
What does tinea pedis stand for?
tinea ped·is. (pĕd′ĭs) n. See athlete's foot. [New Latin : Medieval Latin tinea, tinea + Latin pedis, genitive of pēs, foot .] American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company.
What is the most effective treatment for tinea pedis?
These include:-
- Hot and humid weather
- Excessive sweating
- Wearing tight-fitting, close-toed, or occlusive footwear for prolonged periods
- Wearing wet socks and shoes
- Having diabetes or a weakened immune system
- Walking barefoot in certain areas such as public walkways, swimming pools, locker rooms, shared showers, and saunas
What is different between tinea pedis and tinea cruris?
Tinea pedis, Tinea manuum, and (A):Tinea cruris refer to Tinea corporis that is limited to the foot, hand, and groin, respectively. There is otherwise little special about them. History lesson: The term tinea has an interesting origin. A worm of a moth would sometimes grow on a woolen blanket.
What is the life cycle of tinea pedis?
Tinea pedis or athlete's foot is a fungal infection of the skin on the foot often occurring between the toes and sometimes on the heel. Tinea pedis is highly contagious and can be contracted through either direct or indirect contact. The severity of infection varies and can last as little as a week or two to as long as a month or more.
See more
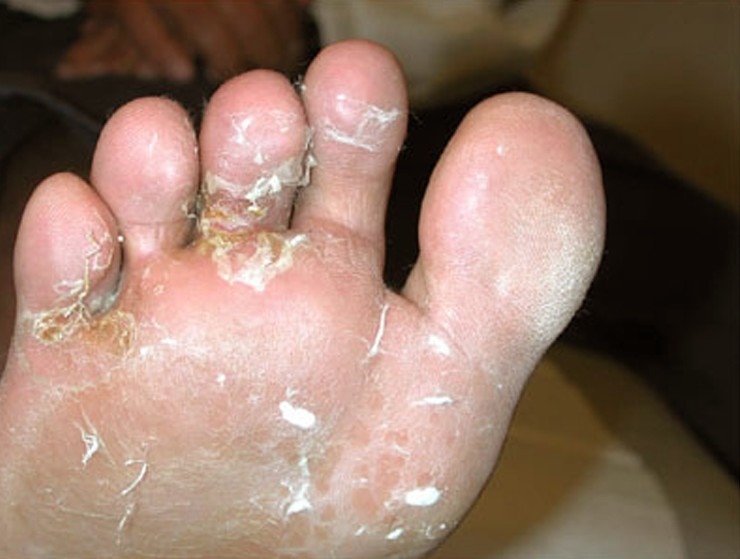
What is tinea pedis caused by?
Tinea pedis or foot ringworm is an infection of the feet affecting soles, interdigital clefts of toes, and nails with a dermatophyte fungus. It is also called athlete's foot. [1][2][3] The infection is caused by the dermatophyte, Trichophyton rubrum which was once endemic to many parts of Africa, Asia, and Australia.
What do you mean by tinea pedis?
Athlete's foot (tinea pedis) is a fungal skin infection that usually begins between the toes. It commonly occurs in people whose feet have become very sweaty while confined within tight-fitting shoes.
How do you get tinea pedis?
Athlete's foot occurs when the tinea fungus grows on the feet. You can catch the fungus through direct contact with an infected person, or by touching surfaces contaminated with the fungus. The fungus thrives in warm, moist environments. It's commonly found in showers, on locker room floors, and around swimming pools.
Does tinea pedis go away?
Athlete's foot doesn't typically go away on its own. If it's left untreated, it can spread to other areas of your body, including your: Nails: Fungal nail infections can be more difficult to treat. They are often more resistant to many treatments.
What happens if you don't treat tinea pedis?
If left untreated, it can spread to a nail and cause a fungal nail infection. The infection can spread to other areas of skin, such as the hands, but that rarely happens. Very rarely, and only in severe cases of athlete's foot, it can also lead to a bacterial infection.
How do you get rid of tinea?
For a mild case of tinea versicolor, you can apply an over-the-counter antifungal lotion, cream, ointment or shampoo. Most fungal infections respond well to these topical agents, which include: Clotrimazole (Lotrimin AF) cream or lotion. Miconazole (Micaderm) cream.
Is tinea on feet contagious?
Tinea is a contagious fungal skin infection. The most commonly affected areas include the feet, groin, scalp and beneath the breasts. Tinea can be spread by skin-to-skin contact or indirectly through towels, clothes or floors.
How do you get rid of tinea pedis fast?
Like hydrogen peroxide, rubbing alcohol can help kill off the fungus that's on the surface level of the skin. You can apply it directly to the affected area or soak your feet in a footbath of 70 percent rubbing alcohol and 30 percent water for 30 minutes.
What does tinea look like on feet?
Skin: a red flaky rash that can crack, split and peel; the rash can spread out in a red ring, with normal-looking skin in the middle. This is called 'ringworm', but this can be a little misleading because there is no worm involved. Feet: Itchy, red blisters between the toes, cracked skin. Nails: Thick and crumbly nails.
Can tinea live in shoes?
Skin contact with the fungi, however, is usually not enough to cause athlete's foot. In fact, shoes can carry fungi for quite some time until conditions are good for growth. Favorable conditions for athlete's foot include: Continually sweaty feet.
Should I wear socks to bed with athlete's foot?
