Key Takeaways: Fermentation
- Fermentation is a biochemical reaction that extracts energy from carbohydrates without using oxygen.
- Organisms use fermentation to live, plus it has many commercial applications.
- Possible fermentation products include ethanol, hydrogen gas, and lactic acid.
What products are produced by fermentation?
There are thousands of different types of fermented foods, including:
- cultured milk and yoghurt.
- wine.
- beer.
- cider.
- tempeh.
- miso.
- kimchi.
- sauerkraut.
What are the products of fermentation?
Microbial fermentation services provided by Creative Biogene also include codon optimization, gene synthesis, small-scale expression testing, protein purification and large-scale manufacturing. Fermentation end products range from proteins, enzymes to microbial biomass.
What to expect during fermentation?
- When you first put your SCOBY into your sweet tea in the brewing vessel, it might sink. ...
- At around day 3, you’ll start seeing some opaque white specks dot the top. ...
- By day 4-5 you'll likely see a new, thin layer of SCOBY grow across the top. ...
- You might see some brown stringy yeasty bits. ...
How does the fermentation process actually work?
Key Takeaways: Fermentation
- Fermentation is a biochemical reaction that extracts energy from carbohydrates without using oxygen.
- Organisms use fermentation to live, plus it has many commercial applications.
- Possible fermentation products include ethanol, hydrogen gas, and lactic acid.

What 2 products are produced during fermentation?
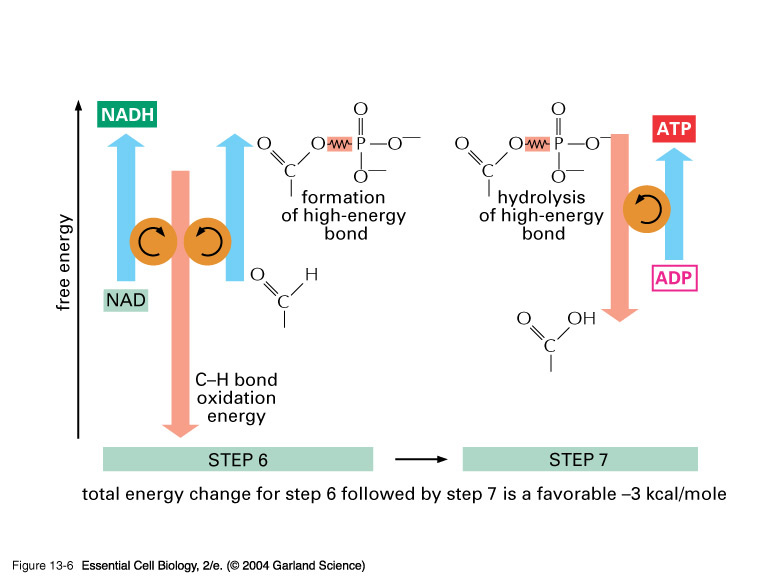
In plant and yeast cells pyruvate is converted into carbon dioxide and a type of alcohol called ethanol . This process is called fermentation and yields only two molecules of ATP per glucose molecule broken down.
What is fermentation and its products?
Fermentation is an anaerobic biochemical process. In fermentation, the first process is the same as cellular respiration, which is the formation of pyruvic acid by glycolysis where net 2 ATP molecules are synthesised. In the next step, pyruvate is reduced to lactic acid, ethanol or other products.
What are three products that are produced by fermentation?
What are fermented foods?cultured milk and yoghurt.wine.beer.cider.tempeh.miso.kimchi.sauerkraut.More items...•
What is produced in fermentation biology?
Fermentation Products Apart from lactate (or lactic acid) and ethanol, other byproducts of fermentation are acetates, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen gas. Acetic acid bacteria are a group of bacteria that will oxidize sugars or ethanol to produce acetic acid.
What are five by-products of fermentation?
