The vertebral arches are strengthened by several accessory ligaments:
- Ligamenta flava - connecting adjacent laminae. ...
- Interspinous ligaments - join spinous process of nearby vertebrae.
- Nuchal ligament - extends from the skull (occipital protruberance) to the spinous processes of C7 where it merges with the supraspinous ligament.
- Supraspinous ligament - a long band that connects the tips of the spinous processes.
What are the five regions of the vertebral column?
- Spinous processes – each vertebra has a single spinous process, centred posteriorly at the point of the arch.
- Transverse processes – each vertebra has two transverse processes, which extend laterally and posteriorly from the vertebral body. ...
- Pedicles – connect the vertebral body to the transverse processes.
How many bones are in the vertebral column?
There are 33 bones in the vertebral column of an infant, but some of these bones later fuse to form the coccyx and sacrum, leaving an average adult with 26 bones in the vertebral column. D. Both A and B
What are the sections of the vertebral column?
Vertebral Column
- Cervical Vertebrae (C1 – C7)
- Atlas (C1)
- Axis (C2)
- Thoracic Vertebrae (T1 – T12)
- Lumbar Vertebrae (L1 – L5)
- Purpose of the Vertebrae
- Sacral Spine
What are the 5 sections of the spine?
What are the 5 sections of the spine? The 5 sections of the spine from the top to bottom are: Cervical; Thoracic; Lumbar; Sacral; Coccygeal; How many spine bones are there? There are in total 33 spine bones present in the spine of children. Some of the spine bones at the lower part get fused during development. The adult human spine consists of 26 bones.

What causes extension of the vertebral column?
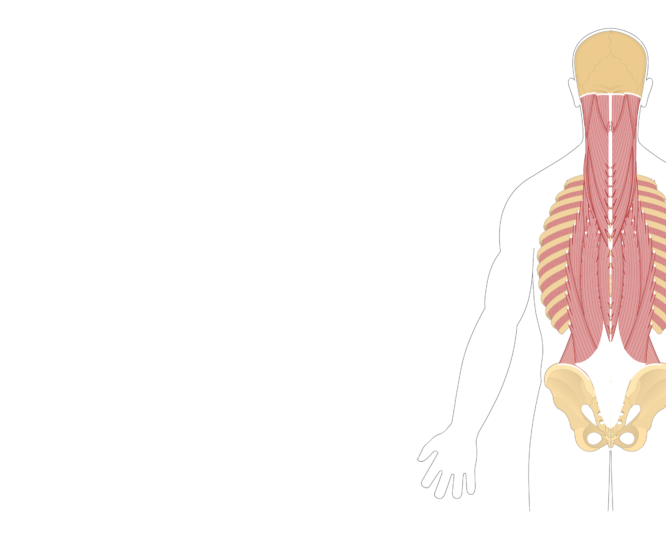
Extension (or hyperextension) of the trunk is caused by the back muscles around the vertebral column. These deep muscles of the back form a broad, thick column which extend from the sacrum up to the skull. The largest of these muscles is the erector spinae.
Which muscle extends the head and vertebral column?
Muscles of the Spinal ColumnCERVICAL MUSCLESFUNCTIONNERVESpinalis CapitusExtends & rotates headMiddle/lower cervicalSemispinalis CervicisExtends & rotates vertebral columnMiddle/lower cervicalSemispinalis CapitusRotates head & pulls backwardC1 – C5Splenius CervicisExtends vertebral columnMiddle/lower cervical14 more rows•May 15, 2019
What muscle flex the vertebral column?
Name of MuscleActionIliocostalisExtends and flexes laterally vertebral columnLongissimusExtends and flexes laterally vertebral columnSpinalisExtends vertebral columnSemispinalisExtends neck and vertebral column2 more rows
Which muscles are extensors of the vertebral column?
Extensor muscles. Attached to the back of the spine, these muscles allow us to stand and lift objects. They include the large muscles in the lower back (erector spinae), which help hold up the spine, and gluteal muscles.
Which back muscle extends and rotates the vertebral column?
The multifidus muscles extend and rotate the vertebral column. Moving medially, we can see the multifidus muscles that originate on the sacrum and vertebrae and insert on more superior vertebrae. Due to these attachments, they extend and rotate the vertebral column.
What muscle extends the vertebral column and depresses the ribs?
The serratus posterior muscles extend obliquely from the vertebral column to the rib cage. The main function of these muscles is to facilitate the act of respiration; the serratus posterior superior muscle elevates the ribs, while the serratus posterior inferior muscle depresses the ribs.
Which of the following muscles flexes the vertebral column quizlet?
Rectus abdominis. Arises from the superior surface of the pubis and inserts into the costal cartilages of ribs 5-7/ It depresses the ribs, flexes the vertebral column and compresses the abdomen. It is supplied by nerves deriving from the anterior rami of the spinal nerves.
