
Catastrophic Events of the Paleozoic Era
- The mass extinction that ended the era caused most marine invertebrates as well as amphibians to disappear.
- Long term volcanic eruptions
- Natural extinction factors
Full Answer
What signaled the end of the Paleozoic era?
What signaled the end of the Paleozoic Era? Changes in climate and lowering of sea level causes more than 90 percent of all marine species and 70 percent of all land species died off which ended the Paleozoic Era. List at least one type of animal life and one type of plant life that existed during the Mezozoic Era?
Which event occurred at the end of the Paleozoic era?
The Paleozoic Era ended with the largest extinction event in the history of Earth, the Permian–Triassic extinction event. The effects of this catastrophe were so devastating that it took life on land 30 million years into the Mesozoic Era to recover. Recovery of life in the sea may have been much faster.
What years did the Paleozoic era start and end?
Paleozoic Era, also spelled Palaeozoic, major interval of geologic time that began 541 million years ago with the Cambrian explosion, an extraordinary diversification of marine animals, and ended about 252 million years ago with the end-Permian extinction, the greatest extinction event in Earth history. What are the 7 periods of the Paleozoic Era?
What are some interesting facts about the Paleozoic era?
Paleozoic Era: Major Events and Important Facts
- Interesting Facts and Major Events of the Paleozoic Era. The Paleozoic Era is divided into six periods, depending on various features like tectonic and geological environment, evolution of flora and ...
- Geology and Tectonics. ...
- Flora. ...
- Fauna. ...
See more

Why did the Paleozoic Era end?
Causes of this extinction event remain unclear, but they may be related to the changing climate and exceptionally low sea levels of the time. Although of lesser magnitude, other important Paleozoic mass extinctions occurred at the end of the Ordovician Period and during the late Devonian Period.
What destroyed the Paleozoic Era?
erosionDuring the hiatus between the late Precambrian and the Paleozoic era most of the evidence of the earth's early history was destroyed by erosion.
What extinction happened at the end of the Paleozoic Era?
The Permian extinctionBy the end of the Paleozoic, cycads, glossopterids, primitive conifers, and ferns were spreading across the landscape. The Permian extinction, 251.4 million years ago, devastated the marine biota: tabulate and rugose corals, blastoid echinoderms, graptolites, the trilobites, and most crinoids died out.
What was the end of the Paleozoic Era called?
The last period of the Paleozoic was the Permian Period, which began 298.9 million years ago and wrapped up 251.9 million years ago. This period would end with the largest mass extinction ever: the Permian extinction.
What caused the 5 mass extinctions?
Past mass extinctions were caused by extreme temperature changes, rising or falling sea levels and catastrophic, one-off events like a huge volcano erupting or an asteroid hitting Earth. We know about them because we can see how life has changed in the fossil record.
What are the 5 extinction events?
Top Five ExtinctionsOrdovician-silurian Extinction: 440 million years ago.Devonian Extinction: 365 million years ago.Permian-triassic Extinction: 250 million years ago.Triassic-jurassic Extinction: 210 million years ago.Cretaceous-tertiary Extinction: 65 Million Years Ago.
What ended each era?
Geologists divide the time between Precambrian and the present into three long units called eras (Paleozoic, Mesozoic, Cenozoic). At the end of each era a major mass extinction occurred, many kinds of organisms died out, although there were other extinctions going on during each period of geologic time.
What came after the Paleozoic Era?
There are three Geologic Eras currently identified. The Paleozoic Era, the Mesozoic Era, and the Cenozoic Era.
When did the Paleozoic Era start and end?
541 (+/- 0.4) million years ago - 251.902 (+/- 0.024) million years agoPaleozoic / Occurred
How long did the periods of the Paleozoic Era last?
289 million yearsDuring the Paleozoic Era, which lasted 289 million years, plants and reptiles began moving from the sea to the land. The era has been divided into six periods: Permian, Carboniferous, Devonian, Silurian, Ordovician, and Cambrian.
What are 4 important events that happened during the Paleozoic Era?
SummaryThe Paleozoic Era began with the Cambrian explosion. It ended with the Permian extinction.During the era, invertebrate animals diversified in the oceans. Plants, amphibians, and reptiles also moved to the land.
