- Soil texture
- Soil structure
- Organic matter content and
- Weather.
What are the factors that determine the tilth of soil?
Tilth, Physical condition of soil, especially in relation to its suitability for planting or growing a crop. Factors that determine tilth include the formation and stability of aggregated soil particles, moisture content, degree of aeration, rate of water infiltration, and drainage. The tilth of a soil can change rapidly,...
What are the factors affecting soil formation?
Factors Affecting Soil Formation. Soils form from the interplay of five main factors namely Parent Material, Time, Climate, Relief, and Organisms. It refers to the mineral material or organic material from which the soil is formed.
Why is good soil tilth important for plants?
Because plants are part of the larger soil ecosystem, good tilth also requires adequate fertility and a balanced population of soil organisms. Good tilth enables roots to expand freely and facilitates absorption of water, oxygen, and nutrients.
How fast does the tilth of a soil change?
The tilth of a soil can change rapidly, depending on environmental factors such as changes in moisture.

What causes tilth?
Factors that determine tilth include the formation and stability of aggregated soil particles, moisture content, degree of aeration, rate of water infiltration, and drainage. The tilth of a soil can change rapidly, depending on environmental factors such as changes in moisture.
How do you increase soil tilth?
Additional ways to improve soil tilth include reducing tillage and using cover crops. There are thus a number of approaches to improving the physical quality of the soil, and often a combined approach produces the greatest improvement.
Which soil particle helps with tilth?
Fine-textured, clay soils In addition to routine application of organic matter, microorganisms and earthworms perform a crucial assist to soil tilth. As microorganisms decompose the organic matter, soil particles bind together into larger aggregates, increasing large pore space.
How does soil structure affect the tilth of soil?
Good soil tilth is also associated with good soil structure. This is important because a vast majority of the world's agriculture depends upon rainfall to produce a reliable supply of food, feed, or fiber and when the soil has an unstable structure, infiltration of rainwater into the soil is often very limited.
Why is advantageous soil increasing tilth?
A soil with good tilth has large pore spaces for adequate air infiltration and water movement. (Roots only grow where the soil tilth allows for adequate levels of soil oxygen.) It also holds a reasonable supply of water and nutrients.
What is soil tilth characteristics of good tilth?
A soil with good tilth is “usually loose, friable and well granulated”; a condition that can also be described as the soil's having a good “self-mulching” ability. On the other hand soils with poor tilth are usually dense (compacted), with hard, blocky, or massive structural characteristics.
How can we manage soil tilth?
Soil should be covered year-round by crops, mulches, or cover crops to prevent compaction and erosion by heavy rains and winds. Another strategy for improving both tilth and fertility is to increase soil organic matter (SOM) by adding compost or manure and by growing cover crops and tilling them under.
What is tilth production?
Tilth is a word that describes the prepared soil surface. A rough tilth is created by digging and a fine tilth is created by raking and levelling the soil ready to sow seeds. Mulch is a layer of material that is spread over the surface of the soil to suppress weeds, conserve moisture and warm the soil.
How do you make fine tilth?
0:521:55Fine Tilth - The Veg Gardener's Glossary - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipInstead you rake the soil back and forth crumbling large clumps and breaking down stubborn ones withMoreInstead you rake the soil back and forth crumbling large clumps and breaking down stubborn ones with the back of your rake. Remove any weeds and debris such as stones and voila.
What is soil tilth?
Soil tilth is a dynamic and multifaceted concept that refers to the suitability of a soil for planting and growing crops. A soil with good tilth is “usually loose, friable and well granulated”; a condition that can also be described as the soil's having a good “self-mulching” ability.
What are 5 factors that can destroy soil structure?
Factors affecting soil structureOrganic Matter Content. Increasing organic matter. ... Soil Organisms. Bacteria are very important organism contributing to the structure of the soil. ... Soil Colloids. Factors affecting soil structure also include soil colloids. ... Tillage. ... Freezing and Thawing Cycles. ... Water Movement.
What are some of the factors affecting soil structure?
There are many factors that significantly affect soil structural stability like climate, organic matter content, adsorbed cations, tillage, type of vegetation, plant roots, soil organisms, manurial practices and crop rotation, alternate wetting and drying (Shreeja n.d.).
What is texture in soil?
Texture describes the coarseness/fineness of the mineral component of soil and reflects both the sizes of the mineral particles and their relative abundances. Texture is described as sand, silt or clay.
What is soil made of?
Nearly all soils contain a mixture of sand, silt, and clay. When a soil contains significant proportions of at least two particle types, it is classified as a loam. Loams, in turn, are subclassified by the relative amounts of each texture.
How much of the volume of soil is pore space?
A good soil contains a network of pores that occupy 50% of its volume. Pores range in diameter from microscopic to over 0.05 mm. When fully charged with water, the pore space in a good soil will be roughly half-filled with air and half with water.
What is the solid part of soil?
The solid part is ~45% mineral particles and 5% decomposed organic material by volume. While organic matter is not high on a percentage basis, it is critical in holding soil particles together, storing nutrients, and feeding soil organisms.
What type of soil is best for gardening?
Classic loam soils, which are mostly sand and silt, are the ideal texture for gardening but still need organic matter to achieve optimal soil structure. They have a good balance of macropores and micropores, and have good water holding capacity and permeability.
How does water move in soil?
Water movement is directly related to the size of pores in the soil. In the small pores of clayey soils, water slowly moves in all directions by capillary action.
What is the property of soil water?
Soil water coats the mineral and organic particles and is held by the property of cohesion (the chemical process by which water molecules stick together) in the small pore spaces. Air fills the large pore spaces.
What is the texture of soil?
