Virtue ethics
Virtue ethics are normative ethical theories which emphasize virtues of mind, character and sense of honesty. Virtue ethicists discuss the nature and definition of virtues and other related problems which focuses on the consequences of action. These include how virtues are acquired, how they are applied in various real life contexts, and whether they are rooted in a universal human nature or in a plurality …
Full Answer
What are the strengths and weaknesses of virtue theory?
Virtue Theory is an ethical framework that says that we ought to focus not on what rules to follow, but on what kinds of people (or organizations) we should be, and what kinds of ethical exemplars we ought to imitate.
What is an example of virtue theory?
What does virtue theory mean? Virtue ethics is a broad term for theories that emphasize the role of character and virtue in moral philosophy rather than either doing one's duty or acting in order to bring about good consequences.
What is virtue theory ethics?
Virtue theory synonyms, Virtue theory pronunciation, Virtue theory translation, English dictionary definition of Virtue theory. n. 1. a. Moral excellence and righteousness; goodness. b. An example or kind of moral excellence: the virtue of patience. 2. Archaic Chastity, especially in...
What are virtue ethical theories?
Virtue Ethics (or Virtue Theory) is an approach to Ethics that emphasizes an individual's character as the key element of ethical thinking, rather than rules about the acts themselves (Deontology) or their consequences (Consequentialism).

What is meant by virtue theory?
Virtue ethics is a broad term for theories that emphasize the role of character and virtue in moral philosophy rather than either doing one's duty or acting in order to bring about good consequences.
What is the main idea of virtue theory?
Virtue ethics suggests treating our character as a lifelong project, one that has the capacity to truly change who we are. The goal is not to form virtues that mean we act ethically without thinking, but to form virtues that help us see the world clearly and make better judgments as a result.Feb 16, 2016
What is an example of virtue theory?
They enable us to pursue the ideals we have adopted. Honesty, courage, compassion, generosity, fidelity, integrity, fairness, self-control, and prudence are all examples of virtues.
What is the theory of virtue of ethics?
Virtue Ethics (or Virtue Theory) is an approach to Ethics that emphasizes an individual's character as the key element of ethical thinking, rather than rules about the acts themselves (Deontology) or their consequences (Consequentialism).
Is virtue theory useful when faced with a moral dilemma?
Virtue theory can help those with a moral dilemma, if a person follows certain virtues, but, virtues can be misinterpreted, and mean different things to different people.
How do you become a virtuous person?
What are virtues? Aristotle sees virtues as character traits and tendencies to act in a particular way. We gain them through practice and by copying 'moral exemplars' until we manage to internalize the virtue. We become temperate by practicing temperance, courageous by practicing courage, and so on.May 21, 2018
Why is virtue theory important?
Virtue ethics allows people to maintain personal and interpersonal connections important for the good life. Virtue ethics does not fall victim to moral schizophrenia, which is one advantage it has over most other moral theories.
What is the difference between the rights and virtues theories?
An action is only right if it is an action that a virtuous person would carry out in the same circumstances. A virtuous person is a person who acts virtuously. A person acts virtuously if they "possess and live the virtues"
What is the most overrated virtue?
'Patience is the most overrated virtue'May 29, 2016
Who created virtue theory?
Virtue ethics is a philosophy developed by Aristotle and other ancient Greeks. It is the quest to understand and live a life of moral character. This character-based approach to morality assumes that we acquire virtue through practice.
What is virtue theory Aristotle?
Aristotle replies: “Virtue makes the goal right, practical wisdom the things leading to it” (1144a7–8). By this he cannot mean that there is no room for reasoning about our ultimate end. For as we have seen, he gives a reasoned defense of his conception of happiness as virtuous activity.May 1, 2001
How does Aristotle define virtues?
