
Many other medications have been reported to cause acute dystonic reactions including: anti-depressants of the type that inhibit the reuptake of serotonin calcium antagonists (sometimes used to treat high blood pressure and angina) some anaesthetic agents anticonvulsants such as carbamazepine
Carbamazepine
Carbamazepine is used to prevent and control seizures.
What drugs may cause dysgeusia?
List of Drugs that may cause Dysgeusia (Taste Perversion) Fluconazole. Most Common - Headache, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, indigestion, dizziness and taste perversion.
Can risperidone cause dystonia?
The cases are important in documenting that drug-induced dystonias do occur in patients with dementia, that risperidone appears to have contributed to dystonia among elderly patients, and that the categorization of dystonic reactions needs further clarification. Adystonia is defined as a slow, sustained muscular contraction or spasm.
Does Reglan cause dystonia?
arms, and legs (dystonia). These muscle spasms can cause abnormal movements ... condition that can happen with REGLAN. NMS can cause death and must be 3. treated in a hospital. Symptoms of NMS ...
Does Ativan cause dystonia?
Yes No Ativan (lorazepam): “The Ativan gave me relief from the anxiety that was caused by and affecting the Dystonia. However it didn't treat the Dystonia itself and I ended up having to up my dose all the time and eventually quit taking it because I realized it wasn't treating the root problem.”
What is drug induced acute dystonia?
Acute dystonia, sometimes called an acute dystonic reaction, can occur within hours or days of exposure to a dopamine blocking drug or, less commonly, after an increased dose of a dopamine blocking drug or decreased dose of a concurrent anticholinergic drug (e.g. benztropine).
What causes acute dystonia?
The etiology of acute dystonic reaction is thought to be due to dopaminergic-cholinergic imbalance in the basal ganglia. Reactions usually occur shortly after the initiation of an offending agent or an increased dose of a possible offending agent.
What drug causes uncontrollable muscle spasms?
Stimulant drugs (e.g., amphetamine, methylphenidate, and pemoline) have been known to produce a variety of movement disorders such as dyskinesias, dystonia, stereotypic behavior, and tics.
Can opiates cause dystonia?
[6] Hence, during an opioid abstinent state, opioid receptors will not be activated, resulting in a lack of inhibition of the inhibitory GABAergic interneurons in the VTA, ultimately leading to decreased dopamine neurotransmission to the NA, creating a dopamine depletion state, which in turn causes dystonia.
Does drug induced dystonia go away?
The potential cause of drug induced dystonia is the development of dopamine receptor hypersensitivity after prolonged blockade of these receptors with the use of antipsychotics or anti emetics. In almost all instances, drug induced dystonias are reversible, resolving after the discontinuation of the offending drug.
Is acute dystonia permanent?
There's no cure for dystonia, but medications and therapy can improve symptoms. Surgery is sometimes used to disable or regulate nerves or certain brain regions in people with severe dystonia.
How long does acute dystonia last?
Acute dystonic reactions usually occur within a few hours of taking a causative medication, but onset may be delayed a few days. Untreated the condition gradually resolves over a few days.
Can benzodiazepines cause dystonia?
Drug-induced dystonia (DID) may occur within minutes or hours or even days of exposure to an inciting drug. Gastrointestinal medications such as metoclopramide and levosulpiride were the most frequent cause of DID. DID responded well to benzodiazepines or benztropine and had benign courses.
What medications can cause movement disorders?
The most commonly implicated drugs include antipsychotics, antiemetics (metoclopramide and prochlorperazine) and some calcium channel antagonists with dopamine receptor blocking properties (cinnarizine and flunarizine).
Does gabapentin cause dystonia?
Other movement disorders reported with gabapentin include myoclonus, ataxia, and choreoathetosis. Gabapentin has been used to treat dystonias with variable results. Conclusions: Although gabapentin is widely used and well tolerated, it can cause dystonic reactions, which are reversible after drug withdrawal.
What drugs cause tardive dystonia?
Medicines that most commonly cause this disorder are older antipsychotics, including:Chlorpromazine.Fluphenazine.Haloperidol.Perphenazine.Prochlorperazine.Thioridazine.Trifluoperazine.
Can dystonia be caused by stress?