Texture refers to the size of the particles that make up the soil. The terms sand, silt, and clay refer to relative sizes of the individual soil particles. [Table 1 and Figure 1 and 2]
What is clayey soil?
Clay particles are flat, plate-like, negatively charged particles. They are so tiny in size that it takes 12,000 clay particles in a line to make one inch. Clay feels sticky to the touch. Soils with as little as 20% clay size particles behave like a sticky clayey soil. Soils with high clay content have good water and nutrient holding capacity, but the lack of large pore space restricts water and air movement. Clayey soils are also rather prone to compaction issues.
How does tillage affect soil?
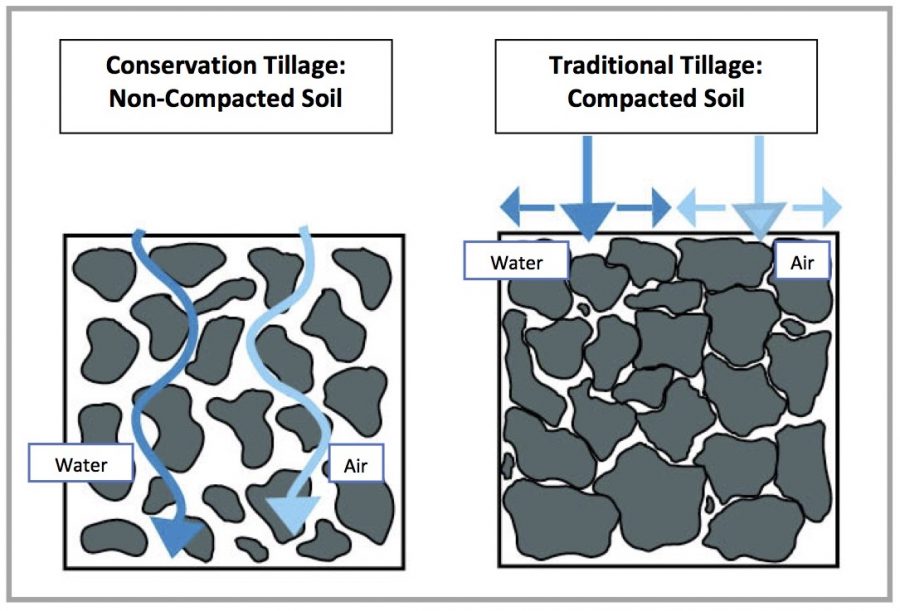
The effect of tillage on soil. However, tillage has all along been contributing negatively to soil quality. Since tillage fractures the soil, it disrupts soil structure, accelerating surface runoff and soil erosion. Tillage also reduces crop residue, which help cushion the force of pounding raindrops. Without crop residue, soil particles become ...
Why is topsoil loss dangerous?
In time, the soil is in danger of yield setbacks due to organic matter and nutrient loss as well as the damage done to the soil's physical properties.
What is tillage used for?
Tillage was used for seedbed preparation, weed suppression, soil aeration, turning over cover crops and forages, burying heavy crop residue, leveling the soil, incorporating manure and fertilizer into the root zone and activating pesticides.
What are the characteristics of soil?
There are many characteristics and indicators of soil quality, including bulk density, good soil pores and water-holding capacity, good infiltration rates and overall tilth, and high levels of organic matter and beneficial soil organisms. Tillage can negatively impact almost every one of those characteristics.
What happens when you tillage over a long period of time?
Frequent tillage over many seasons -- the impact. When frequent tillage is sustained over a period of years, the impact grows even more severe. A total break down of soil structure and overall soil quality is almost assured. A hardpan can develop, effectively cutting off root elongation, crop development and yield.
What is the effect of removal of topsoil?
Removal of topsoil by erosion contributes to a loss of inherent soil fertility levels. Approximately half of plant-available phosphorus is concentrated in topsoil as is nearly all of the plant-available potassium.
Does tillage help with rain?
Tillage also reduces crop residue, which help cushion the force of pounding raindrops. Without crop residue, soil particles become more easily dislodged, being moved or 'splashed' away. This process is only the beginning of the problem. Splashed particles clog soil pores, effectively sealing off the soil's surface, ...
What are the factors that affect soil formation?
Factors Affecting Soil Formation. Soils form from the interplay of five main factors namely Parent Material, Time, Climate, Relief, and Organisms. Parent material: It refers to the mineral material or organic material from which the soil is formed.
How does moisture affect the soil?
Moisture determines the chemical and biological reactions that will occur as the soils are formed. A warmer climate with more rainfall means more vegetative cover and more animal action. It also means more runoff, more percolation, and more water erosion. They all help to determine the kind of soils in an area.
Why are slopes less fertile?
Also, slopes may be exposed to more direct sunlight, which may dry out soil moisture and render it less fertile. Organisms: The source and richness of organic matter are down to the living things (plants and animals) that live on the surface and inside the soils.
Why do plants help soil?
Their roots also hold the soils and protect them from wind and water erosion. They shelter the soils from the sun and other environmental conditions, helping the soils to retain the needed moisture for chemical and bi ological reactions.
How long does it take for soil to form?
Soils can take many years to form. Younger soils have some characteristics from their parent material, but as they age, the addition of organic matter, exposure to moisture, and other environmental factors may change its features. With time, they settle and are buried deeper below the surface, taking time to transform.
What are the things that help with soil aeration?
Fungi, bacteria, insects, earthworms, and burrowing animals help with soil aeration. Worms help break down organic matter and aid decomposition. Animal droppings, dead insects, and animals result in additional decaying organic matter. Microorganisms also help with mineral and nutrient cycling and chemical reactions.
