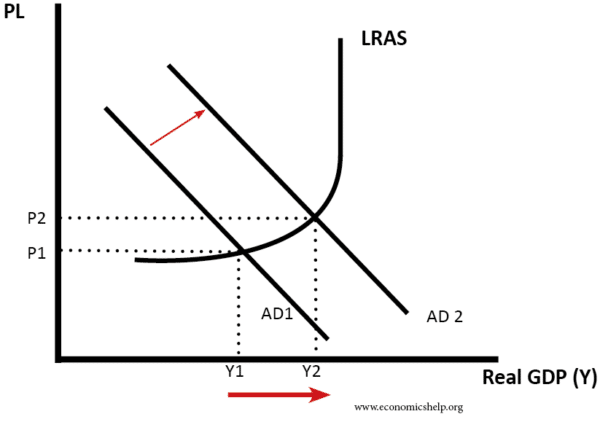
Factors that Affect Aggregate Demand
- 1. Net Export Effect When domestic prices increase, then demand for imports increases (since domestic goods become relatively expensive) and demand for export decreases.
- 2. Real Balances When inflation increases, real spending decreases as the value of money decreases. ...
- 3. Interest Rate Effect Real Interest is the nominal interest rate adjusted to the inflation rate. ...
- 4. Inflation Expectations ...
What would most likely increase aggregate demand?
What would increase aggregate demand? Rising or falling interest rates will affect decisions made by consumers and businesses. Rising household wealth increases aggregate demand while a decline usually leads to lower aggregate demand. Consumers’ expectations of future inflation will also have a positive correlation on aggregate demand.
What are the four determinants of aggregate demand?
- Interest rates work much the same for investment as for consumption. ...
- Physical wealth possessed by the business sector includes capital goods. ...
- Expectations of future economic conditions is also an important determinant working through investment expenditures. ...
- Capital prices are another key determinant working through investment. ...
demand determinants More items...
What are fctors tend to increase the aggregate demand?
The factors of aggregate demand are the factors that influence spending by each of these sectors: Household sector: the factors of household consumption are income, wealth, expectations, demographics, and taxes. Income: an increase in income will increase consumption. Wealth: an increase in wealth will increase consumption.
How does monetary policy affect aggregate demand?
monetary policy, which alters demand slows down the effect through imports: lower demand leads to lower imports and thus, the original drop in GDP will be somewhat lower, as well. Aggregate demand changes feed into prices, wages and employment, which again alters demand and the new equilibrium develops simultaneously.
What are the 4 shifters of aggregate demand?
The aggregate demand curve shifts to the right as the components of aggregate demand—consumption spending, investment spending, government spending, and spending on exports minus imports—rise.
What causes aggregate demand to increase?
Aggregate demand increases when the components of aggregate demand–including consumption spending, investment spending, government spending, and spending on exports minus imports–rise.
What will cause aggregate demand to decrease?
Income and Wealth: As household wealth increases, aggregate demand usually increases as well. Conversely, a decline in wealth usually leads to lower aggregate demand. Increases in personal savings will also lead to less demand for goods, which tends to occur during recessions.
Which of the following will cause a decrease in aggregate demand?
Which of the following would cause a decrease in aggregate demand? -an increase in the price level. -a decrease in foreign incomes, which leads to decreased exports.
Which of the following would increase aggregate demand?
Aggregate demand increases with increase in investment.
Which of the following events would cause an increase in aggregate demand?
Answer and Explanation: The correct answer is b. A decrease in the price level. This causes movement along the aggregate demand curve.
Which one of the following factors will most likely cause an increase in aggregate demand?
Which one of the following factors will most likely cause an increase in aggregate demand? An increase in net exports.
Under what circumstances does aggregate demand increase quizlet?
-Increase in money supply (Aggregate Expansion) will increase Aggregate Demand. -If US households buy more foreign goods, AD shifts down. -Exchange Rates (Foreign Depreciation, Foreign Growth Rates, Foreign Tariffs, etc.) -Supply Curve is upward sloping because at higher prices firms want to supply more.
What are the factors that affect aggregate demand?
The factors affecting aggregate demand are the factors affecting the components of consumption, investment, government expenditure and net exports.
What is aggregate demand?
Aggregate Demand is the total demand for an economy's goods and services. Aggregate demand consists of the sum of consumption, investment, government expenditure and net exports.
What is aggregate demand?
Aggregate demand refers to the total demand for finished goods and services in an economy. Finished products are goods and services that have been fully manufactured – not including intermediate goods that are used as inputs in the production process. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Gross domestic product ...
Which component of aggregate demand shifts the curve to the right?
An increase in any of the components of aggregate demand – consumption spending, investment spending, government spending, and net exports (X-M) – shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right, and a fall in any of these components shifts it to the left.
