
See more
What goes into the duodenum?
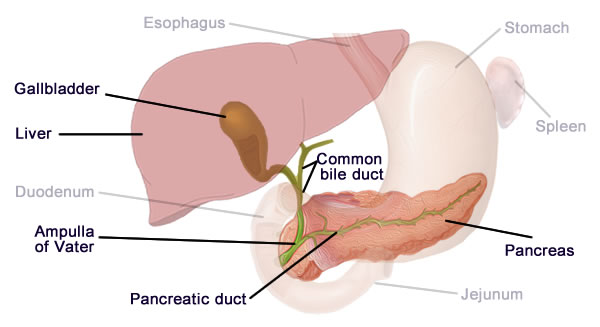
The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine. It is located between the stomach and the middle part of the small intestine, or jejunum. After foods mix with stomach acid, they move into the duodenum, where they mix with bile from the gallbladder and digestive juices from the pancreas.
What organs release secretions into the duodenum?
Pancreas: Your pancreas is located behind your stomach and is attached to both your gall bladder and your small intestines. Among other functions, the pancreas aids in digestion by producing digestive enzymes and secreting them into the duodenum (the first segment of the small intestine).
What are the three juices released in the duodenum?
Correct answer: A. ... ∙ There are three specific secretions in the small intestine which are bile secreted from the liver, pancreatic juice secreted from the pancreas and the intestinal juice secreted from the intestinal epithelium. ... ∙ Gastric juice is present in the stomach and is not present in the small intestine.
How many organs are empty into the duodenum?
Chemical digestion in the small intestine relies on the activities of three accessory digestive organs: the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. The digestive role of the liver is to produce bile and export it to the duodenum.
What two organs are connected to the duodenum?
The duodenum's “C” shape surrounds the pancreas, where it receives pancreatic enzymes for digestion. The duodenum also connects to the liver via a structure called the hepatoduodenal ligament. This junction is where the duodenum receives bile to mix with chyme , an important part of the chemical digestive process.
What is the main function of duodenum?
The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine. The main role of the duodenum is to complete the first phase of digestion. In this section of the intestine, food from the stomach is mixed with enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the gallbladder. The enzymes and bile help break down food.
Can you live without duodenum?
Yes. If you have a Whipple operation, your surgeon removes your duodenum. Without your duodenum, you may have trouble with digestion or nutrient absorption. Your provider may prescribe nutritional supplements or nutrition through an intravenous (IV) line (parenteral nutrition) to prevent malnutrition.
What problems can occur in the duodenum?
Patients with duodenal lesions present with symptoms of dyspepsia or epigastric pain, anorexia, and obstructive symptoms (e.g., early satiety, nausea, vomiting, and weight loss). Duodenal disease can include inflammatory lesions, strictures, and fistulas, and long-standing disease increases the risk of duodenal cancer.
Which organs provide secretions in digestion?
The salivary glands, liver and gall bladder, and the pancreas aid the processes of ingestion, digestion, and absorption. These accessory organs of digestion play key roles in the digestive process. Each of these organs either secretes or stores substances that pass through ducts into the alimentary canal.
What does the pancreas secrete?
The main hormones secreted by the endocrine gland in the pancreas are insulin and glucagon, which regulate the level of glucose in the blood, and somatostatin, which prevents the release of insulin and glucagon.
What are the 3 major digestive secretions?
Saliva moistens dry food and contains salivary amylase, a digestive enzyme that begins the digestion of carbohydrates. Mucus serves as a protective barrier and lubricant inside of the GI tract. Hydrochloric acid helps to digest food chemically and protects the body by killing bacteria present in our food.
What is secreted into the small intestine?
Exocrine cells in the mucosa of the small intestine secrete mucus, peptidase, sucrase, maltase, lactase, lipase, and enterokinase. Endocrine cells secrete cholecystokinin and secretin. The most important factor for regulating secretions in the small intestine is the presence of chyme.
What enzymes does the duodenum secrete?
Digestion enzymes (such as amylase, lipase, and trypsin) are released by acini cells and pass into the pancreatic duct. The pancreatic duct connect...
What enzyme is produced in the duodenum?
The Duodenum Digestive Enzymes It continues within the duodenum with the amylase enzyme, which the pancreas secretes into the duodenum. In addition...
What are the two glands that secrete their juices into the duodenum?
The pancreas secretes its contents into the duodenum via the primary pancreatic duct (duct of Wirsung) located in the duodenal papilla (papilla of...
Which sphincter controls the release of pancreatic enzymes and bile into the duodenum?
The bigger duct joins the common bile duct (which transports bile from the liver and gallbladder) right before entering the duodenum through a shar...
What organ secretes acid and enzymes that digest food?
The pancreatic and small intestine gland cells release digestive enzymes, which chemically break down complex food molecules into simpler ones. Try...
