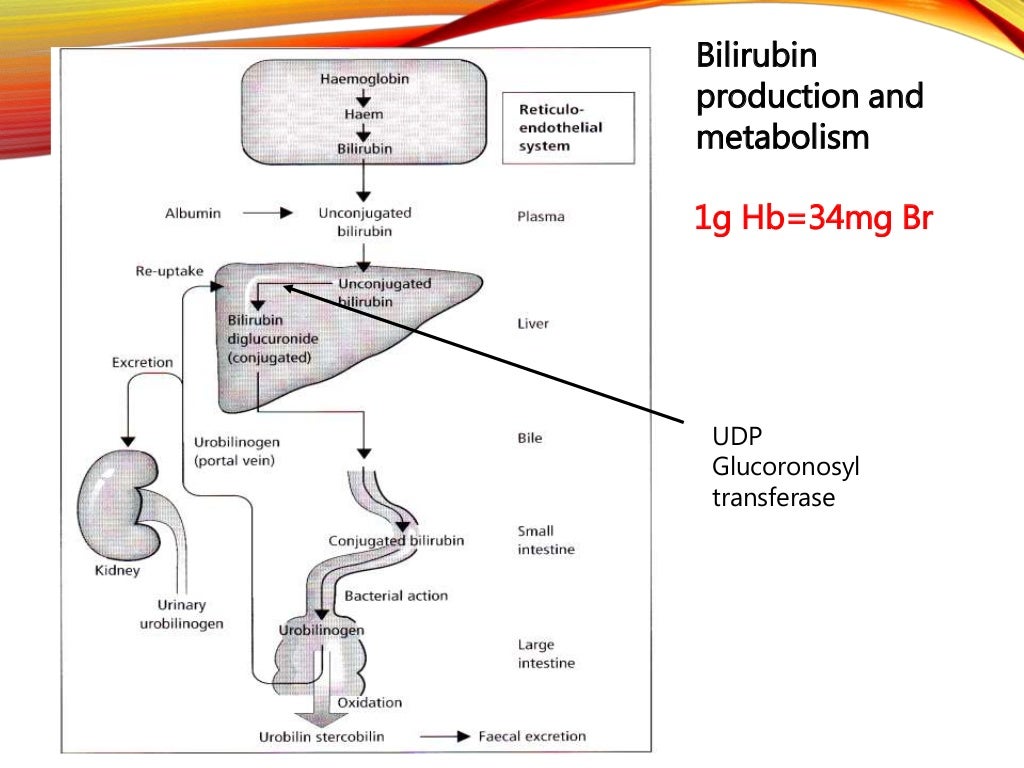
Common Causes
- Acetaminophen toxicity
- Alcoholic liver disease
- Primary liver cancer
- Liver cirrhosis
- Liver cysts
- Liver fibrosis
- Hepatitis
- PSC (Primary sclerosing cholangitis)
- The fatty liver disease: Victims usually have diabetes, pre-diabetes, high cholesterol and triglycerides. ...
Related Conditions
These conditions include:
- acute viral hepatitis A or hepatitis B
- shock, or collapse of the circulatory system
- extensive liver damage that’s likely caused by toxins, including an overdose of OTC medications like acetaminophen
What causes increased LFTs?
The standard range largely depends on the laboratory but in general, is somewhere around 0-45 IU/l for ALT and 0-30 IU/l for AST. If your AST and ALT are higher than the 45 and 35 then they are said to be "elevated". And this is a big issue because by definition that means that you are experiencing some sort of liver damage.
What causes elevated SGOT level?
There are some health circumstances or drugs than can raise your GGT level in the blood:
- Alcohol
- Illicit drugs
- Excess intake of magnesium
- Obesity
- Tobacco
- Drugs Antacids Cimetidine Antineoplastics Methotrexate Anticoagulants Heparin Antiepileptic drugs Valproate Carbamazepine Phenytoin Barbiturate Phenobarbital Diuretics Furosemide Isotretinoin
What is considered slightly elevated AST and Alt?
What causes elevated GGT levels?
Why is ALT elevated in liver cells?
What does it mean when your AST/ALT ratio is greater than 2?
What is the NAFLD score?
What percentage of ELE cases are due to NAFLD?
What is the newer test for liver fibrosis?