What is GDP in economics?
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Gross domestic product (GDP) is a standard measure of a country’s economic health and an indicator of its standard of living. Also, GDP can be used to compare the productivity levels between different countries. and the measure of demand for goods and services at all price levels.
How is CPI determined?
It is determined using the Consumer Price Index. Consumer Price Index (CPI) The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a measure of the aggregate price level in an economy. The CPI consists of a bundle of commonly purchased. , which is a measure of the weighted price of a basket of typically purchased goods and services in the economy.
What is consumption spending?
Consumption Spending (C) Consumption spending (C) is the largest component of an economy’s aggregate demand, and it refers to the total spending of individuals and households on goods and services. Products and Services A product is a tangible item that is put on the market for acquisition, attention, or consumption while a service is an intangible ...
Why is the AD curve downward sloping?
The AD curve is downward sloping since higher price levels correspond to lower demand for goods and services , which is in accordance with the Law of Demand. Here are some of the reasons behind the downward slope of the AD curve: 1. Pigou’s Wealth Effect.
What is Pigou's wealth effect?
Pigou’s Wealth Effect states that consumers are wealthier at lower price levels (assuming that wages are constant). Disposable income is higher at lower price levels and allows consumers to spend more on goods and services, increasing the demand for output.
What Factors Affect Aggregate Demand?
Aggregate demand can be impacted by a few key economic factors. Rising or falling interest rates will affect decisions made by consumers and businesses. Rising household wealth increases aggregate demand while a decline usually leads to lower aggregate demand. Consumers' expectations of future inflation will also have a positive correlation on aggregate demand. Finally, a decrease (or increase) in the value of the domestic currency will make foreign goods costlier (or cheaper) while goods manufactured in the domestic country will become cheaper (or costlier) leading to an increase (or decrease) in aggregate demand.
Why is aggregate demand important?
While aggregate demand is helpful in determining the overall strength of consumers and businesses in an economy , it does pose some limitations. Since aggregate demand is measured by market values, it only represents total output at a given price level and does not necessarily represent quality or standard of living. Also, aggregate demand measures many different economic transactions between millions of individuals and for different purposes. As a result, it can become challenging when trying to determine the causes of demand for analytical purposes.
What Is Aggregate Demand?
Aggregate demand is a measurement of the total amount of demand for all finished goods and services produced in an economy. Aggregate demand is expressed as the total amount of money exchanged for those goods and services at a specific price level and point in time.
What happens to aggregate demand if inflation increases?
Inflation Expectations: Consumers who feel that inflation will increase or prices will rise, tend to make purchases now, which leads to rising aggregate demand. But if consumers believe prices will fall in the future, aggregate demand tends to fall as well.
What is the difference between GDP and aggregate demand?
GDP represents the total amount of goods and services produced in an economy while aggregate demand is the demand or desire for those goods . As a result of the same calculation methods, the aggregate demand and GDP increase or decrease together. Technically speaking, aggregate demand only equals GDP in the long run after adjusting for ...
What is the horizontal X axis of aggregate demand?
If you were to represent aggregate demand graphically, the aggregate amount of goods and services demanded would be placed on the horizontal X-axis, and the overall price level of the entire basket of goods and services would be represented on the vertical Y-axis.
Why did Keynes believe unemployment was a byproduct of insufficient aggregate demand?
Keynes considered unemployment to be a byproduct of insufficient aggregate demand because wage levels would not adjust downward fast enough to compensate for reduced spending. He believed the government could spend money and increase aggregate demand until idle economic resources, including laborers, were redeployed.
What are the components of aggregate demand?
There are four main components of aggregate demand. They are consumption, investment, government spending and net exports (exports minus imports).
What is aggregate demand?
Aggregate demand refers to the demand of all goods and services produced in the economy. Aggregate demand is made up of four components – consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports (exports – imports). Buy Now!
How to calculate aggregate demand?
Aggregate demand is just the met demand of a nations GDP – it is calculated using the formula: Aggregate Demand = Consumption + Investment + Government Spending + (Exports – Imports).
Why is net export important?
Net exports can be crucially important to a nation’s economy. If domestic demand falls, a nation can rely on demand from abroad to help stimulate employment. So when aggregate demand falls in the US, the impact it has can be softened by aggregate demand abroad.
How do interest rates affect consumer demand?
Interest rates. Interest rates can play a big part in creating consumer demand. For instance, lower rates mean less expenditure on mortgage repayments and lower levels of debt repayments. In turn, this can lead back to the first point: higher disposable incomes.
What is GDP in economics?
By contrast, GDP refers to exactly what a nation supplies and produces in the economy . It is impossible to identify what each person would demand at any one point. What’s more, it is even more difficult to quantify it on a nationwide scale. Economists consider everything purchased as a good demanded.
