Type B Tympanogram
- presence of hole inside the eardrum,
- the dissimilarity lies in the ear canal volume,
- a larger volume of the ear canal shows eardrum perforation.
- No identifiable peak in the graph
What is a normal tympanogram?
The tympanogram curve has a normal maximum height that occurs at a pressure close to zero and the width of the curve is normal. This is referred to as a type A tracing. In this figure, the ear canal volume is normal. Likewise, people ask, what does a Tympanogram show?
How to interpret a tympanogram?
How to Read a Tympanogram: Tympanometry is a method of assessing the status of the middle ear. The compliance (inverse of stiffness) of the tympano-ossicular system is charted against various pressure changes. X axis shows the pressure gradient. Y axis shows the compliance. There are three types of tympanograms.
When does a tympanogram look too “flat”?
If the tympanogram is abnormal, it may peak before or after the 0 daPa mark, or a flat line will be plotted if the eardrum doesn't move (due to perforation) or can't move (due to fluid or another cause). Note that daPa stands for decapascals, a unit of air pressure. Why is tympanometry used?
How to interpret tympanogram results?
Types of Tympanograms
- Type A, AS, and AD are considered to be normal
- Type B is considered abnormal, usually indicating that the patient has fluid in the middle ear
- Type C may indicate a blockage or retraction in the eardrum. Patients with a tympanogram graded Type C may need further medical attention.

What causes a type B tympanogram?
Type “B” tympanogram pattern is not diagnostic of middle ear effusion. The same pattern can also be caused when the probe tip hole is occluded by cerumen or by contact with the canal wall. A type “B” pattern will also occur when there is a perforation in the TM, including a tympanostomy tube.
What kind of condition does a type B tympanogram indicate?
A Type B tympanogram shows no clear peak pressure and is relatively flat. If the ear canal volume is normal, the Type B tympanogram may be reflective of an advanced stage of otosclerosis or a middle ear filled with an effusion (possibly caused by an ear infection).
What is Type B hearing?
Type B. Suggests middle ear involvement from fluid (middle ear effusion) There is no identifiable peak. Ear canal volume is normal.
What does an abnormal tympanogram mean?
Abnormal tympanometry test results may suggest: fluid in the middle ear. perforation of the eardrum (tympanic membrane) scarring of the eardrum, which usually results from frequent ear infections. middle ear pressure beyond the normal range.
Do I have eustachian tube dysfunction?
Symptoms of Eustachian tube dysfunction Your ears may feel plugged or full. Sounds may seem muffled. You may feel a popping or clicking sensation (children may say their ear “tickles”). You may have pain in one or both ears.
What type of tympanogram is considered normal?
Tympanogram tracings are classified as type A (normal), type B (flat, clearly abnormal), and type C (indicating a significantly negative pressure in the middle ear, possibly indicative of pathology).
How do you interpret tympanogram results?
How do you read a tympanogram report? A tympanogram will show the results of one eardrum at a time. An “L” on the tympanogram indicates the left eardrum; an “R” indicates the right eardrum. A clinician will mainly look at the peak of each graph.
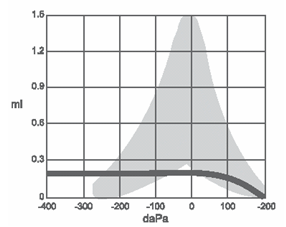
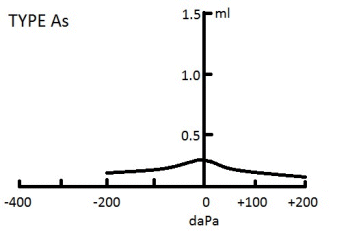
What type of hearing loss is a type as tympanogram?
Otitis media often leads to reduced sound transmission through the middle ear, resulting in temporary hearing loss that resolves when the fluid drains out. This is a tympanograph, which performs the tympanometry test.
What are normal tympanometry results?
Normative tympanometry values. Copied from "The Guide to Tympanometry for Hearing Screening" published by Maico Diagnostics. Typically, pressure is considered "normal" in the range of -150 to +25 daPa. A compliance peak within these normative values suggests a normal middle ear system.
What is Type C tympanogram?
