What do the WISC subtests measure?
The subtest was developed to measure non-verbal reasoning and the ability to understand abstract visual information. The individual is presented with a picture of a pair of scales in which there are missing weights, and they have to choose the correct weights to keep the scales in balance.
What is the difference between WISC-IV and WISC-V?
The WISC-IV required the administration of 10 subtests to calculate the FSIQ and primary index scores, and the WISC V requires 10 subtests for the primary subtests but only 7 subtests for the FSIQ.
Does the WISC-IV provide a full scale IQ?
The WISC-IV is a standardized measure comprised of fifteen subtests (ten core and five supplemental/optional). This instrument provides a Full Scale Intelligence Quotient (FSIQ) and four Composite or Index Scores.
Is WISC-IV an IQ test?
WISC IV subtests. The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC-IV) is an individually administered IQ test used with children aged from 6 to 16. Younger children are tested using the Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence (WPPSI).
What psychological processes are measured by the WISC-V?
The clinician uses specific WISC-V Integrated measures to evaluate the impact of expressive language, memory, executive functioning, visuomotor integration, and basic math skills on measures of intellectual functioning.
What is a WISC cognitive assessment?
The WISC Test (Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children) is an IQ test administered to children between ages 6 and 16 by school districts and psychologists. The objective of the exam is to understand whether or not a child is gifted, as well as to determine the student's cognitive strengths and weaknesses.
Is the WISC-IV reliable and valid?
Reliability for the WISC-IV is high with r = 0.97 for the FSIQ and r = 0.87–94 for the specific intelligence indices.
What Wisc V score is gifted?
While each program has its own entrance requirements, an FSIQ of 115 – 129 is generally considered “mildly gifted,” an FSIQ of 130 – 144 is generally considered moderately gifted, and an FSIQ of 145 to 159 is generally considered “highly gifted.”
Why is the WISC important?
It is important in higher-order thinking, learning, and achievement. It can tap concentration, planning ability, cognitive flexibility, and sequencing skills, but is sensitive to anxiety too.
What is the average IQ of a 5 year old?
IQ Test Averages for KidsAge of ChildAverage IQ4 years oldBetween 5 and 205 years oldBetween 5 and 206 years oldBetween 5 and 207 years oldBetween 10 and 3014 more rows
What is the average IQ of a 10 year old?
The average IQ score for any age group is 100 — the center of the 'normal' range.
What is a high IQ for a 14 year old?
Price, a professor at the Wellcome Trust Centre for Neuroimaging at University College London, and colleagues, tested 33 "healthy and neurologically normal" adolescents aged 12 to 16. Their IQ scores ranged from 77 to 135, with an average score of 112.
What is the WISC V used for?
Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children® Fifth Edition (WISC®-V) is an intelligence test that measures a child's intellectual ability and 5 cognitive domains that impact performance.
What Wisc V score is gifted?
While each program has its own entrance requirements, an FSIQ of 115 – 129 is generally considered “mildly gifted,” an FSIQ of 130 – 144 is generally considered moderately gifted, and an FSIQ of 145 to 159 is generally considered “highly gifted.”
What is the Wechsler scale?
Older children and adults are tested using the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS). You can read more about the WISC-IV here. There are 15 subtests on the WISC-IV but they may not all be used. In addition to subtest scores a combined composite ...
What numbers do you read in a forward tester?
For Digit Span forward tester would read numbers like "2, 3, 9, 1"
What is the WISC IV?
The WISC-IV measures intellectual ability of children from 6 to 16 years. It was developed to provide an overall measure of general cognitive ability, and also measures of intellectual functioning in Verbal Comprehension (VC), Perceptual Reasoning (PR), Working Memory (WM) and Processing Speed (PS). The VC, PR, WM, and PS subscales provide scores for the Verbal Comprehension Index (VCI), the Perceptual Reasoning Index (PRI), the Working Memory Index (WMI), and the Processing Speed Index (PSI), respectively. Together, the VCI, PRI, WMI, and PSI provide the overall level of intelligence, or Full Scale IQ (FSIQ). Although the full version of the WISC-IV has 15 subtests, only ten are considered core, and used more often when testing intelligence (Wechsler, 2003). The core subtests for VC are Vocabulary, Similarities, and Comprehension. The core subtests for PR are Block Design, Picture Concepts, and Matrix Reasoning. The core subtests for WM are Digit Span and Letter-Number Sequencing, and the core subtests for PR are Coding and Symbol Search. The remaining five subtests, which are referred to as supplementary subtests, are Information and Word Reasoning (part of VC), Picture Completion (part of PR), Arithmetic (part of WM), and Cancelation (part of PS).