Stress is a key risk factor for dystonia, a debilitating motor disorder characterized by cocontractions of muscles leading to abnormal body posture. While the serotonin (5HT) system is known to control emotional responses to stress, its role in dystonia remains unclear.
Is acute dystonia reversible?
Dystonic reactions are reversible extrapyramidal effects that can occur after administration of a neuroleptic drug. Symptoms may begin immediately or can be delayed hours to days. Although a wide variety of medications can elicit symptoms, the typical antipsychotics are most often responsible.
Is dystonia a symptom of MS?
Paroxysmal dystonia was the initial manifestation of multiple sclerosis (MS) in eight patients. The disorder was generally characterized by dystonic posturing of unilateral extremities, averaging less than one minute in duration. Facial grimacing and dysarthria occurred in two of the eight patients.
What is the best treatment for dystonia?
To manage dystonia, your provider might recommend a combination of medications, therapy or surgery....Your health care provider might suggest:Physical therapy or occupational therapy or both to help ease symptoms and improve function.Speech therapy if dystonia affects your voice.Stretching or massage to ease muscle pain.
How long does it take for a dopamine blocker to cause acute dystonia?
Acute Dystonia. Acute dystonia, sometimes called an acute dystonic reaction, can occur within hours or days of exposure to a dopamine blocking drug or, less commonly, after an increased dose of a dopamine blocking drug or decreased dose of a concurrent anticholinergic drug (e.g. benztropine). Acute dystonia is more often associated ...
What is focal tardive dystonia?
Focal tardive dystonia often affects the facial muscles, often with akathisia (feelings of inner restlessness). Symptoms of focal dystonia can occur days or years after drug exposure. Symptoms may respond to sensory tricks. Common presentations of tardive dystonia, as compared to dystonia due to other causes, include:
What are the risk factors for tardive dyskinesia?
Risk factors for tardive dyskinesias include elderly age, being female, pre-existing mood disorders, cognitive disturbances, history of substance abuse, diabetes, HIV positive status, and other factors including higher dose or long term use of antipsychotics and treatment with first generation antipsychotic medications.
What is tardive syndrome?
Tardive Syndromes. Drug-induced movement disorders come in different forms and can be caused by a number of medications that alter brain chemistry. The types of drugs most commonly associated with causing movement disorders are dopamine blocking medications (i.e. dopamine antagonist or antidopaminergic medications), ...
Can you discontinue antipsychotics?
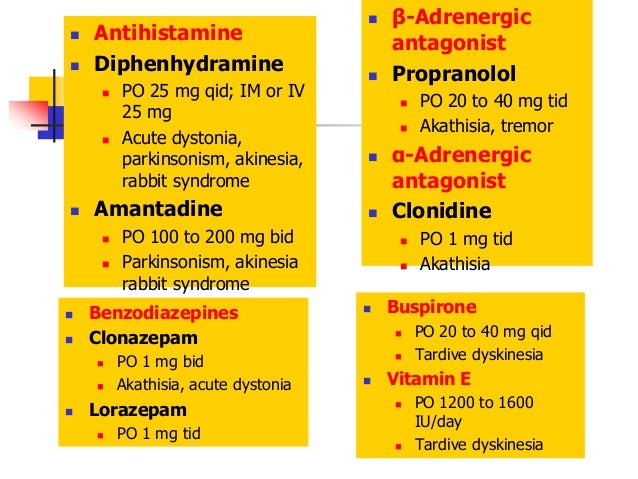
Treatment may include discontinuing the offending drug, though symptoms may persist or worsen during drug withdrawal. There may be individuals, however, for whom discontinuing antipsychotics is not viable but the dosage may be lowered. Oral medications approved by the US Federal Drug Administration (FDA) to suppress tardive dyskinesia symptoms include valbenazine or deutetrabenazine. Additional agents may include tetrabenazine, clonazepam, amantadine, propranolol, and Ginko biloba.
Can tardive dyskinesia cause tongue movements?
The symptoms can include lip-smacking, chewing movements, and tongue movements. This can cause problems with chewing, speaking, swallowing, and dental care. Breathing is sometimes affected depending on the nature of the movements. The limbs and trunk are less commonly affected. Tardive dyskinesias can be accompanied by feelings ...
Can dopamine blockers cause movement disorders?
