- Abstract. Whole Exome Sequencing (WES) is a powerful clinical diagnostic tool for discovering the genetic basis of many diseases.
- Introduction. ...
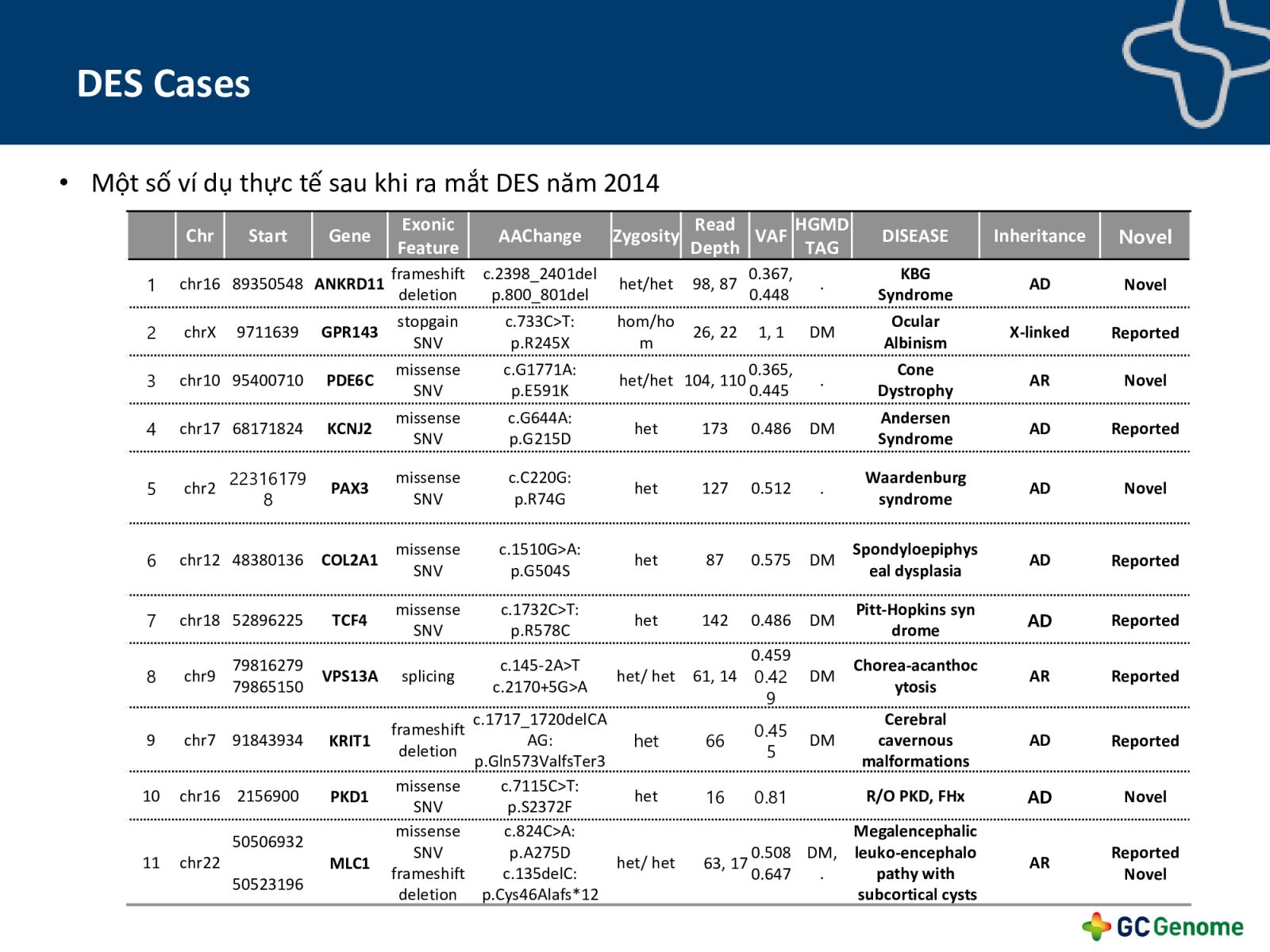
- Results. ...
- Discussion. ...
- Materials and Methods. ...
- Electronic supplementary material
- Acknowledgements. ...
- Author Contributions. ...
- Notes. ...
- Footnotes. ...
