is stuck open or clogged, the AC system will not cool properly. A clogged valve will lead to too little refrigerant, increasing the pressure in the system and causing the AC compressor to overheat.
Will a bad TXV cause coil to freeze?
If you're experiencing problems with your AC unit, a faulty TXV valve could be the cause of it. It can become unresponsive to the signal and allow refrigerant into the evaporator coil, which causes it to freeze.
How do you adjust a TXV valve?
Turn 1/2 turn at a time clockwise to increase superheat or counter-clockwise to decrease superheat; After a 1/2 turn adjustment, replace the panels and allow the system to run and stabilize; Recheck the superheat and not the change; and. Repeat as needed until the maximum setting is reached.
When should I replace my expansion valve?
If your expansion valve is cool and frosty, yet the air conditioning doesn't seem to be blowing cold air out, there's a good chance the valve needs to be replaced.
Where is TXV located?
The TXV Expansion valves reside between the evaporator and condenser in the refrigeration cycle. With the main body made from brass the TXV includes both and inlet and outlet valve. The inlet is located at the bottom while a refrigerator outlet is on the side.
What are the symptoms of a partially blocked filter drier?
The symptoms for a partially plugged filter drier include:Higher-than-normal discharge temperature;High superheats;Low evaporator pressure;Low condensing pressure;Normal-to-a-bit-high condenser subcooling;Low condenser splits;Local cold spot or frost after the restriction;Low amp draw; and.More items...•
How do you know if its a piston or TXV?
A piston system uses the superheat method of charging, and a TXV uses the subcooling method of charging.
Can a bad TXV take out a compressor?
A TXV being restricted will cause the evaporator, compressor, and condenser to be starved of refrigerant. This will cause low suction pressures, high superheats, low amp draws, and low head pressures.
What are the symptoms of a partially blocked filter drier?
The symptoms for a partially plugged filter drier include:Higher-than-normal discharge temperature;High superheats;Low evaporator pressure;Low condensing pressure;Normal-to-a-bit-high condenser subcooling;Low condenser splits;Local cold spot or frost after the restriction;Low amp draw; and.More items...•
What is the usual symptom when the power element of a TXV loses its charge?
Usually when a TXV bulb looses its bulb charge, it looses it slowly. One of the most obvious visual signs that a TXV has lost its bulb charge is if the top of the txv is very rusted. That would be the leak point of the refrigerant.
Where is the TXV in a refrigerator?
TXV. The TXV Expansion valves reside between the evaporator and condenser in the refrigeration cycle. With the main body made from brass the TXV includes both and inlet and outlet valve. The inlet is located at the bottom while a refrigerator outlet is on the side. On the adjacent side is a removable cap where the superheat is adjustable.
What is a thermal expansion valve?
The Thermal Expansion Valve (TXV) is an important piece of equipment in the HVAC industry. The valve is used to control the amount of refrigerant released to the evaporator section. In this way it controls the difference between superheat and the current refrigerant temperature at the evaporator outlet. Therefore, This in turn keeps its saturation temperature at the current evaporating pressure stable. The Thermal Expansion Valve function is the control the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator in response to the cooling load. Additionally, TXV’s measure the superheat at the outlet and react to this by increasing or decreasing the amount of refrigerant flowing into the evaporator to try and maintain a constant superheat.
How does a superheat valve work?
The valve repeats constantly and stabilizes the valve to ensure the correct amount of refrigerant can flow . Finally, The technician can adjust the amount of superheat by turning the adjuster left or right. This changes the sensitivity of the device and therefore allows you to tune the expansion valve and adjust the superheat.
Where does refrigerant enter a valve?
The refrigerant comes from the condenser and enters the valve body through the inlet. It enters as a high-pressure, medium temperature saturated liquid. Afterwards it passes through the valve body and when it leaves, it exits the valve through the outlet where there is a conversion to a low-pressure, low-temperature vapor/liquid mixture.
Why do you need to leave the evaporator as a superheated vapor?
The purpose of this is to ensure that the refrigerant is boiling off and this will leave the evaporator as a slightly superheated vapor and prevent liquid refrigerant entering the compressor. In order to prevent damage or even destroy the device liquids cannot be compressed.
What is a TXV valve?
The TXV is a modulating valve that controls the flow of refrigerant into the evaporating coils. This keeps the system running as efficiently as possible and prevents liquid refrigerant from getting into the compressor, potentially causing a breakdown.
How does a TXV work?
In order to control the flow, the TXV uses a sensing bulb that’s attached near the outlet of the evaporator. This bulb senses what’s called the “superheat” of the refrigerant as it’s about to leave the evaporator.
What to do before TXV replacement?
First of all, before the TXV replacement can begin, the technician must evacuate all the refrigerant from the system, then clean out any oil or contaminants left behind.
What does thermostatic expansion valve do?
As you can see, when it’s working properly, the thermostatic expansion valve helps to keep your system in a perfect balance. Unfortunately, that means when it’s not working properly, your HVAC system is in big trouble.
Why do you need a modulating valve?
Of course, the amount of liquid that can get “boiled” at any given time depends on how much heat is in the air passing over the coils. That’s why you need a modulating valve that can adjust the refrigerant flow so that it’s always precisely the right amount.