Type C tympanograms (Figure 3) are still shaped like a teepee, but are shifted negatively on the graph. This indicates negative pressure in the middle ear space, often consistent with sinus or allergy congestion, or the end-stages of a cold or ear infection.
What does positive pressure on tympanogram mean?
Type P is a peaked tympanogram with positive pressure higher than +50 daPa, often because of AOM with a bulging tympanic membrane. The tympanogram has to be compared with the history and objective findings.
What does it mean to have negative pressure in your ear?
Obstruction or blockage of the eustachian tube results in a negative middle ear pressure, which will cause the ear drum to retract (suck in). In adults this is usually accompanied by some ear discomfort, a fullness or pressure feeling and may result in a mild hearing impairment and ringing in the ear (tinnitus).
What is the peak of a tympanogram?
The peak of a tympanogram is where the eardrum is balanced between negative and positive pressure. By using a template such as Jerger’s classification, it is possible to determine if the tympanic membrane moves freely or if a disorder is present.
What is tympanometry?
Tympanometry is a test where both negative and positive pressure is applied to the middle ear alongside a constant probe tone. Tympanometry assesses how much of the probe tone is absorbed into the middle and inner ear, and how much is reflected. This allows clinicians to form a picture of how the tympanic membrane acts and functions.
What type of tympanogram would suggest wax interference?
Alternatively, a very small ear canal volume with a type B tympanogram would suggest wax interference.
What is a large ear canal volume consistent with?
Tympanometry showed a large ear canal volume, consistent with a tympanic membrane perforation or patent grommet.
Does tympanometry show static compliance?
Tympanometry showed no measurable middle ear pressure or static compliance, consistent with middle ear pathology.
The middle ear and its components
The tympanic membrane (TM) is a thin three-layer membrane, cone-like in shape, that separates the middle ear from the outer segments. During otoscopy, it is expected that a healthy, normal TM will reflect a cone of light, a reflection off of the membrane in the anterior inferior portion of the TM.
When is tympanometry conducted?
Tympanometry assesses the normal (or abnormal) functioning of the middle ear system. In other words, the efficiency of the middle ear. The test itself presents both positive and negative pressures accompanied by a constant probe tone. The test measures the amount of absorption or reflection of the probe tone from the middle ear space.
What does a tympanometer measure?
Tympanometry collects data to test four basic functions of the middle ear. The results of tympanometry are plotted on a graph called a tympanogram. A trained eye is needed to read and interpret a tympanogram, which can require some practice. A typical tympanometry result indicates the following:
Identifying the Data and Measurements on a Tympanogram
Tympanograms are classified by types – Type A, B, C, AS, and AD. Each classification indicates a range that falls between normal and abnormal.
How do you read a tympanogram report?
A tympanogram will show the results of one eardrum at a time. An “L” on the tympanogram indicates the left eardrum; an “R” indicates the right eardrum. A clinician will mainly look at the peak of each graph. The examples below use a 226 Hz probe tone. (Classifications can vary between audiologists, guidelines, countries, and clinics.)
A portable tympanometer that goes where you go
The KUDUwave Pro TMP is a portable audiometry system that integrates bilateral tympanometry for the very first time in the history of audiology. Dual tympanometers are integrated into each KUDUwave earcup enabling tympanometry of both ears without having to switch ears.
What is a tympanogram?
Tympanograms grade the middle ear function of your patients and appear in a graph format that can take a bit of practice to read! Tympanogram results are categorized as either a Type A, Type B, or Type C. Type A results are considered normal. Type B results are considered abnormal (or "flat") and often mean the patient has fluid in the middle ear.
How to tell if a type B is abnormal?
Look for a low, flat line to identify abnormal Type B results. Normal Type A readings show a peak on the graph. Type B tracings look like flat lines with no identifiable peaks. The flat line will appear low on the graph, closer to the horizontal x axis. These are considered abnormal results that require medical attention. Typically, it means there is fluid inside of the middle ear space.
What is compliance in ear?
Compliance is the flexibility of the eardrum when different air pressures are introduced . The level of flexibility indicates how effectively sound is transmitted into the middle ear.
What is the horizontal x axis of the eardrum?