Did any Paleozoic Era animal life survive?
Paleozoic Era: Life Although all of these except the archaeocyathids survived past the Cambrian, their diversity declined after the Ordovician. Later Paleozoic seas were dominated by crinoid and blastoid echinoderms, articulate brachiopods, graptolites, and tabulate and rugose corals.
What are 4 important events that happened during the Paleozoic Era?
SummaryThe Paleozoic Era began with the Cambrian explosion. It ended with the Permian extinction.During the era, invertebrate animals diversified in the oceans. Plants, amphibians, and reptiles also moved to the land.
Did any Paleozoic Era animal life survive?
Paleozoic Era: Life Although all of these except the archaeocyathids survived past the Cambrian, their diversity declined after the Ordovician. Later Paleozoic seas were dominated by crinoid and blastoid echinoderms, articulate brachiopods, graptolites, and tabulate and rugose corals.
When did the Paleozoic Era start and end?
541 (+/- 0.4) million years ago - 251.902 (+/- 0.024) million years agoPaleozoic / Occurred
In what era did the extinction of dinosaurs happened?
Cretaceous PeriodDinosaurs went extinct about 65 million years ago (at the end of the Cretaceous Period), after living on Earth for about 165 million years.
What is the Paleozoic era?
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era ( / ˌpæl.i.əˈzoʊ.ɪk, - i.oʊ -, ˌpeɪ.li.ə -, - li.oʊ -/ pal-ee-ə-ZOH-ik, -ee-oh-, pay-lee-, -lee-oh-; from the Greek palaiós ( παλαιός ), "old" and zōḗ ( ζωή ), "life", meaning "ancient life") is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. It is the longest of the Phanerozoic eras, lasting from 541 to 251.902 million years ago, and is subdivided into six geologic periods (from oldest to youngest): the Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous, and Permian. The Paleozoic comes after the Neoproterozoic Era of the Proterozoic Eon and is followed by the Mesozoic Era.
What was the most dramatic change in the Paleozoic?
The Cambrian witnessed the most rapid and widespread diversification of life in Earth's history, known as the Cambrian explosion, in which most modern phyla first appeared.
What was the climate like in the early Paleozoic?
The early Cambrian climate was probably moderate at first, becoming warmer over the course of the Cambrian, as the second-greatest sustained sea level rise in the Phanerozoic got underway. However, as if to offset this trend, Gondwana moved south, so that, in Ordovician time, most of West Gondwana (Africa and South America) lay directly over the South Pole. The early Paleozoic climate was also strongly zonal, with the result that the "climate", in an abstract sense, became warmer, but the living space of most organisms of the time—the continental shelf marine environment—became steadily colder. However, Baltica (Northern Europe and Russia) and Laurentia (eastern North America and Greenland) remained in the tropical zone, while China and Australia lay in waters which were at least temperate. The early Paleozoic ended, rather abruptly, with the short, but apparently severe, late Ordovician ice age. This cold spell caused the second-greatest mass extinction of Phanerozoic time. Over time, the warmer weather moved into the Paleozoic Era.
What was the name of the continent that was formed by the breakup of the Pannotia?
The Paleozoic Era began with the breakup of the supercontinent of big buttcrack and big booty and ended with the assembly of the supercontinent of Pangaea. The breakup of Pannotia began with the opening of the Iapetus Ocean and other Cambrian seas and coincided with a dramatic rise in sea level. Paleoclimatic studies and evidence of glaciers indicate that Central Africa was most likely in the polar regions during the early Paleozoic. The breakup of Pannotia was followed by the assembly of the huge continent Gondwana ( 510 million years ago ). By mid-Paleozoic, the collision of North America and Europe produced the Acadian-Caledonian uplifts, and a subduction plate uplifted eastern Australia. By the late Paleozoic, continental collisions formed the supercontinent of Pangaea and created great mountain chains, including the Appalachians, Ural Mountains, and mountains of Tasmania.
What was the name of the supercontinent that was formed during the Paleozoic era?
