Common Causes
White Spots in the Mouth: What Causes Them?
- Causes of White Patches in the Mouth. There are many reasons that white patches can develop in the mouth, including different forms of leukoplakia, fungal infections, and various types of ...
- Symptoms
- Diagnosis. ...
- Treatment. ...
- Prevention
- A Word From Verywell. ...
Related Conditions
The most common treatments, after oral hygiene, are:
- Use of local and oral steroids that have effect on T-lymphocytes and reduce inflammation.
- Use of local antibiotics, for example, chlorohexidine, benzidamine.
- Solving vitamin and mineral deficiency, such as B12, iron, folic acid, and avoidance of food allergens.
What would cause a white spot inside the mouth?
Are all white lesions in mouth cancerous? Most leukoplakia patches are noncancerous (benign), though some show early signs of cancer. Cancers on the bottom of the mouth can occur next to areas of leukoplakia. And white areas mixed in with red areas (speckled leukoplakia) may indicate the potential for cancer. Click to see full answer.
What are the most common oral lesions?
- Steroid creams and ointments which are usually the main trigger.
- Beauty products, cleansers and cosmetics applied to the area affected on the face. ...
- Harsh environmental conditions such as strong winds and ultraviolet (UV) light.
- Fluorinated toothpaste can as well cause bumps around mouth as research reveals.
Are all white lesions in mouth cancerous?
What causes white bumps in mouth and a rash?

What is white lesion in mouth?
Leukoplakia is a condition in which one or more white patches or spots (lesions) forms inside the mouth. Leukoplakia is different from other causes of white patches such as thrush or lichen planus because it can eventually develop into oral cancer.
What does a lesion in the mouth look like?
Canker sores may look like small oval-shaped ulcers in your mouth that appear white, gray, or yellow. They may be surrounded by a red “halo” of irritation. They may also appear as a painful red area. Canker sores are also called aphthous stomatitis or aphthous ulcers.
What does a white patch in the mouth look like?
Leukoplakia appears as thick, white patches on the inside surfaces of your mouth. It has a number of possible causes, including repeated injury or irritation. It can also be a sign of precancerous changes in the mouth or mouth cancer.
Why do oral cavity lesions turn white?
Many white lesions involving the oral mucosa are benign and do not require treatment. These include congenital or developmental conditions such as white sponge nevus, keratosis follicularis, hereditary benign intraepithelial dyskeratosis, pachyonychia congenita, and Fordyce granules.
What is the most common oral lesion?
Recurrent minor aphthous stomatitis, typically referred to as canker sores, is the most common recurrent lesion in the mouth, with a higher incidence in females.
When should I be concerned about oral lesions?
A sore in the mouth that doesn`t heal within 2 weeks. White or red lesions or ulcers on the tongue, gums, or lining of the mouth that don`t go away. Soreness or pain in the mouth that persists. A lump or thickening in the cheek area.
What does leukoplakia look like in the mouth?
White patches A white or grayish patch inside your mouth or on your lips is called leukoplakia. An irritant like a rough tooth, broken denture, or tobacco can cause cell overgrowth and produce these patches.
What does a mouth tumor look like?
Oral cancer may present as: patches of rough, white, or red tissue. a hard, painless lump near the back teeth or in the cheek. a bumpy spot near the front teeth.
Are white patches in mouth normal?
Leukoplakia is a condition in which thick, white or grayish patches form usually inside your mouth. Smoking is the most common cause. But other irritants can cause this condition as well. Mild leukoplakia is usually harmless and often goes away on its own.
Are most mouth lesions benign?
Most oral growths are benign. Warts, candidal infections, and repeated trauma are common causes of benign growths. Use of alcohol and tobacco and oral HPV infection are risk factors for cancer. Because cancer is difficult to diagnose by inspection, biopsy is often necessary.
What are the different types of oral lesions?
Large-scale, population-based screening studies have identified the most common oral lesions as candidiasis, recurrent herpes labialis, recurrent aphthous stomatitis, mucocele, fibroma, mandibular and palatal tori, pyogenic granuloma, erythema migrans, hairy tongue, lichen planus, and leukoplakia.
How can you tell the difference between lichen planus and leukoplakia?
3:144:33leukoplakia vs lichen planus : 10 points to differentiate clinicallyYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipHere you can see the greyish pigmentation as lichen prince has inflammatory reaction postMoreHere you can see the greyish pigmentation as lichen prince has inflammatory reaction post inflammatory pigmentation is the typical finding of lichen planus. But it is absent in case of liquor Plataea.
