
What are the indications for regular insulin?
- Insulin regular human may be acceptable for use during pregnancy
- Either animal studies show no risk but human studies are not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies were done and showed no risk
- Insulin regular human is considered safe for use while breastfeeding
What is an example of regular insulin?
insulin glulisine (Apidra) insulin lispro (Humalog) Regular- or short-acting products generally use insulin regular, including: Humulin R Humulin R U-500 Humulin R U-500 KwikPen Iletin Regular Pork...
What are the best brands of insulin?
Some of the best insulin pumps
- Medtronic MiniMed 630G System. This model from Medtronic comes with an optional CGM so a person can also monitor their blood sugar levels using the same device.
- Medtronic MiniMed 770G System. This alternative device from Medtronic is suitable for people with type 1 diabetes aged 2 and older.
- Omnipod Dash. ...
- t:slim X2. ...
What is the drug classification of insulin?
They can be classified into two categories, namely insulin injection and antidiabetic drugs Insulin injection lowers blood glucose level by supplementing the insulin of diabetic patients. Insulin injection can be used in both Type I and Type II diabetes. The injection will usually be used with antidiabetic drugs when treating Type II diabetes.
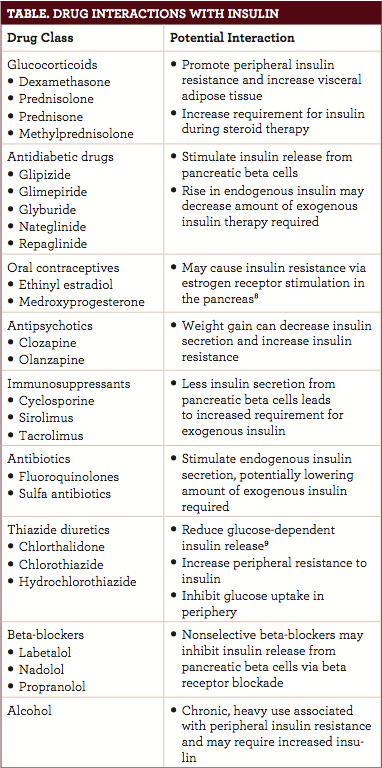
What drug class is NPH insulin?
NPH insulin is an isophane suspension of human insulin and is categorized as an intermediate-acting insulin.
What is the action of regular insulin?
Regular insulin is a short acting form of the synthetic hormone. It helps move glucose from the blood into the body's cells. The cells then use this sugar for energy. Regular insulin typically starts to work within 30 minutes to 1 hour of an injection.
What is another name for regular insulin?
Regular insulinClinical dataTrade namesHumulin R, Novolin R, Actrapid, othersOther namesinsulin injection (soluble), neutral insulin, regular human insulin, human insulin (regular), Toronto insulinAHFS/Drugs.comMonographMedlinePlusa68261113 more rows
Why is regular insulin used?
Regular insulin is a medication used in the management of diabetes mellitus and hyperglycemia of a variety of etiologies. It is in the short-acting insulin class of drugs.
What is the onset of action for regular insulin subcutaneous?
Regular insulin is a short-acting soluble crystalline zinc insulin whose effect appears within 30 min after subcutaneous injection and lasts 4–6 h.
Is regular insulin Intermediate acting?
Regular insulin (Novolin R) is also known as short-acting insulin. It is also used to cover your insulin needs at mealtime, but it can be injected a little bit longer before the meal than rapid-acting insulin.
Is regular insulin short-acting?
Regular insulin is a short-acting human-made insulin. It helps adults and children with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes control their blood sugar levels. Take regular insulin 30 minutes before you eat a meal.
When does regular insulin start working?
Types of insulin: Rapid-acting insulin (such as insulin lispro, insulin aspart, and insulin glulisine) starts working in about 15 minutes. It lasts for 3 to 5 hours. Short-acting insulin (such as regular insulin) starts working in 30 to 60 minutes and lasts 5 to 8 hours.
How Should I Use Regular Insulin?
Follow all directions on your prescription label. Do not use this medicine in larger or smaller amounts or for longer than recommended.Your blood s...
What Happens If I Miss A Dose?
Use the missed dose as soon as you remember. Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Do not use extra medicine to m...
What Happens If I Overdose?
Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222. An insulin overdose can cause life-threatening hypoglycemia.Sympto...
What Other Drugs Will Affect Insulin?
Using certain medicines can make it harder for you to tell when you have low blood sugar. Tell your doctor if you use any of the following: 1. albu...
What is regular insulin?