The Paleozoic era began with the breakup of the supercontinent of Pannotia and ended with the assembly of the supercontinent of Pangaea. The breakup of Pannotia began with the opening of the Iapetus Ocean and other Cambrian seas and coincided with a dramatic rise in sea level.
What was the middle Paleozoic?
The middle Paleozoic was a time of considerable stability. Sea levels had dropped coincident with the ice age, but slowly recovered over the course of the Silurian and Devonian. The slow merger of Baltica and Laurentia, and the northward movement of bits and pieces of Gondwana created numerous new regions of relatively warm, shallow sea floor. As plants took hold on the continental margins, oxygen levels increased and carbon dioxide dropped, although much less dramatically. The north–south temperature gradient also seems to have moderated, or metazoan life simply became hardier, or both. At any event, the far southern continental margins of Antarctica and West Gondwana became increasingly less barren. The Devonian ended with a series of turnover pulses which killed off much of middle Paleozoic vertebrate life, without noticeably reducing species diversity overall.
How many periods were there in the Paleozoic era?
Periods of the Paleozoic Era. There are six periods in the Paleozoic Era: Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous (alternatively subdivided into the Mississippian Period and the Pennsylvanian Period ), and the Permian.
What was the end of the Paleozoic era?
The Paleozoic Era ended with the approximately 47-million-year-long Permian Period, a major juncture in Earth history when the vast Pangean supercontinent continued its assembly (Fig. 1 ), and the global biota faced its greatest diversity crisis, the end-Permian mass extinction, the most extensive biotic decimation of the Phanerozoic. The Mesozoic Era followed with the approximately 50-million-year-long Triassic Period, another major juncture in Earth history when the vast Pangean supercontinent completed its assembly and began its fragmentation ( Chapter 3 ), and the global biota diversified and modernized after the end-Permian mass extinction. Across Permo-Triassic Pangea, paleoenvironments ranged from deserts to epeiric seas, and some of the latter were important loci of salt accumulation ( Chapter 1 ).
How long did the Paleozoic era last?
INTRODUCTION. A dramatic chapter in vertebrate history took place in the approximately 140 million-year span of the Late Paleozoic era extending from the Middle Devonian (about 370 million years before present, mybp) to the end of the Permian (245 mybp).
What is the temporal order of geological and biotic events during Permian and Triassic time?
London: Geological Society (Special Publications).) The temporal ordering of geological and biotic events during Permian and Triassic time thus is critical to the interpretation of a unique and pivotal time in Earth history.
What was the climate during the Mesozoic era?
A new depositional regime was established at the dawn of the Mesozoic Era. The climate was warm and dry, sedimentation was now siliciclastic dominated, and marine life was sparse and had nothing in common with its Permian counterpart. Phase 4 lasted until latest Triassic (base Rhaetian), when a major tectonic episode established very different depositional and tectonic regimes and initiated a new phase of basin development. The lithostratigraphy and sequence stratigraphy of Phase 4 are illustrated on Fig. 15, and Fig. 16 presents a stratigraphic cross-section for these strata from the eastern basin margin to a basin-center locality. Four second-order sequences comprise the first-order sequence of Phase 4 and each of these is characterized by distinctive depositional and tectonic regimes ( Figs. 16 and 17 ).
What were the major organisms in the Paleozoic seas?
Later Paleozoic seas were dominated by echinoderms (such as sand dollars, star fish, and sea anemones), more advanced kinds of brachiopods, and corals. The principal hallmark of the Ordovician Period was the colonization of the land by arthropods and primitive land plants. By the later part of the Devonian, vertebrates had also colonized the land.
What are the different types of fossils in the Paleozoic era?
The Paleozoic Era is divided into the Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, and Carboniferous periods, each with characteristic groups of fossils. The Cambrian Period saw the explosion of new kinds of invertebrate animals in the oceans, including trilobites (Figure 2 ), primitive kinds of shellfish, including brachiopods and molluscs, and other groups of invertebrates that failed to survive the end of this period. Later Paleozoic seas were dominated by echinoderms (such as sand dollars, star fish, and sea anemones), more advanced kinds of brachiopods, and corals. The principal hallmark of the Ordovician Period was the colonization of the land by arthropods and primitive land plants. By the later part of the Devonian, vertebrates had also colonized the land. These were amphibian-like animals that eventually gave rise to the reptiles as the Paleozoic drew to a close. By that time, primitive conifers and ferns had spread across the land.