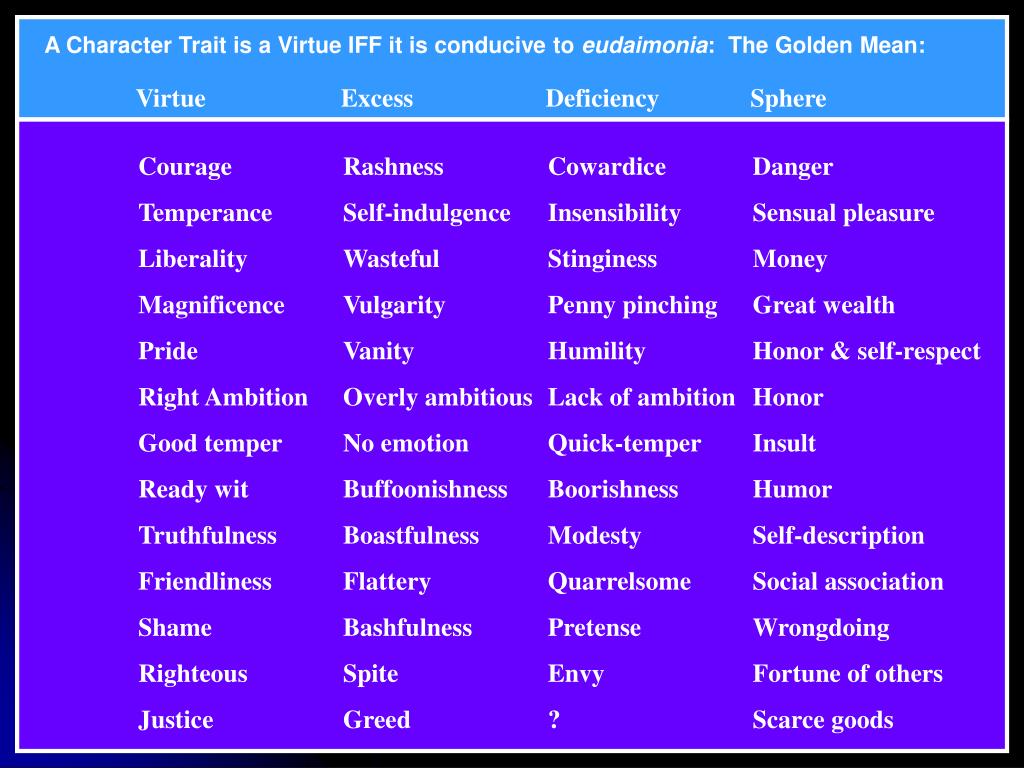
Aristotle defines moral virtue as a disposition to behave in the right manner and as a mean between extremes of deficiency and excess, which are vices.
What is the meaning of virtue?
1. the quality or practice of moral excellence or righteousness. 2. a particular moral excellence: the virtue of tolerance. 3. (Theology) any of the cardinal virtues (prudence, justice, fortitude, and temperance) or theological virtues (faith, hope, and charity) 4. any admirable quality, feature, or trait. 5. chastity, esp in women.
What is the virtue of patience?
b. An example or kind of moral excellence: the virtue of patience. 2. Archaic Chastity, especially in a woman. 3. A particularly efficacious, good, or beneficial quality; advantage: a plan with the virtue of being practical. 4.
What does "archaic" mean?
6. archaic an effective, active, or inherent power or force. 7. by virtue of in virtue of on account of or by reason of. 8. make a virtue of necessity to acquiesce in doing something unpleasant with a show of grace because one must do it in any case.
What are the 4 moral virtues?
Because of this reference, a group of seven attributes is sometimes listed by adding the four cardinal virtues (prudence, temperance, fortitude, justice) and three theological virtues (faith, hope, charity).
What are the 7 virtues in the Bible?
These seven virtues are: Chastity, Temperance, Charity, Diligence, Patience, Kindness & Humility/humble.
What are the criticisms of the virtue of ethics?
Moral philosophy is concerned with practical issues. Fundamentally it is about how we should act. Virtue ethics has criticized consequentialist and deontological theories for being too rigid and inflexible because they rely on one rule or principle. One reply to this is that these theories are action guiding.
What is the common good approach?
In philosophy, economics, and political science, the common good (also commonwealth, common weal, general welfare, or public benefit) refers to either what is shared and beneficial for all or most members of a given community, or alternatively, what is achieved by citizenship, collective action, and active
What are virtues of character?
Virtue, by definition, is the moral excellence of a person. Morally excellent people have a character made-up of virtues valued as good. They are honest, respectful, courageous, forgiving, and kind, for example. Virtues need to be cultivated to become more prevalent in life.