Dopamine blocking drugs can cause a variety of movement disorders including parkinsonism, tardive syndromes, chorea, dystonia, tremor, akathisia, myoclonus, tics, and a very serious condition called neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Movement symptoms may be focal to a specific body part, affect one side of the body, ...
What is the cause of acute dystonia?
Acute dystonia induced by drug treatment can be caused by antipsychotic, antiemetic, and antidepressant drugs
When does acute dystonia occur?
Acute dystonias seem to occur more frequently between 12 00 and 23 00. 16 Sometimes, acute dystonia is diagnosed during maintenance treatment with a depot antipsychotic within a few days after the depot has been administered. 17 The oculogyric crisis is the only form of acute dystonia that may occur while the patient is receiving a stable dose of an antipsychotic drug; it may be provoked by alcohol, emotional stress, fatigue, or suggestion. 18
How long does tardive dystonia last?
Tardive dystonia. The symptoms of tardive dystonia and acute dystonia are practically identical. 1 – 3 However, tardive dystonia occurs only after months or years of treatment with antipsychotic drugs and does not improve rapidly after the administration of anticholinergics.
What to do if dystonia persists?
If the dystonia persists, a search for other underlying illnesses should be made. 1 2 If the patient has an oculogyric crisis that does not respond to anticholinergic drugs, treatment with clonazepam 0.5 to 4 mg may be beneficial. 29.
How long does it take for dystonia to appear?
In 95% of all cases, acute dystonia appears within 96 hours of starting treatment with antipsychotic drugs or after a large increase in the dose. 1 2 6 The dystonia may appear in all muscle groups but is observed mainly in the head and neck area.
How long does it take to cure dystonia?
Drug induced dystonia can be prevented either by adding, during the first four to seven days of treatment, anticholinergic drugs to treatment with antipsychotic drugs or by starting treatment with atypical antipsychotics.
What causes bizarre movements?
Other causes. Temporal epilepsy may cause bizarre behaviour and bizarre movements and can therefore be confused with dystonia. 2 Hypocalcaemia may cause features resembling those of acute dystonia. If treatment for acute dystonia is not successful, serum calcium concentrations should be measured. 2.
How to diagnose drug induced dystonia?
Drug-induced dystonia is diagnosed by the combination of history of exposure to a likely causative medication, plus rapid response to anticholinergic medication. Initial blood work can identify low magnesium or calcium, which can be repleted intravenously. History of a wound and no recent tetanus booster may suggest tetanus. There is no specific diagnostic test for tetanus: it is a clinical diagnosis. Chronicity of symptoms without exposure to causative medication should suggest exploration for other neurologic symptoms, such as tremor or rigidity of Parkinson’s disease. Symptoms since childhood or adolescence may prompt genetic investigation for primary dystonias. EEG can help diagnose partial seizures.
What is dystonia in physiology?
Dystonia is a form of hyperkinetic movement disorder. It is a syndrome of involuntary sustained muscle contractions with frequent repetitive and twisting movements, and/or abnormal postures. Characteristic movements include trismus, mouth opening, grimacing, blepharospasm, glossopharyngeal contraction, stridor, oculogyric crisis, opisthotonos, torticollis, and retrocollis.
How long does dystonia last after discontinuation of a drug?
It should be noted that in some instances, clinical symptoms of dystonia may persist up to months after discontinuation of the offending agent.
How long does it take for a patient to get relief from a drug induced dystonia?
The patient should experience relief of symptoms in 5-10 minutes. If no improvement, check electrolytes and toxicology screens, evaluate for infection, and consider a Neurology consult to evaluate for seizures.
What is an acute neurologic seizure?
Acute neurologic: partial seizures (have history of prior seizures and exhibit focal tonic clonic movements); patients may worry about stroke but this is less likely clinically
Can benzodiazepines help with dystonia?
Giving benzodiazepines prior to trying the above two medications will prevent the clinician from distinguishing if the dystonia is drug-induced, as benzodiazepines will help relieve all types of muscle spasm.
Should antipsychotics be discontinued?
The offending drug agent should be discontinued when possible. If the offending drug has a long half-life, anticholinergic doses to relieve spasms may need to be repeated. In patients who need to continue an antipsychotic drug, prophylaxis can be considered by adding an anticholinergic like benztropine.
Drugs used to treat Dystonia
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