What is whole exome sequencing and how does it work?
Lauren Schlanger, MD, is a board-certified primary care physician with a focus on women's and transgender health. Whole exome sequencing (WES) is a process used to identify changes in your genes. This method is relatively new. As the technology advances, further research and more practical uses are expected to emerge.
Can exome sequencing be used to diagnose diseases?
Exome sequencing. Since these variants can be responsible for both Mendelian and common polygenic diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, whole exome sequencing has been applied both in academic research and as a clinical diagnostic.
Is whole-genome sequencing the most valuable?
Whole-genome sequencing. For translation of identified rare variants into the clinic, sample size and the ability to interpret the results to provide a clinical diagnosis indicates that with the current knowledge in genetics, exome sequencing may be the most valuable.
What does the new whole exome test mean for families?
The test is rapid whole exome sequencing, and it offers great hope: “This quick and accurate new test means rapid diagnosis and reassurance for families when they need it most, and gives babies and children the best chance of a healthy and happy life,” said NHS England chief executive Simon Stevens.

What diseases can whole-genome sequencing detect?
Dominant genetic diseases can also be tested — these diseases have a significant impact on the health of entire families and communities, and they include conditions such as Huntington's disease, Brugada syndrome, certain vascular malformations, neurofibromatosis type 1, Marfan syndrome, familial hypercholesterolemia, ...
What can whole exome sequencing not detect?
Exome sequencing is limited in detecting the following types of mutations (this list might not be exhaustive): large rearrangements. copy number variation mutations (large deletions/duplications) mitochondrial genome mutations.
Why is whole exome sequencing important?
This method allows variations in the protein-coding region of any gene to be identified, rather than in only a select few genes. Because most known mutations that cause disease occur in exons, whole exome sequencing is thought to be an efficient method to identify possible disease-causing mutations.
What can WES detect?
It compares the nucleotide sequence of the sampled DNA with a standard or “normal” DNA sequence. WES can pick up on mutations that are already known to cause disease. It can also detect changes in your genetic code that have not already been linked to a disease.
How accurate is whole exome sequencing?
“On average, we capture and sequence >99.4% of the exome with a quality enabling reliable variant calls. Coverage also refers to how many times each nucleotide is being sequenced.
What is a disadvantage of exome sequencing?
The major limitation of exome sequencing may be the inability to comprehensively represent genomic SVs. Many groups have designed algorithms that use a read depth or read pair-based approach for predicting structural variation; however, these approaches are not very efficient at identifying SVs with exome data.
How long does whole exome testing take?
Whole-exome sequencing typically takes a few months. Once the test is complete, a written report of the results will become part of the patient's electronic medical record, and the provider who ordered the test will follow up with the patient to discuss the results.
How much does exome sequencing cost?
Exome sequencing costs in various cancer and non-cancer patient groups are in the range of US$1292 to $3594 per patient [14, 17, 18]. These compare with per-patient costs of targeted panels of known clinical variants for patients with cancer of US$695 to $2861 (2018 prices) [19,20,21,22].
Is whole genome sequencing worth it?
That's why doctors don't routinely recommend whole genome sequencing. But as the cost of sequencing continues to plummet and companies offer more and more ways for consumers to peer into their DNA, physicians are trying to figure out how genetic data might work into your next check-up.
How many reads for whole exome?
Currently, we target a minimum of 25 million paired-end 150 base reads which will yield an average read-depth of at least 75x.
What is exome sequencing data?
Abstract. Whole exome sequencing (WES) enables the analysis of all protein coding sequences in the human genome. This technology enables the investigation of cancer-related genetic aberrations that are predominantly located in the exonic regions.
What does genome sequencing tell you?
Sequencing DNA means determining the order of the four chemical building blocks - called "bases" - that make up the DNA molecule. The sequence tells scientists the kind of genetic information that is carried in a particular DNA segment.
What is the purpose of whole exome sequencing?
Whole exome sequencing (WES) is a molecular genetic process that can be used to identify alternations in genes. This method is relatively new, and as the technology advances rapidly, further research and the discovery of more practical clinical purposes are expected to emerge. Genetic testing is becoming very popular—you can purchase products ...
How much DNA does an exon contain?
Exons account for only 1 to 2 percent of your total DNA. Each exon actually begins with a nucleotide sequence that prompts protein production to start, and ends with a nucleotide sequence that prompts the termination of protein production.
