How is Trichoblastoma treated?
Occasionally true trichoblastomas may be excised for cosmetic reasons or if they occur in functionally sensitive areas. Treatment options include curettage and electrodesiccation or surgical excision.
What is a Trichoepithelioma?
Trichoepithelioma is a rare benign adnexal neoplasm originating from basal cells of hair follicles. They may appear as solitary or multiple nodules most commonly on the face, though solitary lesion isolation to the eyelid is exceedingly rare.
What is Trichoblastic carcinoma?
Trichoblastic carcinoma is a rare malignant adnexal tumor, which usually occurs on the scalp. There have been reported cases with regional lymph node metastasis.
What is Infundibulocystic basal cell carcinoma?
Infundibulocystic basal cell carcinoma is a rare subtype of the most frequent form of human skin cancer (basal cell carcinoma). It was first described in 1987 and proposed as a new basal cell carcinoma (BCC) variant by Ackerman and Walsh in 1990 [1,2].
What are papillary mesenchymal bodies?
Papillary mesenchymal bodies are distinct fibroblastic aggregations that represent abortive attempts to form the papillary mesenchyme responsible for hair induction. Papillary mesenchymal bodies were observed in 93% of all trichoepitheliomas, 7% of all keratotic BCC, and 0% of all routine BCC.
What mimics basal cell carcinoma?
Histologic mimics of BCC may include nonneoplastic processes (such as follicular induction over dermatofibromas), benign adnexal tumors (especially follicular tumors), or cutaneous carcinomas with basaloid or blue-cell features.
What is a Ganglioneuroma?
Ganglioneuromas are rare tumors that most often start in autonomic nerve cells. Autonomic nerves manage body functions such as blood pressure, heart rate, sweating, bowel and bladder emptying, and digestion. The tumors are usually noncancerous (benign).
What is a Trichofolliculoma?
Trichofolliculoma is a benign tumor of the skin arising from hair follicle tissue. It is most commonly found on the face and nose. It appears as a flesh-colored nodule, which occasionally is whiteish. Histologically, it is often described as a hamartoma with differentiation towards the hair follicle.
Is Trichoblastoma cancerous?
Trichoblastomas are benign tumors with no systemic involvement. They can be locally aggressive, but malignant potential is very rare. However, there is one rare case of a patient who had malignant transformation of a long-standing trichoblastoma with lymphatic and hematogenous metastases.
What is the difference between an adenocarcinoma and carcinoma?
Carcinoma is the most common form of cancer. It starts in the epithelial tissue of your skin or internal organs. Adenocarcinoma is a subtype of carcinoma. It grows in the glands that line the insides of your organs.
What does nut carcinoma stand for?
NUT carcinoma (NC), also known as NUT midline carcinoma, is a type of rare cancer that can grow anywhere in the body. Usually, it is found in the head, neck, and lungs. NC grows from the squamous cells in the body, which are cells that make up the skin and lining of some organs, like the lungs and stomach.
What is the most aggressive subtype of basal cell carcinoma?
Among the three most common BCC histotypes, infiltrative forms are the most aggressive and it has been reported as an independent risk factor for post-surgical recurrence (10). Superficial and nodular BCCs are instead non-aggressive forms, with a very low surgical recurrence (1).
Can you live a long life with basal cell carcinoma?
Survival for most non-melanoma skin cancers is excellent. The 5-year relative survival for BCC is 100%. This means that, on average, all of the people diagnosed with BCC are just as likely to live at least 5 years after their diagnosis as people in the general population.
Is basal cell considered precancerous?
Precancerous skin can be considered a cancer warning sign, as it may naturally progress into squamous or basal cell carcinoma, which are two types of skin cancer that differ in prevalence and prognosis. The main types of precancerous lesions include actinic keratosis, actinic cheilitis, Bowen disease, and leukoplakia.
What is a papillary mass?
Papillary tumors are thin, finger-like growths that start in the bladder lining and extend into the center of the bladder. Sometimes, these cancers stay in the bladder without growing or spreading. But more aggressive types of this cancer can spread to other organs.
What is papillary tissue?
Papillary dermis: The papillary layer is the top layer of your dermis. It's much thinner than the reticular dermis. It consists of collagen fibers, fibroblast cells, fat cells, blood vessels (capillary loops), nerve fibers, touch receptors (Meissner corpuscles) and cells that fight bacteria (phagocytes).