Why are virtue ethics important?
This decision would satisfy the virtuous person because it harmonizes motives and reasons. Virtue ethics allows people to maintain personal and interpersonal connections important for the good life. Virtue ethics does not fall victim to moral schizophrenia, which is one advantage it has over most other moral theories.
What is the difference between virtue and character?
Virtue ethics says that if we do virtuous things (virtues), then we are behaving morally. Virtue ethics considers character traits to be virtues — your character defines the virtues you practice or don't practice, and those make you moral or immoral.
What are practical virtues?
Practical virtues: habituating ourselves to do what is virtuous. Intellectual virtues: seeking theoretical knowledge. As such, while knowledge is important but is not sufficient. Their relation is reciprocal. We need to engage in both in order to approximate ourselves to the acquisition of virtue.
What is Aristotle's ethical framework?
Aristotle sets out to develop his ethical framework in a treatise called Nicomachean Ethics (probably named after his son Nichomacus who edited it), showing how members of a society can live a good and practical life.
What are the three types of good?
Aristotle divides the good into three different kinds: 1 Of the body (physical: healthy, food, drink) 2 External (honor, wealth, status) 3 Of the soul (intellect, virtues, knowledge): we need to attend to the soul.
What is the function of a doctor?
A doctor’s function is to heal/treat people; a carpenter’s is to build good furniture; running shoes, to be durable etc. A good doctor, therefore, is someone who fulfills her function. In a counterargument to Plato’s theory of forms, Aristotle asserts that there is no universal definition of a substance of goodness (in the sense of Plato), ...
What is virtue ethics?
Virtue ethics is a broad term for theories that emphasize the role of character and virtue in moral philosophy rather than either doing one’s duty or acting in order to bring about good consequences. A virtue ethicist is likely to give you this kind of moral advice: “Act as a virtuous person would act in your situation.”.
What is the Aristotelian virtue?
Aristotelian virtue is defined in Book II of the Nicomachean Ethics as a purposive disposition, lying in a mean and being determined by the right reason. As discussed above, virtue is a settled disposition. It is also a purposive disposition. A virtuous actor chooses virtuous action knowingly and for its own sake.
Why is virtue ethics important?
The emphasis on character development and the role of the emotions allows virtue ethics to have a plausible account of moral psychology —which is lacking in deontology and consequentialism. Virtue ethics can avoid the problematic concepts of duty and obligation in favor of the rich concept of virtue.
Why did Aristotle challenge consequentialist and deontological theories?
Both deontological and consequentialist type of theories rely on one rule or principle that is expected to apply to all situations. Because their principles are inflexible, they cannot accommodate the complexity of all the moral situations that we are likely to encounter.
What is agent based theory?
An agent-based theory emphasizes that virtues are determined by common-sense intuitions that we as observers judge to be admirable traits in other people. The third branch of virtue ethics, the ethics of care, was proposed predominately by feminist thinkers.
Is virtue eudaimonist or eudaimonist?
Not all accounts of virtue ethics are eudaimonist. Michael Slote has developed an account of virtue based on our common-sense intuitions about which character traits are admirable. Slote makes a distinction between agent-focused and agent-based theories. Agent-focused theories understand the moral life in terms of what it is to be a virtuous individual, where the virtues are inner dispositions. Aristotelian theory is an example of an agent-focused theory. By contrast, agent-based theories are more radical in that their evaluation of actions is dependent on ethical judgments about the inner life of the agents who perform those actions. There are a variety of human traits that we find admirable, such as benevolence, kindness, compassion, etc. and we can identify these by looking at the people we admire, our moral exemplars.
Why is morality self centered?
Moral praise and blame is attributed on the grounds of an evaluation of our behavior towards others and the ways in that we exhibit, or fail to exhibit, a concern for the well-being of others. Virtue ethics, according to this objection, is self-centered because its primary concern is with the agent’s own character. Virtue ethics seems to be essentially interested in the acquisition of the virtues as part of the agent’s own well-being and flourishing. Morality requires us to consider others for their own sake and not because they may benefit us. There seems to be something wrong with aiming to behave compassionately, kindly, and honestly merely because this will make oneself happier.
