1 Answer
- Molecular weight- GTT (glass transition temperature) is directly proportional to molecular weight of polymer.
- Cross links- GTT is directly proportional to degree of cross links
- Flexibility- GTT is inversely proportional to flexibility.
- Plasticizer – GTT is inversely proportional to plasticization.
- Inter molecular force – GTT is directly proportional to intermolecular force.
What is a glass transition?
Glass Transition. The glass transition is the phenomenon in which a solid amorphous phase exhibits more or less abrupt changes in derivative thermodynamic properties such as heat capacity or thermal expansion: when an amorphous material changes from a solid state to a liquid state on heating or from a liquid to a solid-like state on cooling.
What is definition of glass transition temperature?
What Does Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) Mean? A glass transition temperature ( Tg) is the temperature at which a polymer turns from a ductile material to a hard, brittle material. It is the temperature at which carbon chains start to move.
What does glass transition temperature mean?
The glass transition temperature (Tg) is the temperature of amorphous polymers at which increased molecular mobility results in significant changes in the thermal properties. Plastic products molded with oriented molecules expand differentially, as long as the glass transition temperature is not reached.
What is the glass transition temperature, Tg?
What is a Glass Transition Temperature? | What is Tg? The glass transition temperature (Tg) is somewhat of a misnomer, as it is actually a range of a few degrees Celsius over which a polymeric material transitions from a glassy (rigid) to elastomeric (rubbery) state. The Tg is typically reported as the median of that range of temperatures.

How to measure glass transition?
The glass transition itself appears as a step in the DSC curve for the material. It is typically measured using either the TMA, DMA, or DSC thermal analysis methods. The change in CTE can be measured using TMA while the change in mechanical modulus can be measured by DMA. A good rule of thumb for estimating the Tg is 2/3 of its melting point temperature in Kelvin. The Tg will always be lower than the melting point of the material.
What is the Tg of a polymer?
One of the definitions of Tg that is specific to polymers is as follows: it is the temperature at which molecular chains are able to slide past each other when a force is applied, hen ce the ability to mold and deform polymers without breaking them.
Is glass transition the same as melting?
Keep in mind that the glass transition is not the same as melting it is a totally different physical process. Glass transition does not involve a phase change like melting does, and it only occurs in amorphous polymers or the amorphous portion of a polymer. Only crystalline polymers can undergo a melting phase change.
Do polymers behave differently from metals?
As you know, polymers behave very differently from metals. One aspect of that behavior involves the glass transition temperature. In this blog post, we are going to focus on the glass transition temperature of thermoplastics.
What are the factors that affect glass transition temperature?
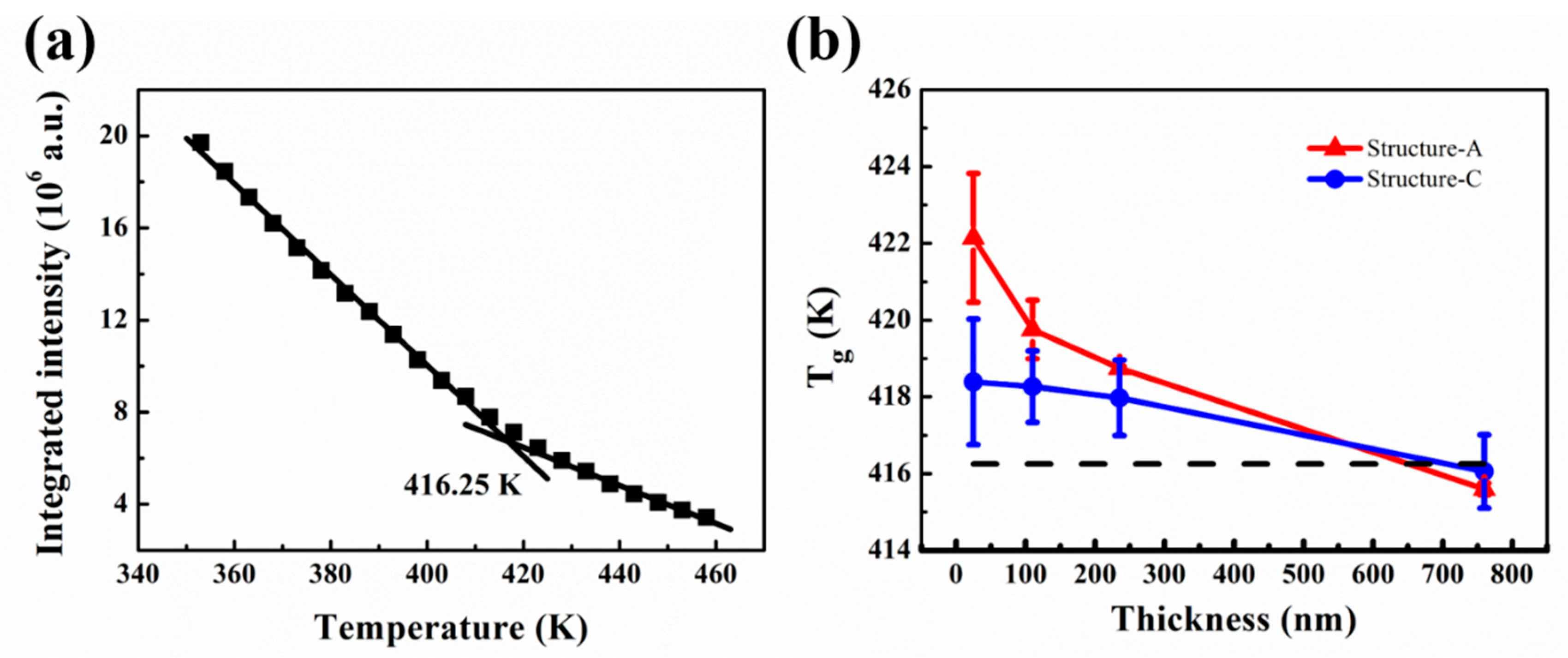
Other factors like branching, alkyl chain length, bond interaction, flexibility of polymer chain, film thickness etc. also have significant impact on glass transition temperature of polymers.