What enzymes do acinar cells secrete?
The pancreas is made up of pancreatic exocrine cells with ducts grouped in clusters known as "acini." Secretory granules containing inactivated dig...
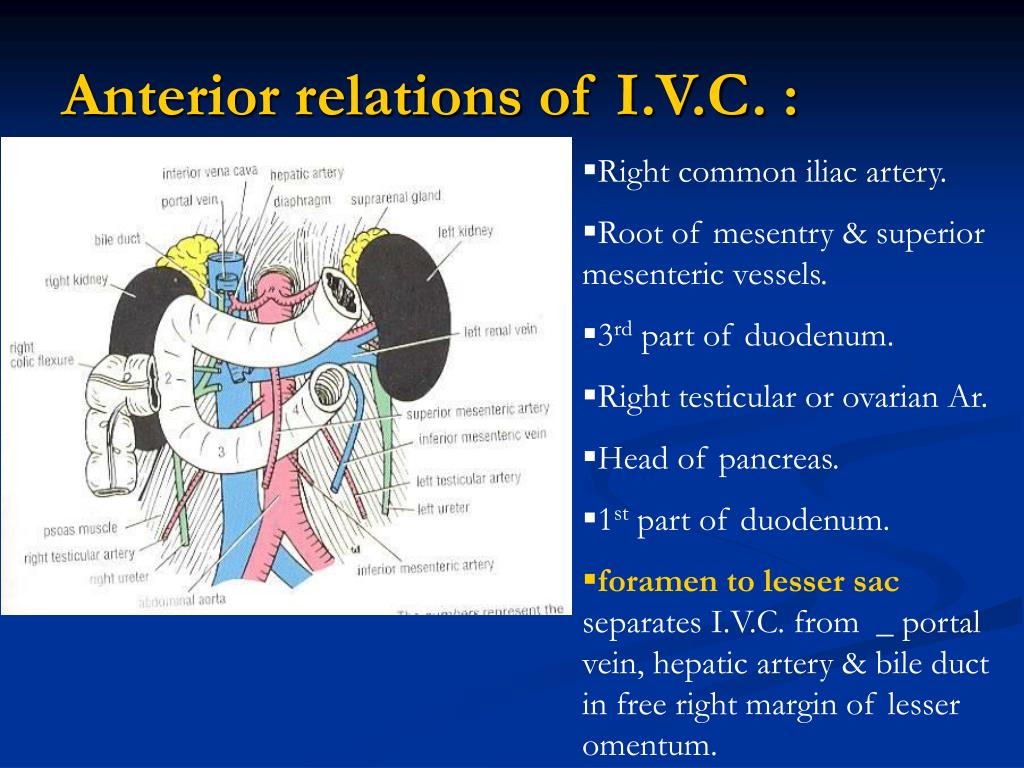
Where does the duodenum receive blood?
Proximal to the 2nd part of the duodenum (approximately at the major duodenal papilla – where the bile duct enters) the arterial supply is from the gastroduodenal artery and its branch the superior pancreaticoduodenal artery. Distal to this point (the midgut) the arterial supply is from the superior mesenteric artery (SMA), and its branch the inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery supplies the 3rd and 4th sections. The superior and inferior pancreaticoduodenal arteries (from the gastroduodenal artery and SMA respectively) form an anastomotic loop between the celiac trunk and the SMA; so there is potential for collateral circulation here.
What is the first part of the duodenum?
The first part of the duodenum is mobile , and connected to the liver by the hepatoduodenal ligament of the lesser omentum. The first part of the duodenum ends at the corner, the superior duodenal flexure. The second part, or descending part, of the duodenum begins at the superior duodenal flexure.
What is the shortest part of the small intestine?
The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest part of the small intestine. In humans, the duodenum is a hollow jointed tube about 25–38 cm (10–15 inches) long connecting the stomach to the jejunum. It begins with the duodenal bulb and ends at the suspensory muscle of duodenum.
What is the role of the duodenum in the digestive system?
The duodenum is largely responsible for the breakdown of food in the small intestine, using enzymes. The duodenum also regulates the rate of emptying of the stomach via hormonal pathways. Secretin and cholecystokinin are released from cells in the duodenal epithelium in response to acidic and fatty stimuli present there when the pylorus opens and emits gastric chyme into the duodenum for further digestion. These cause the liver and gall bladder to release bile, and the pancreas to release bicarbonate and digestive enzymes such as trypsin, lipase and amylase into the duodenum as they are needed.
What is the length of the third part of the duodenum?
The third part, or horizontal part or inferior part of the duodenum is 10~12 cm in length. It begins at the inferior duodenal flexure and passes transversely to the left, passing in front of the inferior vena cava, abdominal aorta and the vertebral column.
Where does the name Duodenum come from?