Wearing socks to bed can help prevent transmission of the fungus. Even if you avoid contact, your partner can still develop athlete's foot if you walk around the house barefoot. The fungus can attach itself to floors when you walk or stand on them.
Can tinea be permanent?
Although many treatments will temporarily clear the yeast fungus, we do not have a permanent cure. Although the infection is gone, the return to normal skin color can take several months. Tinea versicolor – is caused by a normal skin inhabitant – tends to recur.
What are symptoms of tinea?
Ringworm often causes a ring-shaped rash that is itchy, scaly and slightly raised. The rings usually start small and then expand outward. Ringworm of the body (tinea corporis) is a rash caused by a fungal infection. It's usually an itchy, circular rash with clearer skin in the middle.
What is the best treatment for tinea pedis?
Use an antifungal product. After washing and drying your feet, apply an antifungal product. The antifungal terbinafine (Lamisil AT) has been shown to be very effective. Another option is clotrimazole (Lotrimin AF).
What is tinea of the skin?
Tinea versicolor is a common fungal infection of the skin. The fungus interferes with the normal pigmentation of the skin, resulting in small, discolored patches. These patches may be lighter or darker in color than the surrounding skin and most commonly affect the trunk and shoulders.
Is tinea pedis a ringworm?
Ringworm is also called “tinea” or “dermatophytosis.” The different types of ringworm are usually named for the location of the infection on the body. Areas of the body that can be affected by ringworm include: Feet (tinea pedis, commonly called “athlete's foot”)
What Is Tinea Pedis?
Tinea pedis, or athlete’s foot, is a ringworm infection of the foot. This contagious infection commonly affects the skin in between your toes, and at times, your soles, heels, and sides of your feet.
What Is The Best Treatment For Tinea Pedis?
Topical antifungal treatment is usually effective in clearing up most tinea pedis infections. This antifungal therapy may come in creams, lotions, powders, or sprays that are applied directly to the infected site. They are usually applied once or twice a day.
How Long Does Tinea Pedis Take To Heal?
Milder cases can subside within two weeks of proper treatment. In more severe or widespread infections, treatment may take more weeks or even months. If your toenail is infected, it may take up to a few months for the infection to completely clear up.
How Do You Prevent Tinea Pedis?
Tinea pedis is a contagious infection. It can not only spread from one person to another, but it can also spread from your feet to affect other parts of your body. These are some preventative measures you can adopt to prevent getting the infection or spreading the disease to other people.
How long does it take for tinea pedis to heal?
If your tinea pedis does not improve within two weeks of commencing topical antifungal treatment, visit your doctor. Other than that, if you are immunocompromised or have diabetes, and you suspect you have a tinea infection, it is best to see a doctor as well.
What is the ringworm on the side of the foot?
Tinea pedis, or ringworm of the foot, is commonly known as athlete’s foot. It is a fungal infection that frequently begins at the skin between your toes and can affect your soles and side of the feet.
What is the name of the worm that causes discoloration on the skin?
Patches of discoloration on your skin may be a result of another type of tinea infection, known as tinea versicolor.
What is tinea pedis?
Tinea pedis is a superficial fungal infection involving the skin of the foot that is easily treated, but often recurs. It does not mean you are dirty or do not take good care of your skin. The fungus responsible for causing the infection is everywhere. —Dr. Mollie MacCormack
What is the best treatment for tinea pedis?
Always let your doctor know if you have changes in your finger or toenails or rashes in other areas of your body such as your palms or groin. These are other areas prone to fungal infections. And ask your doctor what you should do if the infection spreads or becomes painful. —Dr. MacCormack
What is the fungus on the toes called?
The fungus responsible for causing the infection is everywhere. —Dr. Mollie MacCormack. Tinea pedis, or “athlete’s foot ,” is a common, treatable, fungal infection of the skin on the foot. It usually starts between the toes, but can spread to other areas. Infected skin typically becomes itchy, red, and flaky.
Why do my feet peel?
Skin peeling on the bottom of the feet can most commonly be caused by a fungal infection called athlete's foot, sunburn, dermatitis, or dry skin.
What does it mean when your foot is red?
If you have a red, hot swollen foot; swollen lymph nodes (lumps under the skin) in the foot, leg, or groin; have a fever; or have a deep wound on the foot, these are signs of severe athlete’s foot. See a doctor immediately or go to urgent care or the ER.
What is the term for the thickening and flaking of skin on the foot?
Hyperkeratosis: Thickening and flaking of skin on the foot.
Why do my toes get red?
Read below for more information on causes and treatment options for foot redness. Read more. Toes. Cracks in or Between the Toes. Dry skin between the toes is usually caused by a fungal infection known as athlete's foot . Other causes for cracks between toes can arise from contact dermatitis or skin infections.
Overview
Athlete’s foot is a common fungal (caused by a fungus) infection. Athlete’s foot is a form of ringworm. Tinea pedis is another name for athlete’s foot. Tinea is another name for ringworm, and pedis means foot or feet. Athlete’s foot causes an itchy, stinging, burning rash on the skin on one or both of your feet.
Diagnosis and Tests
Your healthcare provider can typically diagnose athlete’s foot by examining your feet and reviewing your symptoms.
Management and Treatment
Athlete’s foot rarely goes away on its own. If left untreated, it’s more likely to spread to other parts of your body.
Prevention
Thoroughly wash your feet and the skin between your toes with antibacterial soap.
