
- Type A Tympanogram Type A resembles a teepee and shows a normal middle ear system that has no fluid and an intact tympanic membrane. ...
- Tympanogram Type AD Type AD shoes high Compliant middle ear system and compliance of more than 1.5 ml. ...
- Tympanogram Type AS Type AS indicates less Compliant middle ear system and compliance of fewer than 0.3 ml. ...
What does a type B tympanogram mean?
What does a flat Tympanogram mean? A flat tympanogram (type B) means a stiff tympanic membrane and predicts fluid in the middle ear (a positive predictive value of approximately 90%). A normal tympanogram (type A) means a middle ear without fluid and an intact tympanic membrane (a negative predictive value up to more than 95%).
How to interpret a tympanogram?
How to Read a Tympanogram: Tympanometry is a method of assessing the status of the middle ear. The compliance (inverse of stiffness) of the tympano-ossicular system is charted against various pressure changes. X axis shows the pressure gradient. Y axis shows the compliance. There are three types of tympanograms.
When does a tympanogram look too “flat”?
If the tympanogram is abnormal, it may peak before or after the 0 daPa mark, or a flat line will be plotted if the eardrum doesn't move (due to perforation) or can't move (due to fluid or another cause). Note that daPa stands for decapascals, a unit of air pressure. Why is tympanometry used?
What is normal tympanometry?
range of 0.5 to 1.5 cc is typically considered normal, while for adults the range is 0.5 to 2.00 cc. This value is reported by the tympanometer, but not shown on the tympanogram graph. In general, classification of tympanograms is as follows: Type A tympanograms normal middle ear pressure Peak between +50 daPa to –200 daPa for children
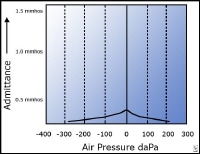
What does a type as tympanogram indicate?
Immittance Audiometry A Type A tympanogram indicates normal middle ear status. Reduced mobility of the tympanic membrane caused by a stiffened middle ear system can cause a shallow peak on the tympanogram, called a Type As tympanogram.
What is the peak pressure for a Type C tympanogram?
Type C tympanogram Type C tympanograms exhibit the following characteristics: Sharp peak. Middle ear pressure below -99 mmH2O. Static compliance between 0.3-1.6 cc in adults.
What does a Type C tympanogram look like?
Type C tympanograms (Figure 3) are still shaped like a teepee, but are shifted negatively on the graph. This indicates negative pressure in the middle ear space, often consistent with sinus or allergy congestion, or the end-stages of a cold or ear infection.
How do you read tympanogram results?
How do you read a tympanogram report? A tympanogram will show the results of one eardrum at a time. An “L” on the tympanogram indicates the left eardrum; an “R” indicates the right eardrum. A clinician will mainly look at the peak of each graph.
Is Type A tympanogram normal?
Tympanogram tracings are classified as type A (normal), type B (flat, clearly abnormal), and type C (indicating a significantly negative pressure in the middle ear, possibly indicative of pathology).
What are normal tympanometry results?
Middle ear pressure values ranging from +50 daPa to –200 daPa for children, and +50 daPa to –50 daPa for adults is generally considered normal. The compliance of the middle ear system is a measure of how well the system responds to sound.
What can cause a type B tympanogram?
Type “B” tympanogram pattern is not diagnostic of middle ear effusion. The same pattern can also be caused when the probe tip hole is occluded by cerumen or by contact with the canal wall. A type “B” pattern will also occur when there is a perforation in the TM, including a tympanostomy tube.
What type of tympanogram is conductive hearing loss?
Conductive hearing loss is often associated with Type B. Type C Tympanogram – This result tells us the person's Eustachian tube isn't working well. They could be just contracting or just recovering from otitis media.
How is fluid in middle ear diagnosis?
An instrument called a pneumatic otoscope is often the only specialized tool a doctor needs to diagnose an ear infection. This instrument enables the doctor to look in the ear and judge whether there is fluid behind the eardrum. With the pneumatic otoscope, the doctor gently puffs air against the eardrum.
What does positive pressure on tympanogram mean?
Type P is a peaked tympanogram with positive pressure higher than +50 daPa, often because of AOM with a bulging tympanic membrane. The tympanogram has to be compared with the history and objective findings.
What does middle ear effusion mean?
Otitis media with effusion (OME) is a collection of non-infected fluid in the middle ear space. It is also called serous or secretory otitis media (SOM). This fluid may accumulate in the middle ear as a result of a cold, sore throat or upper respiratory infection.
What does negative middle ear pressure mean?
Obstruction or blockage of the eustachian tube results in a negative middle ear pressure, which will cause the ear drum to retract (suck in). In adults this is usually accompanied by some ear discomfort, a fullness or pressure feeling and may result in a mild hearing impairment and ringing in the ear (tinnitus).
What does positive pressure on tympanogram mean?
Type P is a peaked tympanogram with positive pressure higher than +50 daPa, often because of AOM with a bulging tympanic membrane. The tympanogram has to be compared with the history and objective findings.
What does a double peak tympanogram mean?
Double‑peak tympanometry with an intact tympanic membrane may indicate diseases causing severe erosion in the EAC.
What is negative middle ear pressure?
Obstruction or blockage of the eustachian tube results in a negative middle ear pressure, which will cause the ear drum to retract (suck in). In adults this is usually accompanied by some ear discomfort, a fullness or pressure feeling and may result in a mild hearing impairment and ringing in the ear (tinnitus).
What is a highly compliant middle ear system?
Type Ad. Suggests a highly compliant middle ear system. Peak is between +/- 100 daPa. Compliance is more than 1.5 ml.
What is a tympanogram?