The name duodenum is from Medieval Latin , short for intestīnum duodēnum digitōrum, which may be translated: intestine of twelve finger-widths (in length), from Latin duodēnum, genitive pl. of duodēnī, twelve each, from duodecim, twelve. The Latin phrase intestīnum duodēnum digitōrum is thought to be a loan-translation from the Greek word dodekadaktylon (δωδεκαδάκτυλον), literally "twelve fingers long." The intestinal section was so called by Greek physician Herophilus (335–280 BC) for its length, about equal to the breadth of 12 fingers.
Why do ulcers occur in the duodenum?
Ulcers of the duodenum commonly occur because of infection by the bacteria Helicobacter pylori. These bacteria, through a number of mechanisms, erode the protective mucosa of the duodenum, predisposing it to damage from gastric acids. The first part of the duodenum is the most common location of ulcers since it is where the acidic chyme meets the duodenal mucosa before mixing with the alkaline secretions of the duodenum. Duodenal ulcers may cause recurrent abdominal pain and dyspepsia, and are often investigated using a urea breath test to test for the bacteria, and endoscopy to confirm ulceration and take a biopsy. If managed, these are often managed through antibiotics that aim to eradicate the bacteria, and PPIs and antacids to reduce the gastric acidity.
How many parts does the duodenum have?
The duodenum can be divided into four parts: superior, descending, inferior and ascending. Together these parts form a ‘C’ shape, that is around 25cm long, and which wraps around the head of the pancreas.
Which part of the duodenum is covered anteriorly and posteriorly?
The initial 3cm of the superior duodenum is covered anteriorly and posteriorly by visceral peritoneum, with the remainder retroperitoneal (only covered anteriorly).
What is the name of the muscle that connects the duodenum to the aorta?
Located at the duodenojejunal junction is a slip of muscle called the suspensory muscle of the duodenum.
What are the two parts of the small intestine?
Jejunum and Ileum. The jejunum and ileum are the distal two parts of the small intestine. In contrast to the duodenum, they are intraperitoneal. They are attached to the posterior abdominal wall by mesentery (a double layer of peritoneum).
Where is the jejunum attached?
They are attached to the posterior abdominal wall by mesentery (a double layer of peritoneum). The jejunum begins at the duodenojejunal flexure. There is no clear external demarcation between the jejunum and ileum – although the two parts are macroscopically different.
Which veins drain into the portal vein?
The veins of the duodenum follow the major arteries and drain into the hepatic portal vein. Lymphatic drainage is to the pancreatoduodena l and superior mesenteric nodes. Jejunum and Ileum. The arterial supply to the jejunoileum is from the superior mesenteric artery.
What are the three parts of the small bowel?
Anatomically, the small bowel can be divided into three parts: the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
How long is the duodenum?
Like any part of the body, the duodenum can become inflamed and painful. The duodenum is a C-shaped tube that is approximately 12 inches in length. The partially digested food from the stomach, and the digestive juices from the pancreas and the gallbladder empty into the duodenum.
What is the duodenum's defense mechanism?
Under normal circumstances, the duodenum has many defense mechanisms against the highly acidic stomach contents. A large amount of mucus that coats the walls of the duodenum prevents stomach acid and digestive enzymes from destroying the duodenal wall. In addition, water and alkaline secretions from the gallbladder and the pancreas help to dilute and neutralize the stomach acid.
What is duodenitis?
Duodenitis refers to an inflammation of the duodenum. It is frequently associated with gastritis (inflammation of the stomach), and occurs as a consequence of repeated irritation of the mucosal lining inside the duodenum. Duodenitis may also lead to the formation of open sores or ulcers in the duodenal wall. All of these conditions may cause pain along with a host of other symptoms like changes in appetite, nausea and bloating.
Why does my duodenum hurt?
Causes of Duodenum Pain. The following are some of the conditions that may result in duodenal pain: Duodenitis and duodenal ulcers: Inflammation of the duodenum often causes duodenal pain. Duodenal ulcers cause pain after coming in contact with food and acid.
What is the term for the formation of outpouchings from the walls of the duodenum?
Duodenal diverticula: Duodenal diverticula refer to the formation of outpouchings from the walls of the duodenum. Infection and inflammation of these diverticula can cause pain and other acute symptoms. Rupture of such diverticula can lead to very serious complications.
What is the name of the intestine that is inflamed?
Duodenitis (Inflamed Duodenum) – Causes, Symptoms, Treatment. The small intestine of our digestive tract begins after the stomach, and is subdivided into three distinct parts: duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine. It is continuous with the terminal part of the stomach at the proximal end and with ...
Why is the duodenum at risk of getting inflamed?
Since the duodenum receives the acidic gastric contents as well as strong digestive juices, it is constantly at risk of getting injured and inflamed. Inflammation of the duodenum is referred to as duodenitis.
What is the function of the duodenum?