What is WES used for?
WES can be used to look for patterns to find the genetic cause of a medical disease. Your chromosomes are molecules that contain your genetic code. (You have 23 pairs of chromosomes—these are also called DNA molecules.) They are composed of long strands of nucleotide molecules. Your body reads the sequence of the nucleotides on your chromosomes ...
What is a microarray genetic test?
Also described as microarray genetic testing, these studies compare a small section of your DNA to known genes or to a selected DNA sequence to find alterations or known mutations in a specific area on a chromosome.
What is the name of the whole set of chromosomes?
Exome . All of the exons in your whole entire set of chromosomes are referred to as the exome. Whole ex ome genome sequencing looks at your whole exome to identify abnormalities that could be responsible for a disease or a health problem.
What is chromosomal analysis?
Chromosomal analysis is also described karyotyping. This test can analyze all of your chromosomes to see if there are changes, such as an extra copy of a chromosome or a missing chromosome. Chromosomal testing can also detect substantial changes in chromosome structure, such as elongated or short chromosomes.
Does insurance cover WES testing?
Cost. It is important that you check the cost of testing, and also check whether your health insurance will cover the cost of the test. WES is a relatively new type of technology and your insurance company may or may not cover the cost, depending on their policies.
How does exome sequencing help diagnose disease?
Exome sequencing can be used to diagnose the genetic cause of disease in a patient. Identification of the underlying disease gene mutation (s) can have major implications for diagnostic and therapeutic approaches, can guide prediction of disease natural history, and makes it possible to test at-risk family members. There are many factors that make exome sequencing superior to single gene analysis including the ability to identify mutations in genes that were not tested due to an atypical clinical presentation or the ability to identify clinical cases where mutations from different genes contribute to the different phenotypes in the same patient.
Why is exome sequencing important?
Motivation and comparison to other approaches. Exome sequencing is especially effective in the study of rare Mendelian diseases, because it is an efficient way to identify the genetic variants in all of an individual's genes. These diseases are most often caused by very rare genetic variants that are only present in a tiny number of individuals;
What was the first company to offer exome sequencing services to consumers?
Knome was the first company to offer exome sequencing services to consumers, at a cost of several thousand dollars. Later, 23andMe ran a pilot WES program that was announced in September 2011 and was discontinued in 2012. Consumers could obtain exome data at a cost of $999.
What is the next generation sequencing platform?
There are many Next Generation Sequencing sequencing platforms available, postdating classical Sanger sequencing methodologies. Other platforms include Roche 454 sequencer and Life Technologies SOLiD systems, the Life Technologies Ion Torrent and Illumina's Illumina Genome Analyzer II (defunct) and subsequent Illumina MiSeq, HiSeq, and NovaSeq series instruments, all of which can be used for massively parallel exome sequencing. These 'short read' NGS systems are particularly well suited to analyse many relatively short stretches of DNA sequence, as found in human exons.
What is the exome sequencing workflow?
Exome sequencing, also known as whole exome sequencing ( WES ), is a genomic technique for sequencing all of the protein-coding regions of genes in a genome (known as the exome ). It consists of two steps: the first step is to select only the subset of DNA that encodes proteins.
What are the challenges of sequencing?
Challenges associated with the analysis of this data include changes in programs used to align and assemble sequence reads. Various sequencing technologies also have different error rates and generate various read-lengths which can pose challenges in comparing results from different sequencing platforms.
How to capture genomic regions of interest?
To capture genomic regions of interest using in-solution capture, a pool of custom oligonucleotides (probes) is synthesized and hybridized in solution to a fragmented genomic DNA sample. The probes (labeled with beads) selectively hybridize to the genomic regions of interest after which the beads (now including the DNA fragments of interest) can be pulled down and washed to clear excess material. The beads are then removed and the genomic fragments can be sequenced allowing for selective DNA sequencing of genomic regions (e.g., exons) of interest.
What is exome sequencing?
ExomeSeq is a test that looks at most of the genes. This test may be useful for patients whose medical and family histories suggest a genetic cause for their signs and symptoms. Most patients who have whole exome sequencing (WES) have had other genetic testing that did not find a genetic cause of their condition.
What is the exome?