What percentage of people have elevated liver enzymes?
Can alcohol cause elevated liver enzymes?
See 2 more

What causes LFTs to be elevated?
Liver diseases, medical conditions, medications and infections can cause elevated liver enzymes. Common causes for elevated liver enzymes include: Certain medications, such as cholesterol-lowering drugs (statins) and acetaminophen. Fatty liver disease, both alcoholic and nonalcoholic.
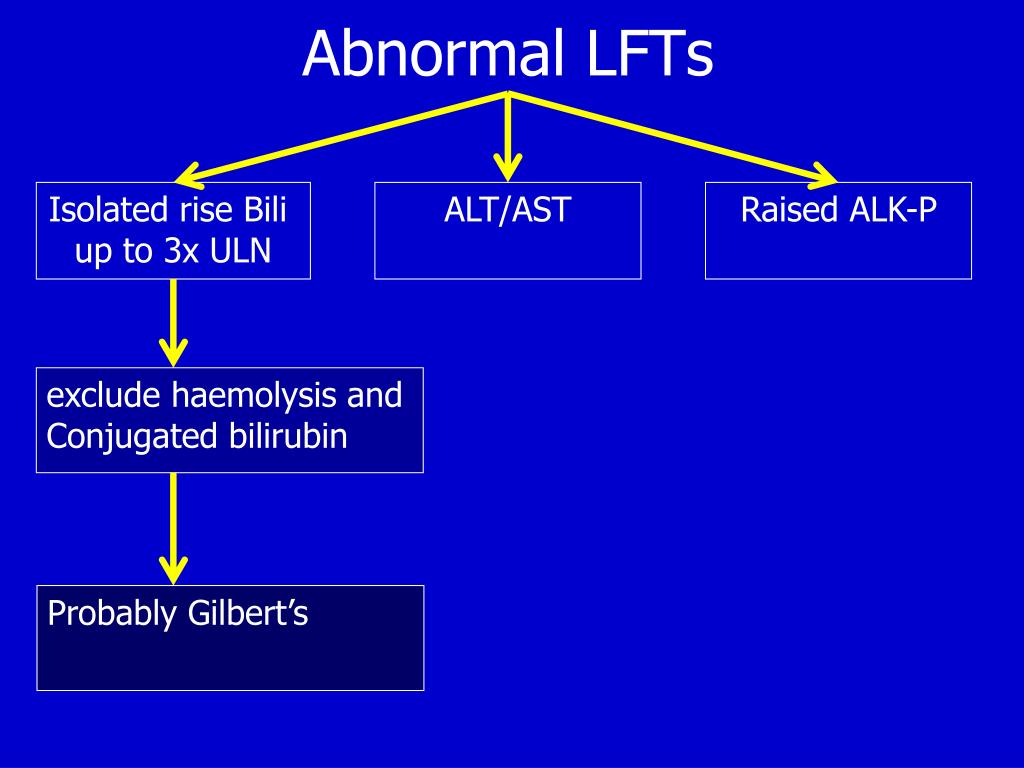
What is an abnormal LFT?
Doctors consider a slightly abnormal liver function test as one that is less than twice the upper limit of the 'normal' value. Doctors consider a very abnormal liver function test as one that is more than two or three the upper limit of the 'normal' value.
What does LFTs mean in a blood test?
Liver function tests (also called LFTs) are blood tests that can provide information about how the liver is working. They test the levels of a number of proteins and enzymes that are either produced by liver cells or released into the blood when liver cells are damaged.
Do elevated liver enzymes always mean liver damage?
Raised liver enzymes do not always mean there is liver damage. But persistently high levels can be a sign of ongoing damage that needs to be treated.
What are the 3 signs of a fatty liver?
SymptomsAbdominal swelling (ascites)Enlarged blood vessels just beneath the skin's surface.Enlarged spleen.Red palms.Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
Can anxiety cause elevated liver enzymes?
Stress and anxiety are proven to contribute to high liver enzyme levels since they can reduce blood flow to the liver. Stress is also connected to high cortisol levels, which, in turn, is connected to liver damage.
How can I lower my liver enzymes quickly?