What is a TXV valve?
The thermostatic expansion valve (TXV) is a precision device, which is designed to regulate the rate at which liquid refrigerant flows into the evaporator. This controlled flow is necessary to maximize the efficiency of the evaporator while preventing excess liquid refrigerant from returning to the compressor (floodback).
How does a thermostatic expansion valve work?
As the thermostatic expansion valve regulates the rate at which liquid refrigerant flows into the evaporator, it maintains a proper supply of refrigerant by matching this flow rate against how quickly the refrigerant evaporates (boils off) in the evaporator coil. To do this, the TXV responds to two variables: the temperature of the refrigerant vapor as it leaves the evaporator (P1) and the pressure in the evaporator itself (P2). It does this by using a movable valve pin against the spring pressure (P3) to precisely control the flow of liquid refrigerant into the evaporator (P4):
When did the thermostatic expansion valve change to 13 SEER?
Since the minimum efficiency regulation changed to 13 SEER in January 2006, most OEM systems now incorporate a thermostatic expansion valve (TXV) style metering device as the standard for air conditioning systems. It is now extremely important for the HVAC technician to understand the design and operation of this type of valve.
What is restricted by the valve pin?
Here is a closer view of the TXV in operation. The flow of the liquid refrigerant is restricted by the valve pin. As the flow is restricted, several things happen:
How does a TXV valve work?
There are three different forces at work in a TXV: bulb pressure, spring pressure, and evaporator pressure (see Figure 4). Bulb pressure comes from the bulb that is mounted at the outlet of the evaporator; the bulb senses the suction temperature and drives the diaphragm down if there is an increase. Spring pressure is constant and pushes up against the diaphragm, counter to the bulb pressure. The spring pressure is calibrated when the valve is set by the equipment manufacturer or the installer. Evaporator pressure pushes the diaphragm up when the suction pressure increases and comes from the evaporator load on the system, which varies according to different operating conditions, such as room temperature changes. Based on the balance between these three pressures, the valve will either open or close.
What is a TXV?
A thermostatic expansion val ve (TXV) (see Figure 1) is a refrigeration and air conditioning throttling device that controls the amount of refrigerant liquid injected into a system’s evaporator—based on the evaporator outlet temperature and pressure—called the superheat. Figure 2 shows the different phases and pressures the refrigerant goes through as it is pumped through the system, moving through the evaporator, the compressor, the condenser, and the throttling device which injects liquid refrigerant into the evaporator before it moves into the compressor.
What Is a TXV?
The TXV in your central air conditioning system is a metering device that's designed to regulate the refrigerant flow into the evaporator. It adjusts the flow based on the cooling load to ensure the refrigerant level in the evaporator is correct. Too little refrigerant makes the unit work harder. Excess refrigerant can cause it to build up at the bottom of the input line in the evaporator.
Why is a TXV important?
It's a small component, but the TXV plays an important role in your system's operation. It helps the unit work more efficiently, which can save on your utility bills and keep your system running well without excess wear. If your TXV isn't working correctly , it can cause the system to work harder and could lead to internal damage to some of the HVAC components.
How to find a TXV?
To find the TXV, grab a flashlight and head to the evaporator unit, typically installed in line with a furnace or the indoor air handler of your central air conditioning system . The liquid line coming from the systems condenser connects to the inlet port on the TXV valve. The equalization line stretches from the valve and connects to the suction line via an access port on the line.
Where is the sensing bulb on a TXV?
The sensing bulb sits near the outlet of the evaporator and is typically strapped to the top of the suction line with a clamp. It might be covered with insulation tape to ensure it only senses the refrigerant rather than ambient temperatures. The bulb's job is to sense temperature changes, which result in movement of the diaphragm inside the TXV valve. This increases or decreases the flow of refrigerant through the valve to maximize system efficiency.
What is thermal expansion valve?
A thermal expansion valve causes the air conditioner to operate more efficiently. A faulty valve may cause your air conditioner to work harder, resulting in possible damage to other components. The first step in troubleshooting or replacing a thermal expansion valve is knowing its location. Advertisement.
Where should the bulb be mounted on an expansion valve?
The bulb should be mounted to the top of the output line , as mounting it to the underside of the line can give false readings to the expansion valve and cause it to malfunction. This may be caused by oil lying in the bottom of the output line. Advertisement. references. Alpine Home Air: Thermostatic Expansion Valves.
What is a TX valve?
A thermal expansion valve or thermostatic expansion valve (often abbreviated as TEV, TXV, or TX valve) is a component in vapor-compression refrigeration and air conditioning systems that controls the amount of refrigerant released into the evaporator and is intended to regulate the superheat of the refrigerant that flows out of the evaporator to a steady value. Although often described as a "thermostatic" valve, an expansion valve isn't able to regulate the evaporator's temperature to a precise value. The evaporator's temperature will only vary with the evaporating pressure, which will have to be regulated through other means (such as by adjusting the compressor's capacity).
What is an expansion valve?
