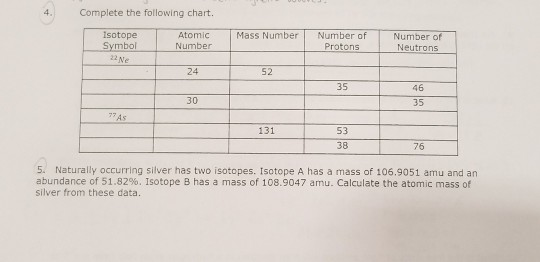
What element has a mass of 152?
Samarium-152Samarium-152 | Sm - PubChem.
What element has a mass number of 154?
Samarium-154 | Sm - PubChem.
What element has a mass number of 153?
Samarium | Sm (Element) - PubChem.
What element has a mass number of 151?
Properties of Europium-151 Isotope:Properties of Europium-151 Isotope:EUROPIUM-151Atomic Mass (Da)150.9198502Relative Isotopic Mass150.9198502Neutron Number (N)88Atomic Number (Z)6325 more rows
What has a mass number of 119?
UnunenniumPronunciation/ˌuːn.uːnˈɛniəm/ ( listen) (OON-oon-EN-ee-əm)Alternative nameselement 119, eka-franciumUnunennium in the periodic table25 more rows
How do you find the mass number?
Together, the number of protons and the number of neutrons determine an element's mass number: mass number = protons + neutrons. If you want to calculate how many neutrons an atom has, you can simply subtract the number of protons, or atomic number, from the mass number.
How many protons does europium 152 have?
Protons and Neutrons in Europium Europium is a chemical element with atomic number 63 which means there are 63 protons in its nucleus.
How many protons neutrons and electrons does a neutral atom of europium 152 contain?
Europium has 63 protons, 89 neutrons and 63 electrons. Here I have given a very simple method for finding the protons, neutrons and electrons of europium atom. Let's dive right into it!
What is the 200th element?
Polonium-200 atom | Po - PubChem.
What is the element 150?
Schrodium is the provisional non-systematic name of a theoretical element with the symbol So and atomic number 150. Schrodium was named in honor of Erwin Schrödinger (1887–1961), who developed his equation for quantum mechanics.
Who discovered element 63?
In 1839 Carl Mosander separated two other elements from it: lanthanum and one he called didymium which turned out to be a mixture of two rare earths, praseodymium and neodymium, as revealed by Karl Auer in 1879.
What is the abundance of Eu 153?
Owing to the fact that europium has only two stable isotopes, in 1969, the standard atomic weight was assessed as Ar(Eu) = 151.96(1)....Europium.IsotopeAtomic mass (Da)Isotopic abundance (amount fraction)153Eu152.921 237(9)0.5219(6)1 more row
What is the mass number of sodium?
22.989769 uSodium / Atomic mass
Is element 137 possible?
Because electrons have non zero rest mass, they cannot exceed the vacuum speed of light according to Einstein's theory of relativity. Thus, atoms with Z > 137 cannot exist.
What is the mass number of all elements?
The Elements, sorted by Atomic MassAtomic NumberSymbolAtomic Weight (amu, g/mol)9F18.99840310Ne20.17911Na22.9897712Mg24.30571 more rows
What is the mass number of copper?
63.546 uCopper / Atomic mass
How many protons does samarium have?
Samarium is a chemical element with atomic number 62 which means there are 62 protons and 62 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Samarium is Sm.
How are atomic nuclei determined?
Properties of atomic nuclei (atomic mass, nuclear cross-sections) are determined by the number of protons and number of neutrons (neutron number). It must be noted, especially nuclear cross-sections may vary by many orders from nuclide with the neutron number N to nuclide with the neutron number N+1. For example, actinides with odd neutron number are usually fissile (fissionable with slow neutrons) while actinides with even neutron number are usually not fissile (but are fissionable with fast neutrons). Heavy nuclei with an even number of protons and an even number of neutrons are (due to Pauli exclusion principle) very stable thanks to the occurrence of ‘paired spin’. On the other hand, nuclei with an odd number of protons and neutrons are mostly unstable.
What are the two forces that make up the nucleus?
Atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons, which attract each other through the nuclear force, while protons repel each other via the electric force due to their positive charge. These two forces compete, leading to various stability of nuclei. There are only certain combinations of neutrons and protons, which forms stable nuclei.
What is the atomic mass of an atom?
The atomic mass is the mass of an atom. The atomic mass or relative isotopic mass refers to the mass of a single particle, and therefore is tied to a certain specific isotope of an element. The atomic mass is carried by the atomic nucleus, which occupies only about 10 -12 of the total volume of the atom or less, but it contains all the positive charge and at least 99.95% of the total mass of the atom. Note that, each element may contain more isotopes, therefore this resulting atomic mass is calculated from naturally-occuring isotopes and their abundance.
How do neutrons stabilize the nucleus?
Neutrons stabilize the nucleus, because they attract each other and protons , which helps offset the electrical repulsion between protons. As a result, as the number of protons increases, an increasing ratio of neutrons to protons is needed to form a stable nucleus. If there are too many or too few neutrons for a given number of protons, the resulting nucleus is not stable and it undergoes radioactive decay . Unstable isotopes decay through various radioactive decay pathways, most commonly alpha decay , beta decay , gamma decay or electron capture. Many other rare types of decay, such as spontaneous fission or neutron emission are known.
How to determine the stability of an isotope?
To determine the stability of an isotope you can use the ratio neutron/proton (N/Z). Also to help understand this concept there is a chart of the nuclides, known as a Segre chart. This chart shows a plot of the known nuclides as a function of their atomic and neutron numbers. It can be observed from the chart that there are more neutrons than protons in nuclides with Z greater than about 20 (Calcium). These extra neutrons are necessary for stability of the heavier nuclei. The excess neutrons act somewhat like nuclear glue. Only two stable nuclides have fewer neutrons than protons: hydrogen-1 and helium-3.
What is the unit of measure for mass?
The unit of measure for mass is the atomic mass unit (amu). One atomic mass unit is equal to 1.66 x 10 -24 grams. One unified atomic mass unit is approximately the mass of one nucleon (either a single proton or neutron) and is numerically equivalent to 1 g/mol.
How many neutrons are in neon?
For instance, it can be determined experimentally that neon consists of three isotopes: neon-20 (with 10 protons and 10 neutrons in its nucleus) with a mass of 19.992 amu and an abundance of 90.48%, neon-21 (with 10 protons and 11 neutrons) with a mass of 20.994 amu and an abundance of 0.27%, and neon-22 (with 10 protons and 12 neutrons) with a mass of 21.991 amu and an abundance of 9.25%. The average atomic mass of neon is thus:
How much does a mole of water weigh?
One molecule of water (H 2 O) would weigh 18.02 amu (2×1.00797 amu for H + 15.9994 amu for O), and a mole of water molecules would weigh 18.02 grams. The original periodic table of the elements published by Dimitri Mendeleev in 1869 arranged the elements that were known at the time in order of increasing atomic weight, ...
What is the atomic mass of an element?
The atomic mass of an element is the average mass of the atoms of an element measured in atomic mass unit (amu, also known as daltons, D). The atomic mass is a weighted average of all of the isotopes of that element, in which the mass of each isotope is multiplied by the abundance of that particular isotope. (Atomic mass is also referred ...
