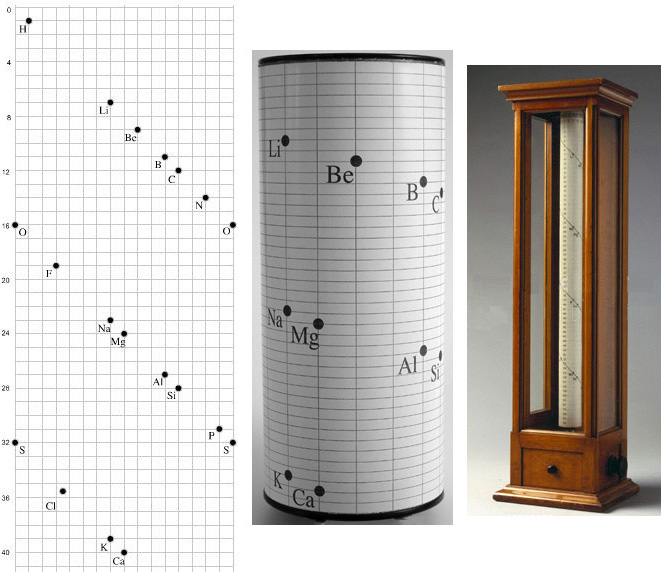

What elements did Mendeleev know about?
These elements are:-
- Gallium
- Germanium
- Scandium
- Technetium
What element was predicted by Mendeleev?
What are the 7 unknown elements?
- Eka-boron (scandium)
- Eka-aluminium (gallium)
- Eka-manganese (technetium)
- Eka-silicon (germanium)
How did Mendeleev group the elements?
Which group has the most elements?
- In group 1 of the periodic table, all the elements except hydrogen (H) are alkali metals.
- The alkaline Earth metals make up group 2 of the periodic table.
- All the elements in groups 3–12 are transition metals.
- These groups each contain one or more metalloids.
- Group 17 consists of the nonmetals called halogens.
How did mendelevium the element get its name?
The element Mendelevium was discovered by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in year 1955 in United States. Mendelevium derived its name from Dmitri Mendeleev, chemist and inventor Mendelevium Presence: Abundance in Nature and Around Us
See more
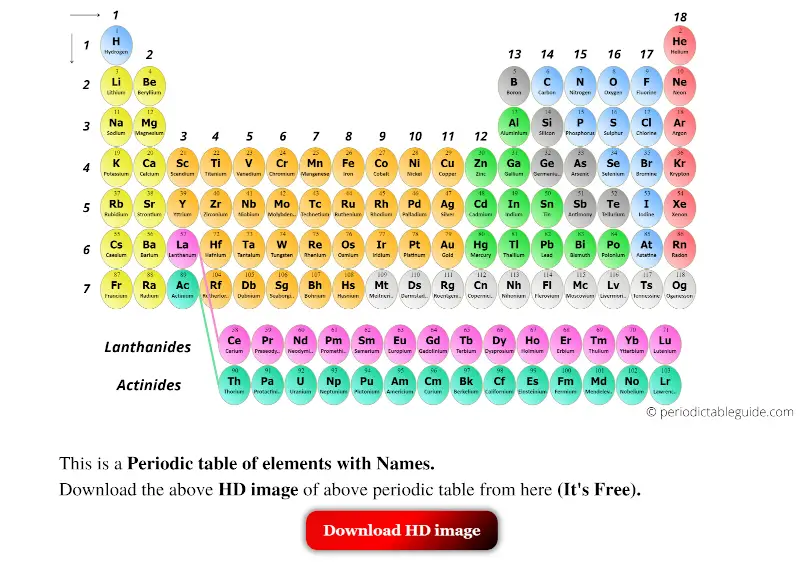
Which element was predicted by Mendeleev?
The three elements predicted by Mendeleev from the gaps in his periodic table were known as eka-boron, eka-aluminium and eka-silicon.
Who discovered element 101?
Glenn T. SeaborgMendelevium / DiscovererGlenn Theodore Seaborg was an American chemist whose involvement in the synthesis, discovery and investigation of ten transuranium elements earned him a share of the 1951 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Wikipedia
Why was mendelevium named after Mendeleev?