Although often described as a "thermostatic" valve, an expansion valve isn't able to regulate the evaporator's temperature to a precise value. The evaporator's temperature will only vary with the evaporating pressure, which will have to be regulated through other means (such as by adjusting the compressor's capacity).
What is a block type valve?
For automotive applications, a type of externally equalized thermal expansion valve, known as the block type valve, is often used. In this type, either a sensing bulb is located within the suction line connection within the valve body and is in constant contact with the refrigerant that flows out of the evaporator's outlet, ...
What is an internal equalized valve?
Internally equalized valves can be used on single circuit evaporator coils having low-pressure drop. If a refrigerant distributor is used for multiple parallel evaporators (rather than a valve on each evaporator) then an externally equalized valve must be used.
How does a TEV work?
Basic construction of a TEV. The flexible diaphragm actuates the poppet valve, an increasing pressure in the sensing bulb will press down on the poppet and open the valve further. There is also an adjustable spring providing a closing force on the valve which controls the superheat.
What is a pilot operated thermostatic expansion valve?
A pilot-operated thermostatic expansion valve, the upper valve is an externally balanced TEV, flow through this valve opens the larger lower valve.
What is the purpose of a stepper motor in an electronic valve?
Most electronic valves use a stepper motor hermetically sealed inside the valve to actuate a needle valve with a screw mechanism , on some units only the stepper rotor is within the hermetic body and is magnetically driven through the sealed valve body by stator coils on the outside of the device.
What is the TXV Valve?
The thermostatic expansion valve, also known as a TXV valve, is a component within a refrigeration device that controls the amount of refrigerant that enters into the system. When the TXV valve is faulty, the evaporator within the system can either have too much refrigerant or not enough.
What are the problems with TXV valves?
There are many problems that come from problematic TXV valves, including short cycling high superheats, and more. To find out whether the problems you are experiencing with your refrigeration unit are a result of a faulty TXV valve, there are some steps you can take to locate the source of the problem.
How much does a TXV valve cost?
In general, a TXV valve can cost anywhere from $100 to $200. Another consideration when pricing parts is that there are thermal expansion valves specifically designed for different types of systems. Some of these are more expensive than others.
How to tell if TXV valve is bad?
Continuous operation is another telltale sign of a bad TXV valve. If the expansion valve doesn’t turn itself off because the sensor is faulty, and excess of gas will build up within the system and the compressor will run non-stop.
How much does it cost to replace a TXV valve?
It costs an average of $300 to professionally replace a TXV valve, or as little as $100 if you do it yourself. Labor costs $150, on average, but it varies based on your location and the complexity of the project. It generally only takes 2 hours or less to replace a TXV valve, but long jobs can make TXV replacement cost $650 or more.
What happens if a TXV valve is faulty?
When the TXV valve is faulty, the evaporator within the system can either have too much refrigerant or not enough. There are many problems that come from problematic TXV valves, including short cycling high superheats, and more. To find out whether the problems you are experiencing with your refrigeration unit are a result of a faulty TXV valve, ...
What are the two types of TXVs?
The two types of TXVs that you are most likely to find are externally equalized valves and internally equalized valves. While both types of valves serve the same function, they do so in slightly different ways.

What You Need to Know About Refrigerant Flow
Superheat and Pressure
- The superheatboils the refrigerant inside the bulb and as it boils it creates pressure. Afterwards, the pressure travels along the hollow Capillary tube and into the Power Head and the Power Head c...
- The expansion valve has a removable cartridge placed inside the inlet. This has an orifice, which works with the valve to control the refrigerant. There are different size cartridges depe…
- The superheatboils the refrigerant inside the bulb and as it boils it creates pressure. Afterwards, the pressure travels along the hollow Capillary tube and into the Power Head and the Power Head c...
- The expansion valve has a removable cartridge placed inside the inlet. This has an orifice, which works with the valve to control the refrigerant. There are different size cartridges depending on t...
- The refrigerant comes from the condenser and enters the valve body through the inlet. It enters as a high-pressure, medium temperature saturated liquid. Afterwards it passes through the valve body...
How The Diaphragm Functions
- The diaphragm is a thin sheet of metal that moves up and down with the pin. Underneath the diaphragm is a spring that can be adjusted to control the superheat. The sensing bulb sits at the outlet o...
- As the refrigerant expands and boils it causes the pressure inside to increase. This pressure increases and makes its way through the capillary tube and travels to the chamber above th…
- The diaphragm is a thin sheet of metal that moves up and down with the pin. Underneath the diaphragm is a spring that can be adjusted to control the superheat. The sensing bulb sits at the outlet o...
- As the refrigerant expands and boils it causes the pressure inside to increase. This pressure increases and makes its way through the capillary tube and travels to the chamber above the diaphragm....
- The sensing bulb at the outlet detects this and the refrigerant inside boils causing an increase in pressure along the capillary tube. This pressure pushes the diaphragm down which pushes the pin d...
Conclusion
- The valve repeats constantly and stabilizes the valve to ensure the correct amount of refrigerant can flow. Finally, The technician can adjust the amount of superheat by turning the adjuster left or right. This changes the sensitivity of the device and therefore allows you to tune the expansion valve and adjust the superheat.