Are lesions in the mouth cancerous?
Most oral lesions are traumatic in nature and have no potential for cancer (Figure A). However, some oral lesions have an appearance which may raise suspicion by the dentist.
Do mouth lesions go away?
Although they can be painful, they generally heal on their own without any scarring around 1 to 2 weeks after onset. Some of the most common symptoms associated with minor canker sores include: small, oval-shaped bumps inside the mouth.
How do you treat mouth lesions?
Management and TreatmentUse over-the-counter topical anesthetic, such as Orajel™ or Anbesol®.Drink plenty of water.Practice good oral hygiene to keep your mouth as clean as possible.Rinse your mouth with warm saltwater a few times each day.Avoid hot and spicy foods until the ulcer heals.
What are the types of oral lesions?
Large-scale, population-based screening studies have identified the most common oral lesions as candidiasis, recurrent herpes labialis, recurrent aphthous stomatitis, mucocele, fibroma, mandibular and palatal tori, pyogenic granuloma, erythema migrans, hairy tongue, lichen planus, and leukoplakia.
Mixed Red and White Patches
A mixture of red and white patches in your mouth, called erythroleukoplakia, is an abnormal cell growth that’s more likely to become cancerous. If...
Canker Sores: Painful, but Not Dangerous
Know how to distinguish a canker sore from something more serious. A canker sore inside your mouth often burns, stings, or tingles before it’s visi...
Make Friends With Your Dentist
A regular dental checkup twice a year is an important cancer screening tool. These visits give your dentist the chance to detect any signs of oral...
Why is biopsy important?
Biopsy is essential to rule out carcinoma. Because it is virtually impossible to distinguish between these benign entities and carcinoma, biopsy is essential. If dysplasia is demonstrated, consider such lesions premalignant. They have the propensity to transform into carcinoma in situ or invasive squamous cell carcinoma.
What causes white mucosal lesions?
OVERVIEW OF CAUSES. White mucosal lesions may result from thickening of one or several layers of the oral epithelium. They vary in size and depth, generally have an irregular outline, and may be solitary or multifocal. Common sites are the buccal mucosa, lateral border of the tongue, floor of the mouth, and hard palate.
What causes mucosal abnormalities?
Their causes include infectious agents, metabolic disorders, endocrinopathies, injuries, neoplasms, developmental abnormalities, genetic syndromes, and immunologic disturbances.
Where does leukokeratosis occur?
Leukokeratosis, which can arise at any site in the oral cavity, occurs most often on the buccal mucosa and least often on the soft palate and gingiva (Figure 1). Peak incidence is in midlife, and men are more frequently affected.
What is the term for a white plaque in the mouth?
The term “leukokeratosis” is often used generically to describe any white, plaquelike lesion of the oral cavity. “Leukoplakia” is similarly applied by some authors.6 Others reserve the term “leukoplakia” for lesions that show dyskeratosis on histologic examination; they designate the remaining lesions “pachyderma orale.”7
What is the term for the thickening of the outer keratin layer?
Hyperkeratosis (thickening of the outer keratin layers), parakeratosis (persistence of pyknotic nuclei in the outer epithelial layer), acanthosis (enlargement or edema of the spinous layer of the skin), and dyskeratosis may be seen.
What causes inflammation of the tongue and lips?
The remainder of the tongue, soft palate, lips, and gingiva are less often involved. Chronic inflammation heads the list of many possible causes, but genetic disorders, infectious agents, and chemical substances may also be operative.
What is a white spot on the lip called?
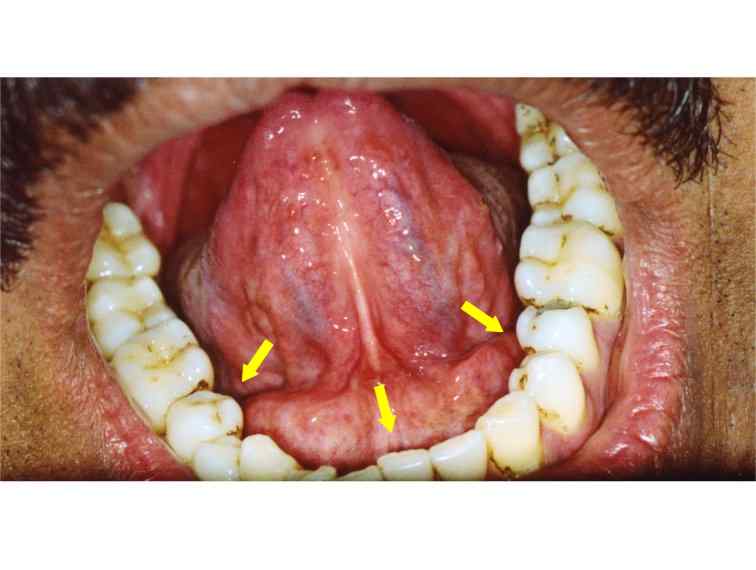
Asymptomatic. Multiple in number. Yellow in color. Flat or slightly elevated spots usually in the Lip or Buccal Mucosa. These are some of the White lesions seen in the Oral Cavity most of which as you can see are Asymptomatic and Benign and some of these can be Pre Malignant like Lichen Planus or Leukoplakia etc.