The exome includes only the exons (the parts used to make proteins ). The introns and other non-coding sequences of DNA are not part of the exome. If you think of the genome as all of the action in a football game, the exome is like the game highlights with many of the important plays. Genetic Testing Show.
What does genetic testing show?
Genetic Testing Show. There are several types of genetic tests. Some genetic tests “read” the genetic code of a single gene to see if that gene has any changes. Other genetic tests look for extra or missing pieces of DNA. Whole exome sequencing reads through the exons of most of the genes all at once. Mutations Show.
Why is WES important?
WES is one of the most extensive genetic tests available. Because WES looks at more genes than most genetic tests, it may find a genetic cause for your or your child’s signs and symptoms even if previous genetic testing did not.
How long does DNA stay in the lab?
The laboratory will keep leftover DNA for WES for two years, and may discard those samples after two years. The laboratory will store the information from this test for 20 years. The data will be stored on a protected computer and will be kept safe.
How many copies of genes are there in the human body?
People generally have two copie s of most genes, one copy from each parent. Parts of a Gene Show.
Can WES find a genetic cause?
It is possible that WES will find a genetic cause of your or your child’s condition. Identifying the genetic cause of your or your child’s symptoms may change your medical treatment, but may or may not help predict the outcome of the condition. Negative Results.
Why is whole exome sequencing important?
Because most known mutations that cause disease occur in exons, whole exome sequencing is thought to be an efficient method to identify possible disease-causing mutations. However, researchers have found that DNA variations outside the exons can affect gene activity and protein production and lead to genetic disorders--variations ...
What is the purpose of whole genome sequencing?
Another method, called whole genome sequencing, determines the order of all the nucleotides in an individual's DNA and can determine variations in any part of the genome. While many more genetic changes can be identified with whole exome and whole genome sequencing than with select gene sequencing, the significance of much ...
What is the name of the part of the genome that is used to sequence the exons?
These pieces, called exons, are thought to make up 1 percent of a person's genome. Together, all the exons in a genome are known as the exome , and the method of sequencing them is known as whole exome sequencing. This method allows variations in the protein-coding region of any gene to be identified, rather than in only a select few genes.
What is the name of the method used to identify genetic variations?
Two methods, whole exome sequencing and whole genome sequencing, are increasingly used in healthcare and research to identify genetic variations; both methods rely on new technologies that allow rapid sequencing of large amounts of DNA. These approaches are known as next-generation sequencing (or next-gen sequencing).
What is next generation sequencing?
These approaches are known as next-generation sequencing (or next-gen sequencing). The original sequencing technology, called Sanger sequencing (named after the scientist who developed it, Frederick Sanger), was a breakthrough that helped scientists determine the human genetic code, but it is time-consuming and expensive. ...
What is the name of the process of determining the order of DNA building blocks?
Determining the order of DNA building blocks (nucleotides) in an individual's genetic code, called DNA sequencing, has advanced the study of genetics and is one technique used to test for genetic disorders.
How long does it take to sequence a human genome?
Next-generation sequencing has sped up the process (taking only days to weeks to sequence a human genome) while reducing the cost. With next-generation sequencing, it is now feasible to sequence large amounts of DNA, for instance all the pieces of an individual's DNA that provide instructions for making proteins.
Why is the exome important?
The advantages. Because the exome represents only a fraction of the DNA in the whole genome, it can be sequenced more easily and interpreted more quickly, meaning potentially faster results for patients .
What is the exome?
What is an exome? The parts of our DNA that code for proteins are known as ‘ exons ’ . These make up around 2% of the human genome and are collectively known as the exome. The exome is the best studied and most well understood part of the genome, and is where the vast majority of known disease-casing variants are found.
How many babies have the sex test?
The test has been used for 80 babies and children since it was introduced in the NHS in October 2019, and more than half of these children received a diagnostic result. Around 700 young patients are expected to benefit from the new test each year.
Is there disease causing variant outside the exome?
Though we know less about the areas of the genome that are not responsible for coding for proteins (see our articles about ’junk’ DNA and unlocking the secrets of the genome ), there are disease-causing variants outside the exome.
Is the NHS offering genome sequencing?
The NHS has committed to offering whole genome sequencing to children with cancer and rare genetic disorders as part of the 2019 Long Term Plan, which aims to incorporate genomics and personalised medicine across the NHS, including sequencing half-a-million genomes by 2024. –.