The products are of many types: alcohol, glycerol, and carbon dioxide from yeast fermentation of various sugars; butyl alcohol, acetone, lactic acid, monosodium glutamate, and acetic acid from various bacteria; and citric acid, gluconic acid, and small amounts of antibiotics, vitamin B12, and riboflavin (vitamin B2) ...
What gas is produced in fermentation?
Carbon dioxide (CO₂)Carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas released during fermentation process.
What is an example product of fermentation?
Fermentation is a process used to produce wine, beer, yogurt and other products.
Does fermentation produce ATP?
Fermentation is the process of producing ATP in the absence of oxygen, through glycolysis alone. Recall that glycolysis breaks a glucose molecule into two pyruvate molecules, producing a net gain of two ATP and two NADH molecules.
What are the products of fermentation respiration?
As the seeds respire they take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide at roughly the same rate.
What is fermentation in short answer?
Fermentation is the process in which a substance breaks down into a simpler substance . Fermentation refers to the metabolic process by which organic molecules ( mainly carbohydrates, such as starch or a sugar) are converted into acids, gases, or alcohol in the absence of oxygen or any electron transport chain.
What do fermentation means?
/ˌfɜː.menˈteɪ.ʃən/ a process of chemical change in food or drink because of the action of yeast or bacteria, which may cause it to produce bubbles or heat, or turn sugars in it into alcohol: Ethanol is an alcohol produced by fermentation of sugars.
What is fermentation simple explanation?
fermentation Add to list Share. Fermentation is the process in which a substance breaks down into a simpler substance. Microorganisms like yeast and bacteria usually play a role in the fermentation process, creating beer, wine, bread, kimchi, yogurt and other foods.
What is fermentation called?
“Fermentation is an anaerobic process in which energy can be released from glucose even if oxygen is not available.”
What are the products of industrial fermentation?
The products are of many types: alcohol, glycerol, and carbon dioxide from yeast fermentation of various sugars; butyl alcohol, acetone, lactic acid, monosodium glutamate, and acetic acid from various bacteria; and citric acid, gluconic acid, and small amounts of antibiotics, vitamin B 12, and riboflavin (vitamin B 2) from mold fermentation . Ethyl alcohol produced via the fermentation of starch or sugar is an important source of liquid biofuel.
What is the first step in fermentation?
The generation of pyruvate through the process of glycolysis is the first step in fermentation. The term fermentation now denotes the enzyme-catalyzed, energy-yielding pathway in cells involving the anaerobic breakdown of molecules such as glucose. In most cells the enzymes occur in the soluble portion of the cytoplasm.
What is the sequence of glucose to pyruvate called?
The sequence from glucose to pyruvate is often called the Embden–Meyerhof pathway, named after two German biochemists who in the late 1920s and ’30s postulated and analyzed experimentally the critical steps in that series of reactions. glycolysis.
What is the breakdown of molecules in anaerobic processes?
Anaerobic breakdown of molecules. In the 1920s it was discovered that, in the absence of air , extracts of muscle catalyze the formation of lactate from glucose and that the same intermediate compounds formed in the fermentation of grain are produced by muscle.
What is an encyclopedia editor?
Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. ...
When was glycolysis first defined?
Test your knowledge with this quiz! Glycolysis, the breakdown of sugar, was originally defined about 1930 as the metabolism of sugar into lactate. It can be further defined as that form of fermentation, characteristic of cells in general, in which the six-carbon sugar glucose is broken down into two molecules of the three-carbon organic acid, ...
Where do enzymes occur in cells?
In most cells the enzymes occur in the soluble portion of the cytoplasm. The reactions leading to the formation of ATP and pyruvate thus are common to sugar transformation in muscle, yeasts, some bacteria, and plants. Get a Britannica Premium subscription and gain access to exclusive content. Subscribe Now.
Why is lactic acid converted into something else?
alcoholic fermentation. Reasons to go further and convert lactic acid into something else include: The acidity of lactic acid impedes biological processes.
How to avoid contamination in a fermentor?