Regular insulin is a medication used in the management of diabetes mellitus and hyperglycemia of a variety of etiologies. It is in the short-acting insulin class of drugs. This activity outlines the mechanism of action, adverse event profile, labeled and off-labeled indications, contraindications, monitoring, and toxicity for regular insulin pertinent for members of the healthcare team in the management of patients with diabetes mellitus and related conditions.
How many amino acids are in insulin?
Insulin, a natural endogenous hormone synthesized and secreted by pancreatic beta cells, has a structure of 51 amino acids.
What are the symptoms of insulin toxicity?
Most of the symptoms of insulin toxicity are related to hypoglycemia and electrolyte abnormalities . They can categorize into neuroglycopenic and catecholaminergic symptoms. The latter appear first are characterized by tachycardia, sweating, tremors. If blood glucose continues to decrease, neuroglycopenic symptoms appear. They can be from a mild mental status alteration to seizures and coma. Patients that present with hypoglycemia can have diaphoresis, hypotension, and bradycardia. Elevated doses of insulin can lead to water and salt retention and result in dilutional hyponatremia and hypokalemia. [23]
What is the effect of insulin on the alpha and beta receptors?
The conformational change of the binding between insulin and the alpha and beta receptors enables ATP to bind and activate tyrosine kinase, which causes receptor autophosphorylation.[11] Through activation of these signaling pathways, insulin has a potent regulation metabolic effect.
What happens when insulin is released from the extracellular space?
Insulin causes a potassium shift from the extracellular space to the intracellular space and can cause profound hypokalemia and result in muscle cramps, lethargy, cardiac arrhythmias, and even death.
How long does insulin last in DM?
Insulin's regular onset of effect is 1 hour, peaks at 2 to 4 hours, and the duration of the effect lasts 4-hours.
How does insulin affect glycogen synthesis?
In terms of glucose production, glycogen breakdown to synthesis in the liver is facilitated by inhibiting glycogen phosphorylase and the stimulation of glycogen synthesis through the effects of insulin directly.[12] Indirectly, insulin is involved in several pathways, such as a decrease in the flow of fatty acids to the liver and glucagon secretion inhibition to some extent, by direct inhibition of the glucagon gene in pancreatic alpha cells. [13]
What is regular insulin?
Insulin is a hormone that works by lowering levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood. Regular insulin is short-acting and starts to work within 30 minutes after injection, peaks in 2 to 3 hours, and keeps working for up to 8 hours.
Why is insulin used in diabetes?
Regular insulin is used to improve blood sugar control in adults and children with diabetes mellitus.
What should I avoid while using regular insulin?
Do not change the brand of insulin or syringe you are using without first talking to your doctor or pharmacist. Some brands are interchangeable, while others are not. Your doctor and/or pharmacist know which brands can be substituted for one another.
How to know if you have an insulin overdose?
Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222. Insulin overdose can cause life-threatening hypoglycemia. Symptoms include drowsiness, confusion, blurred vision, numbness or tingling in your mouth, trouble speaking, muscle weakness, clumsy or jerky movements, seizure (convulsions), or loss of consciousness.
What are the side effects of insulin?
low potassium - leg cramps, constipation, irregular heartbeats, fluttering in your chest, increased thirst or urination, numbness or tingling, muscle weakness or limp feeling. Common insulin side effects may include: thickening or hollowing of the skin where you injected the medicine.
What are the symptoms of insulin allergy?
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of insulin allergy: redness, swelling, sweating, itchy skin rash over the entire body, trouble breathing, fast heartbeats, feeling like you might pass out, or swelling in your tongue or throat.
How long after insulin is used should you eat?
After using regular insulin, you should eat a meal within 30 minutes.
What is insulin used for?
Insulin regular (human) is used along with a healthy diet and exercise to control high blood sugar in people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
What happens if you don't have insulin?
If you have type 1 diabetes, your pancreas doesn’t make insulin. If you have type 2 diabetes, your body doesn’t make enough insulin, or it can’t properly use the insulin that it makes. Without enough insulin, the sugar will stay in your bloodstream, causing high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia).
How long should you eat after insulin injection?
You should eat a meal within 30 minutes of injecting insulin regular (human).
What is the A1C test?
glycosylated hemoglobin (A1C) levels. This test measures your blood sugar control over the last two to three months.
Is insulin a regular?
Prescription insulin regular (human) comes as an injectable solution, a powder for inhalation, and an intravenous injection.
Can you share insulin syringes?
Do not share insulin vials, syringes, or prefilled pens with other people . Sharing or reusing needles or syringes with another person puts you and others at risk for various infections.
Can insulin cause a whole body reaction?