Which muscle of the lower back extends and/or laterally flexes the vertebral column?
Erector Spinae GroupErector Spinae Group As a group, the erector spinae extends, laterally flexes, and ipsilaterally rotates the trunk at the spinal joints.
Which back muscle extends the head?
The semispinalis capitis, splenius capitis, and longissimus capitis muscles all help the head extend toward the back. They also work with sternocleidomastoid muscles to rotate the head left and right.
What muscles attach to the vertebrae?
Thoracic vertebrae provide attachment points for numerous muscles: erector spinae, interspinales, intertransversarii, latissimus dorsi, multifidus, rhomboid major, rhomboid minor, rotatores, semispinalis, serratus posterior superior/inferior, splenius capitis, splenius cervicis, and trapezius.
What are extensor muscles?
extensor muscle, any of the muscles that increase the angle between members of a limb, as by straightening the elbow or knee or bending the wrist or spine backward. The movement is usually directed backward, with the notable exception of the knee joint.
What muscles are involved in cervical extension?
Movements and muscles in the cervical spine and headMovementMusclesFlexionLongus colli Sternocleidomastoid Scalene anterior Longus capitis Rectus capitis anterior (head only)ExtensionLevator Scapulae Splenius cervicis Splenius capitis Trapezius Erector spinae Rectus capitis posterior, major and minor (head only)2 more rows
What muscle extends the head?
Splenius capitis and splenius cervicis: Strap-like muscles in the back of your neck that help you extend and rotate your head. Suboccipital muscles: Four muscles just below the occipital bone at the base of your skull. They help extend your head in different directions.
Which back muscle extends the head?
The semispinalis capitis, splenius capitis, and longissimus capitis muscles all help the head extend toward the back. They also work with sternocleidomastoid muscles to rotate the head left and right.
What muscle moves the shoulder and extends the head?
The trapezius is a muscle that starts at the base of your neck, goes across your shoulders and extends to the middle of your back. The trapezius (traps muscle) helps you move your head, neck, arms, shoulders and torso.
What muscles attach to the vertebrae?
Thoracic vertebrae provide attachment points for numerous muscles: erector spinae, interspinales, intertransversarii, latissimus dorsi, multifidus, rhomboid major, rhomboid minor, rotatores, semispinalis, serratus posterior superior/inferior, splenius capitis, splenius cervicis, and trapezius.
What is the function of the vertebral column?
The vertebral column has four main functions: Protection – encloses and protects the spinal cord within the spinal canal. Support – carries the weight of the body above the pelvis. Axis – forms the central axis of the body. Movement – has roles in both posture and movement.
Which part of the vertebrae has larger bodies?
It is the weight-bearing component, and vertebrae in the lower portion of the column have larger bodies than those in the upper portion (to better support the increased weight).
What connects the vertebrae to the transverse processes?
Pedicles – connect the vertebral body to the transverse processes. Lamina – connect the transverse and spinous processes. Articular processes – form joints between one vertebra and its superior and inferior counterparts. The articular processes are located at the intersection of the lamina e and pedicles.
What is the lateral and posterior aspect of each vertebrae?
The vertebral arch forms the lateral and posterior aspect of each vertebrae. In combination with the vertebral body, the vertebral arch forms an enclosed hole – the vertebral foramen. The foramina of all the vertebrae line up to form the vertebral canal, which encloses the spinal cord.
How many bones are in the vertebral column?
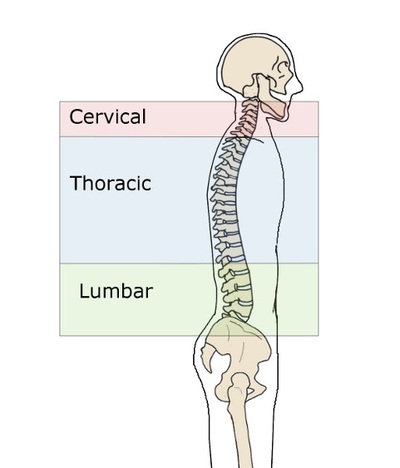
The vertebral column is a series of approximately 33 bones called vertebrae, which are separated by intervertebral discs. The column can be divided into five different regions, with each region characterised by a different vertebral structure.
What are the two structures of the vertebrae?
All vertebrae share a basic common structure . They each consist of an anterior vertebral body, and a posterior vertebral arch.
How many lumbar vertebrae are there?
Lumbar Vertebrae. There are five lumbar vertebrae in most humans, which are the largest in the vertebral column. They are structurally specialised to support the weight of the torso. Lumbar vertebrae have very large vertebral bodies, which are kidney shaped.
What are the functions of the vertebrae?