Who administers the ADISC IV?
All psychological tasks were administered by research assistants, who were advanced masters or doctoral students in clinical psychology, and under the supervision of registered clinical psychologists. The research assistants were provided with extensive supervised training and practice by the psychologists prior to them collecting data. This training for the ADISC-IV included observations of it being administered by the registered psychologists. The research assistants commenced administering the ADISC-IV once they had attained competence in its administration, as assessed by the registered psychologists.
What is the ECV of a bifactor model?
For the WISC-IV bifactor model, a number of past studies have reported on the explained common variance (ECV; Reise et al., 2013a), as well as the omega hierarchical (ωh) and omega subtests (ωs; McDonald, 1999; Zinbarg et al., 2005) of the general and specific factors, respectively. The ECV of a general factor is the common variance explained by the general factor divided by the total common variance. The ECV of a specific factor is the common variance explained by the specific factor divided by the total common variance. The ECV of the general factor will be high whenever there is little common variance beyond that of the general factor. Thus high values indicate the presence of a general dimension in the bifactor model (Reise et al., 2013a). The ωhvalue of the general factor can be interpreted as a model-based index of the internal consistency reliability of the total scale (Brunner et al., 2012). The ωhcan also be interpreted as an estimator of how much variance in summed (standardized) scores can be attributed to the single general factor (McDonald, 1999). It is obtained by dividing the amount of variance explained by the general factor in a scale by the total amount of variance explained by all the items in the scale. The ωsvalue of a specific factor can be interpreted as a model-based index of the internal consistency reliability of the specific scale, and an estimator of how much variance in summed (standardized) scores can be attributed to the specific factor (McDonald, 1999; Brunner et al., 2012). It is computed by dividing the amount of variance explained by the specific factor by the total amount of variance explained by all the items in the scale. The values for ωhand ωsrange from 0 to 1, with 0 indicating no reliability and 1 reflecting perfect reliability. According to Reise et al. (2013a), ωhand ωsvalues of at least 0.75 are preferred for meaningful interpretation of a scale.
What is the ML procedure for CFA?
The ML procedure indicates statistical fit in terms of ML χ2values. However, as χ2values are inflated by large sample sizes, the fit of the models was examined using three approximate fit indices: root mean squared error of approximation (RMSEA), comparative fit index (CFI), and Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI). The guidelines suggested by Hu and Bentler (1998)are that RMSEA values close to 0.06 or below be taken as good fit, 0.07 to <0.08 as moderate fit, 0.08 to 0.10 as marginal fit, and >0.10 as poor fit. For the CFI and TLI, values of 0.95 or above are taken as indicating good model-data fit, and values of 0.90 and <0.95 are taken as acceptable fit. As not all the models in the study are nested (Canivez, 2014; Watkins et al., 2013), meaningful differences between well-fitting models were examined in terms of ΔCFI of 0.002 or higher (Meade et al., 2008). The Akaike information criterion (AIC) values were also used. The AIC considers statistical goodness-of-fit as well as model parsimony, with smaller values representing a better fit.
How are reading and arithmetic abilities measured?
Reading and arithmetic abilities were measured using the WRAT-3. The reading test in the WRAT-3 has letters and individual words that the individual has to name or pronounce. The arithmetic test has two parts. The first part covers counting, reading number symbols, and verbally presented simple arithmetic problems. The second requires the individual to calculate up to 40 arithmetic problems. This is a paper and pencil task. Both the reading and arithmetic tests have sound reliability and validity (Wilkinson, 1993).
Does IQ correlate with academic achievement?