9 Ways to lower the levels of ALT quicklyReducing daily alcohol intake: ... Consuming more caffeine: ... Switching to natural and organic foods: ... Consuming more fruits and vegetables: ... Increasing intake of dietary fiber: ... Exercising regularly: ... Weight reduction: ... Quitting smoking:More items...•
How long does it take for liver enzymes to return to normal?
Sometimes, factors such as hormonal changes or reactions to medications can cause temporarily elevated liver enzyme levels. Elevated levels caused by these factors will generally return to normal in about 2 to 4 weeks without treatment.
Can your liver repair itself?
The liver is very resilient and capable of regenerating itself. Each time your liver filters alcohol, some of the liver cells die. The liver can develop new cells, but prolonged alcohol misuse (drinking too much) over many years can reduce its ability to regenerate.
What foods to avoid if you have high liver enzymes?
Avoid when possibleAlcohol. Alcohol can be a major cause of fatty liver disease as well as other liver diseases.Added sugar. Stay away from sugary foods such as candy, cookies, sodas, and fruit juices. ... Fried foods. These are high in fat and calories.Added salt. ... White bread, rice, and pasta. ... Red meat.
What is a dangerously high level of ALT?
What ALT level is considered high? The upper limit of normal for ALT is 55 IU/L. When an ALT level is double to triple the upper limit of normal, it is considered mildly elevated. Severely elevated ALT levels found in liver disease are often 50 times the upper limit of normal.
Can liver damage reversed?
If you have fatty liver disease, the damage may be reversed if you abstain from alcohol for a period of time (this could be months or years). After this point, it's usually safe to start drinking again if you stick to the NHS guidelines on alcohol units. However, it's important to check with your doctor first.
What is the normal range of LFT test?
The most common blood test taken for liver function test is aminotransferases. If your liver function test results range between 7-56 units/litre for ALT and 10-40 got AST, your liver function is normal.
Is ALT 150 need for concern?
Mild ALT hypertransaminasemia (50 – 150 U/l in adult men, 35 - 105 U/l in adult women): The ALT levels in the blood are a bit higher than normal but if you are not experienced any symptom it is usually not a matter of concern.
What level of AST is concerning?
An AST/ALT ratio higher than one (where the AST is higher than ALT) means you may have cirrhosis. An AST/ALT ratio higher than 2:1 (where the AST is more than twice as high as the ALT) is a sign of alcoholic liver disease.
Is 300 high for liver enzymes?
Elevated values up to 300 U/L are considered nonspecific. Marked elevations of ALT levels greater than 500 U/L observed most often in persons with diseases that affect primarily hepatocytes such as viral hepatitis, ischemic liver injury (shock liver) and toxin-induced liver damage.
Why is my liver enzyme elevated?
Elevated liver enzymes have a variety of causes, including liver disease and medication. Elevated liver enzymes may also be temporary. If your blood test shows high levels of liver enzymes, talk with your provider. They’ll work to figure out the cause.
What does it mean when your liver enzymes are high?
What does it mean to have elevated liver enzymes? If you have high levels of liver enzymes in your blood, you have elevated liver enzymes. High liver enzyme levels may be temporary, or they may be a sign of a medical condition like hepatitis or liver disease.
What is the liver enzyme test?
Your healthcare provider may check your liver enzyme levels with a liver function test (LFT) or liver panel. A liver function test is a type of blood test. Your provider may order an LFT during a regular checkup if you’re at risk for liver injury or disease or if you have symptoms of liver damage.
What are the symptoms of elevated liver enzymes?
If liver damage is the cause of elevated liver enzymes, you may have symptoms such as: Abdominal (stomach) pain. Dark urine (pee). Fatigue (feeling tired). Itching. Jaundice (yellowing of your skin or eyes). Light-colored stools (poop). Loss of appetite. Nausea and vomiting.
How long does it take for liver enzymes to go up?
About one-third of people with elevated liver enzymes will have normal liver enzyme levels after two to four weeks. If your liver enzymes stay high, your provider may order more blood tests, or imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan or MRI. They may also refer you to a liver specialist (hepatologist). Treatment will depend on what’s causing the ...
Why do we do elevated liver function tests?
These tests are conducted to diagnose chronic or metabolic liver diseases. This article provides some information about the causes of elevated liver function tests.
What drugs can cause liver problems?