Insulin regular (human) can cause a severe, whole-body allergic reaction. Symptoms can include:
HOW DO INSULINS WORK?
Insulins are a class of drugs used to treat type 1 (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
HOW ARE INSULINS USED?
Insulins are indicated to improve glycemic control in patients with T1DM and T2DM along with a proper diet and exercise.
How many drugs does insulin interact with?
Insulin Regular Human has moderate interactions with at least 100 different drugs. Insulin Regular Human has mild interactions with at least 83 different drugs. This information does not contain all possible interactions or adverse effects.
What Is Insulin and How Does It Work?
Insulin Regular Human is used with a proper diet and exercise program to control high blood sugar in people with diabetes. Controlling high blood sugar helps prevent kidney damage, blindness, nerve problems, loss of limbs, and sexual function problems. Proper control of diabetes may also lessen your risk of a heart attack or stroke.
What are the risks of using insulin with caution?
Use with caution in patients with decreased insulin requirements: Diarrhea, nausea /vomiting, malabsorption, hypothyroidism, renal impairment, and hepatic impairment. Use with caution in patients with increased insulin requirements: Fever, hyperthyroidism, trauma, infection, and surgery.
How much insulin is needed for a prepubertal child?
The average total daily insulin requirement for pre-pubertal children varies from 0.7-1 unit/kg/day but may be much lower
When to use rapid or short acting insulin?
Rapid- or short-acting insulin should be used before or at mealtimes to satisfy the remainder balance of the total daily insulin requirements. Premixed combinations are available that deliver a rapid- or short-acting component at the same time as the intermediate- or long-acting component. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
How long before or after meal to administer insulin?
Administration. Administer within 15 minutes before a meal or immediately after a meal. Dosing Considerations. Dosage of human insulin, which is always expressed in USP units, must be based on the results of blood and urine glucose tests and must be carefully individualized to optimal effect.
Can rapid changes in serum glucose cause hypoglycemia?
Rapid changes in serum glucose may induce symptoms of hypoglycemia; increase monitoring with changes to insulin dosage, co-administered glucose lowering medications, meal pattern, physical activity; and in patients with renal impairment or hepatic impairment or hypoglycemia unawareness
What is biosynthetic insulin used for?
Biosynthetic insulins are used as replacement therapy in patients with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) to restore their ability to properly metabolize carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Insulin administration also facilitates the replenishment of liver glycogen stores. The time course of action of the various insulins ...
How does insulin affect glucose levels?
The exogenously administered insulins exert their primary effect of lowering blood glucose levels via the promotion of glucose uptake into peripheral skeletal muscle and adipose tissue , the inhibition of glycogenolysis (the hydrolysis of glycogen to glucose), and the inhibition of gluconeogenesis (hepatic glucose production). Insulin also regulates fat metabolism by enhancing the storage of fat (lipogenesis) and inhibiting the mobilization of fat for energy in adipose tissues (lipolysis and free fatty acid oxidation). In addition, insulin regulates protein metabolism (through increasing protein synthesis and inhibiting proteolysis in muscle tissue). Biosynthetic insulins are used as replacement therapy in patients with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) to restore their ability to properly metabolize carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Insulin administration also facilitates the replenishment of liver glycogen stores.
Is insulin contraindicated for hypoglycemia?
Insulin is contraindicated during episodes of hypoglycemia. Patients at risk for hypoglycemia include those who are geriatric or who have brittle diabetes, have received an overdose of insulin, have a delayed or decreased food intake, or are undergoing an excessive amount of exercise relative to their usual insulin dose. Additionally, patients with renal impairment may be at increased risk of hypoglycemia.
Does angiotensin II antagonist affect insulin?
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists, and guanethidine may enhance the hypoglycemic effects of insulin. Patients should therefore be monitored closely for changes in glycemic control. [50223] [21961] [42591]
Can thiazide diuretics increase blood glucose levels?
Thiazide diuretics can decrease the hypoglycemic effects of insulin by producing an increase in blood glucose levels. It appears that the effects of thiazides on glucose control are dose-dependent and low doses can be used without significant effects. Patients on insulin therapy should be monitored for changes in blood glucose control. Insulin dosage adjustments may be necessary. [50223]
Can beta blockers cause hypoglycemia?
Beta-blockers can inhibit the compensatory actions of epinephrine's response to hypoglycemia. As such, hypoglycemia can be prolonged. Additionally, beta-blockers can mask the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, especially tachycardia. Beta-blockers have also been associated with increasing blood glucose concentrations. While beta-blockers may have negative effects on glycemic control, they reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke in patients with diabetes. [51005] Furthermore, their use should not be avoided in patients with compelling indications for beta-blocker therapy (i.e., post-MI, heart failure, etc.) when no other contraindications are present. Decreased mortality has been shown in the post-MI and heart failure populations when beta-blockers are used, especially in patients with coexisting diabetes mellitus. [50223]
Does insulin increase hypoglycemia?