What is the most common test method for determining the glass transition temperature of plastics?
The most usual test method to determine Glass Transition Temperature of plastics is ASTM E1356. This test method covers the assignment of the glass transition temperatures of materials using differential scanning calorimetry or differential thermal analysis.
What is a polymer made of?
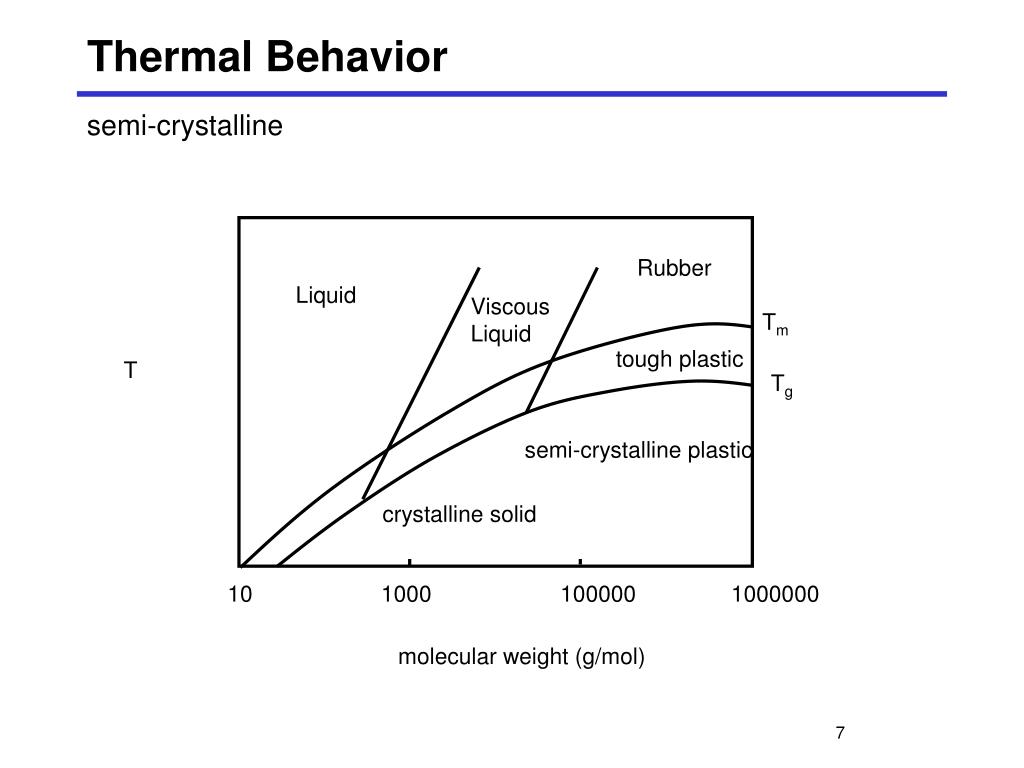
Polymers (plastics, elastomers or rubber) are made up of long chains of molecules and may be amorphous or crystalline. The structure of a polymer is defined in terms of crystallinity.
What temperature is used to identify polymers?
This temperature (measured in °C or °F) depends on the chemical structure of the polymer and can therefore be used to identify polymers. Amorphous polymers only exhibit a Tg. Crystalline polymers exhibit a Tm (melt temperature) and typically a Tg since there is usually an amorphous portion as well (“semi”-crystalline).
What is the transition from glass to rubber?
The transition from the glass to the rubber-like state is an important feature of polymer behavior, marking a region of dramatic changes in the physical properties, such as hardness and elasticity. At Tg, changes in hardness, volume, percent elongation to break and Young’s modulus of solids are mainly seen. Some polymers are used below their Tg (in ...
Why is it important to know the Tg of polymers?
Applications include: Identifying the Tg of polymers is often used for quality control and research and development. Also, it is an important tool used to modify physical properties of polymer molecules.
What polymers are used below their Tg?
Some polymers are used below their Tg (in glassy state) like polystyrene, poly (methyl methacrylate) etc., which are hard and brittle. Their Tgs are higher than room temperature.
Glass Transition
Glass Transition and Melting
- Keep in mind that the glass transition is not the same as melting it is a totally different physical process. Glass transition does not involve a phase change like melting does, and it only occurs in amorphous polymersor the amorphous portion of a polymer. Only crystalline polymers can undergo a melting phase change.
Glass Transition Temperature
- The Tg, referred to as the glass transition temperature, is what characterizes the glass transition. One of the definitions of Tg that is specific to polymers is as follows: it is the temperature at which molecular chains are able to slide past each other when a force is applied, hence the ability to mold and deform polymers without breaking them. When a thermoplastic polymer reaches th…
Quantifying The Glass Transition
- The glass transition itself appears as a step in the DSC curve for the material. It is typically measured using either the TMA, DMA, or DSC thermal analysis methods.The change in CTE can be measured using TMA while the change in mechanical modulus can be measured by DMA. A good rule of thumb for estimating the Tg is 2/3 of its melting point temperature in Kelvin. The T…
Conclusion
- The glass transition temperature, Tg, is the temperature at which polymer chains can slide past each other without breaking. When a polymer is cooled below its Tg, it gets very hard and brittle; when it is heated above its Tg, it becomes very soft and pliable. A good heuristic for estimating the Tg is that it will be about 2/3 the polymers melting...