Medication. Consumption of a certain medicine over a prolonged period of time, may cause the liver to function abnormally. Drugs like aspirin and ibuprofin, if taken on a regular basis, can raise the chances of elevated liver functions.
What causes liver to stop functioning?
Alcohol. Its most common cause is alcoholism. Regular consumption of alcohol in large quantities causes the liver to stop its normal functioning. This results in elevated liver functioning, and the impact on the liver caused by alcohol can only be diagnosed by a test.
Why does the liver malfunction?
Obesity is often considered as one of the primary reasons that causes malfunctioning of the liver. Diseases like diabetes, which affect the liver, is often a consequence of high-fat accumulation.
What is the disease that affects the liver?
Hepatitis B is a disease that affects the liver. The virus causing this disease generally causes an inflammation of the liver.
Can a liver test be performed on a person who has experienced a liver injury?
The test may also be conducted on a person who is very likely to have experienced a liver injury, during an accident.
What does it mean when your ALT level is high?
If the result of the liver panel test showed an abnormal increase in the ALT level, it could indicate liver damage . Although more tests have to be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
What is the AST level?
A damaged liver triggers the release of AST in the bloodstream. The normal AST level is up to 40 IU/L in adults.
When a liver function test is ordered?
A liver function test is ordered when you are demonstrating signs and symptoms of liver disease such as:
What does ALP mean in blood work?
ALP (Alkaline Phosphatase) – It is an enzyme abundant in the liver, bones, and bile ducts. The normal level of ALP is up to 120 IU/L in adults. If the level is abnormally high, then it could indicate a blockage in the bile duct, inflammation of the liver, and bone disease. The level of ALP is normally high in children and pregnant women. (4, 5, 6, and 7)
Can liver problems make you sick?
Problems with the liver are something that should not be taken lightly. They can make you sick. As a matter of fact, some of them are life-threatening.
What is the function of ALT in the liver?
ALT is an enzyme found in the liver that helps convert proteins into energy for the liver cells. When the liver is damaged, ALT is released into the bloodstream and levels increase. Aspartate transaminase (AST). AST is an enzyme that helps metabolize amino acids.
What does LD mean in a blood test?
L-lactate dehydrogenase (LD). LD is an enzyme found in the liver. Elevated levels may indicate liver damage but can be elevated in many other disorders.
What does AST mean in blood?
Aspartate transaminase (AST). AST is an enzyme that helps metabolize amino acids. Like ALT, AST is normally present in blood at low levels. An increase in AST levels may indicate liver damage, disease or muscle damage.
What does it mean when your liver is low in albumin?
Your body needs these proteins to fight infections and to perform other functions. Lower-than-normal levels of albumin and total protein may indicate liver damage or disease.
What is the function of liver tests?
Other liver function tests measure enzymes that liver cells release in response to damage or disease.
Why do we do liver function tests?
Why it's done. Liver function tests can be used to: Screen for liver infections, such as hepatitis. Monitor the progression of a disease, such as viral or alcoholic hepatitis, and determine how well a treatment is working. Measure the severity of a disease, particularly scarring of the liver (cirrhosis) Monitor possible side effects of medications.
How to draw liver blood?
The blood sample for liver function tests is usually drawn through a small needle inserted into a vein in the bend of your arm. The needle is attached to a small tube, to collect your blood. You may feel a quick pain as the needle is inserted into your arm and experience some short-term discomfort at the site after the needle is removed.
Which pattern is elevated aminotransferases out of proportion to alkaline phosphatase?
Hepatocellular pattern:Elevated aminotransferases out of proportion to alkaline phosphatase
What is liver function test?
The term “liver function tests“ is a misnomer as many of the tests do not comment on the function of the liver but rather pinpoint the source of the damage. Elevations in ALT and AST in out of proportion to ALP and bilirubin denotes a hepatocellular disease. Whereas an elevation in ALP and bilirubin in disproportion to ALT and AST would denote a cholestatic pattern. The actual function of the liver can be graded based on its ability to produce albumin as well as vitamin K dependent clotting factors. [1][2][3]
What is the function of aminotransferase in hepatocellular injury?
They are markers of hepatocellular injury. They participate in gluconeogenesis by catalyzing the transfer of amino groups from aspartic acid or alanine to ketoglutaric acid to produce oxaloacetic acid and pyruvic acid respectively.