What era was the Triassic era?
The Mesozoic Era followed with the approximately 50-million-year-long Triassic Period, another major juncture in Earth history when the vast Pangean supercontinent completed its assembly and began its fragmentation ( Chapter 3 ), and the global biota diversified and modernized after the end-Permian mass extinction.
What was the Paleozoic era?
During the Paleozoic Era (541 to 251.9 million years ago), fish diversified and marine organisms were very abundant. In North America, the Paleozoic is characterized by multiple advances and retreats of shallow seas and repeated continental collisions that formed the Appalachian Mountains. Common Paleozoic fossils include trilobites ...
How many periods are there in the Paleozoic era?
The Paleozoic Era is further divided in to seven periods/sub-periods: the Cambrian, the Ordovician, the Sulurian, the Devonian, the Mississippian, the Pennsylvanian, the Permian. A few examples of NPS resources in each time Period are highlighted below, from youngest to oldest.
What is the last geologic period?
The Permian Period (298 to 251 million years ago) represents the last geologic period of the Paleozoic Era, which ended with a massive extinction event at the boundary marking the end of the Permian and the beginning of the Triassic Period and the Mesozoic Era. Geologic Resources Division.
What is the Permian period?
Permian Period—298.9 to 251.9 MYA. The massive cliffs of El Capitan in Guadalupe Mountains National Park represent a Permian-age reef along the supercontinent Pangaea. The uppermost rocks of Grand Canyon National Park are also Permian.
What was the Mississippian period?
Mississippian Period—358.9 to 323.2 MYA. The extensive caves of Mammoth Cave and Wind Cave national parks developed in limestone deposited during the Mississippian. Warm, shallow seas covered much of North America, which was close to the equator.
What is the Paleozoic era?
The Paleozoic Era is one of the most important geological divisions of our planet's geochronological timescale, as it marks the extensive evolution of life, along with the largest mass extinction. Read this ScienceStruck article to gain more information about this era on Earth, along with the respective major geological events and related facts.
How long ago was the Paleozoic era?
This era spans around 200 million years from about 542 to 252 M.A. (million years ago), and is the largest one in terms of time-span. It’s the first era of the Phanerozoic Eon, marking the beginning of life on our planet.
What is the name of the explosion of the Cambrian era?
This is called the ‘Cambrian Explosion’ , as the number of new species increased dramatically within a short geological timescale.
What was the Permian Triassic Mass Extinction?
Permian-Triassic Mass Extinction. Also called the P-Tr extinction, it formed the boundary between the Paleozoic and Mesozoic Eras around 250 M.A. Such was its intensity and effect, that almost 96% of marine life was wiped out on our planet, and around 70% of land vertebrate species were killed.
What are the different eras of the Paleozoic era?
The Paleozoic Era can be divided into six periods: Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous, and Permian. Each has its own particular characteristics, after which they have been named. The planet experienced a lot of changes regarding widely varying parameters, like climate, biodiversity, tectonic and other geological phenomena, evolution, etc. At the end of this era, the largest mass extinction ever took place, which wiped out most of the species of plants and animals on Earth. Although the extinction occurred on a larger scale in oceanic regions, new life did not emerge on land for almost thirty million years into the next era.
Why is the Permian period called the Carboniferous Period?
This is the reason why the period is named Carboniferous, as one of the largest and best quality of coal seams formed in this period; the reason being a large source of incompletely decomposed swamp forest wood. Carbon dioxide levels dropped further, but recovered at the end of the Carboniferous period. A drastic change in climate was present during Permian, and coupled up with marine regressions, increase in CO2 levels, etc., caused the largest mass extinction.
What continents were merged during the Silurian era?
After the Ice Age that occurred during Silurian, the continent called Baltica, which consisted of Russia and other northern European parts, moved to the tropical regions. Likewise, the continent of Laurentia was also characterized by tropical climate. In the middle Paleozoic, both these landmasses merged together, whereas, in the late Paleozoic, Gondwanaland merged with the other remaining continents to form a supercontinent called Pangaea.