These enzymes and juices are secreted from your gallbladder, liver, and pancreas into your intestine. The duodenum also releases hormones to help with digestion.
What causes ulcers in the lining of the duodenum?
This is sometimes called peptic duodenitis. Duodenitis Causes. There are a few causes of duodenitis. . Infection. The most common cause of duodenitis is a bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
What is the diagnosis of duodenitis?
Duodenitis Diagnosis. Duodenitis Treatment. Complications of Duodenitis. Duodenitis is an intestinal condition caused by inflammation in your duodenum lining. It can sometimes happen along with gastritis, which is inflammation in your stomach lining. When they happen together, they are called gastroduodenitis.
How do you know if you have duodenitis?
Sometimes, people have duodenitis without any symptoms. Other people have digestive symptoms like: 1 Feeling full soon after eating 2 Gas 3 Bloating 4 Feeling sick 5 Throwing up 6 Cramping 7 Burning 8 Iron deficiency anemia#N#
What causes ulcers and duodenitis?
Alcohol and smoking. Drinking alcohol, smoking cigarettes, and chewing betel quid are all linked to ulcers and duodenitis. . Celiac disease. This autoimmune disease causes your body to make immune proteins against gluten, a protein in wheat.
What causes duodenitis in the stomach?
Other intestinal diseases. Other diseases like Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, can also cause duodenitis.
Why do we need stool samples?
Stool samples to test for other infections
What is the function of the thoracic duct?
3) Transporting excess interstitial fluid back to the heart. True or false, correct the statement if necessary: The thoracic duct drains lymph from the right upper limb and the right side of the head, neck, and thorax.
Which organ contains macrophages that destroy old or damaged erythrocytes?
Spleen: Filters blood and houses phagocytes. Red pulp contains macrophages that destroy old or damaged erythrocytes. White pulp contains T-lymphocytes, B-lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells that help to remove pathogens from the blood.
Where does gas exchange take place?
Pulmonary gas exchange takes place across the respiratory membrane. Oxygen from the air in the alveoli diffuses into the blood and carbon dioxide from the blood diffuses into the air in the alveoli to be exhaled.
Does thickening the respiratory membrane slow gas exchange?
Predict the effect this would have on the efficiency of gas exchange. Explain your reasoning. Thickening of the respiratory membrane slows gas exchange. The low solubility of oxygen in the interstitial fluid and the accumulation of the fluid in the membrane means oxygen must diffuse across a greater distance.
Is the tonsil encapsulated?
As you learned, the tonsils are only partially encapsulated. How does this better enable them to perform their function? How does this also place them at greater risk for infection?
Overview
Structure
The duodenum is a 25–38 cm (10-15 inch) C-shaped structure lying adjacent to the stomach. It is divided anatomically into four sections. The first part of the duodenum lies within the peritoneum but its other parts are retroperitoneal.
The first part, or superior part, of the duodenum is a continuation from the pylorus to transpyloric plane. It is superior to the rest of the segments, at the vertebral level of L1. The duodenal bulb, abo…
Function
The duodenum is largely responsible for the breakdown of food in the small intestine, using enzymes. The duodenum also regulates the rate of emptying of the stomach via hormonal pathways. Secretin and cholecystokinin are released from cells in the duodenal epithelium in response to acidic and fatty stimuli present there when the pylorus opens and emits gastric chyme into the duodenum for further digestion. These cause the liver and gall bladder to release bile, and …
Clinical significance
Ulcers of the duodenum commonly occur because of infection by the bacteria Helicobacter pylori. These bacteria, through a number of mechanisms, erode the protective mucosa of the duodenum, predisposing it to damage from gastric acids. The first part of the duodenum is the most common location of ulcers since it is where the acidic chyme meets the duodenal mucosa before mixing with the alkaline secretions of the duodenum. Duodenal ulcers may cause recurrent abdominal p…
History
The name duodenum is from Medieval Latin, short for intestīnum duodēnum digitōrum, which may be translated: intestine of twelve finger-widths (in length), from Latin duodēnum, genitive pl. of duodēnī, twelve each, from duodecim, twelve. The Latin phrase intestīnum duodēnum digitōrum is thought to be a loan-translation from the Greek word dodekadaktylon (δωδεκαδάκτυλον), literally "twelve fingers long." The intestinal section was so called by Greek physician Herophilus (c.335–…
Accessory organs
The primary digestive function of the liver is to generate bile. The gallbladder stores bile made from the liver. It travels into the duodenum. The pancreas makes enzymes that break down protein, fat and carbohydrates. The pancreas also makes bicarbonate which neutralizes the acid from the stomach.
Other animals
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine may be used instead of duodenum. In mammals the duodenum may be the principal site for iron absorption.
See also
• Pancreas
• Choledochoduodenostomy - a surgical procedure to create a connection between the common bile duct (CBD) and an alternative portion of the duodenum.