What are the clinical features of white lesions?
Clinical Features of White Lesions of the Oral cavity: 1. Lichen Planus – Clinical Features. Bilateral – seen on both sides of the oral cavity. Asymptomatic most of the times, except when there is erosion of the lesion. Buccal mucosa is the most common location, tongue, gingiva and palate are the less common locations. White Striae are seen.
What is white lesions in the mouth?
White Lesions of the Oral cavity is the pathological change in color of the Soft tissue in the Oral cavity, these lesions can be seen on Tongue, Buccal Mucosa, Floor of the mouth, Palate, Back of the mouth etc. Most White lesions of the Oral cavity are Benign and in most cases are Precancerous conditions which require immediate treatment.
Where is leukoedema located?
Located mostly on buccal mucosa extending up to lips along the occlusal line from bicuspid (premolars) to Molars. Leukoedema disappears when the cheeks are stretched – typical feature to distinguish this lesion from others. 4. Hairy Leukoplakia – Clinical Features.
What is white plaque on the tongue?
Elevated white plaques seen on the Tongue, buccal mucosa, palate etc which can be scrapped off leaving eroded, bleeding surface. Painful or Symptomatic. Seen in Immunocompromised patients, poor hygiene, prolonged use of systemic antibiotics, systemic diseases, reduced immune response, chronic infections. Seen in patients with poorly fitting ...
Is a white tongue precancerous?
So most of the White lesions being Precancerous, it is important to properly diagnose the disease which it is associated with and to know the cause of the lesion so it can be treated .
How long does it take for a canker sore to heal?
Pain from canker sores generally subsides in a few days, and the sores usually heal without treatment in one or two weeks. However, if sores are large, persistent and painful, your dentist might prescribe a corticosteroid ointment, an antimicrobial mouth rinse, a prescription or suggest an over-the-counter medication to reduce the irritation and pain.
What is the name of the white rash on the inside of the mouth?
1. Canker Sores . Canker sores are painful white ulcers in the mouth surrounded by an area of redness. They appear most often on the inside the cheeks, inside the lips, and your tongue. Canker sores are different from cold sores, which are caused by the contagious herpes virus, and canker sores are not contagious.
What is the white line on my tongue?
Hairy leukoplakia is a type of leukoplakia that can affect people whose immune systems are compromised by disease or medications. Hairy leukoplakia will cause fuzzy, white patches on your tongue, and it's often mistaken for oral thrush. 4. Common and Less Serious Causes. It is common and quite normal for people to have a white line along ...
Why are my mouth ulcers white?
Mouth ulcers are white because of thick layers of skin cells that form over the ulcer during the healing process. Damage to the mucosa caused by a rough tooth or the irregular surface of a denture or a filling.
What is the treatment for hairy leukoplakia?
However, chronic hairy leukoplakia will require treatment with an antiviral medication. 2. For Thrush (Candidiasis) The goal for any treatment of oral thrush is to stop the rapid spread of the fungus, and the best approach depends on your age, your overall health, and the cause of the infection.
Why is my tongue pink?
The mouth and tongue are lined with a special type of skin called mucosa; it appears mostly pink because it is thinner than your normal skin. Sometimes a change in its appearance is normal, and other times it can be an indication of illness or injury. White patches in mouth is a thick area in the lining of the mouth ...
What causes thrush in mouth?
2. Thrush (Candidiasis) Thrush is a mouth infection caused by an overgrowth of the Candida fungus that normally lives in many people's mouths.
What does a canker sore look like?
Abnormal cell growth usually appears as flat patches. A canker sore looks like an ulcer, usually with a depression in the center. The middle of the canker sore may appear white, gray, or yellow, and the edges are red. Canker sores are often painful, but they aren’t malignant.
How long does it take for leukoplakia to develop?