Find the horizontal x axis that represents air pressure. The horizontal bottom line of the graph charts air pressure of the eardrum measured in millimeters (ml) of H20. The increments start at -400 on the left aside and increase by 100 to reach +200 on the far-right side.
What does a sharp peak on a ear test mean?
Normal results always have a single sharp peak. Double peaks indicate scarring of the eardrum. The patient should repeat the test to confirm this. Rounded peaks also indicate patients should retake the test.
How to identify a type A tracing?
Identify a Type A tracing by an evenly shaped peak on the graph. A Type A tracing is considered to be a normal result and no medical attention is required. A Type A tracing always looks like a single peak with equal sides on the chart. There are 3 categories that fall within the normal Type A range: Type A, Type AD, and Type AS.
What does a B test mean?
Type B results are considered abnormal (or "flat") and often mean the patient has fluid in the middle ear. Type C results may be caused by a blockage or retraction of the eardrum, which causes significant negative pressure in the middle ear.
What is a type B tympanogram?
Type B tympanograms are a flat line (Figure 2), which is consistent with middle ear pathology, such as fluid or infection behind the ear drum.
What does flat tympanogram mean?
Subsequently, question is, what does a flat Tympanogram mean? Maximum compliance of the middle ear system occurs when the pressure in the middle ear cavity is equal to the pressure in the external auditory canal. Type B tympanograms are a flat line (Figure 2), which is consistent with middle ear pathology, such as fluid or infection behind the ear drum.
Why is tympanometry not reliable?
Tympanometry is not reliable in infants younger than seven months because of the highly compliant ear canals of infants. Tympanogram tracings are classified as type A (normal), type B (flat, clearly abnormal), and type C (indicating a significantly negative pressure in the middle ear, possibly indicative of pathology).
What is a tympanometer?
Tympanometry checks whether someone can get the treatment for the hearing loss by a hearing aid or not and whether the treatment will give relief or not. Tympanometer consist of the following; air pump, a probe with a loudspeaker, a microphone, and a manometer. There is no risk related to the tymp test.
What does tympanometry show?
The tympanometry result indicates; ear canal volume (cm3), the max pressure (daPa), and the peak compliance (ml). The test plays a crucial role in distinguishing between conductive hearing loss and sensorineural hearing loss.
How Is Tympanometry Performed?
Tympanometry is performed by a hearing healthcare professional or a doctor. The test can be performed in any hearing clinic by any of the audiologist/professional.
What is the tymp test?
The graphics representation of tymp test data is the tympanogram. Tympanogram represents the relationship between the air pressure in the ear canal and the movement of the eardrum, or tympanic membrane, and the tiny bones in the air-filled middle ear space.
What is the role of tympanometry in the eardrum?
Tympanometry provides some extra information Eustachian Tube Functioning.
Why do you need a tymp test for otoscopy?
Otoscopy test with tympanometry enhances the reliability of the diagnosis as there are several ear canal and eardrum abnormalities that in some cases cause might cause different types of abnormalities which can easily be traced through tympanogram. The graphics representation of tymp test data is the tympanogram.
What is the middle ear test?
There are many tests that makeup through evaluation and act like pieces of a puzzle which when put together helps to determine the type and cause of hearing loss. One such middle ear test is tympanometry. Tympanometry is a type of test which is helpful in determining if the hearing loss can be helped by hearing aid or any medical treatment is ...
What is tympanometry test?
Tympanometry is a test of middle ear functioning. It looks at the flexibility (compliance) of the eardrum to changing air pressures, indicating how effectively sound is transmitted into the middle ear. This objective test also allows us to view the functioning of the Eustachian Tube, the upper auditory pathways and the reflex contraction from the middle ear muscles. Impedance testing is crucial in distinguishing a conductive loss from a sensorineural hearing loss. A typical tympanometry result indicates the ear canal volume (cm3), the max pressure (daPa) and the peak compliance (ml).
What does an audiogram represent?
An audiogram represents an individual’s hearing ability by frequency (pitch) and intensity (volume). The softest sounds that a person can hear at a particular frequency is called their hearing threshold. This is usually represented by markings on their graph; red represents the right ear and blue represents the left.