Is lymphoma epithelial or mesenchymal?
Although leukemia or lymphoma cells of hematological malignancy are embryonically developed from the mesoderm, the so-called EMT, or mesenchymal–epithelial transition (MET), was rarely reported in previous studies.
What are the warning signs of basal cell carcinoma?
SymptomsA shiny, skin-colored bump that's translucent, meaning you can see a bit through the surface. ... A brown, black or blue lesion — or a lesion with dark spots — with a slightly raised, translucent border.A flat, scaly patch with a raised edge. ... A white, waxy, scar-like lesion without a clearly defined border.
How do I know if my basal cell carcinoma has metastasized?
Basal and squamous cell cancers don't often spread to other parts of the body. But if your doctor thinks your skin cancer might spread, you might need imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans.
Where do basal cell cancers usually begin?
Basal cell carcinoma These cancers start in the basal cell layer, which is the lower part of the epidermis. These cancers usually develop on sun-exposed areas, especially the face, head, and neck. They tend to grow slowly.
Is there a cure for Trichoepithelioma?
All in all, as a benign tumor, trichoepithelioma can be managed safely with surgical removal. Alternatives include dermal abrasion and laser surgery, curettage although these options may be associated with an increased rate of recurrence.
Should pilomatrixoma be removed?
A pilomatricoma is a rare but usually harmless skin tumor that mostly affects children and young adults. While pilomatricoma tumors usually don't cause any problems, your doctor might recommend surgical removal to prevent them from getting larger over time.
What does a Trichoepithelioma look like?
What does desmoplastic trichoepithelioma look like? Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma typically present as a firm skin-coloured to red, annular (ring-shaped) plaque with a central dimple. It is usually found on the upper cheek.
Is pilomatrixoma cancerous?
Pilomatricoma, also known as pilomatrixoma, is a type of noncancerous (benign) skin tumor associated with hair follicles. Hair follicles are specialized structures in the skin where hair growth occurs. Pilomatricomas occur most often on the head or neck, although they can also be found on the arms, torso, or legs.
What is a trichoblastoma?
What is trichoblastoma? Trichoblastoma is a small benign hair follicle tumour originating from follicular germinative cells. It is thought to be a variant of trichoepithelioma.
What is the treatment of trichoblastoma?
Trichoblastoma is a benign follicular tumour that requires no treatment. However, because of its association with basal cell carcinoma and the chance that it may transform into trichoblastic carcinoma, additional biopsy or complete surgical excision or Mohs micrographic surgery should be considered if there is uncertainty about the diagnosis.
What is the difference between trichoepithelioma and trichoblastoma?
The main difference between trichoblastomas and trichoepitheliomas is the depth at which they arise in the dermis. Trichoblastomas are found in the deep dermis and subcutaneous tissue, whereas trichoepitheliomas are more superficial.
What is the only definitive diagnosis for trichoblastoma?
A small biopsy (when a tiny piece of skin is removed under local anaesthetic) is the only definitive diagnosis for trichoblastoma. The histology of trichoblastoma will differentiate it from other skin tumours that have similar clinical presentations, these include trichoepithelioma and basal cell carcinoma.
Can trichoblastomas be excised?
Occasionally true trichoblastomas may be excised for cosmetic reasons or if they occur in functionally sensitive areas. Treatment options include curettage and electrodesiccation or surgical excision.
What is a trichoblastoma?
Trichoblastoma is a term originally proposed by Headington 35 to designate tumors with a relatively primitive appearance resembling embryonic hair, accompanied by certain distinctive changes in the surrounding stroma. Although the terminology has suffered numerous permutations since Headington's original description, trichoblastoma is still recognized as a useful designation for tumors exhibiting these features. Three distinctive variants or stages in the development of this tumor were originally recognized—trichogenic trichoblastoma, trichoblastic trichoblastoma, and trichoblastic fibroma—depending on the relative proportion and maturity of epithelium versus stroma. Because of the significant histologic overlap among these variants and their similar clinical evolution regardless of the stage of the lesion, the unified term benign trichogenic tumor has been proposed for these neoplasms. 36 The lesions generally present as firm, well-circumscribed nodules located anywhere within the dermis; they can vary in size from 1 cm to 5 cm. They are characterized histologically by a proliferation of small basaloid cells arranged in cords, sheets, or discrete clusters that show prominent peripheral palisading. The cords of basaloid cells often grow as thin trabeculae that tend to branch out and often anastomose in a fibroepitheliomatous fashion (Fig. 49-38). The tumor cells are generally surrounded by a cellular stroma resembling perifollicular mesenchyma. Follicular differentiation may be observed in the form of foci resembling hair root structures or by the formation of structures that closely resemble the primitive hair papilla and hair bulb. Occasional mitoses may be scattered throughout the lesion without portending aggressive behavior.