The patches may be rough and hard and difficult to scrape off. Leukoplakia generally develops slowly, over a period of weeks or months.
What does it mean when you have a red patch on your tongue?
A patch on your tongue, gums, tonsils, or the lining of your mouth can signal trouble. A white or red patch inside your mouth or on your lips may be a potential sign of squamous cell carcinoma. There is a wide range in how oral cancer may look and feel. The skin may feel thicker or nodular, or there may be a persistent ulcer or erosion.
Where is erythroplakia found?
You may find erythroplakia anywhere in your mouth, but it occurs most often in the floor of the mouth underneath the tongue or on your gums behind your back teeth.
How to reduce the risk of mouth cancer?
You can also cut down your risk of developing mouth cancer by avoiding tobacco products, including “dip” or “chew” and cigarettes, which have all been connected to mouth cancer. Last medically reviewed on April 10, 2017.
What is the red and white stuff in your mouth called?
A mixture of red and white patches in your mouth, called erythroleukoplakia, is an abnormal cell growth that’s more likely to become cancerous. If red and white patches last more than two weeks, you should see your dentist. You may see these mouth abnormalities before you feel them. In the early stages, mouth cancer may cause no pain.
What is it called when you have a white patch on your cheek?
A white or grayish patch inside your mouth or on your lips is called leukoplakia, or keratosis. An irritant like a rough tooth, broken denture, or tobacco can cause cell overgrowth and produce these patches. The habit of chewing the inside of your cheek or lips can also lead to leukoplakia.
What Do Mouth Sores Look Like?
The majority of mouth sores are round or oval, with a white or yellow center and a red border.
Types of Mouth Sores
Canker sores, also called aphthous ulcers, develop within the oral cavity. 3 They appear as small ulcers with a white, yellow, or gray center and a flat red border.
What Causes Mouth Sores?
You can develop mouth sores due to oral cancer, viral, fungal, or bacterial infections.
What Other Symptoms May Accompany Mouth Sores?
Mouth sores usually produce redness and pain, particularly while eating and drinking. They may also make the area surrounding the sore feel hot or tingly.
What Health Issues Can Mouth Sores Indicate?
Although mouth sores can be mild, harmless, and disappear within a few days, some mouth sores can be a sign of cancer, viral infection, bacterial infection, or fungal infection.
How to Get Rid of Sores in the Mouth
Most mouth ulcers will go away without treatment. However, if your mouth ulcers are frequent and painful, there are various things you can do to manage the condition.
How long does it take for a cancerous oral lesions to heal?
Signs and symptoms. The signs and symptoms of precancerous and cancerous oral lesions may include: A sore in the mouth that doesn`t heal within 2 weeks. White or red lesions or ulcers on the tongue, gums, or lining of the mouth that don`t go away. Soreness or pain in the mouth that persists. A lump or thickening in the cheek area.
How long does it take for a dental lesion to disappear?
The area in your mouth around the lesion may be stained with a special dye. The dye binds to precancerous and cancerous cells, staining only these cells. After a few hours, the color from the dye will disappear. Cytology. Your dental professional may scrape the surface of the lesion to obtain cells. The cells are then sent to a lab and checked ...
What is the best way to find out if a lesion is precancerous or cancerous?
Your entire mouth, including your lips and teeth, will be checked. A biopsy or other tests may also be done. Biopsy. This is the best way to find out if a lesion is precancerous or cancerous. During a biopsy, the area around the lesion will be numbed.
What is a precancerous oral cancer?
Precancerous oral lesions are abnormal cell growths in or around the mouth. They may become cancer. Cancerous oral lesions are life-threatening cell changes in the mouth. These lesions need to be found early to give you a better chance for a cure.
What are the lichen planus lesions?
Skin. Lesions usually appear as purplish, flat-topped bumps that are often itchy. Genitals. Lesions on the female genitalia often cause pain or burning and discomfort with intercourse.
Why do people with lichen planus need regular monitoring?
Symptoms can usually be managed, but people who have oral lichen planus need regular monitoring because they may be at risk of developing mouth cancer in the affected areas.
What is the white patch on the inside of the cheek?
Oral lichen planus. This white lacelike patch on the interior surface of the cheek is typical for oral lichen planus. Oral lichen planus (LIE-kun PLAY-nus) is an ongoing (chronic) inflammatory condition that affects mucous membranes inside your mouth.
What causes lichen planus?
Causes. It's not known what causes oral lichen planus. However, T lymphocytes — certain white blood cells involved in inflammation — appear to be activated in oral lichen planus. This could indicate an immune disorder, and genetic factors may be involved. But more research is needed to determine the exact cause.
