
What does V1 T1 V2 T2 mean in chemistry?
What does v1 t1 v2 t2 mean? Charles Law Formula: V1/T1=V2/T2. This law was then used later on to determine the volume or temperature of a gas. Equations like the one below are now used.
What is the formula for P1v1 V1 T1?
P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2. ii. Note: the temperature (T) is expressed in degrees absolute. How do you convert to Charles Law? Based on the definition of Charles’ law, we can write the Charles’ law equation in the following way: V₁ / T₁ = V₂ / T₂ , where V₁ and T₁ are initial volume and temperature, respectively.
What is VT2 and VT1?
Also observed by way of a person’s breathing during exercise is VT2, or the second ventilatory threshold. It is a higher marker of intensity than VT1.
What is the relationship between P1v1 and P2v2?
The relationship for Boyle’s Law can be expressed as follows: P1V1 = P2V2, where P1 and V1 are the initial pressure and volume values, and P2 and V2 are the values of the pressure and volume of the gas after change.
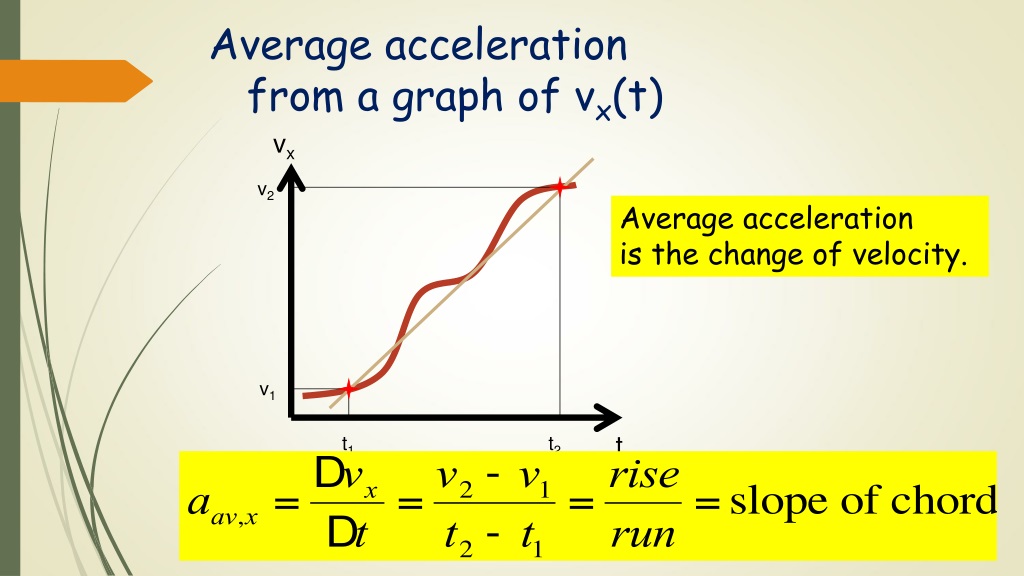
What type of relationship is V1 T1 V2 T2?
1:115:25Charles' Law - Volume and Temperature - V1/T1=V2/T2YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipMust be in Kelvin cannot stress that enough.MoreMust be in Kelvin cannot stress that enough.
What is P1 T1 P2 T2?
Gay Lussac's law defines the relationship between the pressure and temperature of a gas. As per this law, “The pressure of a given gas is proportional to its temperature, at a constant volume.” This law is mathematically represented as: P1 × T1 = P2 × T2.
What does this volume difference V1 V2 represent?
V1 = Volume at one state. V2 = Volume at another state. (KMT) – since a decrease in volume means that the gas particles will hit the wall more often, then there. is an increase in the pressure. Charles's Law – If amount and pressure of a gas are constant, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to temperature.
What is T1 in chemistry?
T1 limits the time between receipt of characters within a message block after the length byte has been received. It continues to limit the time until the receipt of the second checksum byte. [ SEMI E4-91] Search the Dictionary for More Terms.
What is v1 n1 v2 n2?
Avogadro's Law: V1n1=V2n2. Avogadro's Law also explains how when the temperature and pressure are constant, volume is directly proportional to gas amount (in moles), which means that as the volume increases, so does the amount of gas. Avogadro's Law also states that: Vn=k, where k is the proportionality constant.
How do you get v2 in combined gas law?
3:046:47Combined Gas Law - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipTimes p1 times v1 divided by t1 equals p2 times v2 now again I want to get this P 2 out of theMoreTimes p1 times v1 divided by t1 equals p2 times v2 now again I want to get this P 2 out of the numerator here. So that I can get v2 by itself so I'm gonna divide both sides of the equation by p2.