The risk of hypoglycemia may increase with the use of insulin in combination with other antidiabetic agents such as alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, metformin, thiazolidinediones, or oral sulfonylureas. In addition, pioglitazone and troglitazone should be administered with caution as the combined use of insulin with these drugs significantly increases the risk of heart failure or edema.
How are insulins classified?
Insulins also are classified by the timing of their action in your body – specifically, how quickly they start to act, when they have a maximal effect and how long they act.Insulin analogs have been developed because human insulins have limitations when injected under the skin.
How Do Different Types Of Insulin Work?
Which insulin is right for you? The chart below will help you understand how the various insulin medications work and why your doctor has prescribed them for you. Insulin is injected into the fat tissue which helps it absorb into the bloodstream. Some insulin medications work faster than others, but don't last as long. And some insulins last longer but work more gradually than others. There are three characteristics that define types of insulin. Onset: How long it takes for the insulin to start lowering blood glucose Peak time: Time after injection when the insulin is the most effective at lowering blood glucose Duration: How long the insulin keeps lowering blood glucose Insulin is prescribed by matching the characteristics of a particular insulin with the individual needs of the patient . Some people are on only one kind of insulin, while others take a combination of insulin medication to customize good glucose control. There are six main types of insulin available: Rapid-acting: These include Apidra, Humalog, and Novolog. They have an onset in less than 15 minutes, peak in 30 to 90 minutes, and duration of three to five hours. Regular (short-acting): These include Humulin R and Novolin R. They have an onset of ahalf an hour to one hour, a peak of two to fourhours, and duration of three to five hours. Intermediate-acting: These include Humulin N and Novolin N. They have an onset of one to three hours, a peak of eight hours, and duration of 12 to 16 hours. Long-acting: These include Levemir an Lantus. They have an onset of one hour, minimal or no peak, and a duration of 2 Continue reading >>
How is insulin lispro produced?
Insulin lispro is produced by recombinant DNA technology utilizing a non-pathogenic laboratory strain of Escherichia coli. Insulin lispro differs from human insulin in that the amino acid proline at position B28 is replaced by lysine and the lysine in position B29 is replaced by proline.
What is the difference between insulin and insulin analogs?
Insulin analogs are now replacing human insulin in the US. Insulins are categorized by differences in onset, peak, duration, concentration, and route of delivery. Human Insulin and Insulin Analogs are available for insulin replacement therapy. Insulins also are classified by the timing of their action in your body – specifically, how quickly they start to act, when they have a maximal effect and how long they act.Insulin analogs have been developed because human insulins have limitations when injected under the skin. In high concentrations, such as in a vial or cartridge, human (and also animal insulin) clumps together. This clumping causes slow and unpredictable absorption from the subcutaneous tissue and a dose-dependent duration of action (i.e. the larger dose, the longer the effect or duration). In contrast, insulin analogs have a more predictable duration of action. The rapid acting insulin analogs work more quickly, and the long acting insulin analogs last longer and have a more even, “peakless” effect. Background Insulin has been available since 1925. It was initially extracted from beef and pork pancreases. In the early 1980’s, technology became available to produce human insulin synthetically. Synthetic human insulin has replaced beef and pork insulin in the US. And now, insulin analogs are replacing human insulin. Characteristics of Insulin Insulins are categorized by differences in: Onset (how quickly they act) Peak (how long it takes to achieve maximum impact) Duration (how long they last before they wear off) Concentration (Insulins sold in the U.S. have a concentration of 100 units per ml or U100. In other countries, additional concentrations are available. Note: If you purchase insulin abroad, be sure it is U100.) Route of delivery (whether they a Continue reading >>
What is the peptide that is cleaved into insulin?
Proinsulin, a single-chain 86 amino acid peptide, is cleaved into insulin and C-peptide (a connecting peptide); both are secreted in equimolar portions from the beta cell upon stimulation from glucose and other insulin secretagogues.
What happens when insulin clumps?
This clumping causes slow and unpredictable absorption from the subcutaneous tissue and a dose-dependent duration of action (i.e. the larger dose, the longer the effect or duration).
How many amino acids are in insulin?
The insulin molecule consists of 51 amino acids arranged in two chains, an A chain (21 amino acids) and B chain (30 amino acids) that are linked by two disulfide bonds (1) (Figure 1).