Why is my T lymphocyte activated?
However, T lymphocytes — certain white blood cells involved in inflammation — appear to be activated in oral lichen planus. This could indicate an immune disorder, and genetic factors may be involved. But more research is needed to determine the exact cause.
What does it mean when your cheeks are red?
Pain or discomfort. The white, lacy patches may not cause discomfort when they appear on the inside of the cheeks. However, symptoms accompanying red, swollen patches and open sores may include: Burning sensation or pain. Sensitivity to hot, acidic or spicy foods.
Can lichen planus cause scarring?
Rarely, lichen planus may involve the mucous membrane surfaces of the eyes, and can cause scarring and blindness. Esophagus. Lichen planus of the esophagus is rare, but when it occurs, it may result in a narrowing of the esophagus or the formation of tightened, ringlike bands in the esophagus that can make swallowing difficult.
What causes white spots on the side of the mouth?
Lichen planus. Oral lichen planus is chronic inflammation in the mucous membranes in the mouth. It causes white, lacy markings in the mouth, which are not similar to the patchy white marks of leukoplakia. There is still debate regarding the association between lichen planus and cancer. However, some research.
What is a canker sore?
Canker sores are a common condition, with research suggesting that they may affect up to 20%#N#Trusted Source#N#of the general population. They are painful white lesions that occur in various areas inside the mouth.
How many people get oral cancer each year?
Oral cancer accounts for roughly 3% of all cancer diagnoses in the United States, meaning that about 53,000 people in the U.S. receive a diagnosis each year. Some signs of precancerous conditions may be indicators to see a doctor. In many cases, a person may have no noticeable symptoms at first. In this article, we discuss the appearance ...
What is oral cancer?
Oral cancer definition. Oral cancer is cancer that starts in the mouth, or oral cavity, which includes the: lips. tongue. tongue lining. gums. inside of the cheeks. hard palate (the bony roof of the mouth) floor of the mouth below the tongue .
What does mouth cancer look like?
Mouth cancer can appear on the lips or anywhere in the mouth, including the tissues inside the cheeks, the tongue, and the gums. It often causes changes in patches of skin, such as thick growths or sores that do not heal with time. Mouth cancer is a type of head and neck cancer, ...
What are the white spots on the side of the mouth that do not go away when you rub them?
Possible precancerous conditions for oral cancer may include: Leukoplakia: These are white or gray patches in the mouth that do not go away when a person rubs them. Erythroplakia: These are flat or slightly raised areas of tissue that are often red and may bleed easily on scraping.
Can lichen planus cause cancer?
suggests that people with lichen planus may have an increased risk of developing cancer of the lip, tongue, oral cavity, esophagus, and larynx. Anyone with lichen planus should check in with their doctor often for checkups and treatment.
What is the leading cause of oral cancer?
Cancer is most likely to result from infections that involve the tongue and base of the tongue into the throat. The type of HPV called HPV 16 causes most oral cancers related to HPV.
What is the best test for HPV?
The most useful test for HPV is a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test. A PCR test takes a tiny fragment of the DNA that scientists have extracted from cells in a sample of mucus and amplifies it, making countless identical copies.
How long does it take for oral cancer to go away?
Signs and symptoms of oral cancer include: a sore or painful bump that does not go away within 3 weeks. difficulty swallowing or the feeling of things sticking together when trying to swallow. discoloration (red, white, or black) of the soft tissues in the mouth. swollen but painless tonsils.
How many types of STI are there in the US?
Human papillomavirus is the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI) in the United States. There are more than 100 different types of the virus, about 40 of which can infect the mouth, throat, and genitals. In most cases, the immune system clears human papillomavirus (HPV) from the body before it can cause a full infection and symptoms.
How long does a sore on the tongue last?
seeking medical attention from a doctor or dentist for sores or growths in the mouth or on the tongue that last for more than 2–3 weeks.
How long does a lump in the mouth last?
a lump in the mouth that lasts for at least 3 weeks. a lump that a person feels on the outside of the neck. pain when chewing. a chronic sore throat or cough. persistent hoarseness. numbness or tingling in the lips or tongue. a unilateral, or one-sided, earache that lasts for more than 3 weeks. drooling.
What does "caudilli" mean?
painless. usually slow growing. smooth or slightly calloused. single or multiple in a cauliflower- or cobblestone-like mass. anywhere in the mouth, but frequently on the tongue, soft palate at the back or roof of the mouth, and lips.