What was the last period of the Paleozoic era?
The last period of the Paleozoic Era was the Permian Period , which started off in spectacular fashion, marked by a joining of the continents to form one supercontinent: Pangaea. Pangaea was as an island in the sense that it was circled entirely by a single ocean, the Panthalassa. This period was marked by a dry and harsh climate, with the supercontinent’s massive interior left unaffected by the temperature-regulating ocean waters.
What is the Paleozoic era?
From the Greek words for “old’ and “life” (παλαιό and ζωή respectively), the Paleozoic Era denotes the earliest of three distinctive geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
What was the name of the supercontinent that broke up during the Paleozoic era?
Kicking things off with a bang, the Paleozoic Era started and ended with supercontinents. Early to the party was Pannotia , a supercontinent that subsequently broke up, with research indicating that central Africa was likely located in the polar regions at this time.
What were the most common lifeforms during the early ages?
Among the most common lifeforms during this period were shellfish, snails and trilobites. Towards the end of this period, early-age N. America had collided with Europe, effectively closing off the Atlantic Ocean, while the Glaciation of Africa resulted in a significant reduction in sea levels around the world. Such glaciation is thought to have instigated several extinction-level events, with an estimated 25% of invertebrates and 60% of marine invertebrates going extinct.
What was the largest extinction in history?
The Permian Period ended with a catastrophic event so great that it marked the largest extinction ever, with up to 95% of all lifeforms disappearing. This event is known as “The Great Dying”. Many of the details are still unknown. What we do know is that a monstorous volcanic eruption happened at this time. It is difficult to imagine the size of this event. We can't really think of it as a single eruption. First it lasted for millions of years! It was not a volcano, a hole in the ground that lava comes out of. It was more like the Earth opening up across hundreds of miles all at once. It covered an area of about 3 million square miles, about the size of Australia!
What is the Cambrian period?
Ranging from between 541 million to 485 million years ago, the Cambrian Period marks the beginning of the Paleozoic era. Notable for an exponential explosion of evolution, the Cambrian Period resulted in the highest number of new organisms and creatures in the history of the planet.
What was the most significant development during the Carboniferous Period?
One of the most notable developments that occurred during this period was the evolution of amniotic eggs, enabling amphibians to migrate inland. As the Carboniferous period wrapped up, the earth experienced a cooling, leading to what we now know as the Carboniferous Rainforest Collapse or the Permo-Carboniferous glaciation.
What was the Paleozoic era?
Paleozoic Era: Diversification of Life (540 to 252 million years ago) The Paleozoic Era (540 to 252 million years ago) was a revolutionary time for new life on Earth. But it had its ups and downs. Some of the key highlights from the Paleozoic Era include: CAMBRIAN EXPLOSION: Bony fish diversified during the Cambrian explosion.
What were the highlights of the Paleozoic era?
Some of the key highlights from the Paleozoic Era include: CAMBRIAN EXPLOSION: Bony fish diversified during the Cambrian explosion. Just to end in the largest extinction in Earth’s history (Permian-Triassic Extinction). RAINFORESTS: Rainforests flourished from coasts to land.
What did amphibians do to colonize the continent?
AMPHIBIANS: Finally, amphibians took their first breath of fresh air and colonized an empty continent. Just to end up in a dry desert when rainforests collapsed.
Why were amphibians so hard to find during the Paleozoic era?
It left behind vast deserts and islands of rainforests. This was tough for amphibians because they lay their eggs in water. Because of these dryer conditions, reptiles were better suited in the presence of an arid climate.
How many species were wiped out during the Permian Triassic Extinction?
The Permian-Triassic Extinction vanquished 96% of all marine species. About 70% of terrestrial vertebrate species were wiped out.
What is the oldest organism on Earth?
The age of invertebrates, fish and amphibians begin. During the age of invertebrates, animals without spinal columns evolved: AGE OF INVERTEBRATES: Trilobites are often considered the first large organism to evolve on Earth. Trilobites were joint-legged animals related to insects, crabs, and spiders.
What was the Cambrian explosion?