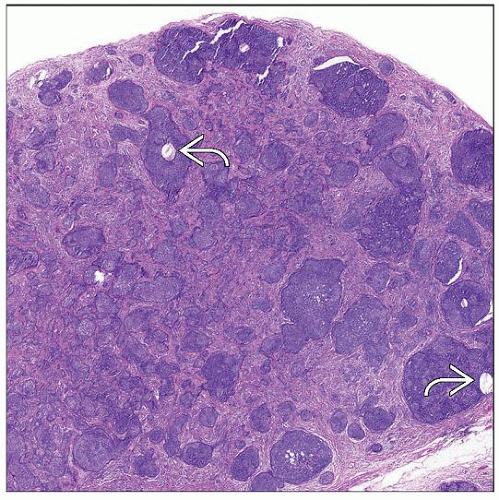
What is high magnification of a trichoblastoma?
High magnification of a trichoblastoma shows a lobular basaloid proliferation associated with a cellular, fibrotic stroma . Note the prominent stromal-stromal retraction artifact .
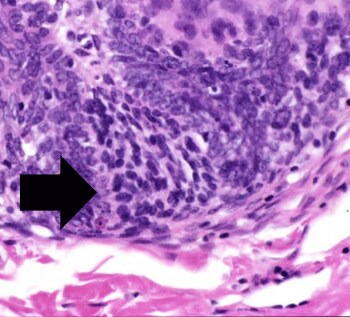
What is a clinical photograph of a nodular lesion on the eyelid of a patient with?
Clinical photograph shows a nodular lesion on the eyelid of a patient with a history of multiple trichoblastomas and trichoepitheliomas (TEs).
Is trichoblastic carcinosarcoma a metaplastic carcinoma?
192,193 The authors believed that the two cases were authentic carcinosarcomas and not examples of metaplastic carcinoma . 193 Both tumors were composed of two discrete components: the first was epithelial with some basaloid cells with frequent mitotic figures, nuclear atypia and focal nuclear crowding; the second was a stromal component which was composed of pleomorphic spindle-shaped cells with some bizarre multinucleated cells in this high-grade lesion. 192,193 The epithelial cell component stained for cytokeratin (AE1/AE3) and the stromal component for vimentin but not cytokeratin. 193 There was no recurrence of either tumor at follow-up. Further cases have since been reported. An underlying B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia was present in one case of trichoblastic carcinosarcoma, and also in a trichogenic carcinoma in the same series. 194
Does trichoma have sebaceous differentiation?
Trichoblastoma can show sebaceous differentiation in some cases. Scattered clear cells with multivacuolated cytoplasm are identified .
Is BCC a follicular differentiation?
This example of BCC showed areas of follicular differentiation (i.e., infundibulocystic type BCC); however, foci comedonecrosis are also identified , consistent with BCC.
Is TB a superficial lesion?
Trichoblastoma (TB) is closely related to TE, which may be considered a superficial type of TB. While the histologic findings are similar, TB is typically a larger and deeper nodular lesion, which may even extend into the subcutaneous tissue.
What is trichoblastoma?
In 1993, Ackerman proposed a new classification and suggested that the term trichoblastoma encompass all adnexal neoplasms of follicular germinative cells that show benign features, including sharp circumscription, smooth borders, and symmetrical growth patterns.
What is the diagnosis of trichoblastoma?
The diagnosis of trichoblastoma is considered when an asymptomatic raised skin-colored lesion appears on the scalp or the face of an individual. Cosmesis regarding the size or location of the lesion is a major patient concern associated with trichoblastomas.
What is the most common benign neoplam?