How Genes Work
Exome
- All of the exons in your entire set of chromosomes are referred to as the exome. WES, then, looks at your whole exome to identify changes that could be responsible for a disease or a health problem. WES is quite thorough, and it looks at all of the genes in your body. Keep in mind, though, that it does not examine introns at all. Introns may have s...
Process
- WES uses a blood sample to analyze your genes. Every cell in your body has a full copy of all 46 chromosomes, so blood cells work fine for this type of test. WES can pick up on mutations that are already known to cause disease. It can also detect changes in your genetic code that have not already been linked to a disease.
Considerations
- If you or your child is going to have WES done, you need to be aware of the implications. There are a variety of things to consider before undergoing WES. They include privacy concerns, but also how you will handle what you now know about yourself. This is one area where you may wish to make a genetic counseling appointment, and have professionals discuss what the findings mea…
Deciding on A Test
- There are several similar genetic tests that evaluate your chromosomes differently than WES, and there are strengths and weaknesses for each different type of test.
Genetic Counseling
- As with other kinds of genetic tests, WES may deliver results that seem alarming or that are hard to understand. The field of genetics has grown so quickly that it feels hard to keep up, but there are professionals trained in genetic counseling to help you sort through such personal information. Whether you're concerned about cancer after some troubling test results, or you wa…
Summary
- The field of genetics is changing the approach to medical care, and people know more than ever about how genes affect their health. That will only become more true in the future. For now, there are a number of tests including the WES. These genetic tests may be used for a range of different reasons, but they're all meant to help you protect your health or understand why it changed. The …
A Word from Verywell
- WES is still a relatively new method of genetic testing and it isn't yet clear how it can best be used. If treatment for a genetic condition is targeted, as in the case of many new drugs, you may have a lot to gain through the test. Even if the tests don't change your care, they still may help with your prognosis or with advice for at-risk family members. But it's a lot of information, so be sure to ca…
Overview
Exome sequencing, also known as whole exome sequencing (WES), is a genomic technique for sequencing all of the protein-coding regions of genes in a genome (known as the exome). It consists of two steps: the first step is to select only the subset of DNA that encodes proteins. These regions are known as exons—humans have about 180,000 exons, constituting about 1% of the human geno…
Applications of exome sequencing
By using exome sequencing, fixed-cost studies can sequence samples to much higher depth than could be achieved with whole genome sequencing. This additional depth makes exome sequencing well suited to several applications that need reliable variant calls.
Current association studies have focused on common variation across the genome, as these are the easiest to identify with our current assays. However, disease-causing variants of large effec…
Motivation and comparison to other approaches
Exome sequencing is especially effective in the study of rare Mendelian diseases, because it is an efficient way to identify the genetic variants in all of an individual's genes. These diseases are most often caused by very rare genetic variants that are only present in a tiny number of individuals; by contrast, techniques such as SNP arrays can only detect shared genetic variants that are common to many individuals in the wider population. Furthermore, because severe dise…
Technical methodology
Target-enrichment methods allow one to selectively capture genomic regions of interest from a DNA sample prior to sequencing. Several target-enrichment strategies have been developed since the original description of the direct genomic selection (DGS) method in 2005.
Though many techniques have been described for targeted capture, only a fe…
Comparison with other technologies
There are multiple technologies available that identify genetic variants. Each technology has advantages and disadvantages in terms of technical and financial factors. Two such technologies are microarrays and whole-genome sequencing.
Microarrays use hybridization probes to test the prevalence of known DNA sequences, thus they cannot be used to identify unexpected genetic changes. In contrast, the high-throughput sequen…
Data analysis
The statistical analysis of the large quantity of data generated from sequencing approaches is a challenge. Even by only sequencing the exomes of individuals, a large quantity of data and sequence information is generated which requires a significant amount of data analysis. Challenges associated with the analysis of this data include changes in programs used to align and assemble sequence reads. Various sequencing technologies also have different error rates …
Ethical implications
New technologies in genomics have changed the way researchers approach both basic and translational research. With approaches such as exome sequencing, it is possible to significantly enhance the data generated from individual genomes which has put forth a series of questions on how to deal with the vast amount of information. Should the individuals in these studies be allowed to have access to their sequencing information? Should this information be shared with …
See also
• DNA profiling
• Genetic counseling
• Personalized medicine
• Transcriptomics
• Whole genome sequencing