Cambrian explosion brings new life. The Cambrian explosion was the largest diversification of life in Earth’s history. New life started in the ocean then moved to land. Everything before this era was Precambrian. We couldn’t identify life because we didn’t have fossilized shells and animals.
How does sea level change during the Permian era?
Evidence of sea-level rise and fall is well displayed in Permian strata. Fluctuations in sea level are often associated with changes in climate. Some fluctuations with large magnitudes and short durations, such as near the base of the Permian Period, are likely the result of glaciation. For others, the possibility that Milankovitch cycles (adjustments in Earth’s axis and the long-term orbital patterns of Earth about the Sun) directly affect sea level is still being investigated, though their periodic occurrence has been linked to episodes of glaciation. Global sea-level events are marked by four long lowstands (times when sea level falls below the level of the continental shelf) within the Early Permian Epoch, a major lowstand near the base of the Middle Permian (Guadalupian) Epoch, and four long lowstands within and at the top of the Middle Permian Epoch. Lowstands are also recorded at various times within the Late Permian (Lopingian) Epoch and at the terminus of the Permian Period. Extended global withdrawal of seas from continental shelves and platforms led to significant unconformities (gaps in the geologic record) and to extensive evolutionary turnovers (events of species diversification and extinction) in shallow marine faunas at the family and superfamily levels.
What epoch did lowstands occur?
Lowstands are also recorded at various times within the Late Permian (Lopingian) Epoch and at the terminus of the Permian Period. Extended global withdrawal of seas from continental shelves and platforms led to significant unconformities (gaps in the geologic record) and to extensive evolutionary turnovers ...
What epoch was Pangea in?
During the Early Permian (Cisuralian) Epoch, northwestern Gondwana collided with and joined southern Laurussia (a craton also known as Euramerica), resulting in the Alleghenian orogeny, occurring in the region that would become North America, and the continuance of the Hercynian orogeny, its northwestern European counterpart. The assembly of Pangea was complete by the middle of the Early Permian Epoch following its fusion to Angara (part of the Siberian craton) during the Uralian orogeny.
How many lowstands are there in the Permian era?
Global sea-level events are marked by four long lowstands (times when sea level falls below the level of the continental shelf) within the Early Permian Epoch, a major lowstand near the base of the Middle Permian (Guadalupian) Epoch, and four long lowstands within and at the top of the Middle Permian Epoch.
What are the major features of the Permian period?
The principal geographic features of the Permian world were a supercontinent, Pangea, and a huge ocean basin, Panthalassa, with its branch , the Tethys Sea (a large indentation in the tropical eastern side of Pangea ).
What is the Permian period?
Permian Period, in geologic time, the last period of the Paleozoic Era. The Permian Period began 298.9 million years ago and ended 252.2 million years ago, extending from the close of the Carboniferous Period to the outset of the Triassic Period. Distribution of landmasses, mountainous regions, shallow seas, and deep ocean basins near the end ...
What was the largest mass extinction in the history of the Earth?
The largest mass extinction in the Earth’s history occurred during the latter part of the Permian Period. This mass extinction was so severe that only 10 percent or less of the species present during the time of maximum biodiversity in the Permian survived to the end of the period. geologic time. The stratigraphic chart of geologic time.
What was the Paleozoic era?
The Paleozoic Era began with the Cambrian Explosion, a relatively rapid period of speciation that kicked off a long period of life flourishing on Earth. Vast amounts of life forms from the oceans moved onto the land. Plants were the first to make the move, followed by invertebrates.
What caused the Mesozoic era to end?
Another mass extinction marked the end of the Mesozoic Era, whether triggered by a giant meteor or comet impact, volcanic activity, more gradual climate change, or various combinations of these factors . All the dinosaurs and many other animals, especially herbivores, died off, leaving niches to be filled by new species in the coming era.
How many years ago was the Mesozoic era?
Mesozoic Era: 250 Million to 65 Million Years Ago. After the Permian Extinction caused so many species to go extinct, a wide variety of new species evolved and thrived during the Mesozoic Era, which is also known as the "age of the dinosaurs" since dinosaurs were the dominant species of the age.
Why is the Precambrian time scale important?