What is Aristotle's moral philosophy?
Aristotle’s moral philosophy called virtue ethics and based on his theory of the golden mean. He wrote about this in his book called Nicomachean Ethics, in which he explains the origin, nature and development of virtues, which are necessary to obtains life’s ultimate goal of happiness. He tries to show that ethical virtues are no different ...
What is Kant's moral duty?
Kant was an 18th century philosopher who examined the roots of philosophy and formed the deontological moral duty theory. This theory assesses the moral integrity of an action, based on its motive, irrespective of its consequence; hence asserting that an action can only be good if, and only if, its maxim is duty to the moral law. The basic structure of Kant 's construction of the moral law is the categorical imperative, which explains that we have a duty to act in the same way every time we are faced with an ethical decision. You do the right thing simply because it is the right thing to do. According to Kant only the categorical imperative provides an enlightened premise for making decisions without relying on any other order i.e.
Why is the death penalty given evenly?
This law is given evenly because as long as the evidence stands to prove that you’re guilty, no matter the race, ethnicity, or age. Most people feel that no one should be put to death because of the crime committed but they shouldn’t have any chance of parole. Others feel that the death penalty is the only justifiable thing in this case. In my opinion, the Hammurabi code was needed during that time period just to control a large amount of people but I just can’t see any nation doing this in modern day. Modern day death penalty is necessary in some cases such as murder and rape.
What is beneficial to Odysseus?
His decisions are beneficial to him, and him only. Odysseus does what he wants, and how it will affect others does not cross his mind. The Kyklops predicament could have been avoided if it were not for Odysseus’ desire to obtain total superiority. And it was unnecessary for Odysseus to glorify his bow and arrow triumph, but given the chance, he took the opportunity to do so. Egotistical behavior tends to be looked down upon, and is considered to be corrupt and reprehensible.
What are some similarities between Machiavelli and Washington?
Niccolò Machiavelli, Baldassare Castiglione and George Washington all had small factors of similarity within their interpretation of an ideal person, some more than others. Machiavelli valued the unpleasant truth, so that people would view the world with a notion of realism. He also always wanted to be in control and make his own decisions without anyone else's opinion to mar his idea of keeping authority with others. And he furthermore pushed the trait of fake sincerity. Instead of truthfully being honest, religious and merciful, he told one that you should fake it, so that when the time arrives, you can switch your personality.
What are Fowler's consequences for his actions?
What are Fowler’s consequences for his actions? When these two killings are compared, the main difference is that Fowler planned and prepared for his murder while Richard acted in the heat of the moment. In the laws eyes that makes Fowler’s killing worse because it is premeditated. Each of these killings has a clear motive or reason but that does not mean they are justified. The legal definition of murder differs depending on where you are, but is best defined as follows, “the killing of a human being by a sane person, with intent, malice aforethought (prior intention to kill the particular victim or anyone who
Did Dick deserve the death penalty?
Dick from In Cold Blood maintained that he was less guilty and did not deserve the death penalty. In stating this, Dick was not correct that he was less guilty. There are justifiable proofs that diminish his chances of being less guilty. These proofs are found within the book and can be represented through his demeanors and actions prior to and after the night. Richard Eugene Hickock (Dick) in In Cold Blood is just as guilty as Perry in that he had clearly displayed his intent for killing the Clutter family.
What does "virtue" mean?
a good or admirable quality or property: the virtue of knowing one's weaknesses. effective force; power or potency: a charm with the virtue of removing warts. virtues, an order of angels. Compare angel (def. 1). manly excellence; valor. SEE LESS.
What are the cardinal virtues?
any of the cardinal virtues (prudence, justice, fortitude, and temperance) or theological virtues (faith, hope, and charity) any admirable quality, feature, or trait. chastity, esp in women. archaic an effective, active, or inherent power or force. by virtue of or in virtue of on account of or by reason of.
What is the story of Mulan?
Mulan is the story of 1,500 years of shifting ideas about gender and virtue. The history of Mulan, from a 6th-century ballad to the live-action Disney movie | Constance Grady | September 4, 2020 | Vox. They also found, by analyzing speeches from Senate floor proceedings coded for virtue and vice signals,6 that United States senators were higher in ...
