How does water affect soil compaction?
Simply put, adding water to a dry soil during compaction allows soil particles to slide past one another more easily. Water acts as a lubricant, reducing interparticle friction. Great, so we’ll just add a whole lot of water and compaction will be easy, right? Not quite. We have to consider the incompressible nature of water when we’re adding water.
How does water compaction work with multi strike?
When a Pokémon with Water Compaction is hit by a Water-type move, its Defense rises by two stages. No immunity is granted to Water-type moves, however. If a Pokémon with this Ability is hit by a Water-type multi-strike move, each hit activates this Ability.
What does water compaction do in Pokemon?
Water Compaction (Japanese: みずがため Water Fortifying) is an Ability introduced in Generation VII. It is the signature Ability of Sandygast and Palossand . When a Pokémon with Water Compaction is hit by a Water-type move, its Defense rises by two stages. No immunity is granted to Water-type moves, however.
What is compaction and why is it important?
Compaction increases the bearing capacity of the soil and provides stability by increasing its shear strength. Compaction also helps prevent damage by frost, reduces settlement under dead and live loads, and reduces the permeability of the soil.
What is water compaction?
What happens when a Pokémon is hit by a water type move?
Does water compaction affect battle?
About this website
Water Compaction | Pokémon abilities | Pokémon Database
Sun / Moon Ultra Sun / Ultra Moon: Boosts the Pokémon’s Defense stat sharply when hit by a Water-type move. Sword / Shield B.Diamond / S.Pearl: Boosts the Pokémon’s Defense stat sharply when hit by a Water-type move.
Pokémon Showdown! battle simulator
October's Monthly Ladders. October’s monthly ladders come with all sorts of tricky surprises to serve as treats. The OMotM is Revelationmons, a format where a Pokemon’s move in the first slot dresses up to have the user’s primary typing and if the Pokemon has a secondary typing, the move in the second slot dresses up to have the user’s secondary typing.
What is Soil Compaction
Almost everyone knows “98% compaction” is a common specification in Calgary and across Alberta and that if you’re below 98% compaction, you have to keep compacting the fill. But what exactly are we engineers talking about when we specify a certain compaction percentage?
How Does Water Affect Soil Compaction?
If you’ve ever held a ball of really moist clay, you know how easily you can squish it in your hand and roll it into a ball. This is possible due to the water in the clay acting as a lubricant between the soil particles, allowing them to easily slide past each other and settle in closer together, increasing the density of the material.
How Does The Proctor Test Help?
The Proctor Compaction Test is a fairly simple test that is performed on multiple samples of the same soil. The only difference between each soil sample is their moisture content.
Cause
Fine-grained sediments (clays and silts) within an aquifer system are the main culprits in land subsidence due to groundwater pumping. Fine-grained sediments are special because they are composed of platy grains (imagine the shape of dinner plates).
Effect
The effects of compaction fall into two categories: those on manmade infrastructures and those on natural systems. The greatest effects occur to infrastructures that traverse a subsiding area. In the San Joaquin Valley, the main problems reported are related to water conveyance structures.
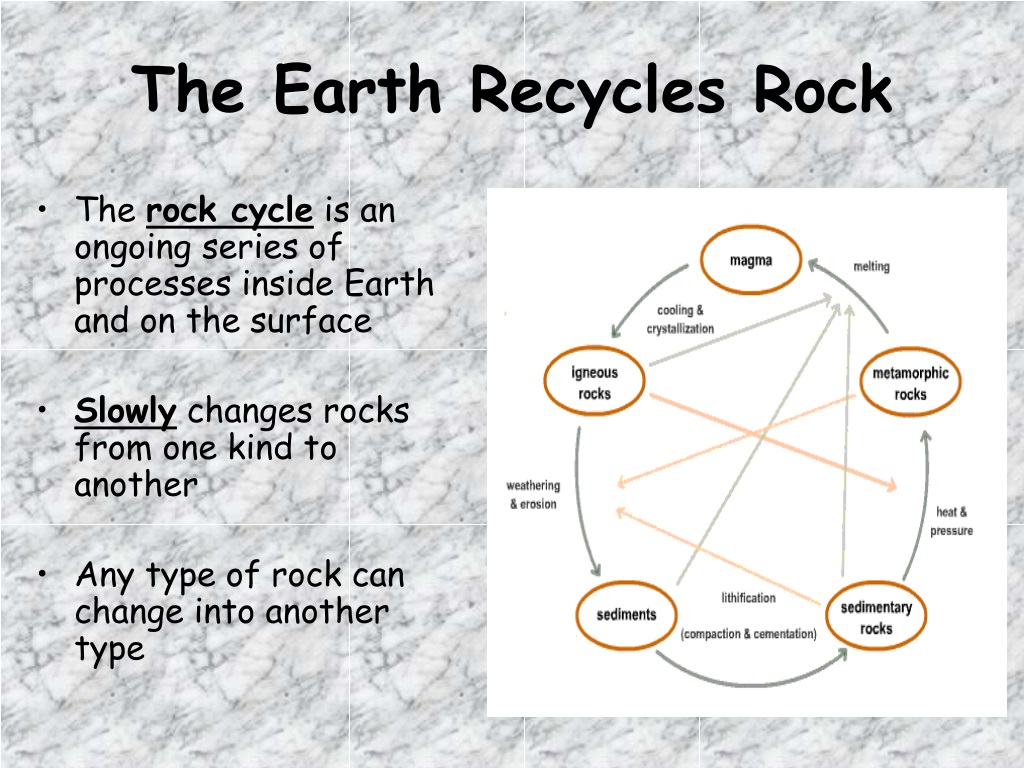
What is compaction?