Another limitation is that although IQ has consistently been shown to be associated with academic achievement (Naglieri and Bornstein, 2003), at present, no study has examined the predictive validity of the factors in the bifactor model of the WISC-IV, modeled in terms of a general factor and the specific factors representing the index scales (VC, PR, WM, and PS). Using multiple regression analysis of observed scores for WISC-IV FSIQ, VCI, PRI, WMI, and PSI, studies involving non-ADHD samples have reported that the index scores provide only slightly additional variance in the prediction of academic achievement scores, including reading and arithmetic (Glutting et al., 2006; Canivez et al., 2014). A recent study (Beaujean et al., 2014), also with a non-ADHD sample that modeled all core and supplementary tests of WISC-IV in terms of the Cattell–Horn–Carroll (CHC; Schneider and McGrew, 2012) theory of cognitive abilities showed that the general factor had a stronger association with reading and arithmetic than any of the specific factors. Similar findings have been reported for the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale- Fourth Edition (WAIS-IV; Wechsler, 2008) bifactor model with a general factor and the factors for the index scales (Kranzler et al., 2015). Based on these findings, it can be speculated that the general intelligence factor would also be associated with the academic abilities of children with ADHD. However, as low reading ability (Gathercole et al., 2006; Alloway et al., 2009; Alloway and Alloway, 2010) and arithmetic ability (Bull and Scerif, 2001; Swanson and Sachse-Lee, 2001) have been linked to poor WM, and as WM defects have been strongly associated with ADHD (Martinussen et al., 2005; Willcutt et al., 2005; Walshaw et al., 2010), the WM specific factor (which captures WM ability that is independent of the general intelligence) may also be associated with academic achievement abilities.
What is the Wisc test?
The WISC is one test in a suite of Wechsler intelligence scales. Subjects 16 and over are tested with the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS), and children ages two years and six months to seven years and seven months are tested with the Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence (WPPSI). There is some overlap between tests: children ...
How long does it take to get a WISC V?
The WISC-V takes 45–65 minutes to administer. It generates a Full Scale IQ (formerly known as an intelligence quotient or IQ score) that represents a child's general intellectual ability.
How many subtests are there for IQ?
Two subtests must be administered to obtain each of the primary index scores; thus, a total of 10 subtests are primary subtests. The Full Scale IQ is derived from 7 of the 10 primary subtests: Both Verbal Comprehension subtests, one Visual Spatial subtest, two Fluid Reasoning subtests, one Working Memory subtest, and one Processing Speed subtest. Verbal Comprehension and Fluid Reasoning are weighted more heavily in the Full Scale IQ to reflect the importance of crystallized and fluid abilities in modern intelligence models (Wechsler, 2014).
What is the age range for the Wechsler intelligence test?
The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children ( WISC) is an individually administered intelligence test for children between the ages of 6 and 16. The Fifth Edition (WISC-V; Wechsler, 2014) is the most recent version.
How many children were in the WISC-V sample?
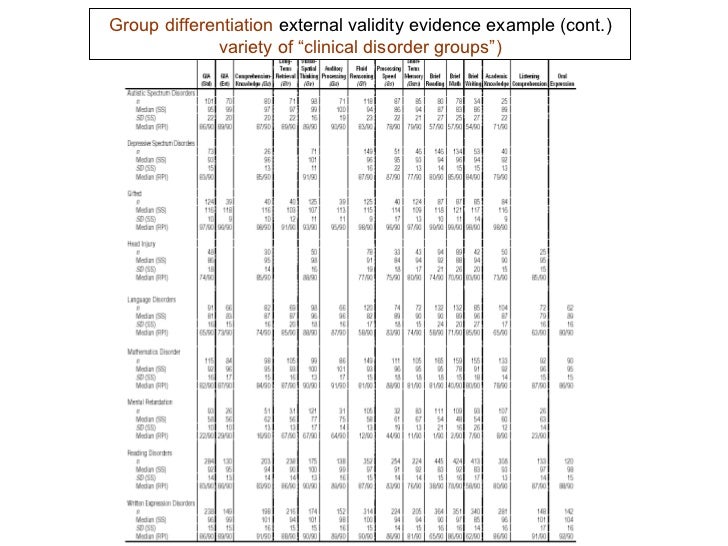
The WISC–V normative sample consisted of 2,200 children between the ages of 6 and 16 years 11 months. In addition to the normative sample, a number of special group samples were collected, including the following: children identified as intellectually gifted, children with mild or moderate intellectual disability, children with specific learning disorders (reading, written expression, and math), children with ADHD, children with disruptive behavior, children who are English Language Learners, children with autism spectrum disorder with language impairment, children with autism spectrum disorder without language impairment, and children with traumatic brain injuries.