What is T1 and T2 in chemistry?
The relationship between volume and temperature is: V1 / T1 = V2 / T2 where V1 and T1 are the initial volume and absolute temperature and V2 and T2 are the final volume and absolute temperature (the Kelvin temperature, not the Celsius temperature).
How do you rearrange p1 T1 p2 T2?
1:417:32Rearranging the Combined Gas Equation - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo they cancel out and we're left with t2 equals t1 times p2 times v2 divided by p1 times v1 let'sMoreSo they cancel out and we're left with t2 equals t1 times p2 times v2 divided by p1 times v1 let's do one more example with a shortcut method. Here's two combined gas login.
How do you know which gas law to use?
If you're not given moles or mass, or not asked to calculate Moles or Mass, do not use the Ideal Gas Law. If you are given Moles or Mass, or asked to calculate Moles or Mass, the only thing you can use is Ideal Gas Law.
What is T2 in chemistry?
T2 limits the time between (1) the sending of ENQ (the code for "Request to Send") and the reception of EOT (the code for "Ready to Receive"); (2) the sending of EOT and the reception of the length byte; and (3) the sending of the checksum byte and the reception of any character. [ SEMI E4-91]
What is the formula for V2?
V₂ = V₁ / T₁ * T₂ . If you prefer to set the final volume and want to estimate the resulting temperature, then the equation of Charles' law changes to: T₂ = T₁ / V₁ * V₂ .
Who discovered the formula v1 t1 V2 T2?
Jacque CharlesIn mathematical terms, the relationship between temperature and volume is expressed as V1/T1=V2/T2. Alright. One of the gas laws that you might come across is called Charles Law, and Charles law was formed by Jacque Charles in France in the 1800s.
What 2 variables does Charles Law relate?
Explanation: Charles’s law defines the direct relationship between temperature and volume. When the parameters of a system change, Charles’s law helps us anticipate the effect the changes have on volume and temperature.
What does v1 t1 v2 t2 mean?
Charles Law Formula: V1/T1=V2/T2. This law was then used later on to determine the volume or temperature of a gas. Equations like the one below are now used. (Temperature must be in complete units i.e K) At 29.0 degrees a sample of nitrogen gas has a volume of 39.0L.
What does p1v1 t1 p2v2 t2 mean?
The general gas equation, namely: i. P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2. ii. Note: the temperature (T) is expressed in degrees absolute.
How do you convert to Charles Law?
Based on the definition of Charles’ law, we can write the Charles’ law equation in the following way: V₁ / T₁ = V₂ / T₂ , where V₁ and T₁ are initial volume and temperature, respectively. Similarly, V₂ and T₂ are the final values of these gas parameters.
What does Boyles law mean?
This empirical relation, formulated by the physicist Robert Boyle in 1662, states that the pressure (p) of a given quantity of gas varies inversely with its volume (v) at constant temperature; i.e., in equation form, pv = k, a constant. …
Is Charles Law direct or inverse?
Boyle’s law states that pressure (P) and volume (V) are inversely proportional. Charles’ law states that volume (V) and temperature (T) are directly proportional. Gay-Lussac’s law states that pressure (P) and temperature (T) are directly proportional.
What are the constant variables in Charles Law?
Charles’s law (also known as the law of volumes) is an experimental gas law that describes how gases tend to expand when heated. A modern statement of Charles’s law is: When the pressure on a sample of a dry gas is held constant, the Kelvin temperature and the volume will be in direct proportion.
What is VT1 in a ventilator?
on March 14, 2017. VT1 is called the first ventilatory threshold. It is a marker of intensity that can be observed in a person’s breathing at a point where lactate begins to accumulate in the blood.
How fast can you reach VT1?
Conversely, a more conditioned person will reach these markers at a higher intensity. For example, he or she may reach VT1 at a running speed of 6 miles per hour.
Can you talk at VT1?
A person who is at VT1 can no longer talk comfortably, —but can still string together a few words—while exercising,. Also observed by way of a person’s breathing during exercise is VT2, or the second ventilatory threshold. It is a higher marker of intensity than VT1.
Is lactate a higher marker of intensity than VT1?
It is a higher marker of intensity than VT1. At VT2, lactate has quickly accumulated in the blood and the person needs to breathe heavily. At this rapid rate of breathing, the exerciser can no longer speak. The exercise duration will necessarily decrease due to the intensity level.