How does tax affect consumption?
If governments increase tax; there is less for consumers to spend. Consequently, this can have a depressing effect on demand. By contrast, if the government reduces tax, it can increase consumer income. In turn, higher consumer incomes will help boost consumption; at least in the short-term.
How does investment affect aggregate supply?
Investment, technology changes that result in productivity improvements and positive institutional changes can increase short-run and long-run aggregate supply. Some factors can only affect Aggregate Supply in the short run.
What happens to short run aggregate supply?
As a result, the Short Run Aggregate Supply will shift to the left.
What happens if inflation goes up?
If consumers expect inflation to go up in the future, they will tend to buy now causing aggregate demand to increase or shift to the right.
What causes supply shocks?
Usually, a huge rise in oil prices can cause a supply shock. Natural catastrophes or hikes in taxes can also shift AS to the left. It is either a leftward shift in the short run AS curve (the one on the left) or by the leftward shift in the vertical long-run AS curve.
What is aggregate supply?
While, the Aggregate Supply is the total of all final goods and services which firms plan to produce. during a specific time period. It is the total amount of goods and services that firms are willing to sell at a given price level in an economy. There are two views on Long Run Aggregate Supply, the Monetarist view and the Keynesian view.
What does the monetarist assumption mean?
Monetarists assume that in the long run there is no unemployment and that the people who want to work, work and the ‘unemployed’ are viewed as voluntarily unemployed. This assumption leads to the concept of ‘Full Employment’ where all factors of production are fully and efficiently employed.
How can governments influence AS?
Governments can influence AS through Supply Side policies and improvements in health and education services. This result can be better imagined by an increase in the Long Run AS. An increase in natural resources can also shift the AS curve to the right.
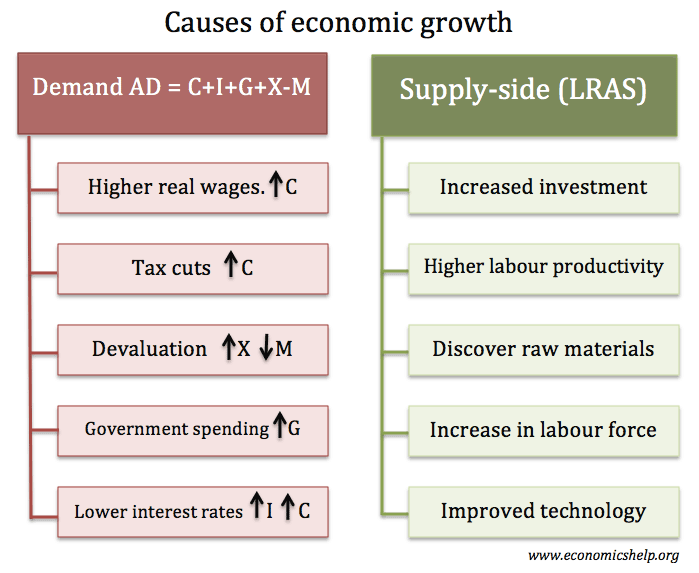
Aggregate Demand – Components
- An economy’s aggregate demand is the sum of all individual demand curves from different sectors of the economy. It is typically the sum of four components:
Shifts in Aggregate Demand
- The aggregate demand curve plots the demand for domestically produced goods and services at all price levels. Real GDP measures the value of gross domestic product adjusted for inflation and provides a more accurate picture of changes in domestic demand than nominal GDP. The AD curve is downward sloping since higher price levels correspond to lower demand for goods and …
Factors That Cause Shifts in Aggregate Demand
- An increase in any of the components of aggregate demand – consumption spending, investment spending, government spending, and net exports (X-M) – shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right, and a fall in any of these components shifts it to the left. A shift from AD to AD1 reflects an increase in aggregate demand. A shift from AD to AD2 reflec...
Additional Resources
- CFI offers the Commercial Banking & Credit Analyst (CBCA)™certification program for those looking to take their careers to the next level. To keep learning and developing your knowledge base, please explore the additional relevant resources below: 1. Law of Demand 2. Consumer Products 3. Nominal GDP vs. Real GDP 4. Pigou Effect
What Is Aggregate Demand?
Understanding Aggregate Demand
Drawbacks of Aggregate Demand
Aggregate Demand Curve
Components of Aggregate Demand
Calculating Aggregate Demand
Factors That Influence Aggregate Demand
- A variety of economic factors can affect the aggregate demand in an economy. Key ones include: 1. Interest Rates: Whether interest ratesare rising or falling will affect decisions made by consumers and businesses. Lower interest rates will lower the borrowing costs for big-ticket items such as appliances, vehicles, and homes. Also, companies will b...
Economic Conditions and Aggregate Demand
Aggregate Demand Controversy
The Bottom Line