Soil compaction occurs when soil particles are pressed together, reducing pore space between them (Figure 1). Heavily compacted soils contain few large pores, less total pore volume and, consequently, a greater density.
How does soil compaction affect soil strength?
Soil compaction changes pore space size, distribution and soil strength. One way to quantify the change is by measuring the bulk density. As the pore space decreases within a soil, the bulk density increases. Soils with a higher percentage of clay and silt, which naturally have more pore space, have a lower bulk density than sandier soils.
How much compaction does a load of 10 tons per axle cause?
Combining heavy axle loads and wet so il conditions increase compaction’s depth in the soil profile. For example, a load of 10 tons per axle or more on wet soils can extend compaction to depths of two feet or more. Because this is well below the depth of normal tillage, the compaction is more likely to persist compared to shallow compaction that can largely be removed by tillage.
Why is compaction increasing in the early season?
Increased potential for compaction early in the cropping season, due to more tillage activity and field traffic.
Why does soil compaction decrease yield?
As soil compaction increases beyond optimum, yields begin to decline. In dry years, soil compaction can lead to stunted, drought-stressed plants due to decreased root growth. Without timely rains and well-placed fertilizers, yields will reduce.
Why is it important to compact corn?
A slightly compacted soil can speed up the rate of seed germination because it promotes good seed-to-soil contact. This is why corn planters have been specifically designed to provide moderate compaction with planter-mounted packer wheels that follow seed placement.
What causes soil to compact?
Causes of compaction. There are several forces, natural and man-induced, that compact a soil (Figure 3). This force can be great, such as from a tractor, combine or tillage implement, or it can come from something as small as a raindrop. Listed below are causes of soil compaction.
What does compaction do to a building?
The process of compaction decreases the likelihood of settlement after a building, roadway, runway or parking lot is constructed. Settlement could result in premature pavement failure, costly maintenance or repairs.
What is Soil Compaction?
Soil compaction is the practice of applying mechanical compactive effort to densify a soil by reducing the void space between soil particles. Compaction occurs when particles are pressed together to reduce the space between them. Highly compacted soils contain very few spaces resulting in soil with higher unit weight. Maximum density is achieved at an optimum moisture content, or OMC, for short.
Why is Soil Compaction Necessary?
Soil compaction is necessary to increase the bearing capacity and stiffness of in-situ (natural state) or chemically modified soils. Compaction increases the shear strength of soils by adding friction from the interlocking of particles. Future settlement of soils is reduced by increasing the stiffness and eliminating voids creating a densified soil. The removal of voids reduces the chance of the soil settling or shrinking or expanding and it decreases water seepage that would lead to deleterious shrinking and swelling soil properties. Shrink / swell properties compromise the pavement structure thereby leading to premature failure of the pavement structure.
What Factors Affect Soil Compaction?
Different types of soil respond differently with respect to compaction. Soils are classified by their particle size and, in some soil categories, by their critical water content values or Atterberg limits. Well-graded granular soils that contain a wide range of particles are preferred in construction applications because they can be easily compacted, thus eliminating voids by interlocking the particles and resisting moisture absorption thereby allowing the soil to support heavier loads as a very dense soil. Poorly graded soils contain a narrow range of particle sizes and are less conducive for construction purposes due to the fact that the soil lacks shear strength, not associated with the non-interlocking particles because of their similar sizes.
What are the Different Methods Used to Compact Soil?