The high cost of sterilizing the fermentor between batches can be avoided using various open fermentation approaches that are able to resist contamination. One is to use a naturally evolved mixed culture. This is particularly favored in wastewater treatment, since mixed populations can adapt to a wide variety of wastes. Thermophilic bacteria can produce lactic acid at temperatures of around 50 °Celsius, sufficient to discourage microbial contamination; and ethanol has been produced at a temperature of 70 °C. This is just below its boiling point (78 °C), making it easy to extract. Halophilic bacteria can produce bioplastics in hypersaline conditions. Solid-state fermentation adds a small amount of water to a solid substrate; it is widely used in the food industry to produce flavors, enzymes and organic acids.
How does batch fermentation work?
Batch fermentation goes through a series of phases. There is a lag phase in which cells adjust to their environment; then a phase in which exponential growth occurs. Once many of the nutrients have been consumed, the growth slows and becomes non-exponential, but production of secondary metabolites (including commercially important antibiotics and enzymes) accelerates. This continues through a stationary phase after most of the nutrients have been consumed, and then the cells die. : 25
What is fermentation in progress?
Fermentation in progress: Bubbles of CO 2 form a froth on top of the fermentation mixture. Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes.
What is the mechanism of fermentation?
Basic mechanisms for fermentation remain present in all cells of higher organisms. Mammalian muscle carries out fermentation during periods of intense exercise where oxygen supply becomes limited, resulting in the creation of lactic acid. In invertebrates, fermentation also produces succinate and alanine.
Why is batch fermentation so expensive?
However, it can be expensive because the fermentor must be sterilized using high pressure steam between batches. Strictly speaking, there is often addition of small quantities of chemicals to control the pH or suppress foaming.
Why is lactic acid good for fermentation?
The acidity of lactic acid impedes biological processes. This can be beneficial to the fermenting organism as it drives out competitors that are unadapted to the acidity. As a result, the food will have a longer shelf life (one reason foods are purposely fermented in the first place); however, beyond a certain point, the acidity starts affecting the organism that produces it.
What could result in the lysis of the culture?
Contamination of a bacterial fermentation with phage could result in the lysis of the culture.
What happens to fermentation products?
Fermentation products accumulate in the fermentation system, which will inhibit the growth and metabolism of microbes.
What happens if a microorganism invades fermentation?
If a foreign microorganism invades the fermentation then the following consequences may occur: 1. The medium would have to support the growth of both the production organism and the contaminant, resulting in a loss of productivity.
How long does it take for mesophilic acid to ferment?
For mesophilic products, fermentation time varies between 12 and 16 h, time that may be necessary to achieve the final acidity of ∼1.0 g of lactic acid/100 ml of final product.
How does AW affect growth?
The effects of aw on growth also depend on temperature, pH, nutrient availability, and other factors. High temperature is a source of stress that is synergistic to water stress. Water activity influences the stability of enzymes and proteins significantly. Addition of ethanol to water can sharply reduce water activity.
What are the most common contaminants in fermenters?
The most common contaminants are Gram-positive spore-forming rods ( Bacillus spp.) usually linked with inadequate medium sterilization, due to the presence of large insoluble medium particles, or poor cleaning of the fermenter prior to sterilization resulting in accumulation of dried broth in crevices and joints.
How many g in a yogurt package?
Yogurt's most popular package is the single serving of 125–150 g. The packaging is obtained preformed, filled, and closed by hot foil seal; generally the process uses form-fill-seal. A schematic representation of the complete yogurt manufacture process is presented in Figure 2.
What is khalpi fermented by?
Khalpi is popular in India. It is fermented by plantarum, L. brevis, and Leuconostoc fallax.
What is Chungkokjang fermented by?
Chungkokjang is popular in Korea. This is fermented by subtilis, B. licheniformis, and B. megaterium.
How many types of fermented soyabean products are there?
There are two types of fermented soyabean products:
What bacteria are in Ugba?