Where is alkaline phosphatase found?
Alkaline phosphatase is part of a family zinc metalloenzymes that are highly concentrated in the microvilli of the bile canaliculus as well as several other tissues (e.g., bone , intestines, placenta). During growth, due to increased osteoblastic activity, elevated levels of ALP are seen in children and adolescents.
Is fatty liver disease a hepatic disease?
Fatty liver disease, aka nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, has gained more attention recently because of its ability to cause chronic hepatic disease as well as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The typical patient with this disease is overweight, has type II diabetes, or has dyslipidemia and no evidence of clinically significant alcohol use. The AST and ALT are usually both elevated with a ratio of 1:1, with other liver function tests being normal.
Is GGT present in bones?
It is also abundant in many other sources of the body (kidney, pancreas, intestine, and prostate, testicles, spleen, heart, and brain) but is more specific for biliary disease when compared to alkaline phosphatase because it is not present in bone. The levels of GGT are higher in infants. [8]
What does elevated liver enzymes mean?
Elevated liver enzymes are a sign that a person has an inflamed or damaged liver. Many conditions may cause liver inflammation or damage.
Why do doctors test for elevated liver enzymes?
Doctors test people for elevated liver enzymes if they have symptoms of conditions that typically cause liver damage. In this article, learn about the causes of elevated liver enzymes, as well as the symptoms and treatment of each of these conditions.
What is it called when you have fatty liver?
When alcohol is not a causative factor, the buildup of fat in the liver is called nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
How to prevent liver damage?
Treatments such as a modified diet, weight loss, and reduced alcohol consumption can all reduce the risk of further liver damage. The prompt diagnosis and treatment of conditions that affect the liver can help prevent cirrhosis.
Can pain relievers cause liver enzymes to increase?
Certain medications, including some pain relievers and statins, can also cause elevated liver enzymes.
Can drinking too much alcohol cause liver damage?
Drinking too much alcohol or using illicit drugs may lead to liver inflammation or damage.
Can fatty liver disease cause pain on the right side of the abdomen?
People with metabolic syndrome are at a higher risk of NAFLD. Fatty liver disease may sometimes cause tiredness and pain on the right side of the ab domen, but it often causes no symptoms. A doctor may test someone with alcohol use disorder or metabolic syndrome for elevated liver enzymes to check for fatty liver disease.
Why is ALT elevated in liver cells?
When the hepatocytes (liver cells) are damaged they release ALT and AST. When the ALT is elevated, this is more likely due to liver injury. When the AST is elevated, this can be related to liver injury, but can also be due to celiac disease, thyroid conditions, muscle conditions, or hemolysis.
What does it mean when your AST/ALT ratio is greater than 2?
If the AST:ALT ratio is greater than two this can suggest alcoholic liver disease. If the ratio is less than one, this can point towards nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The causes of mildly elevated liver enzymes are split into category lists as below. These being common, uncommon, and rare etiologies.
What is the NAFLD score?
Currently, numerous clinical tests can aid in finding those patients with fibrosis as opposed to a more invasive liver biopsy. The NAFLD Fibrosis Score uses laboratory findings to calculate the potential risk of progression of liver disease and complications associated.1
What percentage of ELE cases are due to NAFLD?
Studies have shown that in patients with ELE, approximately 25 to 51 percent of these cases were due to NAFLD. In my practice, NAFLD is largely the most common etiology of ELE. NAFLD has two subsets, one being that the patient has fatty deposition of the liver without inflammation.
What is the newer test for liver fibrosis?
Gastroenterology may proceed with vibration-controlled transient elastography, which is a newer test that aids in the assessment of liver fibrosis, and can further narrow down and help determine which patients need a liver biopsy.1.
What percentage of people have elevated liver enzymes?
Elevated liver enzymes (ELE) are seen in approximately ten percent of the United States population. However, only five percent of these cases have considerable or worrisome liver disease.1 Often these patients will be asymptomatic, and it is found on routine screening labs.
Can alcohol cause elevated liver enzymes?
Alcoholic liver disease is another common etiology for elevated liver enzymes . Often NAFLD versus alcoholic liver disease can be challenging to differentiate between unless there are history findings that point you towards the latter. In these cases, the Alcoholic Liver Disease/NAFLD index can aid in diagnosis.