When was the WISC-R revised?
A revised edition was published in 1974 as the WISC-R (Wechsler, 1974 ), featuring the same subtests. However, the age range was changed from 5–15 to 6–16. The third edition was published in 1991 (WISC-III; Wechsler, 1991) and brought with it a new subtest as a measure of processing speed.
Who developed the Wechsler-Bellevue Intelligence Scale?
The original WISC (Wechsler, 1949), developed by David Wechsler, was an adaptation of several of the subtests that made up the Wechsler–Bellevue Intelligence Scale (Wechsler, 1939), but also featured several subtests designed specifically for it. The subtests were organized into Verbal and Performance scales and provided scores for Verbal IQ (VIQ), Performance IQ (PIQ), and Full Scale IQ (FSIQ).
What is the WISC V?
It is known as WISC-V. Over the years, the WISC test has been updated several times, each time changing the name to represent the proper edition of the test. At times, some institutions will still utilize older versions of the test.
What is the purpose of the WISC?
The WISC essentially outlines students' intellectual strengths and weaknesses and provides insight into their overall cognitive abilities and potential. The test also compares children to peers of a similar age. In the most general terms, the goal is to determine the potential for a child to grasp new information. While this assessment can be a great predictor of potential, the IQ level is, by no means, a guarantee of success or failure.
How to prepare for WISC V?
Your child cannot prepare for WISC-V or other IQ tests by studying or reading. These tests are not designed to test what you know or how much you know, but rather, they are designed to determine the test-taker's capacity to learn. Typically, tests like the WISC consist of tasks that assess various measures of intelligence, including spatial recognition, analytical thinking, mathematical ability, and even short-term memory. As such, just make sure that your child gets plenty of rest and relaxation before the test. The school is accustomed to administering these tests and will instruct your child what to do at the appropriate time.
What is the Wechsler scale?
Updated January 19, 2020. The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC) is an intelligence test which determines an individual child's IQ, or intelligence quotient. It was developed by Dr. David Wechsler (1896-1981), who was the chief psychologist of New York City's Bellevue Psychiatric Hospital. ...
What grades do wechslers test?
Where the Wechsler Test Is Used. Private schools serving children in 4th through 9th grades often use WISC-V as part of their admissions testing procedures, which may be in place of, or in addition to, other admission testing like the SSAT.
Who developed the WISC test?
It was developed by Dr. David Wechsler (1896-1981), who was the chief psychologist of New York City's Bellevue Psychiatric Hospital. The test that is typically administered today is the 2014 revision of the test that was originally devised in 1949. It is known as WISC-V. Over the years, the WISC test has been updated several times, ...
Is IQ a guarantee of success?
While this assessment can be a great predictor of potential, the IQ level is, by no means, a guarantee of success or failure.
How many subtests are there in WISC IV?
The WISC-IV has 15 subtests, 10 of which are core subtests that are usually used to measure the four index scores and Full Scale IQ. The other five are supplemen-tary subtests that can be used if for some reason a core subtest cannot be used or is not appropriate for a particular child.
What is the purpose of the Peach and Apple test?
The test is designed to assess verbal reasoning and the development of concepts.
Can intellectual ability be measured?
It is a central theme of the book that true intellectual ability cannot be measured accurately in the low range. It follows from this that we should not be using cut-off points in diagnosis or making statements about what an individual’s IQ is without a lot of qualification with regard to the test error. However, as things are at the moment, with intellectual disability still being defined in terms of an IQ cut-off point, it is likely that psycho logists will be called upon to make an estimate of what somebody’s true intellectual ability is. What I want to do in this appendix is to look at how we can get the best estimate of an individual’s true intellectual ability.