Ugba is popular in Nigeria. It is fermented by Bacillus ,. Staphylococcus ,. Micrococcus ,. Corynebacterium ,. Alcaligens, and Citrobacter .
What is acidophilus milk made of?
Acidophilus milk is produced from cows milk. These are fermented by acidophilus.
How is fumaric acid produced?
Fumaric Acid is produced from glucose by submerged fermentation process through the use of the filamentous fungi Rhizopus. Lactic acid is produced from potato starch, molasses and whey through the use of bacteria Lactobacillus bulgaricus, Lactobacills delbrueckii.
How is citric acid made?
Citric Acid is produced from cane molasses, fruit pulp, and sugars by submerged fermentation process through the use of yeast Aspergillus niger. It is used as the treatment for kidney patients.
What is fermented milk?
Fermented milk product with Lactobacillus acidophilus bacteria. A type of fermented milk that tastes like cottage cheese or plain yogurt. A traditional sweet, low- or non-alcohol (depending on recipes) Japanese drink made from fermented rice.
What is Garum made of?
Garum was a fish sauce made from the fermentation of fish entrails, used as a condiment in the cuisines of ancient Greece, Rome, and Byzantium.
What is cabbage relish?
A type of lightly fermented cabbage relish. It is typical in Salvadoran cuisine and that of other Central American countries, and is usually made with cabbage, onions, carrots, and sometimes lime juice. A vegetarian food item made with a fermented batter derived from rice and chickpea splits.
What is a fermented rice batter?
Made from a thin, wide sheet of steamed fermented rice batter filled with seasoned ground pork, minced wood ear mushroom, and minced shallots. A fermented milk product made from whey, with a very low alcohol content. Water in which wheat or barley bran, sometimes sugar beet or a slice of bread have fermented.
What is a kiviaq?
A fermented dairy product. A fermented maize dumpling. Kiviak or kiviaq is a traditional wintertime Inuit food made of auks, a type of seabird, preserved in a seal skin. A traditional salted and fermented fish dish originating in the Izu Islands, and often eaten with sake, shōchū, or a local drink called Shima Jiman.
What is the acid in pickled food?
Many pickled or soured foods are fermented as part of the pickling or souring process, but many are simply processed with brine, vinegar, or another acid such as lemon juice.
What is Tibicos water made of?
Tibicos water crystals made with Muscovado. This is a list of fermented foods, which are foods produced or preserved by the action of microorganisms.
What is fumaric acid?
Fumaric acid is produced by Rhizopus sp. Gibberellic acid is produced by Gibberella fujikuroi from wheat bran. SEE MORE: 245 Products of Fermentation (food, drinks and medicine) What are the Products of Lactic Acid Fermentation.
What are the end products of fermentation?
The End Products of Fermentation are produced from different types of fermentation: Ethanol and carbon dioxide are produced from alcohol fermentation (ethanol fermentation). They are produced by fungi, notably by yeast. Lactic acids are produced from homolactic acid fermentation.
What is the name of the plant that produces galactosidase?
Galactosidaseis produced by Kluyveromyces laccisfrom whey + corn or wheat bran.
What is ethanol made of?
Ethanol is produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Kluyveromyces fragillis from fruit pomace, sweet sorghum, beet, com, carob pods. It is used as beer, wine, and fuel. Acetone, isopropanol, and butanol are produced by Clostridium acetobutylicum from molasses. Glycerol is produced by Saccharomyces sp. from molasses.
How are pyruvic acids produced?
These pyruvic acids are produced from glucose through glycolysis process. Several end products of fermentation are produced with the help of several bacteria. These end products of fermentation have been using to meet our various needs.
What is the source of glucoamylaseis?
Glucoamylaseis produced by Aspergillus niger / A. oryzae from cassava, wheat bran, corn.
What is the name of the compound that is produced by Clostridium acetobutylicum?
Acetone, isopropanol, and butanolare produced by Clostridium acetobutylicum from molasses.