There are several methods used to compact soil. All methods involve a static and/or dynamic force along with manipulation of the soil. Static force uses the pressure of a weight to physically and continuously compact soil. Manipulation, such as kneading or shearing the soil in alternating movements, can compact soil at greater depths. In conjunction with pressure and manipulation, dynamic force can be applied by adding a vibrating mechanism. Vibratory compaction methods use different amplitudes (the amount of movement on an axis) and frequencies (the speed of the movement) to apply force in alternating directions, usually by the use of a rotating weight, to deliver rapid blows to the surface. This rearranges the soil particles so compaction not only occurs at the top layers but also in the deeper layers of the soil. Another dynamic method of soil compaction is impact compaction using a falling weight. This method is capable of compacting soil at deeper depths as well.
How do you do a Soil Compaction Test?
Several compaction testing methods can be used to determine the degree of compaction. Preliminary in-situ testing at the project site is important to understand what conditions are present initially. Sand cone testing, the use of a balloon densometer or Shelby Tube are all viable options but most commonly a nuclear density gauge is utilized to test for compaction in the field (ASTM D6938-08a). Laboratory methods generally involve compacting soil into molds at to obtain the soil density. For example the moisture density test (commonly referred to as the Proctor tests) (D698 and D1557) specifies compacting soil in a specified volume mold using standardized weight from a specified height. These requirements make for a controlled and reproducible amount of compacting force and provide the maximum density and optimum moisture content of a soil.
What Does 95 Percent Compaction Mean?
95 percent compaction means that the soil has been compacted to 95 percent of the possible density of the soil through compactive efforts. Maximum dry density, along with optimum moisture content, is determined in the laboratory and provides the target for field compaction. 95 percent is often used as a target compaction threshold to ensure that construction projects are erected on a solid platform. The compactive threshold will be provided by the designing engineer and will be based on the bearing capacity required for the final load to be structurally stable.
How does compaction work?
Compaction can be carried out by vibration, impact, kneading, or pressure, depending on the soil type whether cohesive or granular. Cohesive soils like clay, which are dense and closely bound, become plastic when wet and hard when dry.
What is the purpose of compaction?
Compaction ensures stable and settlement-free construction or installation. Compaction increases the bearing capacity of the soil and provides stability by increasing its shear strength. Compaction also helps prevent damage by frost, reduces settlement under dead and live loads, and reduces the permeability of the soil.
What Does Compaction Mean?
Compaction is the process of increasing the density of soil by mechanical means. It results in the rearrangement of soil particles and the reduction of voids. Soils that are highly compacted contain very few voids resulting in soil having a higher unit weight. The soil in its natural state is loosely bound and therefore compaction is necessary to increase its bearing capacity.
What are the factors that affect soil compaction?
Many factors affect soil compaction such as soil type, moisture content, compactor types, the thickness of lift, contact pressure, speed of rolling, and the number of rollers passes. The first three factors are explained in brief: · Soil Type. The degree of soil compaction depends on the type of soil being compacted.
What is the process of compaction of soil?
Soil compaction takes place when pore spaces between soil particles are drastically reduced by compacting using mechanical means. Well-compacted soils are highly dense with less total pore volume and very few large pores. Compacted soils also have a lower rate of water infiltration and drainage. Soils with a higher percentage of clay and silt have more pore space and hence a lower bulk density than sandy soils.
Why do we need soil compaction?
All types of construction processes require soil compaction to prevent the settlement of soil over time. Settlement can cause damage to the structure by inducing bending stresses and even tilt the structure where compaction is not adequate. Compaction ensures stable and settlement-free construction or installation.
How to increase water content in soil?
Water content in dry soil can be increased by spreading water. For wet soils, chemical drying is preferred by using Portland cement or lime-based reagents that absorb water. Different types of soil compaction rollers can be used such as single or double drums, vibratory mechanisms, or dozer blades.
Why add water to dry soil?
Simply put, adding water to a dry soil during compaction allows soil particles to slide past one another more easily.
What happens if you add too much water to a soil?
Adding too much water will cause air voids to be filled with water, limiting how closely soil particles can be pushed together.
Why can't soil particles be pushed together?
If we haven’t added enough water, soil particles cannot be pushed together due to high interparticle friction forces.
Does soil compaction depend on moisture?
Soil compaction depends on a few factors, not the least of which is moisture content. No contractor wants to pay for a water truck if they think they can just pound the backfill until it passes a compaction test.
What is water compaction?
Water Compaction (Japanese: みずがため Water Fortifying) is an Ability introduced in Generation VII. It is the signature Ability of Sandygast and Palossand .
What happens when a Pokémon is hit by a water type move?
When a Pokémon with Water Compaction is hit by a Water-type move, its Defense rises by two stages. No immunity is granted to Water-type moves, however. If a Pokémon with this Ability is hit by a Water-type multi-strike move, each hit activates this Ability.
Does water compaction affect battle?
Water Compaction has no effect outside of battle.