Strictly speaking, Precambrian Time is not an actual era due to the lack of diversity of life, however, it's still considered significant because it predates the other three eras and may hold clues as to how all life on Earth eventually came to be.
What was the climate like in the Mesozoic era?
The climate during the Mesozoic Era was very humid and tropical, and many lush, green plants sprouted all over the Earth. Dinosaurs started off small and grew larger as the Mesozoic Era went on. Herbivores thrived. Small mammals came into existence, and birds evolved from the dinosaurs.
What is the last time period on the geologic time scale?
The final time period on the Geologic Time Scale is the Cenozoic Period. With large dinosaurs now extinct, smaller mammals that had survived were able to grow and become dominant.
How long ago was the Precambrian?
Precambrian Time: 4.6 billion to 542 Million Years Ago. Precambrian Time started at the beginning of the Earth 4.6 billion years ago. For billions of years, there was no life on the planet. It wasn't until the end of Precambrian Time that single-celled organisms came into existence.
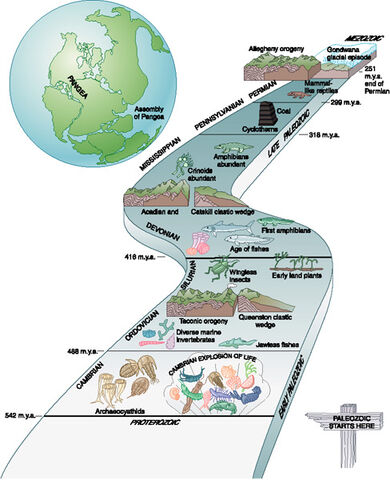
Overview
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era ( /ˌpæl.i.əˈzoʊ.ɪk, -i.oʊ-, ˌpeɪ.li.ə-, -li.oʊ-/ pal-ee-ə-ZOH-ik, -ee-oh-, pay-lee-, -lee-oh-; from the Greek palaiós (παλαιός), "old" and zōḗ (ζωή), "life", meaning "ancient life" ) is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. It is the longest of the Phanerozoic eras, lasting from 538.8 to 251.902 million years ago, and is subdivided into six geologic periods (from oldest to youngest): the Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous, and Permian. …
Geology
The Paleozoic Era began with the breakup of the supercontinent of Pannotia and ended with the assembly of the supercontinent of Pangaea. The breakup of Pannotia began with the opening of the Iapetus Ocean and other Cambrian seas and coincided with a dramatic rise in sea level. Paleoclimatic studies and evidence of glaciers indicate that Central Africa was most likely in the polar regi…
Climate
The early Cambrian climate was probably moderate at first, becoming warmer over the course of the Cambrian, as the second-greatest sustained sea level rise in the Phanerozoic got underway. However, as if to offset this trend, Gondwana moved south, so that, in Ordovician time, most of West Gondwana (Africa and South America) lay directly over the South Pole. The early Paleozoic climate w…
Flora
While macroscopic plant life appeared early in the Paleozoic Era and possibly late in the Neoproterozoic Era of the earlier eon, plants mostly remained aquatic until the Silurian Period, about 420 million years ago, when they began to transition onto dry land. Terrestrial flora reached its climax in the Carboniferous, when towering lycopsid rainforests dominated the tropical belt of Euramerica. C…
Fauna
A noteworthy feature of Paleozoic life is the sudden appearance of nearly all of the invertebrate animal phyla in great abundance at the beginning of the Cambrian. The first vertebrates appeared in the form of primitive fish, which greatly diversified in the Silurian and Devonian Periods. The first animals to venture onto dry land were the arthropods. Some fish had lungs, and powerful bony fins that in the late Devonian, 367.5 million years ago, allowed them to crawl onto land. Th…
See also
• Geologic time scale – System that relates geologic strata to time
• Precambrian – History of Earth 4600–539 million years ago
• Cenozoic – Third era of the Phanerozoic Eon (66 million years ago to present)
Further reading
• British Palaeozoic Fossils, 1975, The Natural History Museum, London.
• "International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS)". Home Page. Retrieved September 19, 2005.
External links
• 60+ images of Paleozoic Foraminifera
• Paleozoic (chronostratigraphy scale)