Tympanograms grade the middle ear function of your patients and appear in a graph format that can take a bit of practice to read! Tympanogram results are categorized as either a Type A, Type B, or Type C. Type A results are considered normal. Type B results are considered abnormal (or "flat") and often mean the patient has fluid in the middle ear.
What does a sharp peak on a ear test mean?
Normal results always have a single sharp peak. Double peaks indicate scarring of the eardrum. The patient should repeat the test to confirm this. Rounded peaks also indicate patients should retake the test.
What is compliance in ear?
Compliance is the flexibility of the eardrum when different air pressures are introduced . The level of flexibility indicates how effectively sound is transmitted into the middle ear.
What is the horizontal x axis of the eardrum?
Find the horizontal x axis that represents air pressure. The horizontal bottom line of the graph charts air pressure of the eardrum measured in millimeters (ml) of H20. The increments start at -400 on the left aside and increase by 100 to reach +200 on the far-right side.
How to tell if a type B is abnormal?
Look for a low, flat line to identify abnormal Type B results. Normal Type A readings show a peak on the graph. Type B tracings look like flat lines with no identifiable peaks. The flat line will appear low on the graph, closer to the horizontal x axis. These are considered abnormal results that require medical attention. Typically, it means there is fluid inside of the middle ear space.
How to identify a type A tracing?
Identify a Type A tracing by an evenly shaped peak on the graph. A Type A tracing is considered to be a normal result and no medical attention is required. A Type A tracing always looks like a single peak with equal sides on the chart. There are 3 categories that fall within the normal Type A range: Type A, Type AD, and Type AS.
What does a B test mean?
Type B results are considered abnormal (or "flat") and often mean the patient has fluid in the middle ear. Type C results may be caused by a blockage or retraction of the eardrum, which causes significant negative pressure in the middle ear.
What is the purpose of a tympanogram?
A tympanogram provides information regarding the compliance of the middle ear system (how well sound passes through the eardrum to the middle ear system), ear canal volume, and middle ear pressure. Compliance is plotted vertically on the tympanogram, and is measured in ml or mmho.
What does a larger ear canal volume mean?
In some cases, these tympanograms are seen when there is a hole in the ear drum; the difference lies in the ear canal volume: a larger ear canal volume indicates a perforation in the ear drum. Figure 2. Type B tympanogram.
The middle ear and its components
The tympanic membrane (TM) is a thin three-layer membrane, cone-like in shape, that separates the middle ear from the outer segments. During otoscopy, it is expected that a healthy, normal TM will reflect a cone of light, a reflection off of the membrane in the anterior inferior portion of the TM.
When is tympanometry conducted?
Tympanometry assesses the normal (or abnormal) functioning of the middle ear system. In other words, the efficiency of the middle ear. The test itself presents both positive and negative pressures accompanied by a constant probe tone. The test measures the amount of absorption or reflection of the probe tone from the middle ear space.
What does a tympanometer measure?
Tympanometry collects data to test four basic functions of the middle ear. The results of tympanometry are plotted on a graph called a tympanogram. A trained eye is needed to read and interpret a tympanogram, which can require some practice. A typical tympanometry result indicates the following:
Identifying the Data and Measurements on a Tympanogram
Tympanograms are classified by types – Type A, B, C, AS, and AD. Each classification indicates a range that falls between normal and abnormal.
How do you read a tympanogram report?
A tympanogram will show the results of one eardrum at a time. An “L” on the tympanogram indicates the left eardrum; an “R” indicates the right eardrum. A clinician will mainly look at the peak of each graph. The examples below use a 226 Hz probe tone. (Classifications can vary between audiologists, guidelines, countries, and clinics.)
A portable tympanometer that goes where you go
The KUDUwave Pro TMP is a portable audiometry system that integrates bilateral tympanometry for the very first time in the history of audiology. Dual tympanometers are integrated into each KUDUwave earcup enabling tympanometry of both ears without having to switch ears.
What is a tympanogram?
Understanding and Interpreting a Tympanogram. 1. Tympanogram: plots compliance changes of the Tympanic Membrane (TM) versus air pressure in the EAC. 2. Peak: point on the tympanogram that represents the point of maximum compliance, in which pressure of the external ear canal equals the pressure of the middle ear space (function of eustachian tube) ...
Which point on the tympanogram represents the point of maximum compliance?
2. Peak: point on the tympanogram that represents the point of maximum compliance, in which pressure of the external ear canal equals the pressure of the middle ear space (function of eustachian tube)
What does A'D mean in a TM?
3. A’d’: “deep” peak (hypercompliant), TM flaccid; suggests ossicular discontinuity or a “monomeric” TM
What is the difference between a less compliant TM and a less compliant TM?
The greater the positive or negative pressure in the ear canal, greater the “acoustic stiffness” of the tympanic membrane and lower is the compliance. Less compliant TM absorbs less sound and reflects more sound.
What is tympanometry test?
Tympanometry is a test of middle ear functioning. It looks at the flexibility (compliance) of the eardrum to changing air pressures, indicating how effectively sound is transmitted into the middle ear. This objective test also allows us to view the functioning of the Eustachian Tube, the upper auditory pathways and the reflex contraction from the middle ear muscles. Impedance testing is crucial in distinguishing a conductive loss from a sensorineural hearing loss. A typical tympanometry result indicates the ear canal volume (cm3), the max pressure (daPa) and the peak compliance (ml).
What does an audiogram represent?
An audiogram represents an individual’s hearing ability by frequency (pitch) and intensity (volume). The softest sounds that a person can hear at a particular frequency is called their hearing threshold. This is usually represented by markings on their graph; red represents the right ear and blue represents the left.