The vertebrae are composed of many elements that are critical to the overall function of the spine, which include the intervertebral discs and facet joints. Functions of the Vertebral or Spinal Column Include: Protection. Spinal Cord and Nerve Roots. Many internal organs.
What is the axis of the cervical vertebrae?
The Axis is the second cervical vertebra or C2. It is a blunt tooth–like process that projects upward. It is also referred to as the ‘dens’ (Latin for ‘tooth’) or odontoid process. The dens provides a type of pivot and collar allowing the head and atlas to rotate around the dens.
Which is larger, the pedicles or the thoracic spine?
The pedicles are longer and wider than those in the thoracic spine. The spinous processes are horizontal and more squared in shape. The intervertebral foramen (neural passageways) are relatively large but nerve root compression is more common than in the thoracic spine.
Which vertebrae increase in size from T1 through T12?
The thoracic vertebrae increase in size from T1 through T12. They are characterized by small pedicles, long spinous processes, and relatively large intervertebral foramen (neural passageways), which result in less incidence of nerve compression.
How many bones are in the spinal column?
The spinal column (or vertebral column) extends from the skull to the pelvis and is made up of 33 individual bones termed vertebrae. The vertebrae are stacked on top of each other group into four regions: Term. # of Vertebrae. Body Area.
What is the C1 and C2 of the cervical spine?
The cervical spine is further divided into two parts; the upper cervical region (C1 and C2), and the lower cervical region (C3 through C7). C1 is termed the Atlas and C2 the Axis. The Occiput (CO), also known as the Occipital Bone, is a flat bone that forms the back of the head.
What is the C1 vertebra?
Atlas (C1) The Atlas is the first cervical vertebra and therefore abbreviated C1. This vertebra supports the skull. Its appearance is different from the other spinal vertebrae. The atlas is a ring of bone made up of two lateral masses joined at the front and back by the anterior arch and the posterior arch.
What is the spinal column?
The vertebral column is also known as the spinal column or spine (Figure 1). It consists of a sequence of vertebrae (singular = vertebra), each of which is separated and united by an intervertebral disc. Together, the vertebrae and intervertebral discs form the vertebral column.
How many vertebrae are in the adult vertebral column?
Figure 1. Vertebral Column. The adult vertebral column consists of 24 vertebrae, plus the sacrum and coccyx. The vertebrae are divided into three regions: cervical C1–C7 vertebrae, thoracic T1–T12 vertebrae, and lumbar L1–L5 vertebrae. The vertebral column is curved, with two primary curvatures (thoracic and sacrococcygeal curves) and two secondary curvatures (cervical and lumbar curves).
Why are cervical vertebrae smaller than lumbar vertebrae?
Thus, cervical vertebrae are smaller than lumbar vertebrae due to differences in the proportion of body weight that each supports. Thoracic vertebrae have sites for rib attachment, and the vertebrae that give rise to the sacrum and coccyx have fused together into single bones.
How many vertebrae are there in the human body?
The vertebral column originally develops as a series of 33 vertebrae, but this number is eventually reduced to 24 vertebrae, plus the sacrum and coccyx. The vertebral column is subdivided into five regions, with the vertebrae in each area named for that region and numbered in descending order.
What is the function of the vertebrae and discs?
Together, the vertebrae and intervertebral discs form the vertebral column. It is a flexible column that supports the head, neck, and body and allows for their movements. It also protects the spinal cord , which passes down the back through openings in the vertebrae. Figure 1. Vertebral Column.
How to identify excess vertebral curves?
Excessive vertebral curves can be identified while an individual stands in the anatomical position. Observe the vertebral profile from the side and then from behind to check for kyphosis or lordosis. Then have the person bend forward. If scoliosis is present, an individual will have difficulty in bending directly forward, and the right and left sides of the back will not be level with each other in the bent position.
Why do vertebral curves increase?
These curves increase the vertebral column’s strength, flexibility, and ability to absorb shock. When the load on the spine is increased, by carrying a heavy backpack for example, the curvatures increase in depth (become more curved) to accommodate the extra weight. They then spring back when the weight is removed.
Which vertebrae are inserted?
insertion: spinous processes of the 3rd and 4th more superior vertebrae
Which vertebrae have spinous processes?
spinous processes of inferior thoracic and superior lumbar vertebrae
What is transverse insertion?
insertion: transverse processes of superior vertebrae and inferior surfaces of ribs
Which vertebrae join the iliocostalis?
broad aponeurosis and transverse processes of inferior thoracic and superior lumbar vertebrae, joins iliocostalis
Which processes involve the superior vertebrae and inferior surfaces of ribs?
transverse processes of superior vertebrae and inferior surfaces of ribs
Which vertebrae have upper ribs and transverse process?
upper ribs and transverse process of last cervical vertebra
Which cartilages have inferior surfaces?
inferior surfaces of costal cartilages (R5-R7) and xiphoid process