It was the first identification of a new element one atom at a time, yet also the last to use chemical processes2. The new element was named after Dmitri Mendeleev, specifically because he had predicted the chemical properties of yet-unknown elements using their position in his classification system.
Which metals have been named after Dmitri Mendeleev?
Discovery date1955Discovered byAlbert Ghiorso and colleaguesOrigin of the nameMendelevium is named for Dmitri Mendeleev who produced one of the first periodic tables.Allotropes
What group of elements did Mendeleev put in 1902?
In 1902, having accepted the evidence for elements helium and argon, Mendeleev placed these noble gases in Group 0 in his arrangement of the elements. As Mendeleev was doubtful of atomic theory to explain the law of definite proportions, he had no a priori reason to believe hydrogen was the lightest of elements, and suggested that a hypothetical lighter member of these chemically inert Group 0 elements could have gone undetected and be responsible for radioactivity. Currently some periodic tables of elements put lone neutrons in this place, and it matches Mendeleev's predictions fairly well.
Who published the periodic table?
Dmitri Mendeleev published a periodic table of the chemical elements in 1869 based on properties that appeared with some regularity as he laid out the elements from lightest to heaviest.
What is the mass of scandium?
Mendeleev had predicted an atomic mass of 44 for ekaboron in 1871, while scandium has an atomic mass of 44.955908. In 1871, Mendeleev predicted the existence of a yet-undiscovered element he named eka-aluminium (because of its proximity to aluminium in the periodic table ).
Which element is the heavier proto-helium?
The heavier of the hypothetical proto-helium elements Mendeleev identified with coronium, named by association with an unexplained spectral line in the Sun's corona.
Who predicted the existence of uranium and thorium?
The existence of an element between thorium (90) and uranium (92) was predicted by Mendeleev in 1871. In 1900, William Crookes isolated protactinium (91) as a radioactive material deriving from uranium that he could not identify.
Did the periodic table distinguish rare earth elements from transition elements?
Initial versions of the periodic table did not distinguish rare earth elements from transition elements, helping to explain both why Mendeleev's predictions for heavier unknown elements did not fare as well as those for the lighter ones and why they are not as well known or documented.
Is thorium an actinide?
Since the acceptance of Glenn T. Seaborg 's actinide concept in 1945, thorium , uranium and protactinium have been classified as actinides; hence, protactinium does not occupy the place of eka- tantalum (under 73) in group 5. Eka-tantalum is actually the synthetic superheavy element dubnium (105).
What element is named after famous scientists?
Of those elements named for famous scientists, none occur naturally; they are all products of nuclear reactions in the laboratory and are extremely rare. Bohrium.
What is the name of the element that was created by the scientists?
Curium. Created artificially by particle bombardment of plutonium, curium is a radioactive element first produced in 1944. It was developed in the U.S. by scientists Albert Ghiorso, Ralph James and Glenn Seaborg. The element is named for radioactivity pioneers Pierre and Marie Curie.
Why are elements named on the periodic table?
The elements of the periodic table have all been named based on a number of factors. Some elements are named for colors and given the Latin or Greek word which depicts it. Other elements are named for the region or town they were first discovered. Several have been named after some of history's prominent scientific minds.
When was Fermium discovered?
Fermium. In bombardment experiments on plutonium, the radioactive element fermium was discovered in the U.S. in 1952. As with many of the other synthetic elements, it exists in amounts far too small to have practical uses outside the laboratory.
When was bohrium first discovered?
Bohrium. The radioactive element bohrium was first created in 1981 in a German laboratory by Peter Armbruster and Gottfried Munzenberg. It was named after the Danish physicist Niels Bohr, who helped develop important theories of the structure of atoms in the 1930s. Curium.
What was Mendeleev's valence?
Mendeleev realized that these values did not fit in his periodic table, and doubled both to valence 6 and atomic weight 240 (close to the modern value of 238).
What did Mendeleev contribute to chemistry?