The most common benign neoplams associated with nevus sebaceous are trichoblastoma and syringocystadenoma papilliferum, and the most common malignant neoplasm is basal cell carcinoma. The youngest patient seen with trichoblastoma was a 4-year-old with nevus sebaceous.
How old is the youngest patient with solitary trichoblastoma?
The youngest patient seen with solitary trichoblastoma was an 11-year-old girl.
Does trichoblastoma recur?
Because of their dermal location, trichoblastomas treated with laser ablation have a tendency to recur.
Is excision a good option for trichoblastoma?
Complete excision is the best surgical option for patients with trichoblastomas for several reasons. Trichoblastoma is commonly a solitary lesion and basal cell carcinoma is an important differential diagnosis that needs to be ruled out. In addition, all adnexal tumors can extend deep into the dermis.
Is trichoblastoma malignant or benign?
Trichoblastomas are benign tumors with no systemic involvement. They can be locally aggressive, but malignant potential is very rare. However, there is one rare case of a patient who had malignant transformation of a long-standing trichoblastoma with lymphatic and hematogenous metastases.
What is the name of the cancer that flares up after fludarabine?
Davidovitz Y, Ballin A, Meytes D . Flare-up of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin following fludarabine therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Acta Hematol 1997; 98: 44–6.
Is TC a malignant transformation?
The path ogenesis of the TC is unknown. Malignant transformation may have been provoked by dysregulation of B-cell function and impairment of immune cell function secondary to the CLL ( 13 ). Various publications confirm an excess of Merkel cell carcinomas, basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas, and more aggressive variants of squamous cell carcinoma after non-Hodgkin's lymphoma ( 14, 15, 16 ). Other secondary cancers, however, particularly noncutaneous cancers such as renal cell carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma, are related to therapy for the non-Hodgkin's lymphoma ( 17, 18, 19 ). Therapy-induced skin cancer can be ruled out in our patient as his B-CLL was not treated. Lack of p53 expression in the TC implies mechanisms other than p53 mutations are responsible for malignant transformation.
Is trichoblastoma a tumor?
A “malignant trichoblastoma,” however, has not been described and does not represent an accepted entity and would not do justice to the vast majority of benign appendage tumors with germinative follicular differentiation. The described neoplasm was a highly aggressive tumor that necessitated systemic treatment. Therapy planning was expectantly complicated by the lack of experience with such a tumor. Response to radiation and chemotherapy was short-lived, and the TC proved ultimately to be therapy resistant. P-glycoprotein ( MDR-1 gene product) positivity in the primary TC may be related to the tumor cell resistance to cytotoxic drugs, and it is intriguing to speculate about its usefulness to predict treatment failure in solid tumors similar to leukemias ( 20 ).
Is adnexal tumor a trichogenic tumor?
Trichogenic adnexal tumors are rare neoplasms, the vast majority of which are benign. They have been separated in the past into trichoblastic fibromas, trichogenic trichoblastomas (TBs), and trichogenic myxomas according to their relative contents of epithelial and mesenchymal components ( 1 ). Other authors use the term TB for all benign cutaneous neoplasms that are constituted mostly of germinative follicular cells, and distinguish five patterns: large nodular, small nodular, cribriform, racemiform, and retiform ( 2 ). Histologic differentiation of TB ranges from rudimentary to mature forms of bulbs and papillae, outer and inner root sheaths, and hair ( 2 ). Variants of TB, such as a giant TB ( 3 ), adamantinoid TB (cutaneous lymphadenoma) ( 4 ), pigmented TB ( 5 ), a rippled-pattern TB ( 6 ), and nodular desmoplastic TB ( 7 ), have been reported. To our knowledge, no “malignant trichoblastomas” or malignant transformations have been described. We report an exceptional case of malignant hair appendage tumor, which we refer to as trichoblastic carcinoma (TC), in a patient with concomitant B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) with bone marrow involvement. The primary tumor still showed portions of benign TB with multiple transitions to malignant proliferations with rudimentary trichogenic differentiation. The metastases consisted predominantly of undifferentiated cells whose trichogenic derivation could be confirmed only by demonstration of hair keratin expression in frozen material. We present a detailed analysis of this exceptional case along with a discussion of the cause and differential diagnosis of malignant hair appendage tumors.