The Russian chemist and science historian Lev Chugaev characterized him as "a chemist of genius, first-class physicist, a fruitful researcher in the fields of hydrodynamics, meteorology, geology, certain branches of chemical technology (explosives, petroleum, and fuels, for example) and other disciplines adjacent to chemistry and physics, a thorough expert of chemical industry and industry in general, and an original thinker in the field of economy." Mendeleev was one of the founders, in 1869, of the Russian Chemical Society. He worked on the theory and practice of protectionist trade and on agriculture.
How many children did Mendeleyev have?
Mendeleyev was the final child, that is certain, and the number the reliable sources have is 13. ". Gordin's book specifically says that Mendeleev's mother bore her husband "seventeen children, of whom eight survived to young adulthood", with Mendeleev being the youngest. See: Johnson, George (3 January 2006).
What did Mendeleev do?
Mendeleev also investigated the composition of petroleum, and helped to found the first oil refinery in Russia. He recognized the importance of petroleum as a feedstock for petrochemicals. He is credited with a remark that burning petroleum as a fuel "would be akin to firing up a kitchen stove with bank notes".
How many brothers did Mendeleev have?
Mendeleev was the youngest of 17 siblings, of whom "only 14 stayed alive to be baptized" according to Mendeleev's brother Pavel, meaning the others died soon after their birth. The exact number of Mendeleev's siblings differs among sources and is still a matter of some historical dispute.
Where did Mendeleev go to school?
At the age of 13, after the passing of his father and the destruction of his mother's factory by fire, Mendeleev attended the Gymnasium in Tobolsk. In 1849, his mother took Mendeleev across Russia from Siberia to Moscow with the aim of getting Mendeleev enrolled at the Moscow University.
Where is the sculpture of Mendeleev located?
e. Sculpture in honor of Mendeleev and the periodic table, located in Bratislava, Slovakia. In 1863, there were 56 known elements with a new element being discovered at a rate of approximately one per year. Other scientists had previously identified periodicity of elements.
Why is the element Curium named after Marie Curie?
Curium was named in honor of their contributions to the field of radioactivity. Curium is a radioactive solid metal.
Is curium a commercial compound?
Curium has only been produced in milligram amounts, so no commercial use has been discovered. Several compounds have been created by scientists, such as curium dioxide, curium chloride, curium iodide and curium bromide. These compounds are primarily used for basic research. ADVERTISEMENT.

Overview
Original predictions
The four predicted elements lighter than the rare-earth elements, eka-boron (Eb, under boron, B, 5), eka-aluminium (Ea or El, under Al, 13), eka-manganese (Em, under Mn, 25), and eka-silicon (Es, under Si, 14), proved to be good predictors of the properties of scandium (Sc, 21), gallium (Ga, 31), technetium (Tc, 43), and germanium (Ge, 32) respectively, each of which fill the spot in the periodic table assigned by Mendeleev.
Prefixes
To give provisional names to his predicted elements, Mendeleev used the prefixes eka- /ˈiːkə-/, dvi- or dwi-, and tri-, from the Sanskrit names of digits 1, 2, and 3, depending upon whether the predicted element was one, two, or three places down from the known element of the same group in his table. For example, germanium was called eka-silicon until its discovery in 1886, and rhenium was called dvi-manganese before its discovery in 1926.
Other predictions
The existence of an element between thorium (90) and uranium (92) was predicted by Mendeleev in 1871. In 1900, William Crookes isolated protactinium (91) as a radioactive material deriving from uranium that he could not identify. Different isotopes of protactinium were identified in Germany in 1913 and in 1918, but the name protactinium was not given until 1948. Since the acceptance of Glenn T. Seaborg's actinide concept in 1945, thorium, uranium and protactinium have been classi…
Later predictions
In 1902, having accepted the evidence for elements helium and argon, Mendeleev placed these noble gases in Group 0 in his arrangement of the elements. As Mendeleev was doubtful of atomic theory to explain the law of definite proportions, he had no a priori reason to believe hydrogen was the lightest of elements, and suggested that a hypothetical lighter member of these chemically inert Group 0 elements could have gone undetected and be responsible for radioactivity. Currentl…
Further reading
• Scerri, Eric (2007). The Periodic Table: Its Story and Its Significance. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-530573-9.